Linux Expect自动交互脚本
https://likegeeks.com/expect-command/
In the previous post, we talked about writing practical shell scripts and we saw how it is easy to write a shell script. Today we are going to talk about a tool that does magic to our shell scripts, that tool is the Expect command or Expect scripting language.
Expect command or expect scripting language is a language that talks with your interactive programs or scripts that require user interaction.
Expect scripting language works by expecting input, then the Expect script will send the response without any user interaction.
You can say that this tool is your robot which will automate your scripts.
If Expect command if not installed on your system, you can install it using the following command:
$ apt-get install expect
Or on Red Hat based systems like CentOS:
$ yum install expect
Table of Contents [hide]
Expect Command
Before we talk about expect command, Let’s see some of the expect command which used for interaction:
spawn Starting a script or a program.
expect Waiting for program output.
send Sending a reply to your program.
interact Allowing you in interact with your program.
- The spawn command is used to start a script or a program like the shell, FTP, Telnet, SSH, SCP, and so on.
- The send command is used to send a reply to a script or a program.
- The Expect command waits for input.
- The interact command allows you to define a predefined user interaction.
We are going to type a shell script that asks some questions and we will make an Expect script that will answer those questions.
First, the shell script will look like this:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
#!/bin/bash
echo "Hello, who are you?"
read $REPLY
echo "Can I ask you some questions?"
read $REPLY
echo "What is your favorite topic?"
read $REPLY
|
Now we will write the Expect scripts that will answer this automatically:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
#!/usr/bin/expect -f
set timeout -1
spawn ./questions
expect "Hello, who are you?\r"
send -- "Im Adam\r"
expect "Can I ask you some questions?\r"
send -- "Sure\r"
expect "What is your favorite topic?\r"
send -- "Technology\r"
expect eof
|
The first line defines the expect command path which is #!/usr/bin/expect .
On the second line of code, we disable the timeout. Then start our script using spawn command.
We can use spawn to run any program we want or any other interactive script.
The remaining lines are the Expect script that interacts with our shell script.
The last line if the end of file which means the end of the interaction.
Now Showtime, let’s run our answer bot and make sure you make it executable.
$ chmod +x ./answerbot
$./answerbot
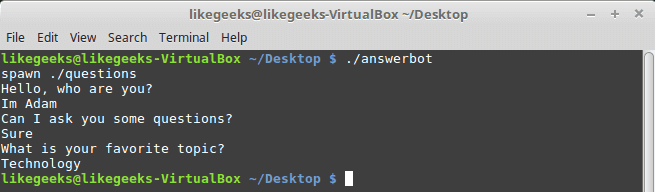
Cool!! All questions are answered as we expect.
If you get errors about the location of Expect command you can get the location using the which command:
$ which expect
We did not interact with our script at all, the Expect program do the job for us.
The above method can be applied to any interactive script or program.Although the above Expect script is very easy to write, maybe the Expect script little tricky for some people, well you have it.
Using autoexpect
To build an expect script automatically, you can the use autoexpect command.
autoexpect works like expect, but it builds the automation script for you. The script you want to automate is passed to autoexpect as a parameter and you answer the questions and your answers are saved in a file.
$ autoexpect ./questions
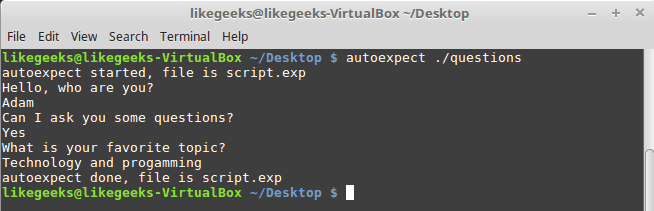
A file is generated called script.exp contains the same code as we did above with some additions that we will leave it for now.
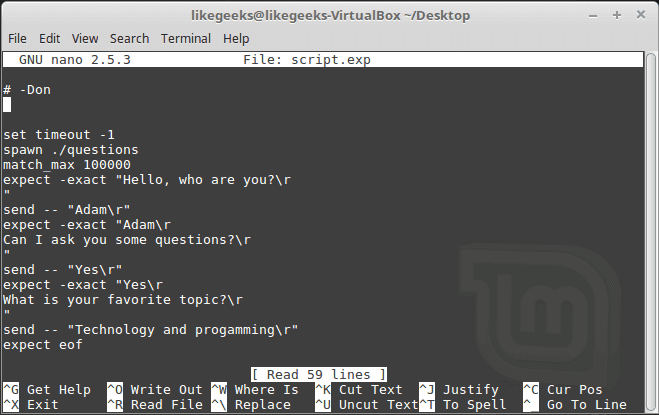
If you run the auto generated file script.exp, you will see the same answers as expected:
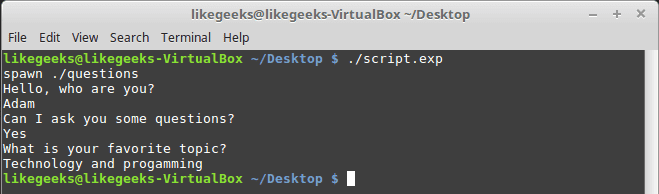
Awesome!! That super easy.
There are many commands that produce changeable output, like the case of FTP programs, the expect script may fail or stuck. To solve this problem, you can use wildcards for the changeable data to make your script more flexible.
Working with Variables
The set command is used to define variables in Expect scripts like this:
set MYVAR 5
To access the variable, precede it with $ like this $VAR1
To define command line arguments in Expect scripts, we use the following syntax:
set MYVAR [lindex $argv 0]
Here we define a variable MYVAR which equals the first passed argument.
You can get the first and the second arguments and store them in variables like this:
|
1
2
3
|
set my_name [lindex $argv 0]
set my_favorite [lindex $argv 1]
|
Let’s add variables to our script:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
#!/usr/bin/expect -f
set my_name [lindex $argv 0]
set my_favorite [lindex $argv 1]
set timeout -1
spawn ./questions
expect "Hello, who are you?\r"
send -- "Im $my_name\r"
expect "Can I ask you some questions?\r"
send -- "Sure\r"
expect "What is your favorite topic?\r"
send -- "$my_favorite\r"
expect eof
|
Now try to run the Expect script with some parameters to see the output:
$ ./answerbot SomeName Programming
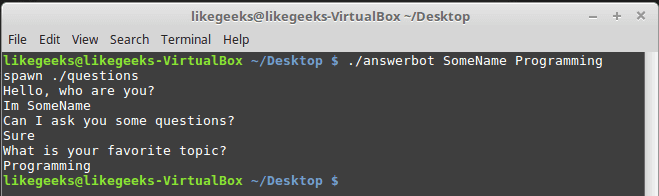
Awesome!! Now our automated Expect script is more dynamic.
Conditional Tests
You can write conditional tests using braces like this:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
expect {
"something" { send -- "send this\r" }
"*another" { send -- "send another\r" }
}
|
We are going to change our script to return different conditions, and we will change our Expect script to handle those conditions.
We are going to emulate different expects with the following script:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
#!/bin/bash
let number=$RANDOM
if [ $number -gt 25000 ]; then
echo "What is your favorite topic?"
else
echo "What is your favorite movie?"
fi
read $REPLY
|
A random number is generated every time you run the script and based on that number, we put a condition to return different expects.
Let’s make out Expect script that will deal with that.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
#!/usr/bin/expect -f
set timeout -1
spawn ./questions
expect {
"*topic?" { send -- "Programming\r" }
"*movie?" { send -- "Star wars\r" }
}
expect eof
|
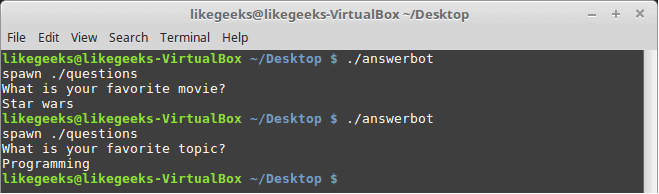
Very clear. If the script hits the topic output, the Expect script will send programming and if the script hits movie output the expect script will send star wars. Isn’t cool?
If else Conditions
You can use if/else clauses in expect scripts like this:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
#!/usr/bin/expect -f
set NUM 1
if { $NUM < 5 } {
puts "\Smaller than 5\n"
} elseif { $NUM > 5 } {
puts "\Bigger than 5\n"
} else {
puts "\Equals 5\n"
}
|
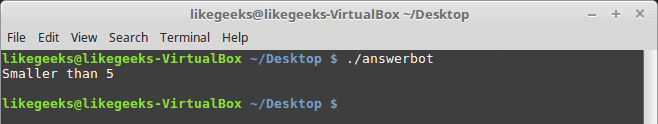
Note: The opening brace must be on the same line.
While Loops
While loops in expect language must use braces to contain the expression like this:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
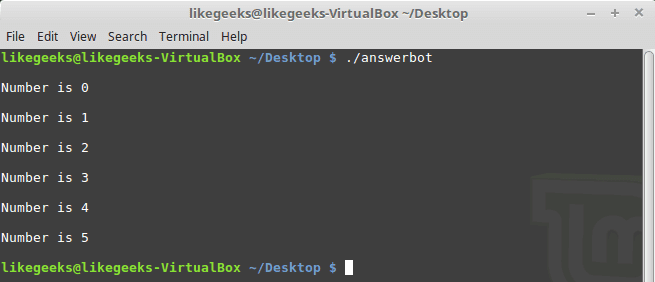
#!/usr/bin/expect -f
set NUM 0
while { $NUM <= 5 } {
puts "\nNumber is $NUM"
set NUM [ expr $NUM + 1 ]
}
puts ""
|
For Loops
To make a for loop in expect, three fields must be specified, like the following format:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
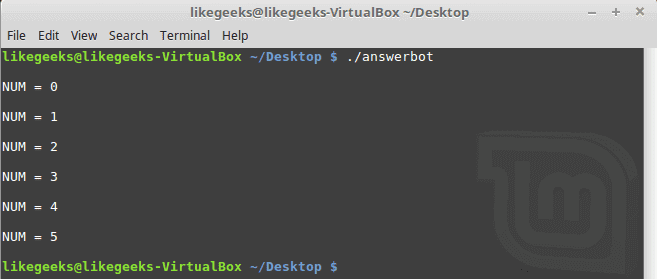
#!/usr/bin/expect -f
for {set NUM 0} {$NUM <= 5} {incr NUM} {
puts "\nNUM = $NUM"
}
puts ""
|
User-defined Functions
You can define a function using proc like this:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
proc myfunc { TOTAL } {
set TOTAL [expr $TOTAL + 1]
return "$TOTAL"
}
|
And you can use them after that.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
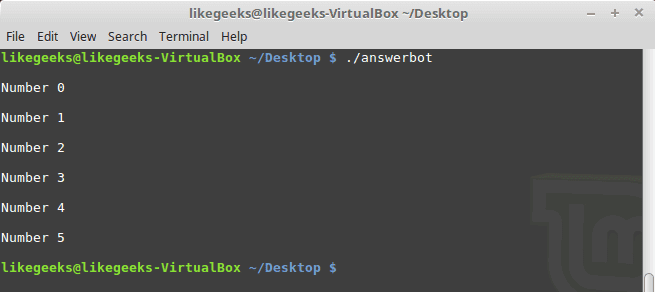
#!/usr/bin/expect -f
proc myfunc { TOTAL } {
set TOTAL [expr $TOTAL + 1]
return "$TOTAL"
}
set NUM 0
while {$NUM <= 5} {
puts "\nNumber $NUM"
set NUM [myfunc $NUM]
}
puts ""
|
Interact Command
Sometimes your Expect script contains some sensitive information that you don’t want to share with other users who use your Expect scripts, like passwords or any other data, so you want your script to take this password from you and continuing automation normally.
The interact command reverts the control back to the keyboard.
When this command is executed, Expect will start reading from the keyboard.
This shell script will ask about the password as shown:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
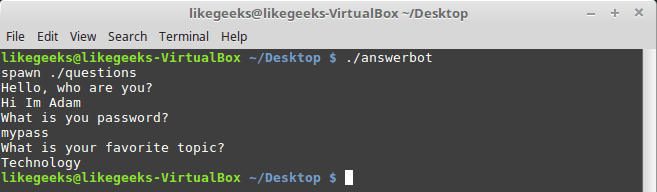
#!/bin/bash
echo "Hello, who are you?"
read $REPLY
echo "What is you password?"
read $REPLY
echo "What is your favorite topic?"
read $REPLY
|
Now we will write the Expect script that will prompt for the password:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
#!/usr/bin/expect -f
set timeout -1
spawn ./questions
expect "Hello, who are you?\r"
send -- "Hi Im Adam\r"
expect "*password?\r"
interact ++ return
send "\r"
expect "*topic?\r"
send -- "Technology\r"
expect eof
|
After you type your password type ++ and the control will return back from the keyboard to the script.
Expect language is ported to many languages like C#, Java, Perl, Python, Ruby and Shell with almost the same concepts and syntax due to its simplicity and importance.
Expect scripting language is used in quality assurance, network measurements such as echo response time, automate file transfers, updates, and many other uses.
I hope you now supercharged with some of the most important aspects of Expect command, autoexpect command and how to use it to automate your tasks in a smarter way.
Thank you.
https://likegeeks.com/expect-command/
Linux Expect自动交互脚本的更多相关文章
- Linux Expect自动化交互脚本简介
相关资料 维基百科:Expect SourceForge:The Expect Home Page TCL脚本言语简介 由于Expect是建立在TCL语言基础上的一个工具,因此首先检查一些TCL常见语 ...
- linux 的 expect 自动交互
https://www.jianshu.com/p/0194cbd70d39 https://www.cnblogs.com/saneri/p/10819348.html 参考 expect是一个自 ...
- Linux Shell自动交互/人机交互的三种方法
如果你要学习linux,你可能会遇到Linux Shell自动交互问题,这里将介绍Linux Shell自动交互的解决方法,在这里拿出来和大家分享一下. 一.背景 shell脚本在处理自动循环或大的任 ...
- Linux Shell 自动交互功能
需求背景: 近日,在安装某软件过程,发现在安装过程需要输入一些信息才能继续下一步操作,在机器数量较少情况下,我们可以单台登录上去完成安装操作,但当机器数量超过一定时,如果再手动登录操作,就会产生大 ...
- SSH批量管理 expect自动交互
SSH批量管理 expect自动交互 原创博文http://www.cnblogs.com/elvi/p/7662908.html # SSH批量管理 # expect自动交互 ########### ...
- 自动交互脚本之expect使用记录
之前一直没怎么用这个命令,意外用了一下,还不错,那这个是干嘛的呢 我们或多或少会远程登录其他服务器,需要执行某项任务,通常需要手动接入,输入密码啊,等等 那我们如何有效的自动执行呢,expect可以解 ...
- expect 实现自动交互脚本
1. 说明 在编写脚本时,可能会遇到需要在另一台主机上执行一个命令,或者在本机拷贝另一台主机内的一个文件.如果两台主机之间没有做互信,就会牵扯到用户输入密码的交互过程,这对编写自动脚本来说, 就行不通 ...
- 脚本_使用expect自动交互远程主机安装软件
#!bin/bash#功能:使用expect工具自动交互密码,远程到其它主机,安装httpd软件#作者:liusingbon#删除~/.ssh/known-hosts后,ssh远程任何主机,系统都会询 ...
- linux expect 即exp脚本交互功能【原】
场景 expect命令用于任何自动化互动的过程. send – 发送字符串到进程 expect – 等待来自进程的特定的字符串 spawn – 启动命令 安装 expect一开始100%不存在, 手动 ...
随机推荐
- sts使用mybatis插件直接生成数据库表的mapper类及配置文件
首先点击help------>Eclipse Marketplace----->在find中搜索mybatis下面图片的第一个 点击installed 还需要一个配置文件generator ...
- Dedesql数据库类详解(二次开发必备教程)
其实数据库类织梦之前就有一个介绍,http://help.dedecms.com/v53/archives/functions/db/,这篇文章讲解了数据库类的一些常见的使用方法,不过没有结合例子去介 ...
- Python_3day
循环 循环是一种控制语句块重复执行的结构 while 适用于广度遍历 for 开发中经常使用 while 循环 当一个条件保持真的时候while循环重复执行语句 while 循环一定要有结束条件, ...
- nginx+gunicorn/uwsgi+python web 的前世今生
我们在部署 flask.django 等 python web 框架时,网上最多的教程就是 nginx+gunicorn/uwsgi 的部署方式,那为什么要这么部署呢,本文就来系统地解释这个问题. 必 ...
- 分布式锁的几种实现方法:redis实现分布式锁
使用失效的方式实现分布式锁(推荐) import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis; /** * 使用redis实现分布式锁(推荐) * */ public class JedLoc ...
- C# 文件基本操作
概括的说,File,FileInfo,FileStream是用于文件 I/O 的类,StreamReader是用于从流读取和写入流的类,使用之前都需using System.IO. 先定义一个TXT文 ...
- Mac下的Web性能压力测试工具:ab(ApacheBench)
Web开发,少不了的就是压力测试,它是评估一个产品是否合格上线的基本标准. ab是一种用于测试Apache超文本传输协议(HTTP)服务器的工具.apache自带ab工具,可以测试Apache.IIS ...
- Python内置函数清单
作者:Vamei 出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/vamei Python内置(built-in)函数随着python解释器的运行而创建.在Python的程序中,你可以随时调用这些 ...
- vue 内存数组变化监听
watch: { carts: { handler(val, oldVal) { subtotal(this.carts); console.log(this.carts) }, deep: true ...
- ldap搭建
yum install openldap openldap-servers openldap-clients -y #检查是否安装成功 slapd -VVopenldap的配置文件都在/etc/ope ...
