【LeetCode】505. The Maze II 解题报告(C++)
- 作者: 负雪明烛
- id: fuxuemingzhu
- 个人博客:http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/
题目地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/the-maze-ii/
题目描述
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolling up, down, left or right, but it won’t stop rolling until hitting a wall. When the ball stops, it could choose the next direction.
Given the ball’s start position, the destination and the maze, find the shortest distance for the ball to stop at the destination. The distance is defined by the number of empty spaces traveled by the ball from the start position (excluded) to the destination (included). If the ball cannot stop at the destination, return -1.
The maze is represented by a binary 2D array. 1 means the wall and 0 means the empty space. You may assume that the borders of the maze are all walls. The start and destination coordinates are represented by row and column indexes.
Example 1:
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array0 0 1 0 00 0 0 0 00 0 0 1 01 1 0 1 10 0 0 0 0Input 2: start coordinate (rowStart, colStart) = (0, 4)Input 3: destination coordinate (rowDest, colDest) = (4, 4)Output: 12Explanation: One shortest way is : left -> down -> left -> down -> right -> down -> right.The total distance is 1 + 1 + 3 + 1 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 12.
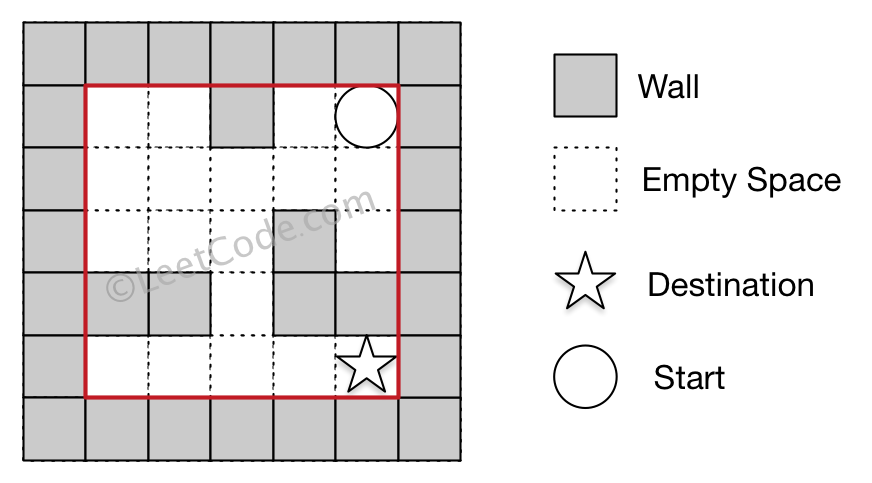
Example 2:
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array0 0 1 0 00 0 0 0 00 0 0 1 01 1 0 1 10 0 0 0 0Input 2: start coordinate (rowStart, colStart) = (0, 4)Input 3: destination coordinate (rowDest, colDest) = (3, 2)Output: -1Explanation: There is no way for the ball to stop at the destination.
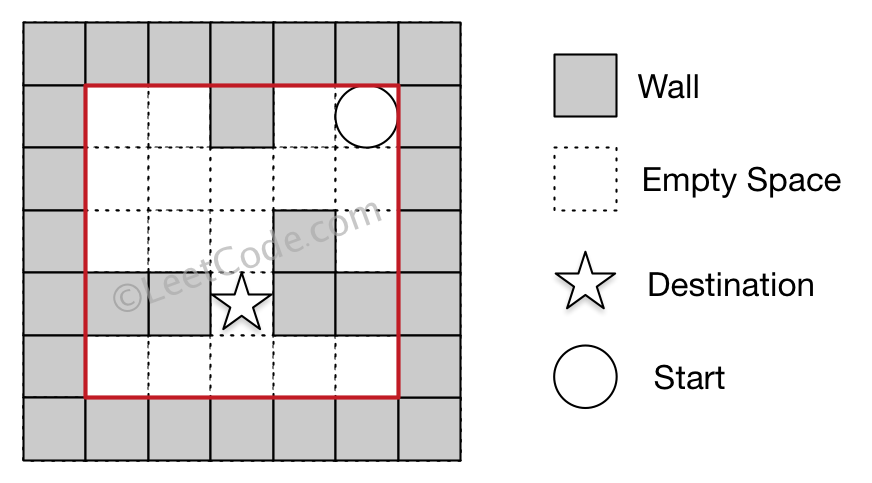
Note:
- There is only one ball and one destination in the maze.
- Both the ball and the destination exist on an empty space, and they will not be at the same position initially.
- The given maze does not contain border (like the red rectangle in the example pictures), but you could assume the border of the maze are all walls.
- The maze contains at least 2 empty spaces, and both the width and height of the maze won’t exceed 100.
题目大意
小球可以向某个方向一直滚动,当撞到边缘或者墙壁时才停止,每次停止时才可以选择下个移动的方向。问小球是否能从起点出发恰好停在目的地,并返回小球滚动到目的地需要的最少步数。
解题方法
BFS
题目要我们求最少的移动步数,很显然我们使用BFS解决。一般的迷宫问题只会移动一个格子,但是这个题目要求我们撞到墙壁才停止,所以我们需要遍历四个方向,判断四个方向分别撞到墙壁时移动的步数和结束位置。当小球移动到该结束位置总的步数比历史上所有的位置都小,该结束位置放入队列中。
一般BFS需要有个visited数组,用来判断每个位置是否访问过,从而判断新位置是否加入队列中。但是这个题目不需要,因为只有当到达一个结置位置总的步数比以前到达这个位置的步数小的时候,才会加入队列,所以是有限制条件的,结果会是有限的,不会无限循环下去。
代码里使用了dp作为访问每个位置的最小步数,默认是INT_MAX。从起点开始,计算出小球能访问到的所有位置,直至再运动已经不能让所有可以停止的点的访问步数缩小时停止。最后返回结束位置的步数。
C++代码如下:
class Solution {public:int shortestDistance(vector<vector<int>>& maze, vector<int>& start, vector<int>& destination) {const int M = maze.size();const int N = maze[0].size();vector<vector<int>> dp(M, vector<int>(N, INT_MAX));queue<vector<int>> que;que.push(start);dp[start[0]][start[1]] = 0;int count = 0;while (!que.empty()) {int size = que.size();vector<int> start = que.front(); que.pop();for (auto dir : dirs) {vector<int> end(2, 0);int step = rolling(maze, dir, start, end);if (dp[end[0]][end[1]] > dp[start[0]][start[1]] + step) {dp[end[0]][end[1]] = dp[start[0]][start[1]] + step;que.push(end);}}}return dp[destination[0]][destination[1]] == INT_MAX ? -1 : dp[destination[0]][destination[1]];}private:vector<vector<int>> dirs = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};int rolling(vector<vector<int>>& maze, vector<int>& curdir, vector<int>& start, vector<int>& end) {end = start;int step = 0;while (true) {int nxt_x = end[0] + curdir[0];int nxt_y = end[1] + curdir[1];if (nxt_x < 0 || nxt_x >= maze.size() || nxt_y < 0 || nxt_y >= maze[0].size()|| maze[nxt_x][nxt_y] == 1) {break;}end[0] = nxt_x;end[1] = nxt_y;step ++;}return step;}};
参考资料:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/the-maze-ii/solution/c-bfs-by-sheng-ben-xin/
日期
2019 年 9 月 20 日 —— 是选择中国互联网式加班?还是外企式养生?
【LeetCode】505. The Maze II 解题报告(C++)的更多相关文章
- 【LeetCode】47. Permutations II 解题报告(Python & C++)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 目录 题目描述 题目大意 解题方法 方法一:递归 方法二:回溯法 日期 题目地址:htt ...
- 【LeetCode】90. Subsets II 解题报告(Python & C++)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客:http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 目录 题目描述 题目大意 解题方法 递归 回溯法 日期 题目地址:https://leet ...
- [LeetCode] 505. The Maze II 迷宫 II
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolli ...
- [LeetCode] 505. The Maze II 迷宫之二
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolli ...
- LeetCode 505. The Maze II
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/the-maze-ii/ 题目: There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces a ...
- 【LeetCode】275. H-Index II 解题报告(Python)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 题目地址: https://leetcode.com/problems/h-index- ...
- 【LeetCode】52. N-Queens II 解题报告(Python & C+)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 目录 题目描述 题目大意 解题方法 全排列函数 回溯法 日期 题目地址:https:// ...
- 【LeetCode】454. 4Sum II 解题报告(Python & C++)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 目录 题目描述 题目大意 解题方法 字典 日期 题目地址:https://leetcod ...
- LeetCode: Pascal's Triangle II 解题报告
Pascal's Triangle II Total Accepted: 19384 Total Submissions: 63446 My Submissions Question Solution ...
随机推荐
- 【R读取报错】解决: Can't bind data because some arguments have the same name
最近读取一个数据时,报如标题的错误. args[1] <- "RT_10-VS-RT_0" all <- read.delim(paste0(args[1]," ...
- linux安全性增加
账户安全问题 Linux 默认会安装很多不必要的用户和用户组,如果不需要某些用户或者组,就要立即删除它,因为账户越多,系统就越不安全,很可能被黑客利用,进而威胁到服务器的安全. Linux系统中可以 ...
- NAT 工作原理
网络地址转换,就是替换IP报文头部的地址信息.NAT通常部署在一个组织的网络出口位置,通过将内部网络IP地址替换为出口的IP地址提供公网可达性和上层协议的连接能力 规定了三个保留地址段落:10.0.0 ...
- 【NetCore】RabbitMQ 封装
RabbitMQ 封装 代码 https://gitee.com/wosperry/wosperry-rabbit-mqtest/tree/master 参考Abp事件总线的用法,对拷贝的Demo进行 ...
- ArrayList总结及部分源码分析
ArrayList源码阅读笔记 1. ArrayList继承的抽象类和实现的接口 ArrayList类实现的接口 List接口:里面定义了List集合的基本接口,ArrayList进行了实现 Rand ...
- Netty4.x 源码实战系列(一): 深入理解ServerBootstrap 与 Bootstrap (1)
从Java1.4开始, Java引入了non-blocking IO,简称NIO.NIO与传统socket最大的不同就是引入了Channel和多路复用selector的概念.传统的socket是基于s ...
- Linux学习 - 系统定时任务
1 crond服务管理与访问控制 只有打开crond服务打开才能进行系统定时任务 service crond restart chkconfig crond on 2 定时任务编辑 crontab [ ...
- 【Linux】【Services】【SaaS】Docker+kubernetes(13. 部署Jenkins/Maven实现代码自动化发布)
1. 简介 Jenkins: 官方网站:https://jenkins.io/ 下载地址:https://jenkins.io/download/ war包下载:http://mirrors.jenk ...
- lucene的索引查询
package com.hope.lucene;import org.apache.lucene.document.Document;import org.apache.lucene.document ...
- SQLServer和java数据类型的对应关系
转载自:https://www.cnblogs.com/cunkouzh/p/5504052.html SQL Server 类型 JDBC 类型 (java.sql.Types) Java 语言类型 ...
