[CENTOS7] 加入Windows域
How To Join CentOS Linux To An Active Directory Domain
Here we’ll show you how to add your Linux system to a Microsoft Windows Active Directory (AD) domain through the command line. This will allow us to SSH into the Linux server with user accounts in our AD domain, providing a central source of cross-platform authentication.
There are a number of ways to do this, however this is the easiest way that I’ve found to do it entirely through the command line.
In this example I am using CentOS 7 and Windows Server 2012 R2, however the version of Windows should not matter. We are assuming that our domain is already setup and configured, we’re simply joining our CentOS server to an existing domain.
Preparing CentOS
First we want to install all of the below packages in CentOS.
yum install sssd realmd oddjob oddjob-mkhomedir adcli samba-common samba-common-tools krb5-workstation openldap-clients policycoreutils-python -y
The CentOS server will need to be able to resolve the Active Directory domain in order to successfully join it. In this instance my DNS server in /etc/resolv.conf is set to one of the Active Directory servers hosting the example.com domain that I wish to join.
[root@centos7 ~]# cat /etc/resolv.conf
search example.com
nameserver 192.168.1.2
Join CentOS To Windows Domain
Now that we’ve got that out of the way we can actually join the domain, this can be done with the ‘realm join’ command as shown below. You will need to specify the username of a user in the domain that has privileges to join a computer to the domain.
[root@centos7 ~]# realm join --user=administrator example.com
Password for administrator:
Once you enter the password for your specific account, the /etc/sssd/sssd.conf and /etc/krb.conf files will be automatically configured. This is really great as editing these manually usually leads to all sorts of trivial problems when joining the domain. The /etc/krb5.keytab file is also created during this process.
If this fails, you can add -v to the end of the command for highly verbose output, which should give you more detailed information regarding the problem for further troubleshooting.
We can confirm that we’re in the realm (Linux terminology for the domain) by running the ‘realm list’ command, as shown below.
[root@centos7 ~]# realm list
example.com
type: kerberos
realm-name: EXAMPLE.COM
domain-name: example.com
configured: kerberos-member
server-software: active-directory
client-software: sssd
required-package: oddjob
required-package: oddjob-mkhomedir
required-package: sssd
required-package: adcli
required-package: samba-common-tools
login-formats: %U@example.com
login-policy: allow-realm-logins
Once this has completed successfully, a computer object will be created in Active Directory in the default computers container as shown below.
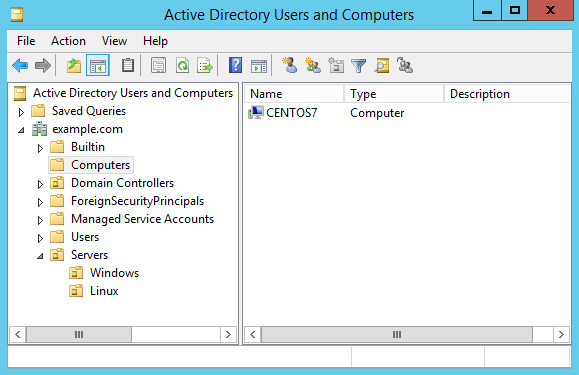
To keep things neat I like to move this into some other organizational unit (OU) for Linux servers rather than leaving things in the default computers container, however this doesn’t really matter for this exercise.
Now that our Linux server is a member of the Active Directory domain we can perform some tests. By default if we want to specify any users in the domain, we need to specify the domain name. For example with the ‘id’ command below, we get nothing back for ‘administrator’, however ‘administrator@example.com’ shows the UID for the account as well as all the groups the account is a member of in the Active Directory domain.
[root@centos7 ~]# id administrator
id: administrator: no such user [root@centos7 ~]# id administrator@example.com
uid=1829600500(administrator@example.com) gid=1829600513(domain users@example.com) groups=1829600513(domain users@example.com),1829600512(domain admins@example.com),1829600572(denied rodc password replication group@example.com),1829600519(enterprise admins@example.com),1829600518(schema admins@example.com),1829600520(group policy creator owners@example.com)
We can change this behaviour by modifying the /etc/sssd/sssd.conf file, the following lines need to change from:
use_fully_qualified_names = True
fallback_homedir = /home/%u@%d
To the below, which does not require the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) to be specified. This also modifies the user directory in /home from having the FQDN specified after the username.
use_fully_qualified_names = False
fallback_homedir = /home/%u
To apply these changes, restart sssd.
[root@centos7 ~]# systemctl restart sssd
Now we should be able to find user accounts without specifying the domain, as shown below this now works where it did not previously.
[root@centos7 ~]# id administrator
uid=1829600500(administrator) gid=1829600513(domain users) groups=1829600513(domain users),1829600512(domain admins),1829600572(denied rodc password replication group),1829600520(group policy creator owners),1829600519(enterprise admins),1829600518(schema admins)
If this is still not correctly working for you, I suggest that you take a look at flushing your sssd cache.
Configuring SSH and Sudo Access
Now that we have successfully joined our CentOS server to the example.com domain, we can SSH in as any domain user from Active Directory with default settings.
[root@centos7 ~]# ssh user1@localhost
user1@localhost's password:
Creating home directory for user1.
We can further restrict SSH access by modifying the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file and make use of things like AllowUsers or AllowGroups to only allow certain user or groups from AD to have access. See our guide to the sshd_config file for further information. Don’t forget to restart sshd if you make any changes to this file in order to apply them.
We can also modify our sudoers configuration to allow our user account from the domain the desired level of access. I usually create an Active Directory group called something like ‘sudoers’, put my user in it, then allow this group sudo access by creating a file in /etc/sudoers.d/ which allows root access to be centrally controlled by AD.
Below is an example of this, the ‘sudoers’ group will have full root access.
[root@centos7 ~]# cat /etc/sudoers.d/sudoers
%sudoers ALL=(ALL) ALL
This group only exists in Active Directory, our Linux server can see that user1 is a member of the sudoers group in Active Directory, and respects this group configuration and allows user1 root privileges as per the above configuration.
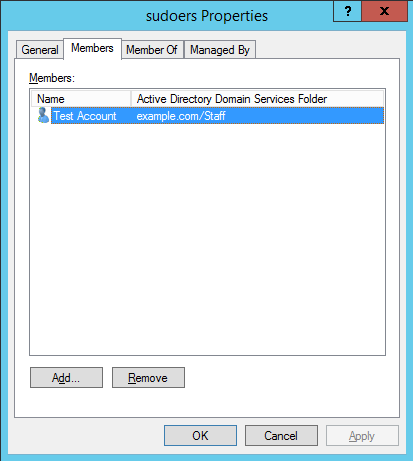
The username of Test Account is ‘user1’.
With this in place, our user1 account in the example.com Active Directory domain will now be able to use the sudo command to run commands with root privileges.
[user1@centos7 ~]$ sudo su
[sudo] password for user1:
[root@centos7 user1]#
[root@centos7 user1]# whoami
root
That’s all there is to it, we can now SSH to a Linux server with a user account from our Active Directory domain and even grant specific users or groups from AD specific levels of access.
Leaving The Domain
If you want to reverse the process and remove yourself from the domain, simply run the ‘realm leave’ command followed by the domain name, as shown below.
[root@centos7 ~]# realm leave example.com
This will complete without any further user input. It will delete the computer object that was created in Active Directory, remove the keytab file, and set the sssd.conf and krb5.conf files back to default.
Summary
We have demonstrated how you can easily add your CentOS Linux system to a Microsoft Windows Active Directory domain, and then grant SSH or sudo access based on the user or group from the domain.
If you have a large number of Linux servers and an existing Windows domain you can easily use this process to add your Linux servers to the Windows domain, allowing for centralised user authentication which is far easier to manage when compared to having local user accounts spread out on every Linux server.
Share this:
- 8Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)8
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Google+ (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to email this to a friend (Opens in new window)
39 Comments.
Maas Salem March 1, 2017 at 12:47 am
Might want to add this.
yum install samba-common-tools -y
– of you wont be able to join the domain. ( error in missing packages.)
Thanks
Hmm I looked over the Ansible config I deploy this to Linux servers with and that package is not installed, although on the two servers I checked they already had that package. I’ll update the post, thanks.
This seems to have been added as a dependency with the above packages in 7.x, at least as of 11/2017.
Hello, very usefull information.
On a my active directory the OS information of my Linux box is empty. Does it the same for you ? How can I solve that?
Thanks in advancedI have the same thing, I haven’t been able to find a way through SSSD to populate that field. I believe with realmd it’s possible by specifying ‘os-name’, however I was not able to get that working in my test.
Hello, for info, I find a way to do it using realmd :
realm join –user=xxxx –computer-ou=OU=LinuxOS –os-name=OracleLinux –os-version=”Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.3″
now I am looking on how to update the os-version & os-name fields when a linux box is already into the AD
t0ta11ed August 18, 2017 at 5:35 am
You can do this in AD with the Powershell command SET-ADCOMPUTER. Helpful article!
Muhammad Khan March 26, 2017 at 3:17 am
Super Article, A very convenient way of integration of Linux & Windows Server. Great Job, Jarrod
-
I haven’t tested with CentOS 6, however I believe it should work. Not sure about HP-UX, I’ve never used it, sorry.
Hello,
it doesn’t work on redhat/centos/oraclelinux 6. some packages are not available. Instead, use adcli package. (avalaible in Centos Mirror repo, if i remember well.)
-
Rafael May 18, 2017 at 5:19 am
Great article, Jarrod. It worked perfectly for me, using CentOS 7.
Just a few comments:
– /etc/krb.conf will be /etc/krb5.conf since we’re using krb5-workstation. At first I was concerned something went wrong but then I realized is was another filename.
– I ran into some odd issues like not all users in domain being able to login, and id command not working for all users. So a colleague suggested installing winbind and it worked like a charm. My AD domain has a trust with another domain and I’m able to login with any user from both domains after installing winbind. I recommend you add it in the packages list.
– You can add Domain Admins group in sudoers so every sysadmin can login in the Linux server and elevate. I used this line/syntax:
%mydomain\\domain\ admins ALL=(ALL) ALL
Any other AD groups with spaces in the name can also be added like this, using a single dash after the word preceding the space.
– When using domains with trust, you may want to use FQDN to specify domain/user. So I can login and put in sudoers users like user1@mydomain1.com and user2@mydomain2.com. Winbind is essential for this.
Thank you very much!
Hello, there is a way for AD windows account to get log in over the file explorer to a specific shared folder on the linux? eg. get log in to her own $HOME on the linux from her Windows Computer?
That should be possible with Samba, you can mount shared directories from either Windows or Linux and authenticate against AD.
-
Nothing in particular comes to mind sorry, it’s not something I’ve personally needed to setup, I’ve just seen the options available in Samba in the past.
-
Thank you so much for the instructions. I was able to join the domain, however, Windows domain users are not able to login to Centos, id username@domain.com gives error “no such user” What am I missing here?
I’ve had similar before, try and clear the SSSD cache then try again: https://www.rootusers.com/how-to-clear-the-sssd-cache-in-linux/
uid=1829600500(administrator@example.com) gid=1829600513
UID and GId was not match with Active Directory.How to match UID and GID with AD
Yes,
i have centos 7 and i am using realm for domain join, after domain join they are showing different UID and GID, that UID and GID was not match with AD.zN_Ars3n September 27, 2017 at 8:44 pm
Hello Jarrod!
I have an issue with adding linux to AD. I added machine to AD with domain admin credentials. When I run ‘realm list’ it shows me that my machine is in my domain but I cannot log in to the system by domain credencials. When I run ‘id admin@mydomain-com.local‘ it shows me message “no such user”. I am using winbindd in this machine too and when I run ‘wbinfo -u’ it shows me all users in my domain. I cleared cache for sssd but it wont helps. Could u help with this issue?Not too sure about winbind, I haven’t personally used it, could you try changing to sssd? I believe it’s better supported.
Mitsos October 13, 2017 at 4:19 pm
Great article !!!
In order to get Operating System info on Active Directory Users & Computers, on a Centos 7 machine you can create a /etc/realmd.conf file and the following data:[active-directory]
os-name = Linux
os-version = CentOS 7[service]
automatic-install = yesThe problem that I am facing is that when I run:
#getent passwd
I do not get any AD accounts, contrary when running id , I get all the info. More over, when I run wbinfo -u, I get errors (I suppose that’s my mistake cos winbind does not work with sssd).hello, in my company we have around 100 domain controller all around the world. often when I join a server to the Active Directory Domain, the server never choose the closest DC (same subnet for example).
Is there a way to fix one or 2 DC to contact?
Thanks.Hello,
do you know how to fix sssd to contact only 1 or 2 dc instead of to contact one randomly?
Regards
Is Active Directory 2016 (Domain Functional Level 2016) also supported with CentOS 6 / 7?
Thank you for your reply
Thanks Jarrod, going forward via LDAP and AD I think you have no choice plus IMHO this is a better option as it’s just like joining a Windows and Apple(still MAC is problematic) machine to the Domain.
The Why not to go forward with LDAP
Clarification regarding the status of Identity Management for Unix (IDMU) & NIS Server Role in Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview and beyond
https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/activedirectoryua/2016/02/09/identity-management-for-unix-idmu-is-deprecated-in-windows-server/We are really looking forward for any such article as mentioned by Gab May 18, 2017 at 8:10 pm
Leave a Comment
NOTE - You can use these HTML tags and attributes:<a href="" title=""> <abbr title=""> <acronym title=""> <b> <blockquote cite=""> <cite> <code> <del datetime=""> <em> <i> <q cite=""> <s> <strike> <strong>
NAME
Website URL
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Subscribe
Receive new post notifications by email for free! Unsubscribe any time.
Email Address
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Categories

Copyright © 2017 RootUsers | Privacy Policy | Terms and Conditions
↑ Top
[CENTOS7] 加入Windows域的更多相关文章
- C#开发中Windows域认证登录2(扩展吉日嘎拉GPM系统)
原文地址:http://www.cuiwenyuan.com/shanghai/post/Windows-AD-Logon-Intergrated-into-Jirigala-GPM-DotNet-B ...
- C#开发中Windows域认证登录2016(扩展吉日嘎拉GPM系统V4.2)
2013年搞公司的OA时,为了统一用户登录,将Windows AD的用户和OA的账号对接,OA用户名的规则就是使用Windows AD的用户名,格式举例:Troy.Cui,原理就是先进行域服务器的认证 ...
- 用PHP实现Windows域验证
系统集成中,可能会有这种需求 Windows 域验证本质上是LDAP验证 但在网上居然找不到详细的技术文档,可见不受待见之极.
- Windows Services windows域账户管理
windows 域账户管理 一.什么是域账户: 域账户是域是网络对象的分组.例如:用户.组和计算机.域中所有的对象都存储在 Active Directory 下.Active Directory 可 ...
- pip在windows域下使用代理安装package方法
首先说明下,本人在公司使用windows域账户代理上网,用pip在线安装package 返回ProxyError,类似Tunnel connection failed: 407 authenticat ...
- 将samba加入到windows域《转载》
将samba加入到windows域 那什么是域呢? 一台Windows计算机,它要么隶属于工作组,要么隶属于域.所以说到域,我们就不得不提一下工作组,工作组是MS的概念,一般的普遍称谓是对等网. 工作 ...
- linux加入windows域之完美方案(转载)
概念理解:1.kdc:可信任的密钥分发中心(KDC, Key Distribution Center).2.Winbind是Samba套件的功能之一.它允许Unix系统利用Windows NT的用户帐 ...
- Windows域的相关操作
一.windows域账户组操作: net group /domain #查看所有组 net group GROUP-NAME /domain #查看某一个组 net group GROUP-NAME ...
- windows 域的安装方法
前面的博客中我们知道了 Windows AD域的升级,下面我谈谈Windows域的安装和卸载. 卸载AD域 配置备份AD域 安装子域 删除子域(必须在根域管理员模式下删除,否则无法删除) 删除命令 导 ...
随机推荐
- python独立环境——virtualenv
安装: pip3 intall virtualenv 创建独立运行环境: 1. 进入项目文件夹根目录 2. 创建环境 Mac:myproject michael$ virtualenv --no- ...
- saltstack快速入门
SALTSTACK是什么? Salt是一种和以往不同的基础设施管理方法,它是建立在大规模系统高速通讯能力可以大幅提升的想法上.这种方法使得Salt成为一个强大的能够解决基础设施中许多特定问题的多任务系 ...
- JAVA使用Gecco爬虫 抓取网页内容(附Demo)
JAVA 爬虫工具有挺多的,但是Gecco是一个挺轻量方便的工具. 先上项目结构图. 这是一个 JAVASE的 MAVEN 项目,要添加包依赖,其他就四个文件.log4j.properties 加上三 ...
- Fiddler 502问题
使用Fiddler的时候遇到下面这个问题:在地址栏想打开个一般处理程序,出现连接本机失败的提示,如下图: 而这在我没打开Fiddler的时候是显示正常的. 查看Fiddler,在嗅探 -> 第二 ...
- .Net Core使用NLog记录日志
参见:https://github.com/NLog/NLog.Web/wiki/Getting-started-with-ASP.NET-Core-2 大致步骤: Nuget中引用NLog及NLog ...
- spring boot 2.0 源码分析(四)
在上一章的源码分析里,我们知道了spring boot 2.0中的环境是如何区分普通环境和web环境的,以及如何准备运行时环境和应用上下文的,今天我们继续分析一下run函数接下来又做了那些事情.先把r ...
- Beta阶段——Scrum 冲刺博客第一天
一.当天站立式会议照片一张 二.每个人的工作 (有work item 的ID),并将其记录在码云项目管理中 昨天已完成的工作 今日是Beta冲刺第一天,昨日没有完成的工作 今天计划完成的工作 实现对i ...
- IOS应用图标尺寸
Table 41-1Size (in pixels) of custom icons and images Asset iPhone 6 Plus (@3x) iPhone 6 and iPhone ...
- 如何获取div距离浏览器顶部的高度,宽度,内容
JS就可以获取了, document.getElementById("DIV的ID或者其它选择").offsetTop;这是离顶部 JQ可以这样: $("#aaa&quo ...
- C# 之String以及浅拷贝与深拷贝
一.String到底是值类型还是引用类型 MSDN 中明确指出 String 是引用类型而不是值类型,但 String 表面上用起来却像是值类型,这又是什么原因呢? 首先从下面这个例子入手: //值 ...
