07.C语言:结构体、共用体、枚举
一、结构体
是一种复合的数据类型,由多个不同类型的数据(为结构体的成员)组成的集合。
在c语言中没有给出结构体这种类型具体的形式(名称),但是给出类定义该结构体类型的方法(格式)。
在使用结构体类型时,必须先定义机构体具体的类型,然后用定义好的类型来定义变量,进而使用变量。
综上,结构体是一种自定义的复合数据类型,在结构体空间中每个成员都有各自的空间。
1.结构体的类型定义:
struct [结构体标签]{
类型名 成员名;
类型名 成员名;
... ...
类型名 成员名;
};
struct student{
int sno;
char name[];
float high;
float score;
};
struct
2.结构体变量的定义:
//1.常规方式定义
struct student1{
int sno;
char name[];
float high;
float score;
};
struct student1 st1; //2.与类型同时定义
struct student2{
int sno;
char name[];
float high;
float score;
}st2; //3.直接定义
struct{
int sno;
char name[];
float high;
float score;
}st3;
structDefine
3.结构体变量的初始化:
1》完全初始化:按定义成员的先后顺序依次给结构体变量中的每一个成员赋值的过程:struct student st = {1001, "刘德华",1.80,99.9};
2》部分初始化:按定义成员的先后顺序依次给结构体变量中的前若干个成员赋值的过程:struct student st = {1001, "刘德华", 1.80};
3》指定成员初始化:不按成员的定义顺序赋值,而是指定结构体变量中的某一些成员赋值的过程:struct student st = {.name = "刘德华", 1.80, .sno = 1001};//指定成员初始化
4.结构体的使用:
1》不能只能赋值,例如:
struct student st;
st = {1001, "刘德华", 1.80, 99.9};//error
2》相同类型结构体变量之间可以相互赋值,例如:
struct student st1 = {1001,"刘德华", 1.80, 99.9};
struct student st2;
st2 = st1;//OK
3》结构体中的成员只能单独使用,例如:
/*******************************************************************
* > File Name: 33-struct.c
* > Author: fly
* > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com
* > Create Time: Sun 08 Oct 2017 11:48:04 AM CST
******************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h> struct student{
int sno;
char name[];
float high;
float score;
}; int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
struct student st1 = {, "刘德华", 1.80, 99.9};//完全初始化
struct student st2; st2.sno = ;
strcpy(st2.name, "peter");
st2.high = 1.89;
st2.score = 98.4;
printf("%d\t%s\t%.2f\t%.2f\n", st1.sno, st1.name, st1.high, st1.score);
printf("%d\t%s\t%.2f\t%.2f\n", st2.sno, st2.name, st2.high, st2.score); return ;
}
struct.c
5.结构体数组:
元素为结构体类型的数组称之为结构体数组。
/*******************************************************************
* > File Name: 34-structArr.c
* > Author: fly
* > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com
* > Create Time: Sun 08 Oct 2017 03:58:37 PM CST
******************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> struct student{
int sno;
char name[];
float high;
float score;
}; int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
struct student st[];
int i; for(i = ; i< ; i++){
printf("Pls input NO[%d]:\n", i);
scanf("%d%s%f%f", &st[i].sno, st[i].name, &st[i].high, &st[i].score);
} for(i = ; i< ; i++){
printf("%d\t%s\t%.2f\t%.2f\n", st[i].sno, st[i].name, st[i].high, st[i].score);
} return ;
}
structArr.c
6.结构体指针:
指向结构体变量的指针称为结构体指针。
/*******************************************************************
* > File Name: 35-structPoint.c
* > Author: fly
* > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com
* > Create Time: Sun 08 Oct 2017 04:08:58 PM CST
******************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> struct student{
int sno;
char name[];
float high;
float score;
}; int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
struct student st1 = {, "刘德华", 1.80, 99.9};
struct student *ps;//ps为结构体指针 ps = &st1; printf("%d\t%s\t%.2f\t%.2f\n", st1.sno, st1.name, st1.high, st1.score);
puts("");
printf("%d\t%s\t%.2f\t%.2f\n", (*ps).sno, (*ps).name, (*ps).high, (*ps).score);
puts("");
printf("%d\t%s\t%.2f\t%.2f\n", ps -> sno, ps -> name, ps -> high, ps -> score); return ;
}
structPoint.c
二、共用体
一种复合的数据类型,它是由多个不同类型的数据组成的集合,这些不同类型的数据称为该共用体的成员。
在C语言中没有给出共用体这种类型具体的形式(名称),但是给出类定义该共用体类型的方法(方法),在使用共用体类型时,必须先定义共用体具体的类型,然后用定义好的类型来定义变量,进而使用变量。
1.共用体类型定义:
/*******************************************************************
* > File Name: 36-unionTypeDefine.c
* > Author: fly
* > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com
* > Create Time: Sun 08 Oct 2017 04:34:53 PM CST
******************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> #if (0)
union [结构体标签]{
类型名 成员名;
类型名 成员名;
... ...;
类型名 成员名;
};
#else//egg
union student{
int sno;
char name[];
float high;
float score;
};
#endif int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
return ;
}
UnionTypeDefine.c
2.共用体变量的定义:
/*******************************************************************
* > File Name: 37-unionVarDefine.c
* > Author: fly
* > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com
* > Create Time: Sun 08 Oct 2017 04:40:50 PM CST
******************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> //1》.常规定义
union student{
int sno;
char name[];
float high;
float score;
};
union student un;
//2》.与类型同时定义
union student{
int sno;
char name[];
float high;
float score;
}un;
//3》.直接定义
union{
int sno;
char name[];
float high;
float score;
}un; int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
return ;
}
unionVarDefine.c
3.使用:
1》不能整体赋值,例如:
union student un;
un = {1001, "刘德华", 1.80, 99.9};//error
2》同类型的共用体之间可以相互赋值,例如:
union student un1, un2;
un1.sno = 1001;
un2 = un1;//OK
3》共用体中的成员只能单独使用,例如:
/*******************************************************************
* > File Name: 38-union.c
* > Author: fly
* > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com
* > Create Time: Sun 08 Oct 2017 04:52:12 PM CST
******************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h> //定义一个共用体类型
union student{
int sno;
char name[];
float high;
float score;
}; int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
union student un1; un1.sno = ;
strcpy(un1.name, "jack");
un1.high = 1.80;
un1.score = 93.5;
printf("%d\t%s\t%f\t%f\n", un1.sno, un1.name, un1.high, un1.score);
puts("***********************************************************"); un1.sno = ;
strcpy(un1.name, "jack");
un1.score = 93.5;
un1.high = 1.80;
printf("%d\t%s\t%f\t%f\n", un1.sno, un1.name, un1.high, un1.score);
puts("***********************************************************"); un1.sno = ;
un1.high = 1.80;
un1.score = 93.5;
strcpy(un1.name, "jack");
printf("%d\t%s\t%f\t%f\n", un1.sno, un1.name, un1.high, un1.score);
puts("***********************************************************"); strcpy(un1.name, "jack");
un1.high = 1.80;
un1.score = 93.5;
un1.sno = ;
printf("%d\t%s\t%f\t%f\n", un1.sno, un1.name, un1.high, un1.score);
puts("***********************************************************"); printf("\n&un1\t=%p\n", &un1);
printf("&un1.sno\t=%p\n", &un1.sno);
printf("&un1.name\t=%p\n", &un1.name);
printf("&un1.high\t=%p\n", &un1.high);
printf("&un1.score\t=%p\n", &un1.score); printf("\n&un1 + 1\t=%p\n", &un1 + );
printf("&un1.sno + 1\t=%p\n", &un1.sno + );
printf("&un1.name + 1\t=%p\n", &un1.name + );
printf("&un1.high + 1\t=%p\n", &un1.high + );
printf("&un1.score + 1\t=%p\n", &un1.score + ); return ;
}
union.c
运行结果:
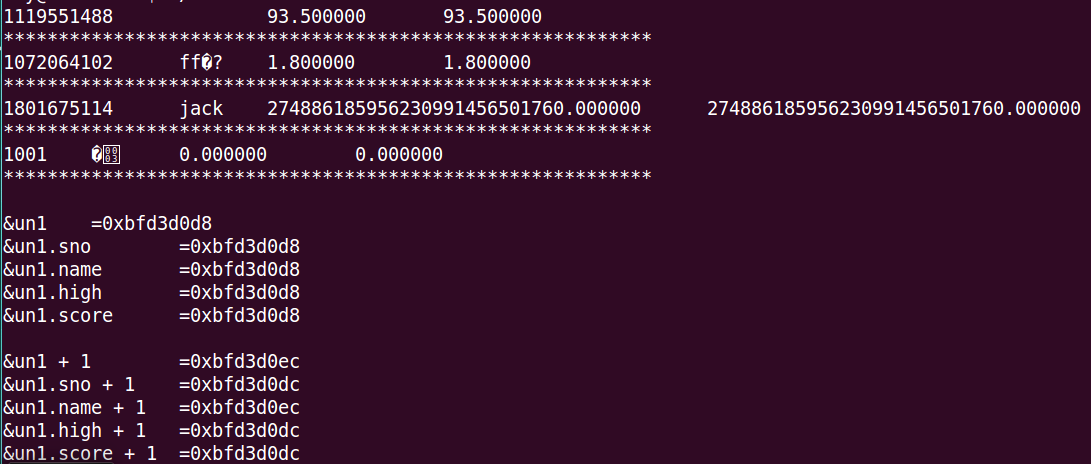
三、枚举
属于基本数据类型,本质上为整型。为了提高程序的可读性。
在某些时候需要给一些整型数据一个取值空间,这时如果直接赋值整型常量,它的含义不是特别的明确,从而导致程序的可读性差。
引入枚举类型之后,可以重新定义整型数据的取值空间,这样可以提高程序的可读性。
1.枚举类型的定义
/*******************************************************************
* > File Name: 39-enum.c
* > Author: fly
* > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com
* > Create Time: Sun 08 Oct 2017 05:35:54 PM CST
******************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> #if (枚举类型的定义)
enum [枚举标签]{
枚举常量;
枚举常量;
......;
枚举常量;
};
#else
/*定义一个枚举类型spectrum*/
enum spectrum{
red, //默认值0
blue, //
green, //
yellow //
}color;
#endif int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
return ;
}
enumTypeDefine.c
2.枚举类型中枚举、常量的值
/*******************************************************************
* > File Name: 40-enum.c
* > Author: fly
* > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com
* > Create Time: Sun 08 Oct 2017 05:42:52 PM CST
******************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> //1》.枚举常量的默认值
enum spectrum{
red, //
blue, //
green, //
yellow //
}color;
//2》.枚举常量也可以指定值
enum spectrum{
red = ,//不是赋值,而是指定枚举常量red代表整型常量10
blue, //the default value :11
green = ,
yellow //the default value :10
}color; int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
return ;
}
enumVal.c
3.使用:
/*******************************************************************
* > File Name: 41-enum.c
* > Author: fly
* > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com
* > Create Time: Sun 08 Oct 2017 05:51:54 PM CST
******************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> enum spectrum{
red, //
blue, //
green, //
yellow //
}color1; int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
enum spectrum color2; color1 = ; //可读性差
color1 = red; //可读性好
printf("color1 = %d\n", color1); color2 = ;
color2 = green;
printf("color2 = %d\n", color2); return ;
}
enum.c
07.C语言:结构体、共用体、枚举的更多相关文章
- C++结构、共用体、枚举
一.结构 结构是C++OOP的基石.学习有关结构的知识僵尸我们离C++的核心OOP更近. 结构是用户定义的类型,同一个结构可以存储多种类型数据,这使得将一个事物的不同属性构成一个对象成为了可能.另外C ...
- 5、数组&字符串&结构体&共用体&枚举
程序中内存从哪里来 三种内存来源:栈(stack).堆(heap).数据区(.date): 栈(stack) 运行自动分配.自动回收,不需要程序员手工干预: 栈内存可以反复使用: 栈反复使用后,程序不 ...
- C语言高级-结构,共用体,文件,链表
C语言结构 标准声明方式 struct student{ int age; char sex; }; 这个可以在main函数中定义: struct student ...
- C语言笔记 09_共用体&typedef&输入|输出
共用体 共用体允许您在相同的内存位置存储不同的数据类型.您可以定义一个带有多成员的共用体,但是任何时候只能有一个成员带有值.共用体提供了一种使用相同的内存位置的有效方式. 定义共用体 为了定义共用体, ...
- 瘋子C语言笔记(结构体/共用体/枚举篇)
(一)结构体类型 1.简介: 例: struct date { int month; int day; int year; }; struct student { int num; char name ...
- C语言基础 (11) 结构体 ,共用体 枚举 typedef
1 课堂回顾 作用域与生命周期 2 static 局部变量 2 打字游戏 3 内存分区代码分析 4 结构体基本操作 (复合类型[自定义类型 #include <stdio.h> #incl ...
- C++复合类型(结构,共用体,枚举)
•结构是用户定义的类型,而结构的声明定义了这种类型的数据属性. 一.关键字struct声明: 定义了一种新类型 struct inflatable{ char name[20];//结构成员 fl ...
- C语言中的共用体(union)和枚举(enum)
1 union union Data{ int i; char ch; float f; }a={1, 'a', 1.5}; //错误 union Data a = {16}; //正确 union ...
- (转)C语言union(联合体 共用体)
一直以来,union都是个很少用到的东西,对于这些不常用的结构往往记不住.这次看书又看到了,还是学习一下吧.一般在Windows API的一些数据结构中才能看到这个union,其实并不复杂.本质上来说 ...
- 不可或缺 Windows Native (8) - C 语言: 结构体,共用体,枚举,类型定义符
[源码下载] 不可或缺 Windows Native (8) - C 语言: 结构体,共用体,枚举,类型定义符 作者:webabcd 介绍不可或缺 Windows Native 之 C 语言 结构体 ...
随机推荐
- 利用 BASE64Encoder 对字符串进行加密 BASE64Decoder进行解密
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/chenyongtu110/article/details/51694323
- query或者JavaScript实现在textarea光标处插入文本
1.Jquery函数实现: $(function() { /* 在textarea处插入文本--Start */ (function($) { $.fn.extend({ insertContent ...
- linux中touch命令参数修改文件的时间戳(转载)
转自:http://os.51cto.com/art/200908/144237.htm linux中touch命令参数不常用,一般在使用make的时候可能会用到,用来修改文件时间戳,或者新建一个不存 ...
- MySQL5.7 windows二进制安装
200 ? "200px" : this.width)!important;} --> 介绍 1.下载解压 下载地址:http://dev.mysql.com/get/Dow ...
- ACM_递推题目系列之三放苹果(递推dp)
递推题目系列之三放苹果 Time Limit: 2000/1000ms (Java/Others) Problem Description: 把M个同样的苹果放在N个同样的盘子里,允许有的盘子空着不放 ...
- 横向移动-广告图(web)
项目 (移动的广告牌) 要求: 1,实现图片一次以移动的方式出现,到最后一张完全出现时,回弹到第一张 2,鼠标放在图片上面图片移动,鼠标离开,图片停止移动 HTML结构 <!DOCTYPE ht ...
- activity间数据传递
传递简单数据 创建两个activity,FirstActivity和TwoActivity,这里将会将数据从FisrtActivity传给TwoActivity. 创建完activity的目录界面如下 ...
- MaskRCNN:三大基础结构DeepMask、SharpMask、MultiPathNet
MaskXRCnn俨然成为一个现阶段最成功的图像检测分割网络,关于MaskXRCnn的介绍,需要从MaskRCNN看起. 当然一个煽情的介绍可见:何恺明团队推出Mask^X R-CNN,将实例分割扩展 ...
- Codeforces_766_D_(并查集)
D. Mahmoud and a Dictionary time limit per test 4 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input ...
- 梦想Android版CAD控件2019.01.23更新
下载地址:http://www.mxdraw.com/ndetail_10121.html?tdsourcetag=s_pcqq_aiomsg1. 增加异步读取CAD,DWG文件函数,MxFuncti ...
