STM32 Controller area network (bxCAN) Identifier filtering
Identifier filtering
In the CAN protocol the identifier of a message is not associated with the address of a node but related to the content of the message.
Consequently a transmitter broadcasts its message to all receivers.
On message reception a receiver node decides - depending on the identifier value - whether the software needs the message or not.
If the message is needed, it is copied into the SRAM.
If not, the message must be discarded without intervention by the software.
To fulfill this requirement, the bxCAN Controller provides 28 configurable and scalable filter banks (27-0) to the application.
In other devices the bxCAN Controller provides 14 configurable and scalable filter banks (13-0) to the application
in order to receive only the messages the software needs.
This hardware filtering saves CPU resources which would be otherwise needed to perform filtering by software.
Each filter bank x consists of two 32-bit registers, CAN_FxR0 and CAN_FxR1. = 2 * 28 = 56 Registers

Scalable width
To optimize and adapt the filters to the application needs, each filter bank can be scaled independently.
Depending on the filter scale a filter bank provides:
One 32-bit filter for the STDID[10:0], EXTID[17:0], IDE and RTR bits.
Two 16-bit filters for the STDID[10:0], RTR, IDE and EXTID[17:15] bits.
Furthermore, the filters can be configured in mask mode or in identifier list mode.
Mask mode
In mask mode the identifier registers are associated with mask registers specifying
which bits of the identifier are handled as must match or as dont care.
Each bit of the register specifies whether the bit of the associated identifier register
must match with the corresponding bit of the expected identifier or not.
0: Dont care, the bit is not used for the comparison --- Don't Care
1: Must match, the bit of the incoming identifier must have the same level
has specified in the corresponding identifier register of the filter -- Do Care.
Identifier list mode
In identifier list mode, the mask registers are used as identifier registers.
Thus instead of defining an identifier and a mask, two identifiers are specified,
doubling the number of single identifiers.
All bits of the incoming identifier must match the bits specified in the filter registers.
Each bit of the register specifies the level of the corresponding bit of the expected identifier.
0: Dominant bit is expected
1: Recessive bit is expected
Filter bank scale and mode configuration
The filter banks are configured by means of the corresponding CAN_FMR register.
To configure a filter bank it must be deactivated by clearing the FACT bit in the CAN_FAR register.
The filter scale is configured by means of the corresponding FSCx bit in the CAN_FS1R register, refer to Figure 342.
The identifier list or identifier mask mode for the corresponding Mask/Identifier registers is configured
by means of the FBMx bits in the CAN_FMR register.
To filter a group of identifiers, configure the Mask/Identifier registers in mask mode.
To select single identifiers, configure the Mask/Identifier registers in identifier list mode.
Filters not used by the application should be left deactivated.
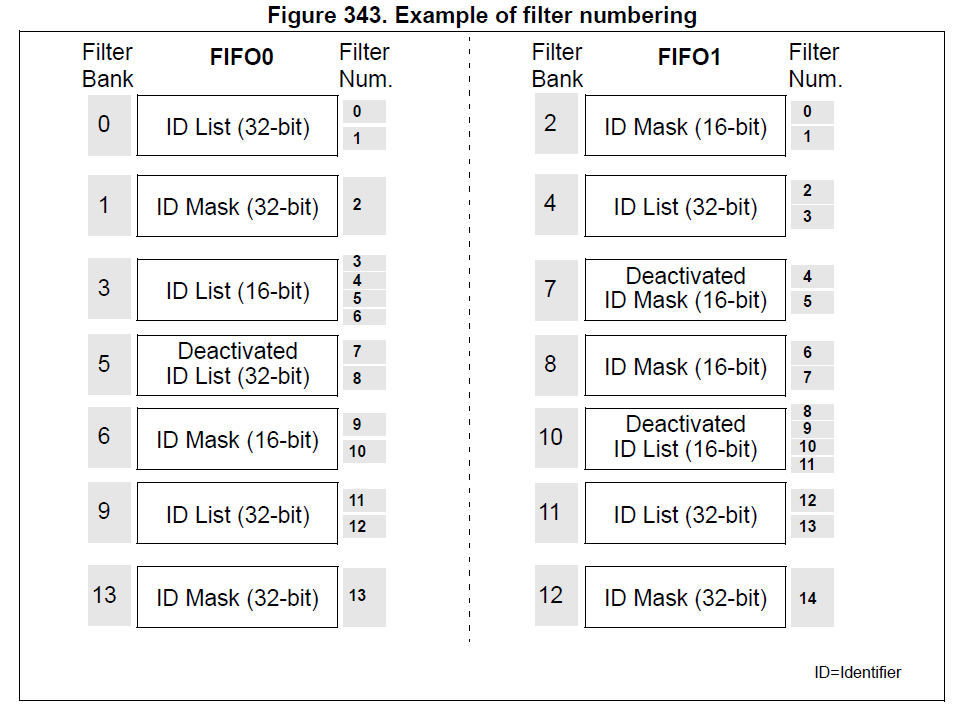
Each filter within a filter bank is numbered (called the Filter Number)
from 0 to a maximum dependent on the mode and the scale of each of the filter banks.
Concerning the filter configuration, refer to Figure 342.
Filter match index
Once a message has been received in the FIFO it is available to the application.
Typically, application data is copied into SRAM locations.
To copy the data to the right location the application has to identify the data by means of the identifier.
To avoid this, and to ease the access to the SRAM locations, the CAN controller provides a Filter Match Index.
This index is stored in the mailbox together with the message according to the filter priority rules.
Thus each received message has its associated filter match index.
The Filter Match index can be used in two ways:
Compare the Filter Match index with a list of expected values.
Use the Filter Match Index as an index on an array to access the data destination location.
For nonmasked filters, the software no longer has to compare the identifier.
If the filter is masked the software reduces the comparison to the masked bits only.
The index value of the filter number does not take into account the activation state of the
filter banks. In addition, two independent numbering schemes are used, one for each FIFO.
Refer to Figure 343 for an example.
Filter priority rules
Depending on the filter combination it may occur that an identifier passes successfully through several filters.
In this case the filter match value stored in the receive mailbox is chosen according to the following priority rules:
A 32-bit filter takes priority over a 16-bit filter.
For filters of equal scale, priority is given to the Identifier List mode over the Identifier Mask mode
For filters of equal scale and mode, priority is given by the filter number (the lower the number, the higher the priority).

The example above shows the filtering principle of the bxCAN. On reception of a message, the identifier is compared first with the filters configured in identifier list mode.
If there is a match, the message is stored in the associated FIFO and the index of the matching filter is stored in the Filter Match Index.
As shown in the example, the identifier matches with Identifier #2 thus the message content and FMI 2 is stored in the FIFO.
If there is no match, the incoming identifier is then compared with the filters configured in mask mode.
If the identifier does not match any of the identifiers configured in the filters, the message is discarded by hardware without disturbing the software.
STM32 Controller area network (bxCAN) Identifier filtering的更多相关文章
- 再谈STM32的CAN过滤器-bxCAN的过滤器的4种工作模式以及使用方法总结
1. 前言 bxCAN是STM32系列最稳定的IP核之一,无论有哪个新型号出来,这个IP核基本未变,可见这个IP核的设计是相当成熟的.本文所讲述的内容属于这个IP核的一部分,掌握了本文所讲内容,就可以 ...
- Real-time storage area network
A cluster of computing systems is provided with guaranteed real-time access to data storage in a sto ...
- 存储区域网络(Storage Area Network,简称SAN)
存储区域网络(Storage Area Network,简称SAN)采用网状通道(Fibre Channel ,简称FC,区别与Fiber Channel光纤通道)技术,通过FC交换机连接存储阵列和服 ...
- mvc action controller area
获取控制器名称: ViewContext.RouteData.Values["controller"].ToString(); 获取Action名称: ViewContext.Ro ...
- linux 下使用 tc 模拟网络延迟和丢包-使用 linux 模拟广域网延迟 - Emulating wide area network delays with Linux
tc 是linux 内置的命令:使用man pages 查看 我们看到,其功能为 show / manipulate traffic control settings,可对操作系统进行流量控制: ne ...
- HDU 2125 Local area network
简单DP,N×M的网格其中有一条边坏掉了,问从起点到终点的放法数 有两种方法,一种是DP很好理解 //#define LOCAL #include <cstdio> #include &l ...
- STM32(12)——CAN
简介: CAN是Controller Area Network,是 ISO 国际标准化的串行通信协议. CAN 控制器根据两根线上的电位差来判断总线电平.总线电平分为显性电平和隐性电平,二者必居其一 ...
- stm32之CAN总线基础
can总线协议概述: CAN是Controller Area Network的缩写,由德国博世公司开发:CAN通过ISO11891以及ISO11519进行了标准化: CAN总线的特点: 1.多 ...
- CAN通信(STM32)
1.CAN是控制器局域网络(Controller Area Network, CAN)的简称 (理论知识不做讲解了,太多了) 2.芯片选用:TJA1050 差分信号输入, 这里的显性电平CANH和CA ...
随机推荐
- [BZOJ 4350]括号序列再战猪猪侠 题解(区间DP)
[BZOJ 4350]括号序列再战猪猪侠 Description 括号序列与猪猪侠又大战了起来. 众所周知,括号序列是一个只有(和)组成的序列,我们称一个括号 序列S合法,当且仅当: 1.( )是一个 ...
- 转载一篇介绍CUDA
鉴于自己的毕设需要使用GPU CUDA这项技术,想找一本入门的教材,选择了Jason Sanders等所著的书<CUDA By Example an Introduction to Genera ...
- Anaconda+django写出第一个web app(九)
今天来学习外键的使用,用外键来连接数据库中的两个表. 当我们的tutorials非常多的时候,目前的显示方式就会使得页面非常凌乱.我们可以考虑把这些教程分为不同的系列,页面只显示标题以及概要等信息,进 ...
- elasticsearch安装ik分词器(极速版)
简介:下面讲有我已经打包并且编辑过的zip包,你可以在下面下载即可. 1.下载zip包.elasticsearch-analysis-ik-1.8.0.jar下面有附件链接[ik-安装包.zip],下 ...
- 012_iTerm2 快捷键大全
标签 新建标签:command + t 关闭标签:command + w 切换标签:command + 数字 command + 左右方向键 切换全屏:command + enter 查找:comma ...
- linux:根据名称杀死进程
参考网址:https://www.cnblogs.com/foohack/p/5359985.html pkill -f "process_name_pattern"
- java虚拟机规范(se8)——java虚拟机结构(三)
2.6. 栈帧 栈帧用于存储数据和部分结果,同样也用于执行动态链接,返回方法的值和分派异常. 当方法被调用的时候会创建一个新的栈帧.当一个方法调用结束时,它对应的栈帧就被销毁了,不管是正常调用结束还是 ...
- SCU 4438:Censor
Censor frog is now a editor to censor so-called sensitive words (敏感词). She has a long text p . Her j ...
- WebStrom配置node.js
Webstrom的注册码: WebStorm 7.0.1注册码 user name:newasp 注册码: ===== LICENSE BEGIN ===== 16417-12042010 00001 ...
- .NET Core 项目经验总结:项目结构介绍 (一)
原文地址(个人博客):http://www.gitblogs.com/Blogs/Details?id=384b4249-15e4-41bf-9cf7-44a3e1e51885 作为一个.NET We ...
