UVA1589 Xiangqi
Xiangqi is one of the most popular two-player board games in China. The game represents a battle between two armies with the goal of capturing the enemy's ``general" piece. In this problem, you are given a situation of later stage in the game. Besides, the red side has already ``delivered a check". Your work is to check whether the situation is ``checkmate".
Now we introduce some basic rules of Xiangqi. Xiangqi is played on a 10 x 9 board and the pieces are placed on the intersections (points). The top left point is (1,1) and the bottom right point is (10,9). There are two groups of pieces marked by black or red Chinese characters, belonging to the two players separately. During the game, each player in turn moves one piece from the point it occupies to another point. No two pieces can occupy the same point at the same time. A piece can be moved onto a point occupied by an enemy piece, in which case the enemy piece is``captured" and removed from the board. When the general is in danger of being captured by the enemy player on the enemy player's next move, the enemy player is said to have ``delivered a check". If the general's player can make no move to prevent the general's capture by next enemy move, the situation is called ``checkmate".
We only use 4 kinds of pieces introducing as follows:

- General: the generals can move and capture one point either vertically or horizontally and cannot leave the `` palace" unless the situation called `` flying general" (see the figure above). ``Flying general" means that one general can ``fly" across the board to capture the enemy general if they stand on the same line without intervening pieces.

- Chariot: the chariots can move and capture vertically and horizontally by any distance, but may not jump over intervening pieces

- Cannon: the cannons move like the chariots, horizontally and vertically, but capture by jumping exactly one piece (whether it is friendly or enemy) over to its target.

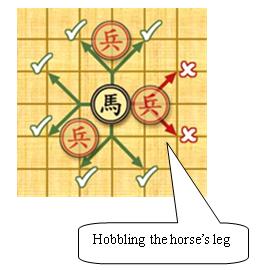
- Horse: the horses have 8 kinds of jumps to move and capture shown in the left figure. However, if there is any pieces lying on a point away from the horse horizontally or vertically it cannot move or capture in that direction (see the figure below), which is called `` hobbling the horse's leg".
Now you are given a situation only containing a black general, a red general and several red chariots, cannons and horses, and the red side has delivered a check. Now it turns to black side's move. Your job is to determine that whether this situation is ``checkmate".
Input
The input contains no more than 40 test cases. For each test case, the first line contains three integers representing the number of red pieces N ( 2 N
N 7) and the position of the black general. The following N lines contain details of N red pieces. For each line, there are a char and two integers representing the type and position of the piece (type char `G' for general, `R' for chariot, `H' for horse and `C' for cannon). We guarantee that the situation is legal and the red side has delivered the check.
7) and the position of the black general. The following N lines contain details of N red pieces. For each line, there are a char and two integers representing the type and position of the piece (type char `G' for general, `R' for chariot, `H' for horse and `C' for cannon). We guarantee that the situation is legal and the red side has delivered the check.
There is a blank line between two test cases. The input ends by `0 0 0'.
Output
For each test case, if the situation is checkmate, output a single word ` YES', otherwise output the word ` NO'.
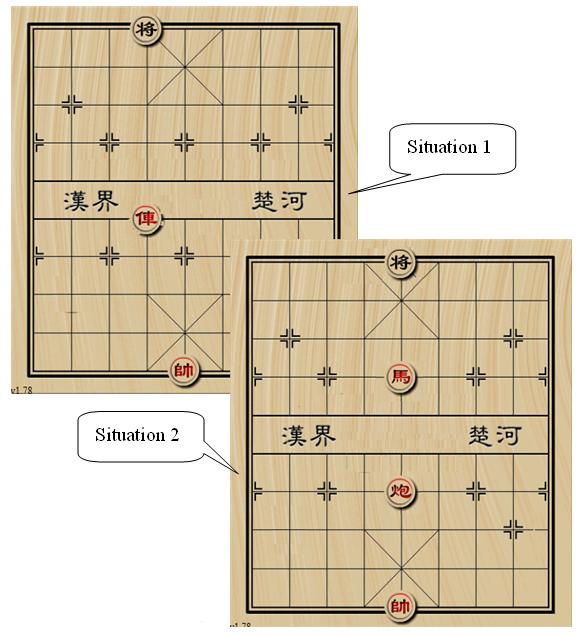
Hint: In the first situation, the black general is checked by chariot and ``flying general''. In the second situation, the black general can move to (1, 4) or (1, 6) to stop check. See the figure below.
Sample Input
- 2 1 4
- G 10 5
- R 6 4
- 3 1 5
- H 4 5
- G 10 5
- C 7 5
- 0 0 0
Sample Output
- YES
- NO
看到这么个问题确实有点头疼,但是仔细想过之后不难用模拟来解决问题,附上代码(略长);
- #include<stdio.h>
- #include<string.h>
- struct L
- {
- int a,b;
- };
- struct L General;
- struct L Chariot[];
- struct L Horse[];
- struct L Cannon[];
- int Qipan[][];
- int n,x,y;
- int tempx,tempy;
- char type[];
- int i1,i2,i3;
- int mainflag;
- int checkGenerals(int,int);
- int checkChariot(int,int,int,int);
- int checkHorse(int,int,int,int);
- int checkCannon(int,int,int,int);
- int checkPoint(int,int);
- int main()
- {
- while(scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&x,&y)==&&n)
- //Pay attention to the point (x,y),which is the black general located.
- {
- memset(Qipan,,sizeof(Qipan));
- //Create a Qipan and define all of it are 0.
- Qipan[x][y]=;
- // When put some point on the broad,transfer it into 1.
- //input the date,and store it into struct General,Chariot,Horse,Cannon.
- i1=i2=i3=;
- for(int i=;i<n;i++)
- {
- scanf("%s%d%d",type,&tempx,&tempy);
- Qipan[tempx][tempy]=;
- if(type[]=='G')
- {
- General.a=tempx;
- General.b=tempy;
- }
- else if(type[]=='R')
- {
- Chariot[i1].a=tempx;
- Chariot[i1++].b=tempy;
- }
- else if(type[]=='H')
- {
- Horse[i2].a=tempx;
- Horse[i2++].b=tempy;
- }
- else if(type[]=='C')
- {
- Cannon[i3].a=tempx;
- Cannon[i3++].b=tempy;
- }
- }
- // Now it's high time to deal with the problem,with all of the dates are stored in order.
- // The first we must check whether the two generals face to face directly.
- if(checkGenerals(x,y))
- {
- printf("NO\n");
- continue;
- }
- mainflag=;
- if(x+<)
- {
- Qipan[x][y]=;
- Qipan[x+][y]++;
- if(checkPoint(x+,y))
- mainflag=;
- Qipan[x][y]=;
- Qipan[x+][y]--;
- }
- if(mainflag)
- {
- printf("NO\n");
- continue;
- }
- if(x->)
- {
- Qipan[x][y]=;
- Qipan[x-][y]++;
- if(checkPoint(x-,y))
- mainflag=;
- Qipan[x][y]=;
- Qipan[x-][y]--;
- }
- if(mainflag)
- {
- printf("NO\n");
- continue;
- }
- if(y+<)
- {
- Qipan[x][y]=;
- Qipan[x][y+]++;
- if(checkPoint(x,y+))
- mainflag=;
- Qipan[x][y]=;
- Qipan[x][y+]--;
- }
- if(mainflag)
- {
- printf("NO\n");
- continue;
- }
- if(y->)
- {
- Qipan[x][y]=;
- Qipan[x][y-]++;
- if(checkPoint(x,y-))
- mainflag=;
- Qipan[x][y]=;
- Qipan[x][y-]++;
- }
- if(mainflag)
- {
- printf("NO\n");
- continue;
- }
- printf("YES\n");
- }
- }
- int checkGenerals(int x,int y)
- {
- if(General.b==y)
- {
- int Flag=;
- for(int i=x+;i<General.a;i++)
- if(Qipan[i][y])
- Flag++;
- if(Flag==)
- return ;
- }
- return ;
- }
- int checkChariot(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
- {
- int Flag;
- int xj1,yj1,xj2,yj2;
- xj1=x1<x2?x1:x2;
- xj2=x1>x2?x1:x2;
- yj1=y1<y2?y1:y2;
- yj2=y1>y2?y1:y2;
- if(x1==x2&&y1==y2)
- return ;
- if(x1==x2)
- {
- Flag=;
- for(int j=yj1+;j<yj2;j++)
- if(Qipan[x1][j])
- Flag=;
- if(Flag==) return ;
- }
- if(y1==y2)
- {
- Flag=;
- for(int i=xj1+;i<xj2;i++)
- if(Qipan[i][y1])
- Flag=;
- if(Flag==) return ;
- }
- return ;
- }
- int checkHorse(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
- {
- if(x1+==x2&&y1+==y2)
- if(Qipan[x1][y1+]==)
- return ;
- if(x1+==x2&&y1-==y2)
- if(Qipan[x1][y1-]==)
- return ;
- if(x1-==x2&&y1+==y2)
- if(Qipan[x1][y1+]==)
- return ;
- if(x1-==x2&&y1-==y2)
- if(Qipan[x1][y1-]==)
- return ;
- if(x1+==x2&&y1+==y2)
- if(Qipan[x1+][y1]==)
- return ;
- if(x1+==x2&&y1-==y2)
- if(Qipan[x1+][y1]==)
- return ;
- if(x1-==x2&&y1+==y2)
- if(Qipan[x1-][y1]==)
- return ;
- if(x1-==x2&&y1-==y2)
- if(Qipan[x1-][y1]==)
- return ;
- return ;
- }
- int checkCannon(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
- {
- int Flag=;
- int xj1,yj1,xj2,yj2;
- xj1=x1<x2?x1:x2;
- xj2=x1>x2?x1:x2;
- yj1=y1<y2?y1:y2;
- yj2=y1>y2?y1:y2;
- if(x1==x2&&y1==y2) return ;
- if(x1==x2)
- {
- for(int j=yj1+;j<yj2;j++)
- if(Qipan[x1][j]) Flag++;
- if(Flag==) return ;
- }
- if(y1==y2)
- {
- for(int i=xj1+;i<xj2;i++)
- if(Qipan[i][y1]) Flag++;
- if(Flag==) return ;
- }
- return ;
- }
- int checkPoint(int x,int y)
- {
- if(checkGenerals(x,y))
- return ;
- for(int i=;i<i1;i++)
- if(checkChariot(Chariot[i].a,Chariot[i].b,x,y))
- return ;
- for(int i=;i<i2;i++)
- if(checkHorse(Horse[i].a,Horse[i].b,x,y))
- return ;
- for(int i=;i<i3;i++)
- {
- if(checkCannon(Cannon[i].a,Cannon[i].b,x,y))
- return ;
- }
- return ;
- }
UVA1589 Xiangqi的更多相关文章
- [刷题]算法竞赛入门经典(第2版) 4-1/UVa1589 - Xiangqi
书上具体所有题目:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1hssH0KO 代码:(Accepted,0 ms) //UVa1589 #include<iostream> #incl ...
- UVA1589——xiangqi
开始碰到这个题时觉得太麻烦了直接跳过没做,现在放假了再次看这个题发现没有想象中那么麻烦,主要是题目理解要透彻,基本思路就是用结构体数组存下红方棋子,让黑将军每次移动一下,看移动后是否有一个红方棋子可以 ...
- 【习题4-1 Uva1589】Xiangqi
[链接] 我是链接,点我呀:) [题意] 在这里输入题意 [题解] 车是可以被吃掉的... 注意这个情况. 其他的模拟即可. [代码] #include <bits/stdc++.h> u ...
- HDU 4121 Xiangqi 我老了?
Xiangqi Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Sub ...
- HDU 4121 Xiangqi 模拟题
Xiangqi Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4121 ...
- Uva - 1589 - Xiangqi
Xiangqi is one of the most popular two-player board games in China. The game represents a battle bet ...
- [算法竞赛入门经典] 象棋 ACM/ICPC Fuzhou 2011, UVa1589 较详细注释
Description: Xiangqi is one of the most popular two-player board games in China. The game represents ...
- Xiangqi(简单模拟)
4746: Xiangqi 时间限制(普通/Java):1000MS/3000MS 内存限制:65536KByte 总提交: 15 测试通过:2 描述 Xiangqi i ...
- TZOJ 4746 Xiangqi(模拟棋盘数组)
描述 Xiangqi is one of the most popular two-player board games in China. The game represents a battle ...
随机推荐
- windows下adb+flash_image刷机
刷机是常事,总要把刷机包放在卡上,然后关机三键一起按到recovery再刷,觉得不爽,麻烦,所以研究出了adb调用flash_image刷system分区,全部脚本windows脚本执行,点点鼠标就o ...
- jQuery自定义函数验证邮箱格式
jQuery.fn.checkEmail = function() { // 自定义jQuery方法 var email_val = $(this).val(); reg = /^\w+([-+.]\ ...
- MVC4.0 上传Excel并存入数据库
这里的这个功能实现在WebForm很好实现,上传阶段简单的一个FileUoLoad控件就搞定了,什么取值,什么上传都是浮云,微软都帮我们封装好了,我们只需要一拖一拽就OK了,但这些在MVC中是不行的! ...
- zoj2562:搜索+数论(反素数)
题目大意:求n以内因子数量最多的数 n的范围为1e16 其实相当于求n以内最大的反素数... 由素数中的 算数基本原理 设d(a)为a的正因子的个数,则 d(n)=(a1+1)(a2+1)..... ...
- vim编辑器的设置文件
vim配置特点: 1.按F5可以直接编译并执行C.C++.java代码以及执行shell脚本,按“F8”可进行C.C++代码的调试 2.自动插入文件头 ,新建C.C++源文件时自动插入表头:包括文件名 ...
- Android apk获取系统权限
Android在apk内部,即通过java代码来进行修改系统文件或者修改系统设置等等,这样需要获取系统权限. 通过直接配置apk运行在System进程内 1. 在应用程序的AndroidManifes ...
- Hadoop 2、配置HDFS HA (高可用)
前提条件 先搭建 http://www.cnblogs.com/raphael5200/p/5152004.html 的环境,然后在其基础上进行修改 一.安装Zookeeper 由于环境有限,所以在仅 ...
- syslog_test.c 简单的syslog函数
#cat syslog_test.c #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<syslog.h> int mai ...
- warning: the `gets' function is dangerous and should not be used.(转)
今天在LINUX下编译C程序时,出现了:warning: the `gets' function is dangerous and should not be used. 这个warning. 百度之 ...
- html5 750 REM JS换算方法
在安卓手机低版本浏览器,如果进页面快速执行的话会出现计算宽度不正确的情况,解决方法是放在onload方法里面执行,但这种解决方式在一些高版本浏览器中会出现页面闪动,所以使用判断浏览器版本的方式来解决, ...
