Spring框架系列(六)--事务Transaction
本文绝大部分内容为转载,原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/trigl/article/details/50968079
除此之外,后面还有延伸内容
事务在企业日常开发中几乎是一定会遇到的,例如一个审核的流程可能涉及到查询、修改、插入等操作,所以保证事务性是很有必要的。一般
就是开启事务支持,然后@Transactional,但是事务不仅仅是这些,可以了解一下细节
事务:
说白了就是一系列操作要么成功,要么失败,最典型的场景就是转账
一、事务四大特性:ACID
1、原子性(Atomicity):
事务是一个原子操作,由一系列动作组成。事务的原子性确保动作要么全部完成,要么完全失败
2、一致性(Consistency):
一旦事务完成(不管成功还是失败),系统必须确保它处于一致的状态,而不会是部分完成部分失败。在现实中的数据不应该被破坏
例如:账户A有1200块钱,账户B有900块钱,一共是2100块钱,A向B转账300块钱,A有900,B有1200,A+B还是2100。这就是一致性
3、隔离性(Isolation):
多个事务会同时处理相同的数据,因此每个事务都应该与其他事务隔离开来,防止数据损坏
4、持久性(Durability):
一旦事务完成,无论发生什么系统错误,它的结果都不应该受到影响,这样就能从任何系统崩溃中恢复过来。通常情况下,事务的结果被写
到持久化存储器中
二、事务三大要素
1、DataSource:事务的真正处理者,如MySQL等
2、TransactionManager:管理事务的处理过程,如打开、提交、回滚
3、事务应用和属性配置:作为一个标识符表明哪些方法要参与事务,一些配置:隔离级别、超时时间等
三、核心接口
Spring事务设计的接口如下:
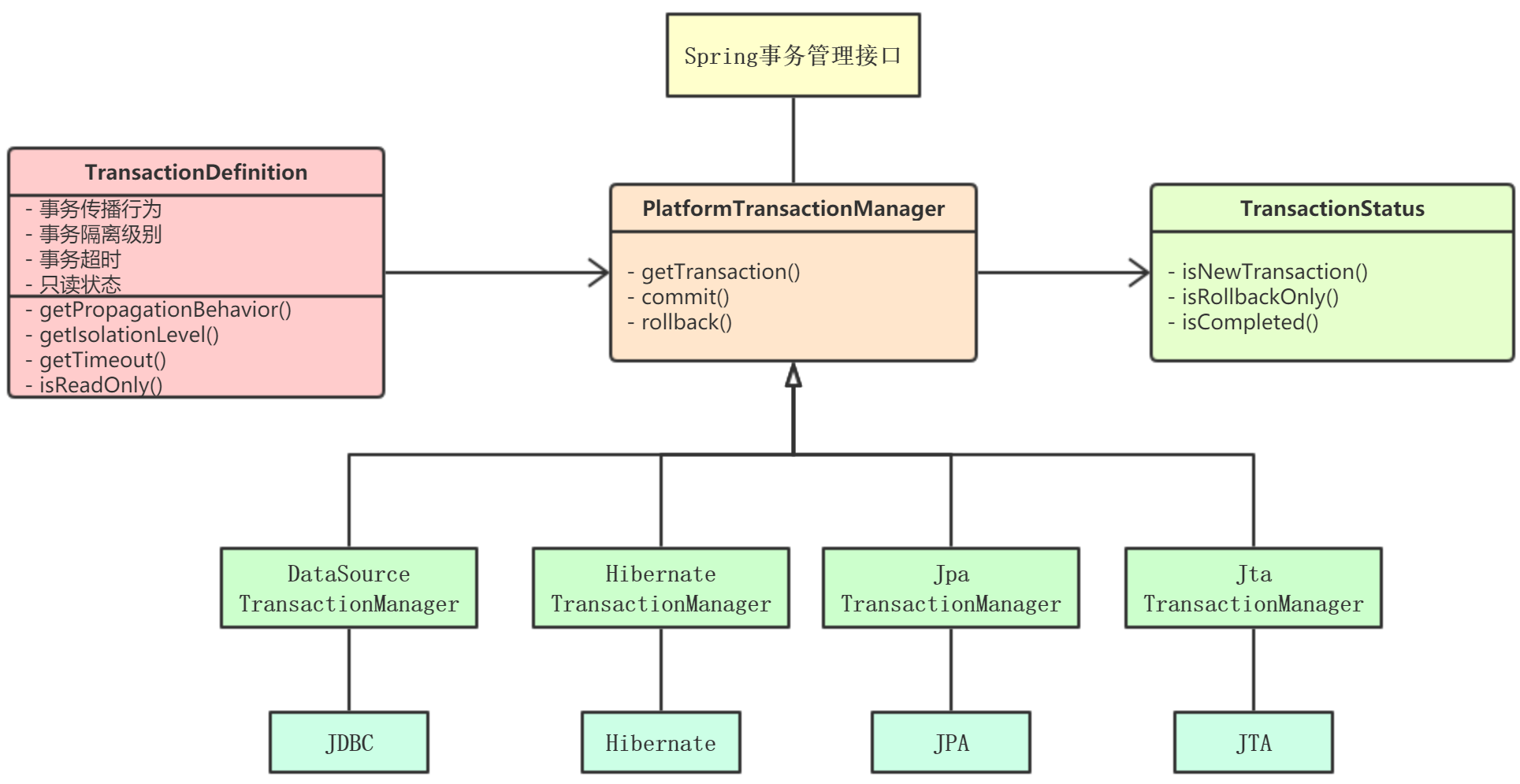
四、事务管理器
Spring并不直接管理事务,而是提供了多种事务管理器,他们将事务管理的职责委托给Hibernate或者JTA等持久化机制所提供的相关平台框架
的事务来实现
PlatformTransactionManager:
Spring事务管理器的接口,通过这个接口,JDBC、Hibernate等提供了对应的任务管理器,进行具体的实现
具体代码:
public interface PlatformTransactionManager {
//由TransactionDefinition得到TransactionStatus对象
TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException;
//提交事务
void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
//回滚事务
void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
}
1、jdbc事务
如果应用程序中直接使用JDBC来进行持久化,DataSourceTransactionManager会为你处理事务边界。为了使用DataSourceTransactionManager
,你需要使用如下的XML将其装配到应用程序的上下文定义中:
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
实际上,DataSourceTransactionManager是通过调用java.sql.Connection来管理事务,而后者是通过DataSource获取到的。通过调用连接的
commit()方法来提交事务,同样,事务失败则通过调用rollback()方法进行回滚。
2、Hibernate事务
如果应用程序的持久化是通过Hibernate实习的,那么你需要使用HibernateTransactionManager。对于Hibernate3,需要在Spring上下文定义
中添加如下的<bean>声明:
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" />
</bean>
sessionFactory属性需要装配一个Hibernate的session工厂,HibernateTransactionManager的实现细节是它将事务管理的职责委托给
org.hibernate.Transaction对象,而后者是从Hibernate Session中获取到的。当事务成功完成时,HibernateTransactionManager将会调用
Transaction对象的commit()方法,反之,将会调用rollback()方法。
3、Java持久化API事务(JPA)
Hibernate多年来一直是事实上的Java持久化标准,但是现在Java持久化API作为真正的Java持久化标准进入大家的视野。如果你计划使用JPA
的话,那你需要使用Spring的JpaTransactionManager来处理事务。你需要在Spring中这样配置JpaTransactionManager:
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" />
</bean>
JpaTransactionManager只需要装配一个JPA实体管理工厂(javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory接口的任意实现)。
JpaTransactionManager将与由工厂所产生的JPA EntityManager合作来构建事务。
4、Java原生API事务
如果你没有使用以上所述的事务管理,或者是跨越了多个事务管理源(比如两个或者是多个不同的数据源),你就需要使用
JtaTransactionManager:
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager">
<property name="transactionManagerName" value="java:/TransactionManager" />
</bean>
JtaTransactionManager将事务管理的责任委托给javax.transaction.UserTransaction和javax.transaction.TransactionManager对象,其中
事务成功完成通过UserTransaction.commit()方法提交,事务失败通过UserTransaction.rollback()方法回滚。
五、基本事务属性的定义
上面讲到的事务管理器接口PlatformTransactionManager通过getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition)方法来得到事务,这个
方法里面的参数是TransactionDefinition类,这个类就定义了一些基本的事务属性。
事务属性可以理解成事务的一些基本配置,描述了事务策略如何应用到方法上。事务属性包含了5个方面,如图所示:
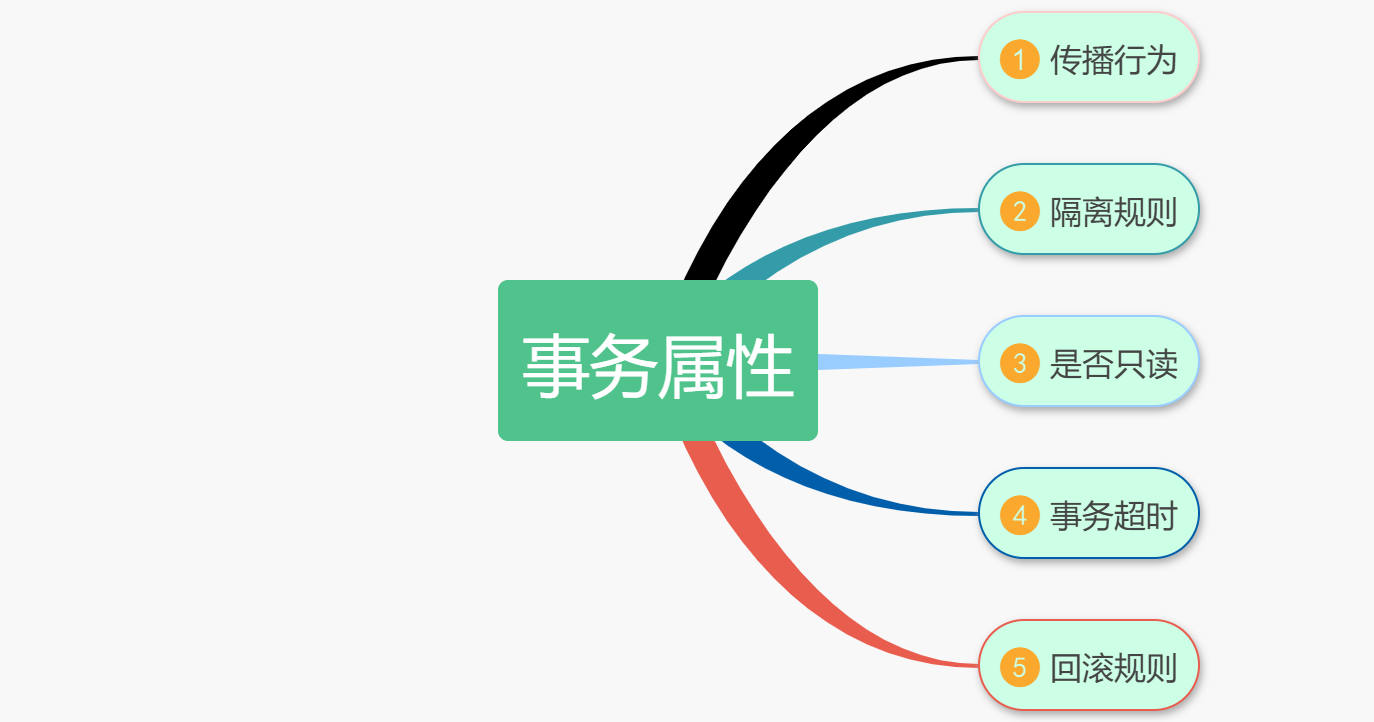
TransactionDefinition代码
public interface TransactionDefinition {
int getPropagationBehavior(); // 返回事务的传播行为
int getIsolationLevel(); // 返回事务的隔离级别,事务管理器根据它来控制另外一个事务可以看到本事务内的哪些数据
int getTimeout(); // 返回事务必须在多少秒内完成
boolean isReadOnly(); // 事务是否只读,事务管理器能够根据这个返回值进行优化,确保事务是只读的
}
5.1).Spring定义了七种传播行为:

具体内容可参考:https://www.open-open.com/lib/view/open1350865116821.html
5.2).隔离级别
定义了一个事务可能受其他并发事务影响的程度
5.2.1).并发事务可能引起的问题
多个事务并发运行,经常会操作相同的数据来完成各自的任务。并发虽然是必须的,但可能会导致一下的问题
1).脏读(Dirty reads):
脏读发生在一个事务读取了另一个事务改写但尚未提交的数据时。如果改写在稍后被回滚了,那么第一个事务获取的数据就是无效的。
2).不可重复读(Nonrepeatable read):
发生在一个事务执行相同的查询两次或两次以上,但是每次都得到不同的数据时。通常是因为另一个并发事务在两次查询期间进行了更新。
例如:
1、第一次:select score from score where stu_id = '1001',结果为78分
2、这时候另一个事务:update score set score = 80 where stu_id = '1001'
3、然后再次查询的时候,就发现1001号同学分数变成80分了
3).幻读(Phantom read):
幻读与不可重复读类似。它发生在一个事务(T1)读取了几行数据,接着另一个并发事务(T2)插入了一些数据时。在随后的查询中,第一
个事务(T1)就会发现多了一些原本不存在的记录。
PS:不可重复读的重点是修改,幻读的重点在于新增或者删除,对于前者, 只需要锁住满足条件的记录。对于后者, 要锁住满足条件及其相近
的记录。
写读是脏读,读写读是不可重复读,where insert where是幻读。
5.2.2).隔离级别
1、DEFAULT:使用底层数据存储的默认隔离级别。MySQL的默认隔离级别是REPEATABLE-READ。
2、READ_UNCOMMITTED:最低的隔离级别,允许读取尚未提交的数据变更,可能会导致脏读、幻读或不可重复读
3、READ_COMMITTED:允许读取并发事务已经提交的数据,可以阻止脏读,但是幻读或不可重复读仍有可能发生
4、REPEATABLE_READ:对同一字段的多次读取结果都是一致的,除非数据是被本身事务自己所修改,可以阻止脏读和不可重复读,但幻读仍有
可能发生
5、SERIALIZABLE:可串行化。最高的隔离级别,完全服从ACID的隔离级别,确保阻止脏读、不可重复读以及幻读,也是最慢的事务隔离级别,
因为它通常是通过完全锁定事务相关的数据库表来实现的
5.3).只读
事务的第三个特性是它是否为只读事务。如果事务只对后端的数据库进行该操作,数据库可以利用事务的只读特性来进行一些特定的优化。通
过将事务设置为只读,你就可以给数据库一个机会,让它应用它认为合适的优化措施。
5.4).事务超时
为了使应用程序很好地运行,事务不能运行太长的时间。因为事务可能涉及对后端数据库的锁定,所以长时间的事务会不必要的占用数据库资
源。事务超时就是事务的一个定时器,在特定时间内事务如果没有执行完毕,那么就会自动回滚,而不是一直等待其结束。
5.5).回滚规则
规则定义了哪些异常会导致事务回滚而哪些不会。默认情况下,事务只有遇到运行期异常时才会回滚,而在遇到检查型异常时不会回滚
但是你可以声明事务在遇到特定的检查型异常时像遇到运行期异常那样回滚。同样,你还可以声明事务遇到特定的异常不回滚,即使这些异常
是运行期异常。
5.6).事务状态
上面讲到的调用PlatformTransactionManager接口的getTransaction()的方法得到的是TransactionStatus接口的一个实现
这个接口的内容如下:
public interface TransactionStatus{
boolean isNewTransaction(); // 是否是新的事物
boolean hasSavepoint(); // 是否有恢复点
void setRollbackOnly(); // 设置为只回滚
boolean isRollbackOnly(); // 是否为只回滚
boolean isCompleted; // 是否已完成
}
在回滚或提交的时候需要应用对应的事务状态。
六、编程式事务
6.1).编程式事务和声明式事务的区别
Spring提供了对编程式事务和声明式事务的支持,编程式事务允许用户在代码中精确定义事务的边界,而声明式事务(基于AOP)有助于用户
将操作与事务规则进行解耦。简单地说,编程式事务侵入到了业务代码里面,但是提供了更加详细的事务管理;而声明式事务由于基于AOP,所以
既能起到事务管理的作用,又可以不影响业务代码的具体实现。
6.2).如何实现?
Spring提供两种方式的编程式事务管理,分别是:使用TransactionTemplate和直接使用PlatformTransactionManager。
6.2.1).使用TransactionTemplate
采用TransactionTemplate和采用其他Spring模板,如JdbcTempalte和HibernateTemplate是一样的方法。它使用回调方法,把应用程序从处理
取得和释放资源中解脱出来。如同其他模板,TransactionTemplate是线程安全的。代码片段:
TransactionTemplate tt = new TransactionTemplate(); // 新建一个TransactionTemplate
Object result = tt.execute(
new TransactionCallback(){
public Object doTransaction(TransactionStatus status){
updateOperation();
return resultOfUpdateOperation();
}
}); // 执行execute方法进行事务管理
使用TransactionCallback()可以返回一个值。如果使用TransactionCallbackWithoutResult则没有返回值。
6.2.2).使用PlatformTransactionManager
DataSourceTransactionManager dataSourceTransactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager(); //定义一个某个框架平台的TransactionManager,如JDBC、Hibernate
dataSourceTransactionManager.setDataSource(this.getJdbcTemplate().getDataSource()); // 设置数据源
DefaultTransactionDefinition transDef = new DefaultTransactionDefinition(); // 定义事务属性
transDef.setPropagationBehavior(DefaultTransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED); // 设置传播行为属性
TransactionStatus status = dataSourceTransactionManager.getTransaction(transDef); // 获得事务状态
try {
// 数据库操作
dataSourceTransactionManager.commit(status);// 提交
} catch (Exception e) {
dataSourceTransactionManager.rollback(status);// 回滚
}
七、声明式事务
7.1).配置方式
注:以下配置代码参考自Spring事务配置的五种方式
根据代理机制的不同,总结了五种Spring事务的配置方式,配置文件如下:
7.1.1).每个Bean都有一个代理
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd"> <bean id="sessionFactory"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.LocalSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml" />
<property name="configurationClass" value="org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration" />
</bean> <!-- 定义事务管理器(声明式的事务) -->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" />
</bean> <!-- 配置DAO -->
<bean id="userDaoTarget" class="com.bluesky.spring.dao.UserDaoImpl">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" />
</bean> <bean id="userDao"
class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionProxyFactoryBean">
<!-- 配置事务管理器 -->
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager" />
<property name="target" ref="userDaoTarget" />
<property name="proxyInterfaces" value="com.bluesky.spring.dao.GeneratorDao" />
<!-- 配置事务属性 -->
<property name="transactionAttributes">
<props>
<prop key="*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
7.1.2).所有Bean共享一个代理基类
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd"> <bean id="sessionFactory"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.LocalSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml" />
<property name="configurationClass" value="org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration" />
</bean> <!-- 定义事务管理器(声明式的事务) -->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" />
</bean> <bean id="transactionBase"
class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionProxyFactoryBean"
lazy-init="true" abstract="true">
<!-- 配置事务管理器 -->
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager" />
<!-- 配置事务属性 -->
<property name="transactionAttributes">
<props>
<prop key="*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean> <!-- 配置DAO -->
<bean id="userDaoTarget" class="com.bluesky.spring.dao.UserDaoImpl">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" />
</bean> <bean id="userDao" parent="transactionBase" >
<property name="target" ref="userDaoTarget" />
</bean>
</beans>
7.1.3).使用拦截器
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd"> <bean id="sessionFactory"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.LocalSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml" />
<property name="configurationClass" value="org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration" />
</bean> <!-- 定义事务管理器(声明式的事务) -->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" />
</bean> <bean id="transactionInterceptor"
class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionInterceptor">
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager" />
<!-- 配置事务属性 -->
<property name="transactionAttributes">
<props>
<prop key="*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean> <bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.BeanNameAutoProxyCreator">
<property name="beanNames">
<list>
<value>*Dao</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="interceptorNames">
<list>
<value>transactionInterceptor</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean> <!-- 配置DAO -->
<bean id="userDao" class="com.bluesky.spring.dao.UserDaoImpl">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" />
</bean>
</beans>
7.1.4).使用tx标签配置的拦截器
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd"> <context:annotation-config />
<context:component-scan base-package="com.bluesky" /> <bean id="sessionFactory"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.LocalSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml" />
<property name="configurationClass" value="org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration" />
</bean> <!-- 定义事务管理器(声明式的事务) -->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" />
</bean> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice> <aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="interceptorPointCuts"
expression="execution(* com.bluesky.spring.dao.*.*(..))" />
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice"
pointcut-ref="interceptorPointCuts" />
</aop:config>
</beans>
7.1.5).全注解
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd"> <context:annotation-config />
<context:component-scan base-package="com.bluesky" /> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/> <bean id="sessionFactory"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.LocalSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml" />
<property name="configurationClass" value="org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration" />
</bean> <!-- 定义事务管理器(声明式的事务) -->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" />
</bean>
</beans>
此时在DAO上需加上@Transactional注解,如下:
package com.bluesky.spring.dao; import java.util.List; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.HibernateDaoSupport;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import com.bluesky.spring.domain.User; @Transactional
@Component("userDao")
public class UserDaoImpl extends HibernateDaoSupport implements UserDao { public List<User> listUsers() {
return this.getSession().createQuery("from User").list();
}
}
7.2).一个声明式事务的实例
注:该实例参考自Spring中的事务管理实例详解
7.2.1).首先是数据库表
book(isbn, book_name, price)
account(username, balance)
book_stock(isbn, stock)
7.2.2).然后是XML配置
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd"> <import resource="applicationContext-db.xml" /> <context:component-scan
base-package="com.springinaction.transaction">
</context:component-scan> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager"/> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean> </beans>
使用的类BookShopDao
package com.springinaction.transaction;
public interface BookShopDao {
// 根据书号获取书的单价
public int findBookPriceByIsbn(String isbn);
// 更新书的库存,使书号对应的库存-1
public void updateBookStock(String isbn);
// 更新用户的账户余额:account的balance-price
public void updateUserAccount(String username, int price);
}
BookShopDaoImpl
package com.springinaction.transaction; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository("bookShopDao")
public class BookShopDaoImpl implements BookShopDao { @Autowired
private JdbcTemplate JdbcTemplate; @Override
public int findBookPriceByIsbn(String isbn) {
String sql = "SELECT price FROM book WHERE isbn = ?"; return JdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Integer.class, isbn);
} @Override
public void updateBookStock(String isbn) {
//检查书的库存是否足够,若不够,则抛出异常
String sql2 = "SELECT stock FROM book_stock WHERE isbn = ?";
int stock = JdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql2, Integer.class, isbn);
if (stock == 0) {
throw new BookStockException("库存不足!");
}
String sql = "UPDATE book_stock SET stock = stock - 1 WHERE isbn = ?";
JdbcTemplate.update(sql, isbn);
} @Override
public void updateUserAccount(String username, int price) {
//检查余额是否不足,若不足,则抛出异常
String sql2 = "SELECT balance FROM account WHERE username = ?";
int balance = JdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql2, Integer.class, username);
if (balance < price) {
throw new UserAccountException("余额不足!");
}
String sql = "UPDATE account SET balance = balance - ? WHERE username = ?";
JdbcTemplate.update(sql, price, username);
} }
BookShopService
package com.springinaction.transaction;
public interface BookShopService {
public void purchase(String username, String isbn);
}
BookShopServiceImpl
package com.springinaction.transaction; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; @Service("bookShopService")
public class BookShopServiceImpl implements BookShopService { @Autowired
private BookShopDao bookShopDao; /**
* 1.添加事务注解
* 使用propagation 指定事务的传播行为,即当前的事务方法被另外一个事务方法调用时如何使用事务。
* 默认取值为REQUIRED,即使用调用方法的事务
* REQUIRES_NEW:使用自己的事务,调用的事务方法的事务被挂起。
*
* 2.使用isolation 指定事务的隔离级别,最常用的取值为READ_COMMITTED
* 3.默认情况下 Spring 的声明式事务对所有的runtime,unchecked Exception进行回滚,通常情况下,默认值即可。Checked exceptions默认不导致回滚
* rollbackFor用来精确配置导致回滚的异常类型
* noRollbackFor用来配置不尽兴回滚的异常类型
* 4.使用readOnly 指定事务是否为只读。 表示这个事务只读取数据但不更新数据,这样可以帮助数据库引擎优化事务。若真的是一个只读取数据库值得方法,应设置readOnly=true
* 5.使用timeOut 指定强制回滚之前事务可以占用的时间。
*/
@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW,
isolation=Isolation.READ_COMMITTED,
noRollbackFor={UserAccountException.class},
readOnly=true, timeout=3)
@Override
public void purchase(String username, String isbn) {
//1.获取书的单价
int price = bookShopDao.findBookPriceByIsbn(isbn);
//2.更新书的库存
bookShopDao.updateBookStock(isbn);
//3.更新用户余额
bookShopDao.updateUserAccount(username, price);
}
}
Cashier
package com.springinaction.transaction;
import java.util.List;
public interface Cashier {
public void checkout(String username, List<String>isbns);
}
CashierImpl:CashierImpl.checkout和bookShopService.purchase联合测试了事务的传播行为
package com.springinaction.transaction; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; @Service("cashier")
public class CashierImpl implements Cashier {
@Autowired
private BookShopService bookShopService; @Transactional
@Override
public void checkout(String username, List<String> isbns) {
for(String isbn : isbns) {
bookShopService.purchase(username, isbn);
}
}
}
BookStockException
package com.springinaction.transaction;
public class BookStockException extends RuntimeException { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; public BookStockException() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
} public BookStockException(String arg0, Throwable arg1, boolean arg2,
boolean arg3) {
super(arg0, arg1, arg2, arg3);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
} public BookStockException(String arg0, Throwable arg1) {
super(arg0, arg1);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
} public BookStockException(String arg0) {
super(arg0);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
} public BookStockException(Throwable arg0) {
super(arg0);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
}
UserAccountException
package com.springinaction.transaction;
public class UserAccountException extends RuntimeException { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; public UserAccountException() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
} public UserAccountException(String arg0, Throwable arg1, boolean arg2,
boolean arg3) {
super(arg0, arg1, arg2, arg3);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
} public UserAccountException(String arg0, Throwable arg1) {
super(arg0, arg1);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
} public UserAccountException(String arg0) {
super(arg0);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
} public UserAccountException(Throwable arg0) {
super(arg0);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
}
测试类
package com.springinaction.transaction; import java.util.Arrays; import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class SpringTransitionTest { private ApplicationContext ctx = null;
private BookShopDao bookShopDao = null;
private BookShopService bookShopService = null;
private Cashier cashier = null;
{
ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("config/transaction.xml");
bookShopDao = ctx.getBean(BookShopDao.class);
bookShopService = ctx.getBean(BookShopService.class);
cashier = ctx.getBean(Cashier.class);
} @Test
public void testBookShopDaoFindPriceByIsbn() {
System.out.println(bookShopDao.findBookPriceByIsbn("1001"));
} @Test
public void testBookShopDaoUpdateBookStock(){
bookShopDao.updateBookStock("1001");
} @Test
public void testBookShopDaoUpdateUserAccount(){
bookShopDao.updateUserAccount("AA", 100);
}
@Test
public void testBookShopService(){
bookShopService.purchase("AA", "1001");
} @Test
public void testTransactionPropagation(){
cashier.checkout("AA", Arrays.asList("1001", "1002"));
}
}
以下内容参考自公众号:java团长
事务注解在类/方法上
@Transactional注解可以标注到类/method上面,如果同时标注,method上面的注解优先级更高
事务注解在类上的继承性
@Transactional注解的作用可以传播到子类,即如果父类标了子类就不用标了。但倒过来就不行了。父类方法需要在子类中重新声明而参与
到子类上的注解,这样才会有事务
事务注解在接口/类上
@Transactional注解可以用在接口上,也可以在类上。在接口上时,必须使用基于接口的代理才行,即JDK动态代理
事实是Java的注解不能从接口继承,如果你使用基于类的代理,即CGLIB,或基于织入方面,即AspectJ,事务设置不会被代理和织入基础设施
认出来,目标对象不会被包装到一个事务代理中。
PS:Spring团队建议注解标注在类上而非接口上
只在public方法上生效?
当采用代理来实现事务时,(注意是代理),@Transactional注解只能应用在public方法上。当标记在protected、private、package-visible
方法上时,不会产生错误,但也不会表现出为它指定的事务配置。可以认为它作为一个普通的方法参与到一个public方法的事务中。
如果想在非public方法上生效,考虑使用AspectJ(织入方式)。
两个不靠谱的例子
1、在Service层抛出Exception,在Controller层捕获,那如果在Service中有异常,那会事务回滚吗?
@Transactional
public Employee addEmployee() throws Exception { Employee employee = new Employee("3y", 23);
employeeRepository.save(employee);
// 假设这里出了Exception
int i = 1 / 0; return employee;
} // Controller调用
@RequestMapping("/add")
public Employee addEmployee() {
Employee employee = null;
try {
employee = employeeService.addEmployee();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return employee; }
表面上看:
因为Service层已经抛出了异常,由Controller捕获。那是否回滚应该由Controller的catch代码块中逻辑来决定,如果catch代码块没有回滚,
那应该是不会回滚。
实际上:
会回滚,只要是Runtime Exception及其子类,和Error都会导致回滚
2、当前类下使用一个没有事务的方法去调用一个有事务的方法,那我们这次调用会怎么样?是否会有事务呢?
// 没有事务的方法去调用有事务的方法
public Employee addEmployee2Controller() throws Exception { return this.addEmployee();
} @Transactional
public Employee addEmployee() throws Exception { employeeRepository.deleteAll();
Employee employee = new Employee("3y", 23); // 模拟异常
int i = 1 / 0; return employee;
}
表面上看:
这跟Spring事务的传播机制有关吧
实际上:
没有关系
解释:
声明式事务采用的是AOP,而AOP底层通过代理实现。所以如果我们在类或者方法上标注注解@Transactional,那么会生成一个代理对象。
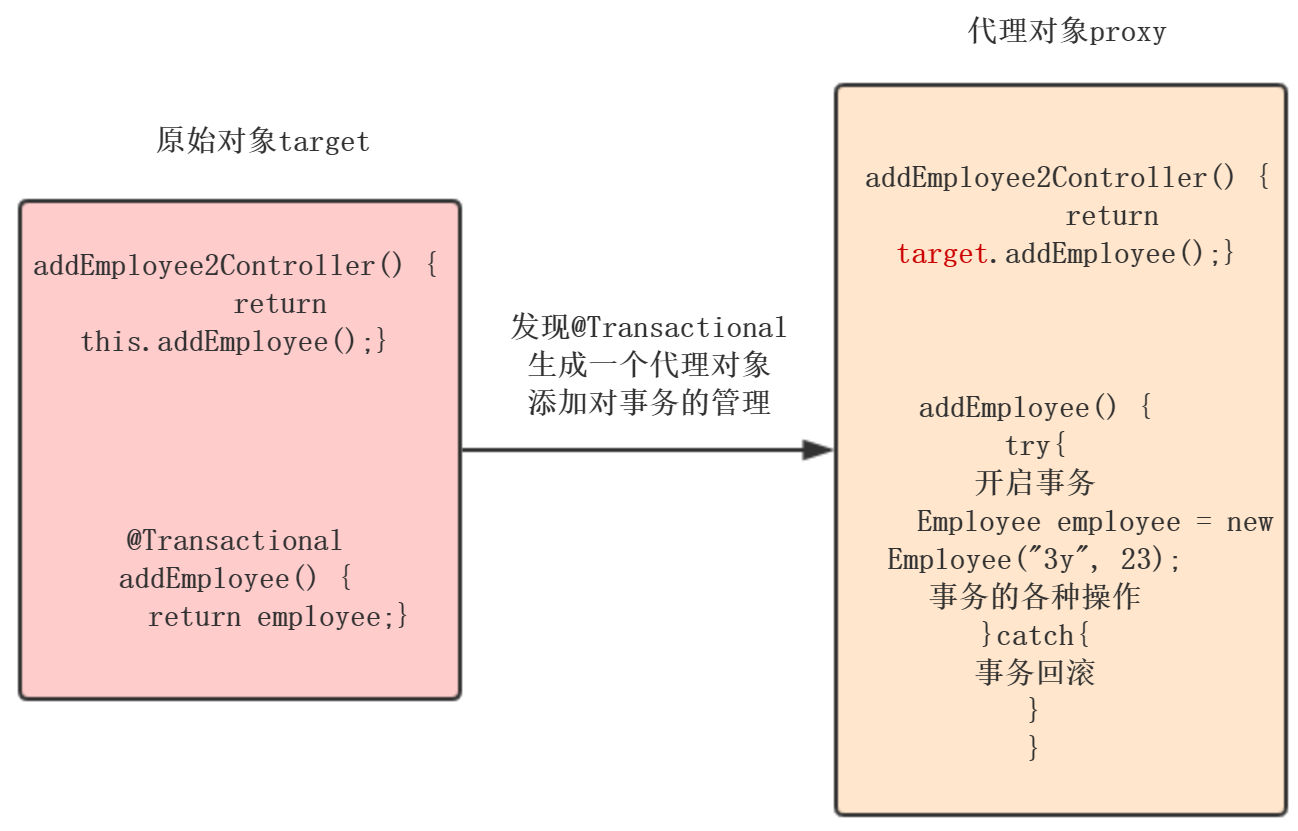
我们得到的是代理(Proxy)对象,调用addEmployee2Controller()方法,而addEmployee2Controller()方法的逻辑是target.addEmployee()
,调用回原始对象(target)的addEmployee()。所以这次的调用压根就没有事务存在,更谈不上说Spring事务传播机制了。
2.1).延伸
如果是在本类中没有事务的方法来调用标注注解@Transactional方法,最后的结论是没有事务的。那如果我将这个标注注解的方法移到别的
Service对象上,有没有事务?
@Service
public class TestService { @Autowired
private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository; @Transactional
public Employee addEmployee() throws Exception { employeeRepository.deleteAll();
Employee employee = new Employee("3y", 23);
// 模拟异常
int i = 1 / 0;
return employee;
} } @Service
public class EmployeeService {
@Autowired
private TestService testService;
// 没有事务的方法去调用别的类有事务的方法
public Employee addEmployee2Controller() throws Exception {
return testService.addEmployee();
}
}
解释:
因为我们用的是代理对象(Proxy)去调用addEmployee()方法,那就当然有事务了
上面的内容属于Spring事务传播机制
PS:
只要是以代理方式实现的声明式事务,无论是JDK动态代理,还是CGLIB直接写字节码生成代理,都只有public方法上的事务注解才起作用。
而且必须在代理类外部调用才行,如果直接在目标类里面调用,事务照样不起作用。
Spring框架系列(六)--事务Transaction的更多相关文章
- Spring 框架系列之事务管理
1.事务回顾 (1).什么是事务: 事务是逻辑上的一组操作,组成这组操作的各个逻辑单元,要么一起成功,要么一起失败. (2).事务特性(ACID) 原子性 :强调事务的不可分割 一致性 :事务的执行的 ...
- Spring框架系列之AOP思想
微信公众号:compassblog 欢迎关注.转发,互相学习,共同进步! 有任何问题,请后台留言联系! 1.AOP概述 (1).什么是 AOP AOP 为 Aspect Oriented Progra ...
- Spring框架系列(4) - 深入浅出Spring核心之面向切面编程(AOP)
在Spring基础 - Spring简单例子引入Spring的核心中向你展示了AOP的基础含义,同时以此发散了一些AOP相关知识点; 本节将在此基础上进一步解读AOP的含义以及AOP的使用方式.@pd ...
- Spring框架系列(11) - Spring AOP实现原理详解之Cglib代理实现
我们在前文中已经介绍了SpringAOP的切面实现和创建动态代理的过程,那么动态代理是如何工作的呢?本文主要介绍Cglib动态代理的案例和SpringAOP实现的原理.@pdai Spring框架系列 ...
- Spring框架系列(2) - Spring简单例子引入Spring要点
上文中我们简单介绍了Spring和Spring Framework的组件,那么这些Spring Framework组件是如何配合工作的呢?本文主要承接上文,向你展示Spring Framework组件 ...
- Spring框架系列(3) - 深入浅出Spring核心之控制反转(IOC)
在Spring基础 - Spring简单例子引入Spring的核心中向你展示了IoC的基础含义,同时以此发散了一些IoC相关知识点; 本节将在此基础上进一步解读IOC的含义以及IOC的使用方式.@pd ...
- Spring框架系列(5) - 深入浅出SpringMVC请求流程和案例
前文我们介绍了Spring框架和Spring框架中最为重要的两个技术点(IOC和AOP),那我们如何更好的构建上层的应用呢(比如web 应用),这便是SpringMVC:Spring MVC是Spri ...
- Spring框架系列(6) - Spring IOC实现原理详解之IOC体系结构设计
在对IoC有了初步的认知后,我们开始对IOC的实现原理进行深入理解.本文将帮助你站在设计者的角度去看IOC最顶层的结构设计.@pdai Spring框架系列(6) - Spring IOC实现原理详解 ...
- Spring框架系列(7) - Spring IOC实现原理详解之IOC初始化流程
上文,我们看了IOC设计要点和设计结构:紧接着这篇,我们可以看下源码的实现了:Spring如何实现将资源配置(以xml配置为例)通过加载,解析,生成BeanDefination并注册到IoC容器中的. ...
随机推荐
- 9种样式CSS3 渐变button集
<!DOCTYPE html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/h ...
- WEB端应该使用DataTable/DataSet吗?
有一次和同事讨论起具体的技术细节,同事说不要用什么实体类,从数据库访问到的数据,直接用DataTable.DataSet 就好.理由是,从获取到的数据集转换成实体类,有一定的性能损耗. 呵呵,性能.我 ...
- srcset
<div id="pg-334-2" class="panel-grid panel-has-style"> <div style=" ...
- 第二次PHP面试题
昨天下午翘班去参加了人生中第二次PHP面试.是一家相对第一家更加专业的互联网公司.效果不如第一家理想,笔试题有点难,而且偏高理论,面试时面试官也还不错,一起探讨,可是他的问题我还是很多都不知道,果然是 ...
- Robot Framework 怎样写好Test Case
1.介绍 这是一个关于如何用Robot Framework写好Test Case的高层次的指导准则 怎样实际的与系统进行交互不在此文档范围内 最重要的准则是使测试用例尽可能的让熟悉此领域的人觉得简单易 ...
- bzoj 3308 九月的咖啡店
题目大意: 求若干个<=n的数 两两互质 使和最大 求这个最大的和 思路: 显然,得到两个结论 1 最终的所有数都只能分解为两个质因数 2 这两个质因数 一个<根号n 一个>根号n ...
- JS复制文件(转)
<script type="text/javascript"> var fso, f; function copyFile() { fso = new ActiveXO ...
- E20171121-sl
contrast n. 对比,对照; 差异; 对照物,对立面; [摄] 反差;
- bzoj 1753: [Usaco2005 qua]Who's in the Middle【排序】
--这可能是早年Pascal盛行的时候考排序的吧居然还是Glod-- #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<algor ...
- JavaScript--DOM节点属性
节点属性 在文档对象模型 (DOM) 中,每个节点都是一个对象.DOM 节点有三个重要的属性 : 1. nodeName : 节点的名称 2. nodeValue :节点的值 3. nodeType ...
