[算法专题] 深度优先搜索&回溯剪枝
1. Palindrome Partitioning
https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-partitioning/
Given a string s, partition s such that every substring of the partition is a palindrome.
Return all possible palindrome partitioning of s.
For example, given s =
"aab",
Return[
["aa","b"],
["a","a","b"]
]
/**
* author : Jianxin Zhou
* email:zhoujx0219@163.com
*
* 该题dfs函数原型如下:
* void partitionHelper(const string &s, vector<vector<string>> &result, vector<string> &path, int pos)
*
* 以aaba举例。
* 1. 首先a为回文,然后对aba进行dfs
* 2. 之后回溯到a时,以aa为回文,然后对ba做dfs
* 3. 回溯到aa,试图以aab为回文,失败;试图以aaba为回文失败;结束。
*
* 注意:如果能顺利的找到一组回文,那么pos最终会等于s.size(),此时可以push到result。
* 如果找不到,例如之前的aaba不是回文,那么就会直接退出循环,没有机会执行下一步递归,也就没有pos等于s.size了。
*
* 实际上,此类题与真正的dfs的差别在于,dfs在回溯时,不会进行剪枝操作。而此类题,由于需要求出所有方案,所以需要剪枝。
*
*/ class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<string>> partition(string s) {
vector<vector<string>> result;
vector<string> path;
partitionHelper(s, result, path, 0);
return result;
} private:
void partitionHelper(const string &s, vector<vector<string>> &result, vector<string> &path, int pos) {
// base case
if (pos == s.size()) {
result.push_back(path);
return;
} for (int i = pos; i < s.size(); i++) {
if (isPalindrome(s, pos, i)) {
path.push_back(s.substr(pos, i - pos + 1));
partitionHelper(s, result, path, i + 1);
path.pop_back();
}
}
} bool isPalindrome(const string &s, int start, int end) {
while (start < end) {
if (s[start] == s[end]) {
start++;
end--;
} else {
break;
}
} return start >= end;
}
};
2. Permutations
https://leetcode.com/problems/permutations/
Given a collection of numbers, return all possible permutations.
For example,
[1,2,3]have the following permutations:
[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2], and[3,2,1].
具体可参加我之前写的文章:[LintCode] Permutations
/**
* 思路:dfs。
*
* 以123举例,
* 1. 首先以1作为head,然后对23做dfs
* 2. 回溯到1, 以2作为head,对13做dfs
* 3. 最后回溯到2,以3作为head,对12做dfs
*
* 注意:例如以2为head,对其余元素做dfs时,那么2不能再取,因此在进行下一轮dfs时,需要标记2为以访问过
*
*/ class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
vector<int> path; bool visited[nums.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
visited[i] = false;
} sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
dfs(nums, result, path, visited);
return result;
} private:
void dfs(const vector<int> &nums, vector<vector<int>> &result, vector<int> &path, bool visited[]) {
// base case
if (path.size() == nums.size()) {
result.push_back(path);
return;
} for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (visited[i] == false) {
path.push_back(nums[i]);
visited[i] = true;
dfs(nums, result, path, visited);
path.pop_back();
visited[i] = false;
} }
}
};
3. Permutations II
https://leetcode.com/problems/permutations-ii/
Given a collection of numbers that might contain duplicates, return all possible unique permutations.
For example,
[1,1,2]have the following unique permutations:
[1,1,2],[1,2,1], and[2,1,1].
要点在于保证相同的数不在同一位置出现两次以上,可以参见我写的这篇文章:[LintCode] Permutations II
class Solution {
public:
/**
* @param nums: A list of integers.
* @return: A list of unique permutations.
*/
vector<vector<int> > permuteUnique(vector<int> &nums) {
// write your code here
vector<vector<int>> paths;
if (nums.empty()) {
return paths;
}
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
bool *visited = new bool[nums.size()]();
vector<int> path;
permuteUniqueHelper(nums, visited, path, paths);
return paths;
}
private:
void permuteUniqueHelper(const vector<int> &nums,
bool visited[],
vector<int> &path,
vector<vector<int>> &paths) {
if (path.size() == nums.size()) {
paths.push_back(path);
return;
}
for (int ix = 0; ix < nums.size(); ix++) {
if (visited[ix] == true || ix > 0 && nums[ix - 1] == nums[ix] && visited[ix - 1] == false) {
continue;
}
visited[ix] = true;
path.push_back(nums[ix]);
permuteUniqueHelper(nums, visited, path, paths);
visited[ix] = false;
path.pop_back();
}
}
};
4 Subsets
https://leetcode.com/problems/subsets/
Given a set of distinct integers, nums, return all possible subsets.
Note:
- Elements in a subset must be in non-descending order.
- The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets.
For example,
If nums =[1,2,3], a solution is:[
[3],
[1],
[2],
[1,2,3],
[1,3],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[]
]
/**
* 思路:找方案,一般都是使用搜索。
*
* 以123为例,在递归还没有开始前,先把空集push到result中,之后:
* 1. 以1位head,对23做dfs,所以pos需要加1,用于分支限界(1 12 13 123)
* 2. 回溯到1,以2为head,对3做dfs (2 23)
* 3. 回溯到3,以3为head,之后循环结束。 (3)
*
*
*/ class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int>& nums) {
// ensure that elements in a subset must be in non-descending order.
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
dfs(nums, res, path, 0);
return res;
} private:
void dfs(const vector<int> &nums, vector<vector<int>> &res, vector<int> &path, int pos) {
res.push_back(path); for (int i = pos; i < nums.size(); i++) {
path.push_back(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, res, path, i + 1);
path.pop_back();
}
}
};
5. Subsets II
https://leetcode.com/problems/subsets-ii/
Given a collection of integers that might contain duplicates, nums, return all possible subsets.
Note:
- Elements in a subset must be in non-descending order.
- The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets.
For example,
If nums =[1,2,2], a solution is:[
[2],
[1],
[1,2,2],
[2,2],
[1,2],
[]
]
同一位置上,前面取过的数,后面就不要再重复取了,当然当i = pos时,这个数必然是第一次取。
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> subsetsWithDup(vector<int> &nums) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
dfs(nums, res, path, 0);
return res;
}
private:
void dfs(const vector<int> &nums, vector<vector<int>> &res, vector<int> &path, int pos) {
res.push_back(path);
for (int i = pos; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (i != pos && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
path.push_back(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, res, path, i + 1);
path.pop_back();
}
}
};
6 Restore IP Addresses
https://leetcode.com/problems/restore-ip-addresses/
Given a string containing only digits, restore it by returning all possible valid IP address combinations.
For example:
Given"25525511135",return
["255.255.11.135", "255.255.111.35"]. (Order does not matter)
/**
* 该题思路与求回文划分相似
*/ class Solution {
public:
vector<string> restoreIpAddresses(string s) {
vector<string> res; size_t len = s.size();
if (len < 4 || len > 12) {
return res;
} vector<string> path;
dfs(s, res, path, 0);
return res;
} private:
void dfs(const string &s, vector<string> &res, vector<string> &path, int pos) {
// base case
if (path.size() == 4) {
if (pos != s.size()) {
return;
} string returnElem;
for (const auto &elem : path) {
returnElem += elem;
returnElem += ".";
}
returnElem.erase(returnElem.end() - 1); res.push_back(returnElem);
return;
} for (int i = pos; i < s.size() && i < pos + 3; i++) {
string tmp = s.substr(pos, i - pos + 1);
if (isValid(tmp)) {
path.push_back(tmp);
dfs(s, res, path, i + 1);
path.pop_back();
}
}
} bool isValid(const string &s) {
// 排除 055 之类的数字
if (s[0] == '0' && s.size() > 1) {
return false;
} int digit = atoi(s.c_str());
return 0 <= digit && digit <= 255;
}
};
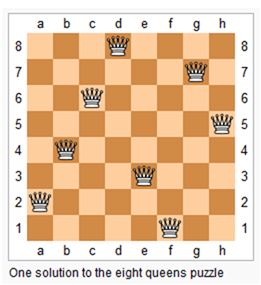
7 N-Queens
http://www.lintcode.com/en/problem/n-queens/#
The n-queens puzzle is the problem of placing n queens on an n×n chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
Given an integer n, return all distinct solutions to the n-queens puzzle.
Each solution contains a distinct board configuration of the n-queens' placement, where
'Q'and'.'both indicate a queen and an empty space respectively.For example,
There exist two distinct solutions to the 4-queens puzzle:[
[".Q..", // Solution 1
"...Q",
"Q...",
"..Q."], ["..Q.", // Solution 2
"Q...",
"...Q",
".Q.."]
]
/**
* 思路:一行一行的取数,例如第一行的皇后放在第1个位置,第二行的皇后放在第3个位置,
* 以此类推,直到最后一行的皇后放在正确的位置,如此视为一个方案,push到result中
*
* 显然,本题使用dfs,每一行可取的位置从0-N-1,
* 需要注意的是,每一行在取位置的时候,需要判断有效性(是否可以相互攻击)。
*/ class Solution {
public:
/**
* Get all distinct N-Queen solutions
* @param n: The number of queens
* @return: All distinct solutions
* For example, A string '...Q' shows a queen on forth position
*/
vector<vector<string> > solveNQueens(int n) {
vector<vector<string>> res;
vector<int> visitedCol; if (n <= 0) {
return res;
} dfs(n, res, visitedCol);
return res;
} private:
void dfs(const int n, vector<vector<string>> &res, vector<int> &visitedCol) {
// base case
if (visitedCol.size() == n) {
res.push_back(draw(visitedCol));
return;
} for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!isValid(visitedCol, i)) {
continue;
} visitedCol.push_back(i);
dfs(n, res, visitedCol);
visitedCol.pop_back();
} } bool isValid(const vector<int> &visitedCol, const int currentCol) {
size_t currentRow = visitedCol.size(); for (int rowIndex = 0; rowIndex < visitedCol.size(); rowIndex++) {
if (currentCol == visitedCol[rowIndex]) {
return false;
} if (currentRow + currentCol == rowIndex + visitedCol[rowIndex]) {
return false;
} if (currentRow - currentCol == rowIndex - visitedCol[rowIndex]) {
return false;
}
} return true;
} vector<string> draw(const vector<int> &visitedCol) { vector<string> ret;
string row;
for (const auto &elem : visitedCol) {
row.clear(); for (int i = 0; i < visitedCol.size(); i++) {
if (i == elem) {
row += "Q";
} else {
row += ".";
}
} ret.push_back(row);
} return ret;
}
};
8 Sudoku Solver
https://leetcode.com/problems/sudoku-solver/
Write a program to solve a Sudoku puzzle by filling the empty cells.
Empty cells are indicated by the character
'.'.You may assume that there will be only one unique solution.
A sudoku puzzle...
...and its solution numbers marked in red.
class Solution {
public:
void solveSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
dfs (board, 0, 0);
}
private:
/**
* 该题需要对sudoku中每一个以‘.’标记的方格进行dfs,
* 1. 如果对当前方格的以1-9这9个数字进行遍历,都不合法,那么不会再往下一个方格进行dfs,直接回溯到上一个方格取下一个数。
* 2. 如果当前方格所取的数合法,那么继续对下一个方格进行dfs,依次下去如果一直合法,那么直到走到sudoku中的最后一个需要放数字的方格,
* 尝试完它的所有选择,再往上回溯。
* 然后,在这边我们只需要一个可行解即可,因此只要当前方格合法,往下的dfs返回true,那么即为一个解,直接返回。
*
*
*
*/
bool dfs(vector<vector<char>> &board, int x, int y) {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
//dfs
if (board[i][j] == '.') {
// k从0-9走完才算走完,但是此处我们只要有一个解,就可以返回了,因此在以下循环中设置了return语句
for (int k = 0; k < 9; k++) {
bool flag;
if (!isValid(board, i ,j, k)) {
continue;
}
board[i][j] = '1' + k;
if (j != 8) {
flag = dfs(board, i, j + 1);
} else {
flag = dfs(board, i + 1, 0);
}
// 当前合法&&下一轮dfs合法,说明找到解
if (flag) {
return true;
}
board[i][j] = '.';
}
// 遍历完9个数,仍然找不到合适的解,则返回false
return false;
}
}
}
// 当所有各自都走完,自然返回true(注意只有当前合法,才会继续往下走,继续往下走的最终结果是越了sudoku的界限)
return true;
}
bool isValid(const vector<vector<char>> &board, int x, int y, int k) {
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 9; i++) // 检查 y 列
if (i != x && board[i][y] == '1' + k)
return false;
for (j = 0; j < 9; j++) // 检查 x 行
if (j != y && board[x][j] == '1' + k)
return false;
for (i = 3 * (x / 3); i < 3 * (x / 3 + 1); i++)
for (j = 3 * (y / 3); j < 3 * (y / 3 + 1); j++)
if ((i != x || j != y) && board[i][j] == '1' + k)
return false;
return true;
}
};
小结1
做搜索的题目,最关键的是要知道对什么对象进行dfs,例如,在sudoku中是对每一个以“.”标记的方格进行dfs,在回文划分中,是对每一个划分的位置进行dfs,在8妃问题中,是对每一行妃子可以在的位置进行dfs。
其次,dfs时,我们需要判断所取的每一个解是否是有效的,最好写一个函数来专门做这件事情。只要当当前对象dfs的数值有效时,才会继续往对下一个对象进行dfs,否则就直接向上回溯了(这点可以参见sudoku中的解释)。
最后,对于每次dfs时,可以对范围进行分支限界。例如回文划分、subset等。
小结2
值得注意的是:到底要对多少对象进行dfs,有时候是很明显的,例如8妃和sudoku问题,8妃就是对8行依次dfs,sudoku就是对所有方格进行dfs。但有时,总共要对多少对象进行dfs并不明显。dfs的递归基要处理的就是dfs完多少个对象就一定要返回(不然就无限dfs下去了)。当然,在sudoku问题中,方格的循环走完返回,这是一个隐含的递归基。
总结:dfs函数中,递归基处理的是dfs多少个对象就要返回。而每次dfs的for循环,往往是每一次dfs的范围。当递归栈最顶层的那个dfs循环走完,搜素就完成了。
小结3
在图论中,往往是从某一个点开始往下dfs,dfs的范围是当前node的所有neighbor,与我们通常的搜索问题不同的是,图论中的dfs在回溯时不会剪枝,总之,找到一条路径就结束了。
[算法专题] 深度优先搜索&回溯剪枝的更多相关文章
- Leetcode之深度优先搜索&回溯专题-679. 24 点游戏(24 Game)
Leetcode之深度优先搜索&回溯专题-679. 24 点游戏(24 Game) 深度优先搜索的解题详细介绍,点击 你有 4 张写有 1 到 9 数字的牌.你需要判断是否能通过 *,/,+, ...
- Leetcode之深度优先搜索&回溯专题-491. 递增子序列(Increasing Subsequences)
Leetcode之深度优先搜索&回溯专题-491. 递增子序列(Increasing Subsequences) 深度优先搜索的解题详细介绍,点击 给定一个整型数组, 你的任务是找到所有该数组 ...
- Leetcode之深度优先搜索&回溯专题-980. 不同路径 III(Unique Paths III)
Leetcode之深度优先搜索&回溯专题-980. 不同路径 III(Unique Paths III) 深度优先搜索的解题详细介绍,点击 在二维网格 grid 上,有 4 种类型的方格: 1 ...
- Leetcode之深度优先搜索&回溯专题-638. 大礼包(Shopping Offers)
Leetcode之深度优先搜索&回溯专题-638. 大礼包(Shopping Offers) 深度优先搜索的解题详细介绍,点击 在LeetCode商店中, 有许多在售的物品. 然而,也有一些大 ...
- 回溯算法 DFS深度优先搜索 (递归与非递归实现)
回溯法是一种选优搜索法(试探法),被称为通用的解题方法,这种方法适用于解一些组合数相当大的问题.通过剪枝(约束+限界)可以大幅减少解决问题的计算量(搜索量). 基本思想 将n元问题P的状态空间E表示成 ...
- [算法入门]——深度优先搜索(DFS)
深度优先搜索(DFS) 深度优先搜索叫DFS(Depth First Search).OK,那么什么是深度优先搜索呢?_? 样例: 举个例子,你在一个方格网络中,可以简单理解为我们的地图,要从A点到B ...
- 算法总结—深度优先搜索DFS
深度优先搜索(DFS) 往往利用递归函数实现(隐式地使用栈). 深度优先从最开始的状态出发,遍历所有可以到达的状态.由此可以对所有的状态进行操作,或列举出所有的状态. 1.poj2386 Lake C ...
- [算法&数据结构]深度优先搜索(Depth First Search)
深度优先 搜索(DFS, Depth First Search) 从一个顶点v出发,首先将v标记为已遍历的顶点,然后选择一个邻接于v的尚未遍历的顶点u,如果u不存在,本次搜素终止.如果u存在,那么从u ...
- 【2018.07.29】(深度优先搜索/回溯)学习DFS算法小记
参考网站:https://blog.csdn.net/ldx19980108/article/details/76324307 这个网站里有动态图给我们体现BFS和DFS的区别:https://www ...
随机推荐
- Sql Server数据库之identity(自增)
一.identity的基本用法 1.identity的含义: identity表示该字段的值会自动更新,通常情况下,不允许直接修改identity修饰的字段,否则编译会报错 2.基本语法 列名 数据 ...
- jdango 使用oss存储
安装django-aliyun-oss2-storage-0.1.5.tar.gz settings文件添加 MEDIA_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'upload/') ...
- Dart 基础重点截取 Dart 2 20180417
官网教程 https://www.dartlang.org/guides/language/language-tour dart是一个单线程的语言,没有多线程 Final and const If y ...
- jq获取图片并转换为base64
html代码: <input type="file" id="file1"/> jq代码: $('#file1').change(function( ...
- swift 需求: 导航栏和HeaderView 使用一个背景图片。
问题界面 需求: 导航栏和HeaderView 使用一个背景图片.解决方案: 让 导航栏 变成透明. override func viewWillAppear(_ animated: Bool) { ...
- Quartz.NET快速入门指南
最近,在工作中遇到了 Quartz.net 这个组件,为了更好的理解项目代码的来龙去脉,于是决定好好的研究一下这个东西.确实是好东西,既然是好东西,我就拿出来分享一下.万丈高楼平地起,我们也从入门开始 ...
- Java Token的原理和生成使用机制
在此之前我们先了解一下什么是Cookie.Session.Token 1.什么是Cookie? cookie指的就是浏览器里面能永久存储数据的一种数据存储功能.cookie由服务器生成,发送给浏览器, ...
- zabbix安装(Ubuntu)
zabbix的安装 Zabbix监控架构至少需要server,agent,web模块.mysql.web部分和server安装在同一台机器上. Zabbix安装前服务器要做时间同步(ntp) 1.创建 ...
- Django跨域(前端跨域)
前情回顾 在说今天的问题之前先来回顾一下有关Ajax的相关内容 Ajax的优缺点 AJAX使用Javascript技术向服务器发送异步请求: AJAX无须刷新整个页面: 因为服务器响应内容不再是整个页 ...
- github管理项目
1.在GitHub上创建一个项目,然后拷贝git地址. 2.在本地打开GIT CMD,然后建立一个文件夹,输入git clone 上面拷贝的git地址. 3.文件夹下会多出一个以你创建的项目名字的文件 ...