思维水题:UVa512-Spreadsheet Tracking
Spreadsheet Tracking
Data in spreadsheets are stored in cells, which are organized in rows (r) and columns (c). Some operations on spreadsheets can be applied to single cells (r,c), while others can be applied to entire rows or columns. Typical cell operations include inserting and deleting rows or columns and exchanging cell contents.
Some spreadsheets allow users to mark collections of rows or columns for deletion, so the entire collection can be deleted at once. Some (unusual) spreadsheets allow users to mark collections of rows or columns for insertions too. Issuing an insertion command results in new rows or columns being inserted before each of the marked rows or columns. Suppose, for example, the user marks rows 1 and 5 of the spreadsheet on the left for deletion. The spreadsheet then shrinks to the one on the right.
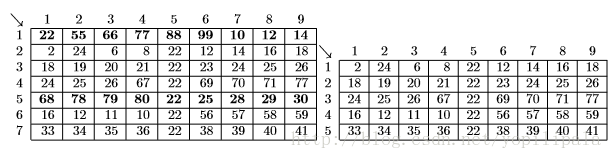
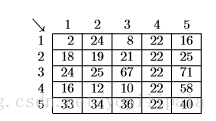
If the user subsequently marks columns 3, 6, 7, and 9 for deletion, the spreadsheet shrinks to this.
If the user marks rows 2, 3 and 5 for insertion, the spreadsheet grows to the one on the left. If the user then marks column 3 for insertion, the spreadsheet grows to the one in the middle. Finally, if the user exchanges the contents of cell (1,2) and cell (6,5), the spreadsheet looks like the one on the right.
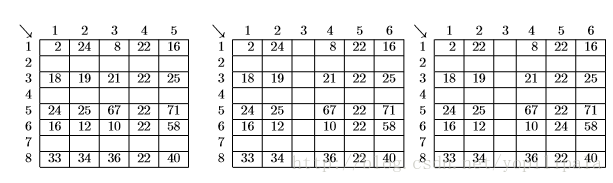
You must write tracking software that determines the final location of data in spreadsheets that result from row, column, and exchange operations similar to the ones illustrated here.
Input
The input consists of a sequence of spreadsheets, operations on those spreadsheets, and queries about them. Each spreadsheet definition begins with a pair of integers specifying its initial number of rows (r) and columns (c), followed by an integer specifying the number (n) of spreadsheet operations. Row and column labeling begins with 1. The maximum number of rows or columns of each spreadsheet is limited to 50. The following n lines specify the desired operations.
An operation to exchange the contents of cell (r1,c1) with the contents of cell (r2,c2) is given by: EX r1 c1 r2 c2
The four insert and delete commands—DC (delete columns), DR (delete rows), IC (insert columns), and IR (insert rows) are given by:
< command > A x1 x2 … xA where < command > is one of the four commands; A is a positive integer less than 10, and x1,…,xA are the labels of the columns or rows to be deleted or inserted before. For each insert and delete command, the order of the rows or columns in the command has no significance. Within a single delete or insert command, labels will be unique.
The operations are followed by an integer which is the number of queries for the spreadsheet. Each query consists of positive integers r and c, representing the row and column number of a cell in the original spreadsheet. For each query, your program must determine the current location of the data that was originally in cell (r,c). The end of input is indicated by a row consisting of a pair of zeros for the spreadsheet dimensions.
Output
For each spreadsheet, your program must output its sequence number (starting at 1). For each query, your program must output the original cell location followed by the final location of the data or the word ‘GONE’ if the contents of the original cell location were destroyed as a result of the operations. Separate output from different spreadsheets with a blank line.
The data file will not contain a sequence of commands that will cause the spreadsheet to exceed the maximum size.
Sample Input
7
9 5
DR 2 1 5
DC 4 3 6 7 9
IC 1 3 IR 2 2 4
EX 1 2 6 5
4
4 8
5 5
7 8
6 5
0 0
Sample Output
Spreadsheet #1
Cell data in (4,8) moved to (4,6)
Cell data in (5,5) GONE
Cell data in (7,8) moved to (7,6)
Cell data in (6,5) moved to (1,2)
解题心得:
- 题意就是给你一个表,然后进行行列的删除、增加空白的行列、两个个表格的交换操作,然后询问原本表中的位置的值在进行一系列操作之后在表中的位置(或者不存在)。
- 这个题思维难度不是很大,但是它要折磨你,很恼火,稍不注意就会写bug,做的方法有很多,我这里用的是简单的模拟。要注意一点就是这个题目上面给的例子并不是样例,只是给你解释一下大概的意思,被坑。
- 如果就模拟,可以建立两个表,一个初始表,一个变化后的表,然后直接对照这两个表就行了,但是在模拟的过程中要注意,每次插入或者删除操作是同时进行的(就是不能在前面的删除操作过程中对下面要进行的行列的操作产生影响),所有在插入或者删除的时候要先从从数值大的行列进行操作,不然先改变前面的行或者列会影响后面的行和列。
- 然后就是输出问题要注意其中一句话,将每两个例子用空白行分离,但最后一个例子后面不打印空行,不注意会PE。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 60;
int maps[2][maxn][maxn];//maps[0][n][m]表示原表,maps[1][n][m]表示改变后表
int op[maxn];
int n,m,q,n1,m1;
char s[maxn];
void EX()
{
int r1,c1,c2,r2;
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&r1,&c1,&r2,&c2);
swap(maps[1][r1][c1],maps[1][r2][c2]);
}
void pre_maps()
{
int t = 1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
maps[0][i][j] = maps[1][i][j] = t++;
}
void DR()
{
int times;
scanf("%d",×);
for(int i=0;i<times;i++)
scanf("%d",&op[i]);
sort(op,op+times);//先对后面的行列进行操作以免产生影响,后面的后面
for(int i=times-1;i>=0;i--)
{
int r = op[i];
for(int i=r;i<=n1;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=m1;j++)
maps[1][i][j] = maps[1][i+1][j];
}
n1-=times;//记录剩下的行列
}
void DC()
{
int times;
scanf("%d",×);
for(int i=0;i<times;i++)
scanf("%d",&op[i]);
sort(op,op+times);
for(int i=times-1;i>=0;i--)
{
int c = op[i];
for(int i=c;i<=m1;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=n1;j++)
maps[1][j][i] = maps[1][j][i+1];
}
m1-=times;
}
void IR()
{
int times;
scanf("%d",×);
for(int i=0;i<times;i++)
scanf("%d",&op[i]);
sort(op,op+times);
for(int i=times-1;i>=0;i--)
{
int r = op[i];
for(int i=n1+1;i>r;i--)
for(int j=1;j<=m1;j++)
maps[1][i][j] = maps[1][i-1][j];
for(int j=1;j<=m1;j++)
maps[1][r][j] = 0;
n1++;
}
}
void IC()
{
int times;
scanf("%d",×);
for(int i=0;i<times;i++)
scanf("%d",&op[i]);
sort(op,op+times);
for(int i=times-1;i>=0;i--)
{
int c = op[i];
for(int i=m1+1;i>c;i--)
for(int j=1;j<=n1;j++)
maps[1][j][i] = maps[1][j][i-1];
for(int i=1;i<=n1;i++)
maps[1][i][c] = 0;
m1++;
}
}
void _find(int r,int c)
{
int va = maps[0][r][c];
for(int i=1;i<=n1;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=m1;j++)
{
if(maps[1][i][j] == va)
{
printf("Cell data in (%d,%d) moved to (%d,%d)\n",r,c,i,j);
return;
}
}
printf("Cell data in (%d,%d) GONE\n",r,c);
}
int main()
{
int Case = 1;
bool flag = false;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m))
{
if(n + m == 0)
break;
if(flag)
printf("\n");//用来输出空行
flag = true;
n1 = n,m1 = m;
memset(maps,0,sizeof(maps));
pre_maps();
int opr;
scanf("%d",&opr);
while(opr--)
{
scanf("%s",s);
if(s[0] == 'E')
EX();
else if(s[0] == 'D' && s[1] == 'R')
DR();
else if(s[0] == 'D' && s[1] == 'C')
DC();
else if(s[0] == 'I' && s[1] == 'R')
IR();
else if(s[0] == 'I' && s[1] == 'C')
IC();
}
int query;
scanf("%d",&query);
printf("Spreadsheet #%d\n",Case++);
while(query--)
{
int r,c;
scanf("%d%d",&r,&c);
_find(r,c);
}
}
return 0;
}
思维水题:UVa512-Spreadsheet Tracking的更多相关文章
- HDU 2674 N!Again(数学思维水题)
题目 //行开始看被吓一跳,那么大,没有头绪, //看了解题报告,发现这是一道大大大的水题,,,,,//2009 = 7 * 7 * 41//对2009分解,看它有哪些质因子,它最大的质因子是41,那 ...
- HDOJ/HDU 1256 画8(绞下思维~水题)
Problem Description 谁画8画的好,画的快,今后就发的快,学业发达,事业发达,祝大家发,发,发. Input 输入的第一行为一个整数N,表示后面有N组数据. 每组数据中有一个字符和一 ...
- 2019年华南理工校赛(春季赛)--I--炒股(简单思维水题)
水题,想想就过了 题目如下: 链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/625/I来源:牛客网 攒机一时爽,一直攒机一直爽. 沉迷攒机的胡老师很快就发现,他每天只能 ...
- Iroha and a Grid AtCoder - 1974(思维水题)
就是一个组合数水题 偷个图 去掉阴影部分 把整个图看成上下两个矩形 对于上面的矩形求出起点到每个绿点的方案 对于下面的矩形 求出每个绿点到终点的方案 上下两个绿点的方案相乘后相加 就是了 想想为什么 ...
- 【CodeForces - 707B】Bakery(思维水题)
Bakery Descriptions 玛莎想在从1到n的n个城市中开一家自己的面包店,在其中一个城市烘焙松饼. 为了在她的面包房烘焙松饼,玛莎需要从一些储存的地方建立面粉供应.只有k个仓库,位于不同 ...
- CodeForces 604C 【思维水题】`
题意: 给你01字符串的长度再给你一个串. 然后你可以在这个串中选择一个起点和一个终点使得这个连续区间内所有的位取反. 求: 经过处理后最多会得到多少次01变换. 例如:0101是4次,0001是2次 ...
- 又一道简单题&&Ladygod(两道思维水题)
Ladygod Time Limit: 3000/1000MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65535/65535KB (Java/Others) Submit S ...
- 【Gym - 100923A】Por Costel and Azerah(思维水题)
Por Costel and Azerah Descriptions 给你n个数 问你,有多少个子序列 的和是偶数 Example Input 233 10 124 2 Output 33 题目链接 ...
- codeforces 804A Find Amir 思维/水题
A few years ago Sajjad left his school and register to another one due to security reasons. Now he w ...
随机推荐
- Centos7.2内网环境安装MySQL5.7.24
1.配置本地yum源 内网环境,首先需要配置本地yum源,以解决MySQL的依赖安装,具体参考该文:点击打开 2.查看服务器环境 uname -a 3.去官网下载MySQL安装包 MySQL官网网址: ...
- zip (ICSharpCode.SharpZipLib.dll文件需要下载)
ZipClass zc=new ZipClass (); zc.ZipDir(@"E:\1\新建文件夹", @"E:\1\新建文件夹.zip", 1);//压缩 ...
- JavaScript 函数(方法)
1 定义 1.1 函数是由事件驱动的或者当它被调用时执行的可重复使用的代码块. 语法: 函数就是包裹在大括号中的代码块,前面使用了关键词 function function 方法名(参数列表){ 代码 ...
- $.ajax同步/异步(async:false/true)
虽然说ajax用来执行异步请求的比较多,但有时还是存在需要同步执行的情况的. 比如:我需要通过ajax取执行请求以返回一个值,这个值在ajax后面是需要使用到的,这时就不能用异步请求了.这时候就需要使 ...
- Python3+selenium3环境搭建笔记
系统:win7 64位浏览器:ie9 64位 chrome70 32位 firefox63 64位python版本:3.6.5 Windows x86 executable installersele ...
- 无法启动 Diagnostic Policy Service(服务错误 1079)的解决方案
问题 在services.msc中手动启动 Diagnostic Policy Service 时,弹出以下提示: ---------------------------服务------------- ...
- LIBCD.lib(crt0.obj) : error LNK2001: unresolved external symbol _main
在创建MFC项目时,如果没有设置好项目参数, 就会在编译时产生很多连接错误, 如我今天遇到的: LIBCD.lib(crt0.obj) : error LNK2001: unresolved exte ...
- Android(java)学习笔记117:SharedPreferences(轻量级存储类)
1.SharedPreferences是Android平台上一个轻量级的存储类,简单的说就是可以存储一些我们需要的变量信息.2个activity 之间的数据传递除了可以他通过intent来传递数据,还 ...
- GCD 代码以及GCD思想
# 欧几里得算法 现在,我们来学习一下欧几里得算法. 欧几里得算法又称辗转相除法,主要用于算求两个正数之间的最大公约数.对于最大公约数这个名称,其英文名称为(Greatest Common Divis ...
- CAD控件的鼠标事件(网页版)
_DMxDrawXEvents::MouseEvent CAD控件中的鼠标事件. 参数 说明 LONG lType 事件类型,1鼠标移动,2是鼠标左键按下,3是鼠标右键按下,4是鼠标左键双击 5是鼠标 ...
