[LeetCode] Smallest Subtree with all the Deepest Nodes 包含最深结点的最小子树
Given a binary tree rooted at `root`, the *depth* of each node is the shortest distance to the root.
A node is deepest if it has the largest depth possible among any node in the entire tree.
The subtree of a node is that node, plus the set of all descendants of that node.
Return the node with the largest depth such that it contains all the deepest nodes in its subtree.
Example 1:
Input: [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
Output: [2,7,4]
Explanation:
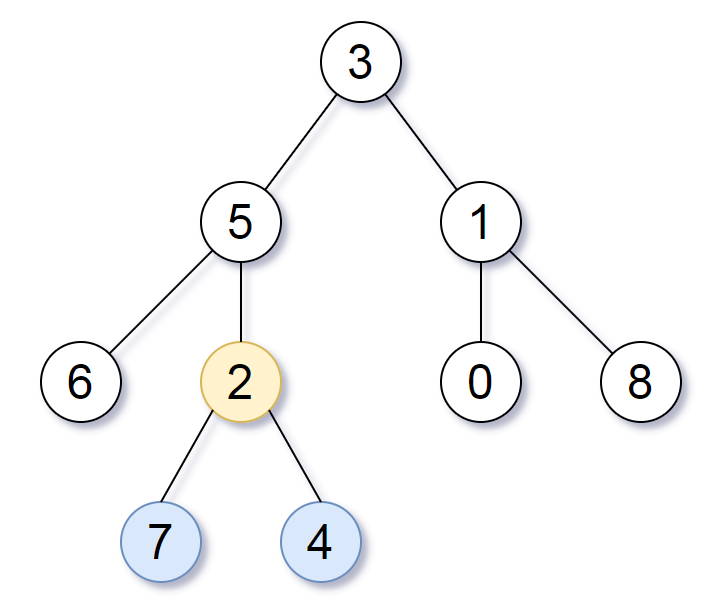
We return the node with value 2, colored in yellow in the diagram.
The nodes colored in blue are the deepest nodes of the tree.
The input "[3, 5, 1, 6, 2, 0, 8, null, null, 7, 4]" is a serialization of the given tree.
The output "[2, 7, 4]" is a serialization of the subtree rooted at the node with value 2.
Both the input and output have TreeNode type.
Note:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be between 1 and 500.
- The values of each node are unique.
这道题给了我们一棵二叉树,让我们找包含所有最深结点的最小子树,就是返回这棵最小子树的根结点。题目中给了一个例子,因为有图,所以可以很直接的看出来最深的结点是7和4,那么包含这两个结点的最小子树的根结点是2,返回即可。其实最深的结点不一定只有两个,可能有很多个,比如对于一棵完全二叉树,即把例子图中的结点7和4去掉后,此时最深的结点就有四个,分别是6,2,0,8,都包含这些结点的子树就是原树本身了,要返回根结点。
通过上述分析,可以发现,子树的最大深度很重要,对于一棵完全二叉树来说,根结点的左右子树的最大深度一定是相同的,此时直接返回根结点即可。若左右子树的最大深度不同,则最深结点一定位于深度大的子树中,可以对其调用递归函数。所以只需要写一个计算最大深度的递归函数,来计算左右子树的最大深度差,再根据这个差值来决定对谁调用当前的递归函数,两个递归函数相互缠绕,画面美极了,参见代码如下:
解法一:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode* root) {
int diff = depth(root->left) - depth(root->right);
return (diff == 0) ? root : subtreeWithAllDeepest(diff > 0 ? root->left : root->right);
}
int depth(TreeNode* node) {
return !node ? 0 : max(depth(node->left), depth(node->right)) + 1;
}
};
上面的解法其实并不高效,因为对于每个结点,都要统计其左右子树的最大深度,有大量的重复计算存在,我们来尝试提高时间复杂度,就不可避免的要牺牲一些空间。递归函数需要返回一个 pair,由每个结点的最大深度,以及包含最深结点的最小子树组成。所以在原函数中,对根结点调用递归函数,并取返回的 pair 中的第二项。
在递归函数中,首先判断结点是否存在,为空的话直接返回一个 {0, NULL} 对儿。否则分别对左右子结点调用递归函数,将各自的返回的 pair 存入 left 和 right 中,然后先分别在 left 和 right 中取出左右子树的最大深度 d1 和 d2,之后就要建立返回值的 pair,第一项为当前结点的最大深度,由左右子树中的最大深度加1组成,而包含最深结点的最小子树由 d1 和 d2 值的大小决定,若 d1>d2,则为 left.second,否则为 right.second,这样我们就把原本的两个递归,揉合到了一个递归函数中,大大提高了运行效率,参见代码如下:
解法二:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode* root) {
return helper(root).second;
}
pair<int, TreeNode*> helper(TreeNode* node) {
if (!node) return {0, NULL};
auto left = helper(node->left), right = helper(node->right);
int d1 = left.first, d2 = right.first;
return {max(d1, d2) + 1, (d1 == d2) ? node : (d1 > d2 ? left.second : right.second)};
}
};
Github 同步地址:
https://github.com/grandyang/leetcode/issues/865
参考资料:
https://leetcode.com/problems/smallest-subtree-with-all-the-deepest-nodes/
https://leetcode.com/problems/smallest-subtree-with-all-the-deepest-nodes/discuss/146808/One-pass
[LeetCode All in One 题目讲解汇总(持续更新中...)](https://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/4606334.html)
[LeetCode] Smallest Subtree with all the Deepest Nodes 包含最深结点的最小子树的更多相关文章
- 865. Smallest Subtree with all the Deepest Nodes 有最深节点的最小子树
[抄题]: Given a binary tree rooted at root, the depth of each node is the shortest distance to the roo ...
- leetcode_865. Smallest Subtree with all the Deepest Nodes
https://leetcode.com/problems/smallest-subtree-with-all-the-deepest-nodes/ 给定一颗二叉树,输出包含所有最深叶子结点的最小子树 ...
- LeetCode 865. Smallest Subtree with all the Deepest Nodes
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/smallest-subtree-with-all-the-deepest-nodes/ 题目: Given a binar ...
- 【LeetCode】865. Smallest Subtree with all the Deepest Nodes 解题报告(Python & C++)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 目录 题目描述 题目大意 解题方法 日期 题目地址:https://leetcode.c ...
- [Swift]LeetCode865. 具有所有最深结点的最小子树 | Smallest Subtree with all the Deepest Nodes
Given a binary tree rooted at root, the depth of each node is the shortest distance to the root. A n ...
- [LeetCode] 1123. Lowest Common Ancestor of Deepest Leaves 最深叶结点的最小公共父节点
Given a rooted binary tree, return the lowest common ancestor of its deepest leaves. Recall that: Th ...
- FB面经 Prepare: LCA of Deepest Nodes in Binary Tree
给一个 二叉树 , 求最深节点的最小公共父节点 . retrun . 先用 recursive , 很快写出来了, 要求用 iterative . 时间不够了... Recursion: 返回的时候返 ...
- Leetcode之深度优先搜索(DFS)专题-1123. 最深叶节点的最近公共祖先(Lowest Common Ancestor of Deepest Leaves)
Leetcode之深度优先搜索(DFS)专题-1123. 最深叶节点的最近公共祖先(Lowest Common Ancestor of Deepest Leaves) 深度优先搜索的解题详细介绍,点击 ...
- LeetCode 1123. Lowest Common Ancestor of Deepest Leaves
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-deepest-leaves/ 题目: Given a rooted b ...
随机推荐
- 项目Alpha冲刺(2/10)
1.项目燃尽图 2.今日进度描述 项目进展 完成数据库和服务器的连接部分,完成了一些应用的基本功能. 问题困难 第一次使用服务器,配置环境部署项目都花了很长时间,学习中存在许多问题. 心得体会 应该早 ...
- Mathematica 2
如今的数值分析,如果没有高等代数的基础,都不好意思打招呼说自己是 "有数学基础". 高等代数,解决问题的一大神器. 1,初等变换 2,特征值 | A-λE | = | λE - A ...
- VS2013创建ASP.NET应用程序描述
你的 ASP.NET 应用程序 恭喜! 你已创建了一个项目 此应用程序包含: 显示“主页”.“关于”和“联系方式”之间的基本导航的示例页 使用 Bootstrap 进行主题定位 身份验证,如果选择此项 ...
- 11:57:24 [org.springframework.kafka.KafkaListenerEndpointContainer#0-0-C-1] WARN o.apache.kafka.clients.NetworkClient - [Consumer clientId=consumer-2, groupId=jiatian_api] 3 partitions have leader……
错误如下: 11:57:24 [org.springframework.kafka.KafkaListenerEndpointContainer#0-0-C-1] WARN o.apache.kaf ...
- PHP提取页面第一张图为缩略图的代码
<?php $p = '/<img.*?src=[\'|\"](.+?)[\'|\"].*?>/i'; preg_match_all($p,$str,$match ...
- 解释内存中的栈(stack)、堆(heap)和静态区(static area)的用法
堆区:专门用来保存对象的实例(new 创建的对象和数组),实际上也只是保存对象实例的属性值,属性的类型和对象本身的类型标记等,并不保存对象的方法(方法是指令,保存在Stack中) 1.存储的全部是对象 ...
- iOS开发之HTTP与HTTPS网络请求
HTTP是互联网中应用最为广泛的一种网络协议,在进入正文之前,先解释什么是网络协议?网络协议为计算机网络中进行数据交换而建立的规则.标准或约定的集合.网络协议是由以下三个要素组成:语义.语法.时序.国 ...
- pwn学习(1)
0x00 简介 入职之后,公司发布任务主搞pwn和re方向,re之前还有一定的了解,pwn我可真是个弟弟,百度了一番找到了蒸米大佬的帖子,现在开始学习. 0x01 保护方式 NX (DEP):堆栈不可 ...
- javaScript -- touch事件详解(touchstart、touchmove和touchend)
HTML5中新添加了很多事件,但是由于他们的兼容问题不是很理想,应用实战性不是太强,所以在这里基本省略,咱们只分享应用广泛兼容不错的事件,日后随着兼容情况提升以后再陆续添加分享.今天为大家介绍的事件主 ...
- Python2.7和3.7区别
区别一:print语法使用 Python2.7 print语法使用 >>> print "Hello Python" Python3.7 print语 ...
