HTTP Streaming Architecture HLS 直播点播 HTTP流架构
小结:
1、
3部分
服务器组件
分发组件
客户端组件
https://developer.apple.com/library/archive/documentation/NetworkingInternet/Conceptual/StreamingMediaGuide/HTTPStreamingArchitecture/HTTPStreamingArchitecture.html#//apple_ref/doc/uid/TP40008332-CH101-SW2
HTTP Streaming Architecture
HTTP Live Streaming allows you to send live or prerecorded audio and video, with support for encryption and authentication, from an ordinary web server to any device running iOS 3.0 or later (including iPad and Apple TV), or any computer with Safari 4.0 or later installed.
Overview
Conceptually, HTTP Live Streaming consists of three parts: the server component, the distribution component, and the client software.
The server component is responsible for taking input streams of media and encoding them digitally, encapsulating them in a format suitable for delivery, and preparing the encapsulated media for distribution.
The distribution component consists of standard web servers. They are responsible for accepting client requests and delivering prepared media and associated resources to the client. For large-scale distribution, edge networks or other content delivery networks can also be used.
The client software is responsible for determining the appropriate media to request, downloading those resources, and then reassembling them so that the media can be presented to the user in a continuous stream. Client software is included on iOS 3.0 and later and computers with Safari 4.0 or later installed.
In a typical configuration, a hardware encoder takes audio-video input, encodes it as H.264 video and AAC audio, and outputs it in an MPEG-2 Transport Stream, which is then broken into a series of short media files by a software stream segmenter. These files are placed on a web server. The segmenter also creates and maintains an index file containing a list of the media files. The URL of the index file is published on the web server. Client software reads the index, then requests the listed media files in order and displays them without any pauses or gaps between segments.
An example of a simple HTTP streaming configuration is shown in Figure 1-1.
Figure 1-1 A basic configuration
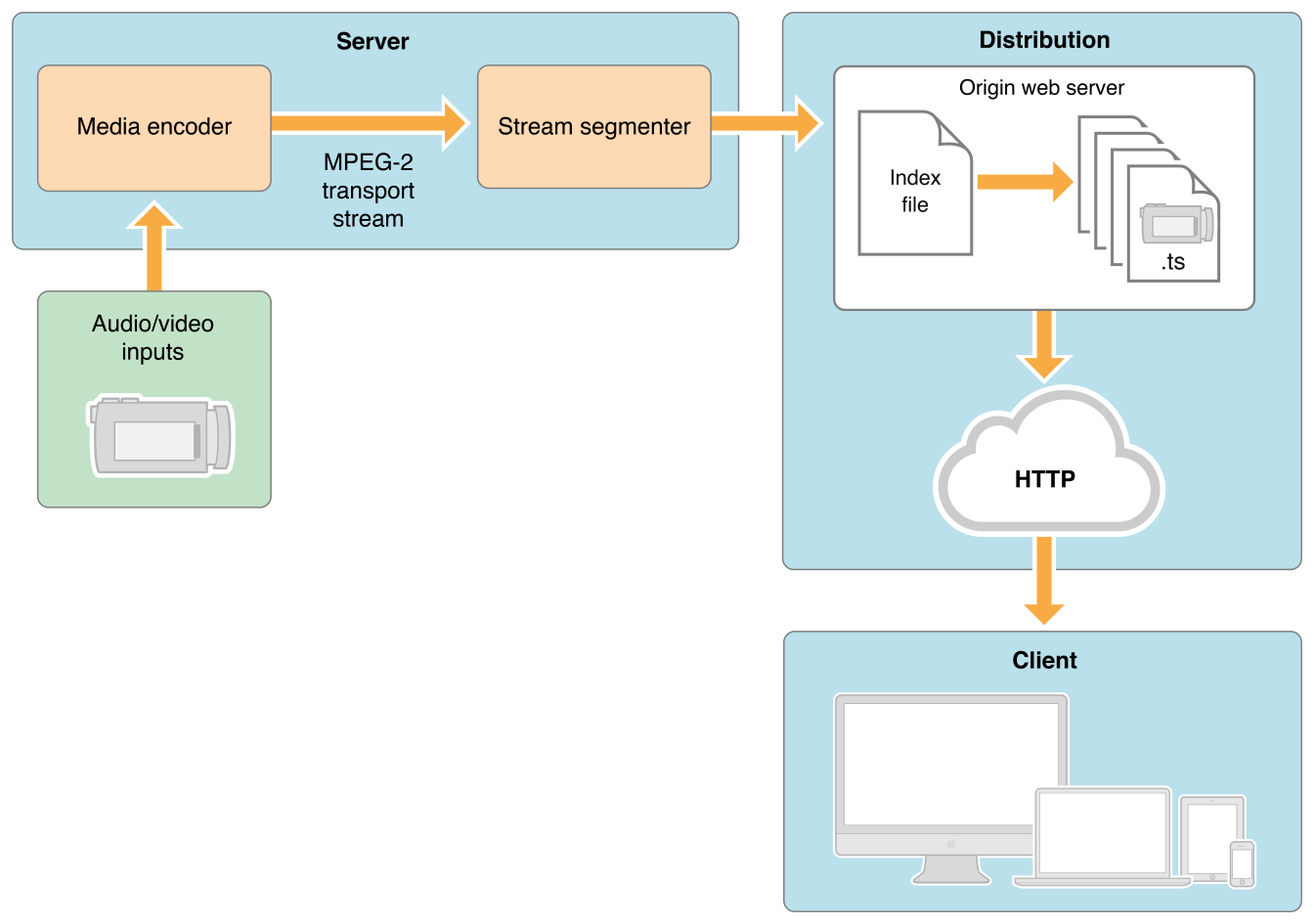
Input can be live or from a prerecorded source. It is typically encoded as MPEG-4 (H.264 video and AAC audio) and packaged in an MPEG-2 Transport Stream by off-the-shelf hardware. The MPEG-2 transport stream is then broken into segments and saved as a series of one or more .ts media files. This is typically accomplished using a software tool such as the Apple stream segmenter.
Audio-only streams can be a series of MPEG elementary audio files formatted as AAC with ADTS headers, as MP3, or as AC-3.
The segmenter also creates an index file. The index file contains a list of media files. The index file also contains metadata. The index file is an .M3U8 playlist. The URL of the index file is accessed by clients, which then request the indexed files in sequence.
Server Components
The server requires a media encoder, which can be off-the-shelf hardware, and a way to break the encoded media into segments and save them as files, which can either be software such as the media stream segmenter provided by Apple or part of an integrated third-party solution.
Media Encoder
The media encoder takes a real-time signal from an audio-video device, encodes the media, and encapsulates it for transport. Encoding should be set to a format supported by the client device, such as H.264 video and HE-AAC audio. Currently, the supported delivery format is MPEG-2 Transport Streams for audio-video, or MPEG elementary streams for audio-only.
The encoder delivers the encoded media in an MPEG-2 Transport Stream over the local network to the stream segmenter. MPEG-2 transport streams should not be confused with MPEG-2 video compression. The transport stream is a packaging format that can be used with a number of different compression formats. The Audio Technologies and Video Technologies list supported compression formats.
Important: The video encoder should not change stream settings—such as video dimensions or codec type—in the midst of encoding a stream. If a stream settings change is unavoidable, the settings must change at a segment boundary, and the EXT-X-DISCONTINUITY tag must be set on the following segment.
Stream Segmenter
The stream segmenter is a process—typically software—that reads the Transport Stream from the local network and divides it into a series of small media files of equal duration. Even though each segment is in a separate file, video files are made from a continuous stream which can be reconstructed seamlessly.
The segmenter also creates an index file containing references to the individual media files. Each time the segmenter completes a new media file, the index file is updated. The index is used to track the availability and location of the media files. The segmenter may also encrypt each media segment and create a key file as part of the process.
Media segments are saved as .ts files (MPEG-2 transport stream files). Index files are saved as .M3U8 playlists.
File Segmenter
If you already have a media file encoded using supported codecs, you can use a file segmenter to encapsulate it in an MPEG-2 transport stream and break it into segments of equal length. The file segmenter allows you to use a library of existing audio and video files for sending video on demand via HTTP Live Streaming. The file segmenter performs the same tasks as the stream segmenter, but it takes files as input instead of streams.
Media Segment Files
The media segment files are normally produced by the stream segmenter, based on input from the encoder, and consist of a series of .tsfiles containing segments of an MPEG-2 Transport Stream carrying H.264 video and AAC, MP3, or AC-3 audio. For an audio-only broadcast, the segmenter can produce MPEG elementary audio streams containing either AAC audio with ADTS headers, MP3 audio, or AC-3 audio.
Index Files (Playlists)
Index files are normally produced by the stream segmenter or file segmenter, and saved as .M3U8 playlists, an extension of the .m3u format used for MP3 playlists.
Note: Because the index file format is an extension of the .m3u playlist format, and because the system also supports .mp3 audio media files, the client software may also be compatible with typical MP3 playlists used for streaming Internet radio.
Here is a very simple example of an index file, in the form of an .M3U8 playlist, that a segmenter might produce if the entire stream were contained in three unencrypted 10-second media files:
#EXT-X-VERSION:3 |
#EXTM3U |
#EXT-X-TARGETDURATION:10 |
#EXT-X-MEDIA-SEQUENCE:1 |
# Old-style integer duration; avoid for newer clients. |
#EXTINF:10, |
http://media.example.com/segment0.ts |
# New-style floating-point duration; use for modern clients. |
#EXTINF:10.0, |
http://media.example.com/segment1.ts |
#EXTINF:9.5, |
http://media.example.com/segment2.ts |
#EXT-X-ENDLIST |
For maximum accuracy, you should specify all durations as floating-point values when sending playlists to clients that support version 3 of the protocol or later. (Older clients support only integer values.) You must specify a protocol version when using floating-point lengths; if the version is omitted, the playlist must conform to version 1 of the protocol.
Note: You can use the file segmenter provided by Apple to generate a variety of example playlists, using an MPEG-4 video or AAC or MP3 audio file as a source. For details, see Media File Segmenter.
The index file may also contain URLs for encryption key files and alternate index files for different bandwidths. For details of the index file format, see the IETF Internet-Draft of the HTTP Live Streaming specification.
Index files are normally created by the same segmenter that creates the media segment files. Alternatively, it is possible to create the .M3U8file and the media segment files independently, provided they conform the published specification. For audio-only broadcasts, for example, you could create an .M3U8 file using a text editor, listing a series of existing .MP3 files.
Distribution Components
The distribution system is a web server or a web caching system that delivers the media files and index files to the client over HTTP. No custom server modules are required to deliver the content, and typically very little configuration is needed on the web server.
Recommended configuration is typically limited to specifying MIME-type associations for .M3U8 files and .ts files.
For details, see Deploying HTTP Live Streaming.
Client Component
The client software begins by fetching the index file, based on a URL identifying the stream. The index file in turn specifies the location of the available media files, decryption keys, and any alternate streams available. For the selected stream, the client downloads each available media file in sequence. Each file contains a consecutive segment of the stream. Once it has a sufficient amount of data downloaded, the client begins presenting the reassembled stream to the user.
The client is responsible for fetching any decryption keys, authenticating or presenting a user interface to allow authentication, and decrypting media files as needed.
This process continues until the client encounters the #EXT-X-ENDLIST tag in the index file. If no #EXT-X-ENDLIST tag is present, the index file is part of an ongoing broadcast. During ongoing broadcasts, the client loads a new version of the index file periodically. The client looks for new media files and encryption keys in the updated index and adds these URLs to its queue.
HTTP Streaming Architecture HLS 直播点播 HTTP流架构的更多相关文章
- 实时监控、直播流、流媒体、视频网站开发方案流媒体服务器搭建及配置详解:使用nginx搭建rtmp直播、rtmp点播、,hls直播服务配置详解
注意:这里不会讲到nginx流媒体模块如何安装的问题,只研究rtmp,hls直播和录制相关的nginx服务器配置文件的详细用法和说明.可以对照这些命令详解配置nginx -rtmp服务 一.nginx ...
- 基于HTTP的直播点播HLS
HLS(HTTP Live Streaming) 是Apple在2009年发布的,可以通过普通的web服务器进行分发的新型流媒体协议.苹果官方对于视频直播服务提出了 HLS 解决方案 ...
- EasyDarwin如何支持点播和RTMP/HLS直播?EasyDSS!
2017年很长很长一段时间没有更新EasyDarwin开源项目了,虽然心里有很多EasyDarwin功能扩展的计划:比如同步录像.同步RTMP/HLS直播输出.拉模式转发优化.Onvif接入.GB28 ...
- 基于HTTP Live Streaming(HLS) 搭建在线点播系统
1. 为何要使用HTTP Live Streaming 可以参考wikipedia HTTP Live Streaming(缩写是 HLS)是一个由苹果公司提出的基于HTTP的流媒体 网络传输协议.是 ...
- 基于HLS(HTTP Live Streaming)的视频直播分析与实现
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/haibindev/archive/2013/01/30/2880764.html HLS(HTTP Live Streaming)的分析: HTT ...
- 将海康大华等网络摄像机RTSP流进行网页Flash rtmp和H5 hls直播的技术方案
前言 再小的技术点也会有他的市场! 一直以来,都有一些不被看好,认为是成本太高,无法大规模展开的软件和产品形态,就好比每一座城市都会有他的著名小吃一样,即使是慕名而来的人源源不断,受众群体也总是有限, ...
- nginx视频直播/点播服务干货分享
一.ubuntu14.04安装nginx及nginx_rtmp_module扩展 nginx根据是否已安装和安装的方式不同,有一下三种方式安装及扩展安装. 1.全新安装nginx和nginx_rtmp ...
- 使用ffmpeg搭建HLS直播系统
[时间:2018-04] [状态:Open] [关键词:流媒体,stream,HLS, ffmpeg,live,直播,点播, nginx, ssegment] 0 引言 本文作为HLS综述的后续文章. ...
- 转: 基于nginx的hls直播系统
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/cjsafty/article/details/9108587 看点: 1. 详细解解答了 nginx rtmp配置过程. 前写了一篇基于nginx的h ...
随机推荐
- 论文阅读笔记:《Contextual String Embeddings for Sequence Labeling》
文章引起我关注的主要原因是在CoNLL03 NER的F1值超过BERT达到了93.09左右,名副其实的state-of-art.考虑到BERT训练的数据量和参数量都极大,而该文方法只用一个GPU训了一 ...
- Lua中__index和__newindex实践
[具有默认值的table] 我们都知道,table中的任何字段的默认值都是nil,但是通过元表,我们可以很容易的修改这一规定,代码如下: function setDefault(tb, default ...
- 【原创】大叔问题定位分享(22)hive同时执行多个insert overwrite table只有1个可以执行
hive 2.1 一 问题 最近有一个场景,要向一个表的多个分区写数据,为了缩短执行时间,采用并发的方式,多个sql同时执行,分别写不同的分区,同时开启动态分区: set hive.exec.dyna ...
- iOS -- Effective Objective-C 阅读笔记 (9)
// 将类的实现方法代码反三到便于管理的数个分类之中. // 类中经常容易填满各种方法, 而这些方法的代码则全部堆在一个巨大的实现文件中, 有时这么做事不合理的,因为即使通过重构把这个类 ...
- select2 下拉搜索控件
1.添加相应的script链接 jquery: <script type="text/javascript" src="http://cdn.bootcss.com ...
- mac svn无法保存密码,JetBrains IDE(WebStrom、IntelliJ IDEA) 反复提示输入密码
一.vim ~/.subversion/config用vim修改以下四个地方store-passwords = yesstore-plaintext-passwords = yesstore-ssl- ...
- #Node.js的fs导入遇到的问题和解决方案
一直在使用VS Code,今天打算用Node.js进行文件IO时候遇到了一些问题,fs是Node.js的核心功能之一,一开始我用Javascript编写fs模块的导入. var fs = requir ...
- 【转】GB2312、GBK和UTF-8三种编码的简要说明
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/hust-yingjie/p/5481966.htmlGB2312.GBK和UTF-8都是一种字符编码,除此之外,还有好多字符编码.只是对于我们 ...
- bool值的底层应用场景
这里我们的if 或者while,还有and,or,not 等都是在内部调用一个对象的bool方法,然后返回True或者是False, a = [0, ] # a = [] # print(bool(a ...
- Fiddler工具使用介绍
Fiddler基础知识 Fiddler是强大的抓包工具,它的原理是以web代理服务器的形式进行工作的,使用的代理地址是:127.0.0.1,端口默认为8888,我们也可以通过设置进行修改. 代理就是在 ...
