加密算法大全图解 :密码体系,对称加密算法,非对称加密算法,消息摘要, Base64,数字签名,RSA,DES,MD5,AES,SHA,ElGamal,
1.
加密算法大全:
**********************************************************************************************************************




**********************************************************************************************************************
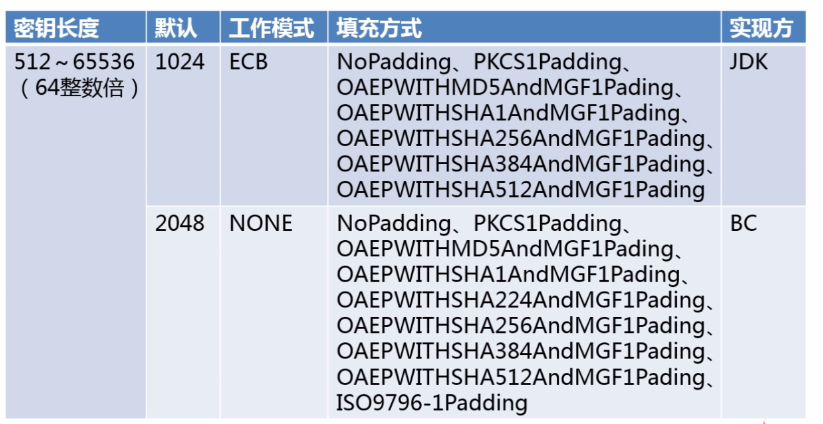
1.非对称加密算法:
DH : Diffie–Hellman key exchange : Diffie-Hellman 密钥交换
Diffie–Hellman (DH) algorithms
Diffie–Hellman key exchange (D–H) is a specific method of securely exchanging cryptographic keys over a public channel and was one of the first public-key protocols as originally conceptualized by Ralph Merkle. D–H is one of the earliest practical examples of public key exchange implemented within the field of cryptography.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diffie%E2%80%93Hellman_key_exchange
ECDH : Elliptic curve Diffie–Hellman 椭圆曲线Diffie-Hellman密钥交换
Elliptic curve Diffie–Hellman (ECDH) is an anonymous key agreement protocol that allows two parties, each having an elliptic curve public–private key pair, to establish a shared secret over an insecure channel.[1][2][3] This shared secret may be directly used as a key, or to derive another key which can then be used to encrypt subsequent communications using a symmetric key cipher. It is a variant of the Diffie–Hellman protocol using elliptic curve cryptography.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elliptic_curve_Diffie%E2%80%93Hellman
ElGamal :
In cryptography, the ElGamal encryption system is an asymmetric key encryption algorithm(非对称密钥加密算法) for public-key cryptography which is based on the Diffie–Hellman key exchange. It was described by Taher Elgamal in 1985.
ElGamal encryption is used in the free GNU Privacy Guard software, recent versions of PGP, and other cryptosystems. The Digital Signature Algorithm is a variant of the ElGamal signature scheme, which should not be confused with ElGamal encryption.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ElGamal_encryption
ECC : Elliptic Curve Cryptography 椭圆曲线密码学
Elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) is an approach to public-key cryptography based on the algebraic structure of elliptic curves over finite fields. ECC requires smaller keys compared to non-ECC cryptography (based on plain Galois fields) to provide equivalent security.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elliptic_curve_cryptography
RSA :
RSA公钥加密算法是1977年由Ron Rivest、Adi Shamirh和Leonard Adleman在(美国麻省理工学院)开发的。RSA取名来自开发他们三者的名字。
RSA is made of the initial letters of the surnames of Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman, who first publicly described the algorithm in 1977.
http://www.emc.com/corporate/about-rsa/index.htm
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RSA
DSA : Digital Signature Algorithm 数字签名算法
The Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA) is a Federal Information Processing Standard for digital signatures.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_Signature_Algorithm
ECDSA : Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm 椭圆曲线数字签名算法
In cryptography, the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) offers a variant of the Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA) which uses elliptic curve cryptography.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elliptic_Curve_Digital_Signature_Algorithm
DSS : ?
Digital Signature Standard 数字签名标准 || Digital Signature Services 数字签名服务
Digital Signature Standard (DSS)
The Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA) is a Federal Information Processing Standard for digital signatures. It was proposed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in August 1991 for use in their Digital Signature Standard (DSS) and adopted as FIPS 186 in 1993.[1] Four revisions to the initial specification have been released: FIPS 186-1 in 1996,[2] FIPS 186-2 in 2000,[3] FIPS 186-3 in 2009,[4] and FIPS 186-4 in 2013.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_Signature_Algorithm
||
Digital Signature Services (DSS) is an OASIS standard.
The Digital Signature Services (DSS) specifications describe two XML-based request/response protocols – a signing protocol and a verifying protocol. Through these protocols a client can send documents to a server and receive back a signature on the documents; or send documents and a signature to a server, and receive back an answer on whether the signature verifies the documents. The DSS Core specifications provide the basic protocols and elements which are adapted to support specific use cases in the DSS profiles.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_Signature_Services
**********************************************************************************************************************













**********************************************************************************************************************
2.对称加密算法:
DES : Data Encryption Standard 数据加密标准
The Data Encryption Standard (DES, /ˌdiːˌiːˈɛs/ or /ˈdɛz/) was once a predominant symmetric-key algorithm for the encryption of electronic data. It was highly influential in the advancement of modern cryptography in the academic world.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_Encryption_Standard
3DES :(Triple DES):密码学中,3DES(或称为Triple DES)是三重数据加密算法(TDEA,Triple Data Encryption Algorithm)块密码的通称.
In cryptography, Triple DES (3DES) is the common name for the Triple Data Encryption Algorithm (TDEA or Triple DEA) symmetric-key block cipher, which applies the Data Encryption Standard (DES) cipher algorithm three times to each data block.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triple_DES
AES:Advanced Encryption Standard 高级加密标准
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), also known as Rijndael[4][5] (its original name), is a specification for the encryption of electronic data established by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2001.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Advanced_Encryption_Standard
PBE : Password Based Encryption 基于口令的加密
Password-based cryptography generally refers to two distinct classes of methods:
- Single-party methods
- Multi-party methods
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Password-based_cryptography
IDEA: International Data Encryption Algorithm 国际数据加密算法
In cryptography, the International Data Encryption Algorithm
(IDEA), originally called Improved Proposed Encryption Standard (IPES),
is a symmetric-key block cipher designed by James Massey of ETH Zurich
and Xuejia Lai and was first described in 1991. The algorithm was
intended as a replacement for the Data Encryption Standard (DES). IDEA
is a minor revision of an earlier cipher, Proposed Encryption Standard
(PES).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/International_Data_Encryption_Algorithm
**********************************************************************************************************************
1




**********************************************************************************************************************
3.消息摘要算法:
MD5 : Message-Digest Algorithm 5 消息摘要算法5
The MD5 message-digest algorithm is a widely used cryptographic hash function producing a 128-bit (16-byte) hash value, typically expressed in text format as a 32 digit hexadecimal number. MD5 has been utilized in a wide variety of cryptographic applications, and is also commonly used to verify data integrity.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MD5
SHA : Secure Hash Algorithm 安全散列算法
The Secure Hash Algorithm is a family of cryptographic hash functions published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) as a U.S. Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS), including:
SHA-0: A retronym applied to the original version of the 160-bit hash function published in 1993 under the name "SHA". It was withdrawn shortly after publication due to an undisclosed "significant flaw" and replaced by the slightly revised version SHA-1.
SHA-1: A 160-bit hash function which resembles the earlier MD5 algorithm. This was designed by the National Security Agency (NSA) to be part of the Digital Signature Algorithm. Cryptographic weaknesses were discovered in SHA-1, and the standard was no longer approved for most cryptographic uses after 2010.
SHA-2: A family of two similar hash functions, with different block sizes, known as SHA-256 and SHA-512. They differ in the word size; SHA-256 uses 32-bit words where SHA-512 uses 64-bit words. There are also truncated versions of each standard, known as SHA-224, SHA-384, SHA-512/224 and SHA-512/256. These were also designed by the NSA.
SHA-3: A hash function formerly called Keccak, chosen in 2012 after a public competition among non-NSA designers. It supports the same hash lengths as SHA-2, and its internal structure differs significantly from the rest of the SHA family.
The corresponding standards are FIPS PUB 180 (original SHA), FIPS PUB 180-1 (SHA-1), FIPS PUB 180-2 (SHA-1, SHA-256, SHA-384, and SHA-512). NIST has updated Draft FIPS Publication 202, SHA-3 Standard separate from the Secure Hash Standard (SHS).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secure_Hash_Algorithm
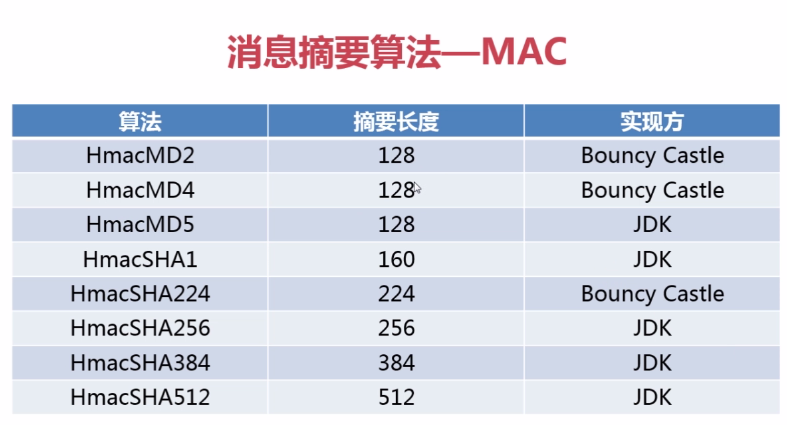
MAC : Message Authentication Code 消息认证码
In cryptography, a message authentication code (MAC) is a short piece of information used to authenticate a message—in other words, to provide integrity and authenticity assurances on the message. Integrity assurances detect accidental and intentional message changes, while authenticity assurances affirm the message's origin.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Message_authentication_code
HMAC : keyed-Hash Message Authentication Code 散列消息认证码
In cryptography, a keyed-hash message authentication code (HMAC) is a specific construction for calculating a message authentication code (MAC) involving a cryptographic hash function in combination with a secret cryptographic key. As with any MAC, it may be used to simultaneously verify both the data integrity and the authentication of a message. Any cryptographic hash function, such as MD5 or SHA-1, may be used in the calculation of an HMAC; the resulting MAC algorithm is termed HMAC-MD5 or HMAC-SHA1 accordingly. The cryptographic strength of the HMAC depends upon the cryptographic strength of the underlying hash function, the size of its hash output, and on the size and quality of the key.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hash-based_message_authentication_code
**********************************************************************************************************************
4.Base64
Base64:




**********************************************************************************************************************
Other: ?
**********************************************************************************************************************

Pretty Good Privacy (PGP):
Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) is a data encryption and decryption computer program that provides cryptographic privacy and authentication for data communication. PGP is often used for signing, encrypting, and decrypting texts, e-mails, files, directories, and whole disk partitions and to increase the security of e-mail communications. It was created by Phil Zimmermann in 1991.[1]
PGP and similar software follow the OpenPGP standard (RFC 4880) for encrypting and decrypting data.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pretty_Good_Privacy
Encrypted Key Exchange (also known as EKE): 加密密钥交换
Encrypted Key Exchange (also known as EKE) is a family of password-authenticated key agreement methods described by Steven M. Bellovin and Michael Merritt.[1] Although several of the forms of EKE in this paper were later found to be flawed [clarification needed], the surviving, refined, and enhanced forms of EKE effectively make this the first method to amplify a shared password into a shared key, where the shared key may subsequently be used to provide a zero-knowledge password proof or other functions.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Encrypted_key_exchange
1
**********************************************************************************************************************
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
加密算法大全图解 :密码体系,对称加密算法,非对称加密算法,消息摘要, Base64,数字签名,RSA,DES,MD5,AES,SHA,ElGamal,的更多相关文章
- Mac和 iOS 下的对称和非对称加密算法的使用
分享在Mac 和 iOS 上使用到的对称和非对称加密算法. 包括RSA,DSA, AES, DES, 3DES 和 blowfish 等等.因为要实现ssh协议, 所以用到了这些算法, 这些算法在ma ...
- Java进阶(八)Java加密技术之对称加密 非对称加密 不可逆加密算法
对称加密 非对称加密 不可逆加密算法 根据密钥类型不同可以将现代密码技术分为两类:对称加密算法(私钥密码体系)和非对称加密算法(公钥密码体系). 1 对称加密算法 原理 对称加密算法中,数据加密和解密 ...
- 第十四章 调试及安全性(In .net4.5) 之 对称及非对称加密
1. 概述 本章内容包括:对称及非对称加密算法..net中的加密类.使用哈希操作.创建和管理签名认证.代码访问权限 和 加密字符串. 2. 主要内容 2.1 使用对称和非对称加密 ① 对称加密:使用同 ...
- Java 加密解密 对称加密算法 非对称加密算法 MD5 BASE64 AES RSA
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. [前言] 本文简单的介绍了加密技术相关概念,最后总结了java中现有的加密技术以及使用方法和例子 [最简单的加密] 1.简单的概念 明文:加密前的 ...
- JAVA加解密 -- 对称加密算法与非对称加密算法
对称加密算法:双方必须约定好算法 DES 数据加密标准:由于不断地被破解 自98年起就已经逐渐放弃使用 AES 目前使用最多的加密方式,官方并未公布加密方式已被破解,替代DES 实现和DES非常接近 ...
- DH、RSA与ElGamal非对称加密算法实现及应用
1.对称加密与非对称加密概述 关于对称加密与非对称加密的概念这里不再多说,感兴趣可以看下我之前的几篇文章,下面说一说两者的主要区别. 对称加密算法数据安全,密钥管理复杂,密钥传递过程复杂,存在密钥泄露 ...
- openssl 非对称加密算法RSA命令详解
1.非对称加密算法概述 非对称加密算法也称公开密钥算法,其解决了对称加密算法密钥分配的问题,非对称加密算法基本特点如下: 1.加密密钥和解密密钥不同 2.密钥对中的一个密钥可以公开 3.根据公开密钥很 ...
- java-信息安全(五)-非对称加密算法RSA
概述 信息安全基本概念: RSA算法(Ron Rivest.Adi Shamir.Leonard Adleman,人名组合) RSA RSA公钥加密算法是1977年由罗纳德·李维斯特(Ron Rive ...
- 非对称加密算法-RSA算法
一.概述 1.RSA是基于大数因子分解难题.目前各种主流计算机语言都支持RSA算法的实现 2.java6支持RSA算法 3.RSA算法可以用于数据加密和数字签名 4.RSA算法相对于DES/AES等对 ...
随机推荐
- 【Android初级】使用setContentView实现页面的转换效果(附源码)
一提到Android中页面的切换,你是不是只想到了startActivity启动另一个Activity? 其实在Android中,可以直接利用setContentView达到类似页面转换效果的!实现思 ...
- 浅谈前端常用脚手架cli工具及案例
前端常用脚手架工具 前端有很多特定的脚手架工具大多都是为了特定的项目类型服务的,比如react项目中的reate-react-app,vue项目中的vue-cli,angular 项目中的angula ...
- 使用remix实现给合约账户转账
实现内容:从remix上的虚拟账户上转账给自己编写的智能合约账户 前提基础:对solidity有一些基础了解,对以太坊的账户机制有一定了解. 账户 在以太坊中账户的唯一标识是地址(address). ...
- 转 12 jmeter性能测试实战--web程序
12 jmeter性能测试实战--web程序 项目背景 项目:XX网站环境:Windows需求:并发登录的性能测试场景:1s增加2个线程,运行2000次(线程数20,Ramp-Up seconds ...
- jmeter的线程数,并发用户数,TPS,RPS 关系解说
背景 在做性能测试的时候,传统方式都是用并发虚拟用户数来衡量系统的性能(站在客户端视角),一般适用于一些网页站点例如首页.H5的压测:而RPS(Requests per second)模式主要是为了方 ...
- 阿姆达尔定律 Amdahl's law
Amdahl's law - Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amdahl%27s_law 阿姆达尔定律(英语:Amdahl's law,Amdahl' ...
- 消息队列扫盲(RocketMQ 入门)
消息队列扫盲 消息队列顾名思义就是存放消息的队列,队列我就不解释了,别告诉我你连队列都不知道似啥吧? 所以问题并不是消息队列是什么,而是 消息队列为什么会出现?消息队列能用来干什么?用它来干这些事会带 ...
- 【PY从0到1】第七节 函数
# 7 第七节 函数 # 函数对于编程语言来说是一块重量级的内容. # 他可以实现或者简化编写的代码. # 编写好特定功能的函数后,就可以重复调用函数来完成任务. # 下面我们就用函数的形式来封装前面 ...
- java架构《并发线程基础一》
1.实现线程常见的两种的方式 : 1:继承extends Thread 2:实现new Runnable 实现其run方法 2.线程安全 结论: 当多个线程访问某一个类(对象或方法)时,这个对象 ...
- Redis挖矿原理及防范
笔者也曾经被挖矿病毒侵袭过,灰常难受,但是其实你只要了解入侵的手段就非常好防范了,今天我们就演示一下如果通过Redis进行提权获取远程服务器的Root用户. 1.首先我们需要一些先决条件 条件一:你首 ...
