【转载】 pytorch之添加BN
原文地址:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40123108/article/details/83509838
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
pytorch之添加BN层
批标准化
模型训练并不容易,特别是一些非常复杂的模型,并不能非常好的训练得到收敛的结果,所以对数据增加一些预处理,同时使用批标准化能够得到非常好的收敛结果,这也是卷积网络能够训练到非常深的层的一个重要原因。
数据预处理
目前数据预处理最常见的方法就是中心化和标准化,中心化相当于修正数据的中心位置,实现方法非常简单,就是在每个特征维度上减去对应的均值,最后得到 0 均值的特征。标准化也非常简单,在数据变成 0 均值之后,为了使得不同的特征维度有着相同的规模,可以除以标准差近似为一个标准正态分布,也可以依据最大值和最小值将其转化为 -1 ~ 1之间,这两种方法非常的常见,如果你还记得,前面我们在神经网络的部分就已经使用了这个方法实现了数据标准化,至于另外一些方法,比如 PCA 或者 白噪声已经用得非常少了。
Batch Normalization
前面在数据预处理的时候,尽量输入特征不相关且满足一个标准的正态分布,
这样模型的表现一般也较好。但是对于很深的网路结构,网路的非线性层会使得输出的结果变得相关,且不再满足一个标准的 N(0, 1) 的分布,甚至输出的中心已经发生了偏移,这对于模型的训练,特别是深层的模型训练非常的困难。
所以在 2015 年一篇论文提出了这个方法,批标准化,简而言之,就是对于每一层网络的输出,对其做一个归一化,使其服从标准的正态分布,这样后一层网络的输入也是一个标准的正态分布,所以能够比较好的进行训练,加快收敛速度。batch normalization 的实现非常简单,
对于给定的一个 batch 的数据 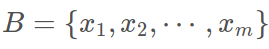 算法的公式如下
算法的公式如下
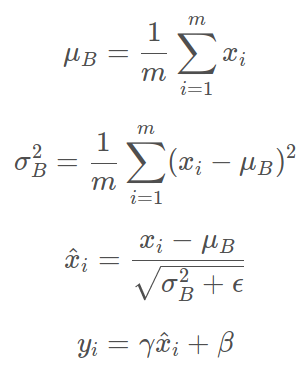
第一行和第二行是计算出一个 batch 中数据的均值和方差,接着使用第三个公式对 batch 中的每个数据点做标准化,ϵϵ 是为了计算稳定引入的一个小的常数,通常取 10−510−5,最后利用权重修正得到最后的输出结果,非常的简单,
实现一下简单的一维的情况,也就是神经网络中的情况
- import sys
- sys.path.append('..')
- import torch
- def simple_batch_norm_1d(x, gamma, beta):
- eps = 1e-5
- x_mean = torch.mean(x, dim=0, keepdim=True) # 保留维度进行 broadcast
- x_var = torch.mean((x - x_mean) ** 2, dim=0, keepdim=True)
- x_hat = (x - x_mean) / torch.sqrt(x_var + eps)
- return gamma.view_as(x_mean) * x_hat + beta.view_as(x_mean)
- x = torch.arange(15).view(5, 3)
x=x.type(torch.float)- gamma = torch.ones(x.shape[1])
- beta = torch.zeros(x.shape[1])
- print('before bn: ')
- print(x)
- y = simple_batch_norm_1d(x, gamma, beta)
- print('after bn: ')
- print(y)
可以看到这里一共是 5 个数据点,三个特征,每一列表示一个特征的不同数据点,使用批标准化之后,每一列都变成了标准的正态分布这个时候会出现一个问题,就是测试的时候该使用批标准化吗?答案是肯定的,因为训练的时候使用了,而测试的时候不使用肯定会导致结果出现偏差,但是测试的时候如果只有一个数据集,那么均值不就是这个值,方差为 0 吗?这显然是随机的,所以测试的时候不能用测试的数据集去算均值和方差,而是用训练的时候算出的移动平均均值和方差去代替
实现以下能够区分训练状态和测试状态的批标准化方法
- def batch_norm_1d(x, gamma, beta, is_training, moving_mean, moving_var, moving_momentum=0.1):
- eps = 1e-5
- x_mean = torch.mean(x, dim=0, keepdim=True) # 保留维度进行 broadcast
- x_var = torch.mean((x - x_mean) ** 2, dim=0, keepdim=True)
- if is_training:
- x_hat = (x - x_mean) / torch.sqrt(x_var + eps)
- moving_mean[:] = moving_momentum * moving_mean + (1. - moving_momentum) * x_mean
- moving_var[:] = moving_momentum * moving_var + (1. - moving_momentum) * x_var
- else:
- x_hat = (x - moving_mean) / torch.sqrt(moving_var + eps)
- return gamma.view_as(x_mean) * x_hat + beta.view_as(x_mean)
下面使用深度神经网络分类 mnist 数据集的例子来试验一下批标准化是否有用
- import numpy as np
- from torchvision.datasets import mnist # 导入 pytorch 内置的 mnist 数据
- from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
- from torch import nn
- from torch.autograd import Variable
使用内置函数下载 mnist 数据集
- train_set = mnist.MNIST('./data', train=True)
- test_set = mnist.MNIST('./data', train=False)
- def data_tf(x):
- x = np.array(x, dtype='float32') / 255
- x = (x - 0.5) / 0.5 # 数据预处理,标准化
- x = x.reshape((-1,)) # 拉平
- x = torch.from_numpy(x)
- return x
- train_set = mnist.MNIST('./data', train=True, transform=data_tf, download=True) # 重新载入数据集,申明定义的数据变换
- test_set = mnist.MNIST('./data', train=False, transform=data_tf, download=True)
- train_data = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
- test_data = DataLoader(test_set, batch_size=128, shuffle=False)
- class multi_network(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self):
- super(multi_network, self).__init__()
- self.layer1 = nn.Linear(784, 100)
- self.relu = nn.ReLU(True)
- self.layer2 = nn.Linear(100, 10)
- self.gamma = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(100))
- self.beta = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(100))
- self.moving_mean = Variable(torch.zeros(100))
- self.moving_var = Variable(torch.zeros(100))
- def forward(self, x, is_train=True):
- x = self.layer1(x)
- x = batch_norm_1d(x, self.gamma, self.beta, is_train, self.moving_mean, self.moving_var)
- x = self.relu(x)
- x = self.layer2(x)
- return x
- net = multi_network()
- # 定义 loss 函数
- criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
- optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), 1e-1) # 使用随机梯度下降,学习率 0.1
- from datetime import datetime
- import torch
- import torch.nn.functional as F
- from torch import nn
- from torch.autograd import Variable
- def get_acc(output, label):
- total = output.shape[0]
- _, pred_label = output.max(1)
- num_correct = (pred_label == label).sum().item()
- return num_correct / total
- #定义训练函数
- def train(net, train_data, valid_data, num_epochs, optimizer, criterion):
- if torch.cuda.is_available():
- net = net.cuda()
- prev_time = datetime.now()
- for epoch in range(num_epochs):
- train_loss = 0
- train_acc = 0
- net = net.train()
- for im, label in train_data:
- if torch.cuda.is_available():
- im = Variable(im.cuda()) # (bs, 3, h, w)
- label = Variable(label.cuda()) # (bs, h, w)
- else:
- im = Variable(im)
- label = Variable(label)
- # forward
- output = net(im)
- loss = criterion(output, label)
- # backward
- optimizer.zero_grad()
- loss.backward()
- optimizer.step()
- train_loss += loss.item()
- train_acc += get_acc(output, label)
- cur_time = datetime.now()
- h, remainder = divmod((cur_time - prev_time).seconds, 3600)
- m, s = divmod(remainder, 60)
- time_str = "Time %02d:%02d:%02d" % (h, m, s)
- if valid_data is not None:
- valid_loss = 0
- valid_acc = 0
- net = net.eval()
- for im, label in valid_data:
- if torch.cuda.is_available():
- im = Variable(im.cuda(), volatile=True)
- label = Variable(label.cuda(), volatile=True)
- else:
- im = Variable(im, volatile=True)
- label = Variable(label, volatile=True)
- output = net(im)
- loss = criterion(output, label)
- valid_loss += loss.item()
- valid_acc += get_acc(output, label)
- epoch_str = (
- "Epoch %d. Train Loss: %f, Train Acc: %f, Valid Loss: %f, Valid Acc: %f, "
- % (epoch, train_loss / len(train_data),
- train_acc / len(train_data), valid_loss / len(valid_data),
- valid_acc / len(valid_data)))
- else:
- epoch_str = ("Epoch %d. Train Loss: %f, Train Acc: %f, " %
- (epoch, train_loss / len(train_data),
- train_acc / len(train_data)))
- prev_time = cur_time
- print(epoch_str + time_str)
- train(net, train_data, test_data, 10, optimizer, criterion)
#这里的 γγ 和 ββ 都作为参数进行训练,初始化为随机的高斯分布,
#moving_mean 和 moving_var 都初始化为 0,并不是更新的参数,训练完 10 次之后,我们可以看看移动平均和移动方差被修改为了多少
#打出 moving_mean 的前 10 项
- print(net.moving_mean[:10])
- no_bn_net = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Linear(784, 100),
- nn.ReLU(True),
- nn.Linear(100, 10)
- )
- optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(no_bn_net.parameters(), 1e-1) # 使用随机梯度下降,学习率 0.1
- train(no_bn_net, train_data, test_data, 10, optimizer, criterion)
可以看到虽然最后的结果两种情况一样,但是如果我们看前几次的情况,可以看到使用批标准化的情况能够更快的收敛,因为这只是一个小网络,所以用不用批标准化都能够收敛,但是对于更加深的网络,使用批标准化在训练的时候能够很快地收敛从上面可以看到,我们自己实现了 2 维情况的批标准化,对应于卷积的 4 维情况的标准化是类似的,只需要沿着通道的维度进行均值和方差的计算,但是我们自己实现批标准化是很累的,pytorch 当然也为我们内置了批标准化的函数,一维和二维分别是 torch.nn.BatchNorm1d() 和 torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(),不同于我们的实现,pytorch 不仅将 γ 和 β 作为训练的参数,也将 moving_mean 和 moving_var 也作为参数进行训练
下面在卷积网络下试用一下批标准化看看效果
- def data_tf(x):
- x = np.array(x, dtype='float32') / 255
- x = (x - 0.5) / 0.5 # 数据预处理,标准化
- x = torch.from_numpy(x)
- x = x.unsqueeze(0)
- return x
- train_set = mnist.MNIST('./data', train=True, transform=data_tf, download=True) # 重新载入数据集,申明定义的数据变换
- test_set = mnist.MNIST('./data', train=False, transform=data_tf, download=True)
- train_data = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
- test_data = DataLoader(test_set, batch_size=128, shuffle=False)
使用批标准化
- class conv_bn_net(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self):
- super(conv_bn_net, self).__init__()
- self.stage1 = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 3, padding=1),
- nn.BatchNorm2d(6),
- nn.ReLU(True),
- nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2),
- nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5),
- nn.BatchNorm2d(16),
- nn.ReLU(True),
- nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
- )
- self.classfy = nn.Linear(400, 10)
- def forward(self, x):
- x = self.stage1(x)
- x = x.view(x.shape[0], -1)
- x = self.classfy(x)
- return x
- net = conv_bn_net()
- optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), 1e-1) # 使用随机梯度下降,学习率 0.1
- train(net, train_data, test_data, 5, optimizer, criterion)
不使用批标准化
- class conv_no_bn_net(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self):
- super(conv_no_bn_net, self).__init__()
- self.stage1 = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 3, padding=1),
- nn.ReLU(True),
- nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2),
- nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5),
- nn.ReLU(True),
- nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
- )
- self.classfy = nn.Linear(400, 10)
- def forward(self, x):
- x = self.stage1(x)
- x = x.view(x.shape[0], -1)
- x = self.classfy(x)
- return x
- net = conv_no_bn_net()
- optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), 1e-1) # 使用随机梯度下降,学习率 0.1
- train(net, train_data, test_data, 5, optimizer, criterion)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ps: 个人补充
本文中给出的 一维 批正则 和 未加批正则的代码:
- #!/usr/bin/env python3
- #encoding:UTF-8
- import torch
- import numpy as np
- import torch.nn.functional as F
- from torch import nn
- from torch.autograd import Variable
- from torchvision.datasets import mnist # 导入 pytorch 内置的 mnist 数据
- from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
- from datetime import datetime
- def batch_norm_1d(x, gamma, beta, is_training, moving_mean, moving_var, moving_momentum=0.1):
- eps = 1e-5
- x_mean = torch.mean(x, dim=0, keepdim=True) # 保留维度进行 broadcast
- x_var = torch.mean((x - x_mean) ** 2, dim=0, keepdim=True)
- if torch.cuda.is_available():
- x_mean=x_mean.cuda()
- x_var=x_var.cuda()
- moving_mean=moving_mean.cuda()
- moving_var=moving_var.cuda()
- if is_training:
- x_hat = (x - x_mean) / torch.sqrt(x_var + eps)
- moving_mean[:] = moving_momentum * moving_mean + (1. - moving_momentum) * x_mean
- moving_var[:] = moving_momentum * moving_var + (1. - moving_momentum) * x_var
- else:
- x_hat = (x - moving_mean) / torch.sqrt(moving_var + eps)
- return gamma.view_as(x_mean) * x_hat + beta.view_as(x_mean)
- def data_tf(x):
- x = np.array(x, dtype='float32') / 255
- x = (x - 0.5) / 0.5 # 数据预处理,标准化
- x = x.reshape((-1,)) # 拉平
- x = torch.from_numpy(x)
- return x
- # 重新载入数据集,申明定义的数据变换
- train_set = mnist.MNIST('./data', train=True, transform=data_tf, download=True)
- test_set = mnist.MNIST('./data', train=False, transform=data_tf, download=True)
- train_data = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
- test_data = DataLoader(test_set, batch_size=128, shuffle=False)
- class multi_network(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self):
- super(multi_network, self).__init__()
- self.layer1 = nn.Linear(784, 100)
- self.relu = nn.ReLU(True)
- self.layer2 = nn.Linear(100, 10)
- self.gamma = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(100))
- self.beta = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(100))
- self.moving_mean = Variable(torch.zeros(100))
- self.moving_var = Variable(torch.zeros(100))
- def forward(self, x, is_train=True):
- x = self.layer1(x)
- x = batch_norm_1d(x, self.gamma, self.beta, is_train, self.moving_mean, self.moving_var)
- x = self.relu(x)
- x = self.layer2(x)
- return x
- net = multi_network()
- # 定义 loss 函数
- criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
- # 使用随机梯度下降,学习率 0.1
- optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), 1e-1)
- def get_acc(output, label):
- total = output.shape[0]
- _, pred_label = output.max(1)
- num_correct = (pred_label == label).sum().item()
- return num_correct / total
- #定义训练函数
- def train(net, train_data, valid_data, num_epochs, optimizer, criterion):
- if torch.cuda.is_available():
- net = net.cuda()
- prev_time = datetime.now()
- for epoch in range(num_epochs):
- train_loss = 0
- train_acc = 0
- net = net.train()
- for im, label in train_data:
- if torch.cuda.is_available():
- im = Variable(im.cuda()) # (bs, 3, h, w)
- label = Variable(label.cuda()) # (bs, h, w)
- else:
- im = Variable(im)
- label = Variable(label)
- # forward
- output = net(im)
- loss = criterion(output, label)
- # backward
- optimizer.zero_grad()
- loss.backward()
- optimizer.step()
- train_loss += loss.item()
- train_acc += get_acc(output, label)
- cur_time = datetime.now()
- h, remainder = divmod((cur_time - prev_time).seconds, 3600)
- m, s = divmod(remainder, 60)
- time_str = "Time %02d:%02d:%02d" % (h, m, s)
- if valid_data is not None:
- valid_loss = 0
- valid_acc = 0
- net = net.eval()
- for im, label in valid_data:
- if torch.cuda.is_available():
- im = Variable(im.cuda())
- label = Variable(label.cuda())
- else:
- im = Variable(im, volatile=True)
- label = Variable(label, volatile=True)
- output = net(im)
- loss = criterion(output, label)
- valid_loss += loss.item()
- valid_acc += get_acc(output, label)
- epoch_str = (
- "Epoch %d. Train Loss: %f, Train Acc: %f, Valid Loss: %f, Valid Acc: %f, "
- % (epoch, train_loss / len(train_data),
- train_acc / len(train_data), valid_loss / len(valid_data),
- valid_acc / len(valid_data)))
- else:
- epoch_str = ("Epoch %d. Train Loss: %f, Train Acc: %f, " %
- (epoch, train_loss / len(train_data),
- train_acc / len(train_data)))
- prev_time = cur_time
- print(epoch_str + time_str)
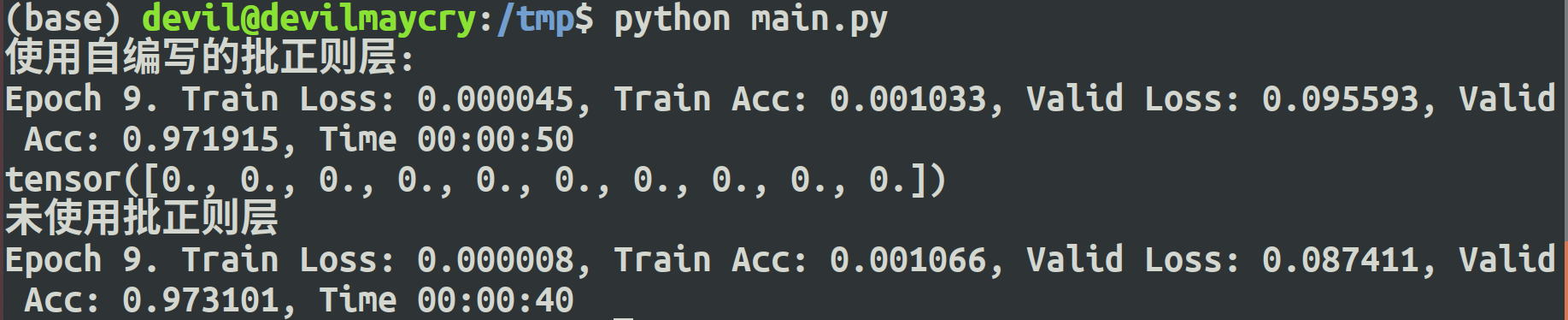
- print("使用自编写的批正则层:")
- train(net, train_data, test_data, 10, optimizer, criterion)
- #################################################
- print(net.moving_mean[:10])
- no_bn_net = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Linear(784, 100),
- nn.ReLU(True),
- nn.Linear(100, 10)
- )
- optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(no_bn_net.parameters(), 1e-1) # 使用随机梯度下降,学习率 0.1
- print("未使用批正则层")
- train(no_bn_net, train_data, test_data, 10, optimizer, criterion)
cnn 二维批正则:
- #!/usr/bin/env python3
- #encoding:UTF-8
- import torch
- import numpy as np
- import torch.nn.functional as F
- from torch import nn
- from torch.autograd import Variable
- from torchvision.datasets import mnist # 导入 pytorch 内置的 mnist 数据
- from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
- from datetime import datetime
- def data_tf(x):
- x = np.array(x, dtype='float32') / 255
- x = (x - 0.5) / 0.5 # 数据预处理,标准化
- x = torch.from_numpy(x)
- x = x.unsqueeze(0)
- return x
- train_set = mnist.MNIST('./data', train=True, transform=data_tf, download=True) # 重新载入数据集,申明定义的数据变换
- test_set = mnist.MNIST('./data', train=False, transform=data_tf, download=True)
- train_data = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
- test_data = DataLoader(test_set, batch_size=128, shuffle=False)
- def get_acc(output, label):
- total = output.shape[0]
- _, pred_label = output.max(1)
- num_correct = (pred_label == label).sum().item()
- return num_correct / total
- criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
- #定义训练函数
- def train(net, train_data, valid_data, num_epochs, optimizer, criterion):
- if torch.cuda.is_available():
- net = net.cuda()
- prev_time = datetime.now()
- for epoch in range(num_epochs):
- train_loss = 0
- train_acc = 0
- net = net.train()
- for im, label in train_data:
- if torch.cuda.is_available():
- im = Variable(im.cuda()) # (bs, 3, h, w)
- label = Variable(label.cuda()) # (bs, h, w)
- else:
- im = Variable(im)
- label = Variable(label)
- # forward
- output = net(im)
- loss = criterion(output, label)
- # backward
- optimizer.zero_grad()
- loss.backward()
- optimizer.step()
- train_loss += loss.item()
- train_acc += get_acc(output, label)
- cur_time = datetime.now()
- h, remainder = divmod((cur_time - prev_time).seconds, 3600)
- m, s = divmod(remainder, 60)
- time_str = "Time %02d:%02d:%02d" % (h, m, s)
- if valid_data is not None:
- valid_loss = 0
- valid_acc = 0
- net = net.eval()
- for im, label in valid_data:
- if torch.cuda.is_available():
- im = Variable(im.cuda())
- label = Variable(label.cuda())
- else:
- im = Variable(im, volatile=True)
- label = Variable(label, volatile=True)
- output = net(im)
- loss = criterion(output, label)
- valid_loss += loss.item()
- valid_acc += get_acc(output, label)
- epoch_str = (
- "Epoch %d. Train Loss: %f, Train Acc: %f, Valid Loss: %f, Valid Acc: %f, "
- % (epoch, train_loss / len(train_data),
- train_acc / len(train_data), valid_loss / len(valid_data),
- valid_acc / len(valid_data)))
- else:
- epoch_str = ("Epoch %d. Train Loss: %f, Train Acc: %f, " %
- (epoch, train_loss / len(train_data),
- train_acc / len(train_data)))
- prev_time = cur_time
- print(epoch_str + time_str)
- class conv_bn_net(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self):
- super(conv_bn_net, self).__init__()
- self.stage1 = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 3, padding=1),
- nn.BatchNorm2d(6),
- nn.ReLU(True),
- nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2),
- nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5),
- nn.BatchNorm2d(16),
- nn.ReLU(True),
- nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
- )
- self.classfy = nn.Linear(400, 10)
- def forward(self, x):
- x = self.stage1(x)
- x = x.view(x.shape[0], -1)
- x = self.classfy(x)
- return x
- net = conv_bn_net()
- optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), 1e-1) # 使用随机梯度下降,学习率 0.1
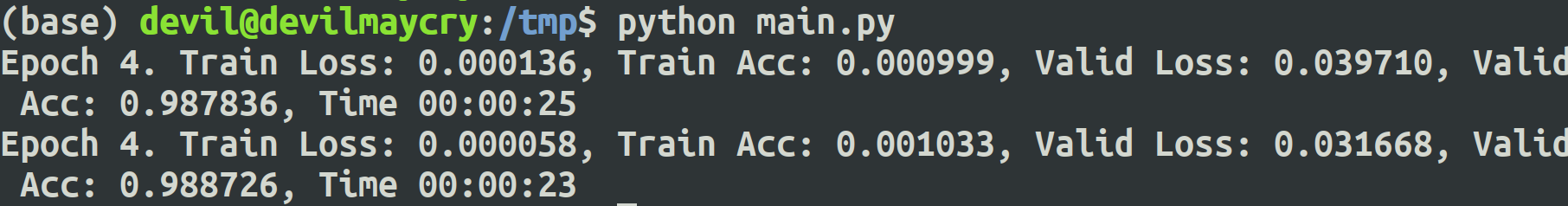
- train(net, train_data, test_data, 5, optimizer, criterion)
- #################################################
- class conv_no_bn_net(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self):
- super(conv_no_bn_net, self).__init__()
- self.stage1 = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 3, padding=1),
- nn.ReLU(True),
- nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2),
- nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5),
- nn.ReLU(True),
- nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
- )
- self.classfy = nn.Linear(400, 10)
- def forward(self, x):
- x = self.stage1(x)
- x = x.view(x.shape[0], -1)
- x = self.classfy(x)
- return x
- net = conv_no_bn_net()
- optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), 1e-1) # 使用随机梯度下降,学习率 0.1
- train(net, train_data, test_data, 5, optimizer, criterion)
【转载】 pytorch之添加BN的更多相关文章
- [转载]PyTorch上的contiguous
[转载]PyTorch上的contiguous 来源:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/64551412 这篇文章写的非常好,我这里就不复制粘贴了,有兴趣的同学可以去看原文,我 ...
- [转载]PyTorch中permute的用法
[转载]PyTorch中permute的用法 来源:https://blog.csdn.net/york1996/article/details/81876886 permute(dims) 将ten ...
- [转载]Pytorch详解NLLLoss和CrossEntropyLoss
[转载]Pytorch详解NLLLoss和CrossEntropyLoss 来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_22210253/article/details/85229988 ...
- [转载]Pytorch中nn.Linear module的理解
[转载]Pytorch中nn.Linear module的理解 本文转载并援引全文纯粹是为了构建和分类自己的知识,方便自己未来的查找,没啥其他意思. 这个模块要实现的公式是:y=xAT+*b 来源:h ...
- 【转载】 Pytorch(1) pytorch中的BN层的注意事项
原文地址: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40100431/article/details/84349470 ------------------------------- ...
- 【转载】Pyqt 添加右键菜单方法
转载地址: http://www.cnblogs.com/yogalau/p/3954042.html?utm_source=tuicool QListWidget 是继承 QWidget 的, 所以 ...
- 【转载】LoadRunner添加windows多台压力机
添加多台压力机 1.前置条件 1)保证压力机上都安装了loadrunner Agent,并启动,状态栏中会有小卫星. 2)添加的压力机与controller所在机器是否在同一个网段,建议关闭防火墙.在 ...
- 【转载】 详解BN(Batch Normalization)算法
原文地址: http://blog.csdn.net/hjimce/article/details/50866313 作者:hjimce ------------------------------- ...
- 转载:mysql添加用户、删除用户、授权、修改密码
mysql添加用户.删除用户.授权.修改密码等 MySql中添加用户,新建数据库,用户授权,删除用户,修改密码1.新建用户. //登录MYSQL @>mysql -u root -p @> ...
随机推荐
- noip2013转圈游戏
题目描述 n个小伙伴(编号从 0到 n−1)围坐一圈玩游戏.按照顺时针方向给 n个位置编号,从0 到 n−1.最初,第 0号小伙伴在第 0号位置,第 1号小伙伴在第 1 号位置,……,依此类推. 游戏 ...
- Struts 2 初步入门(五)之接受参数
1.使用action的属性接受参数 执行顺序为:前端提交参数--->LoginAction.do进行处理--->处理成功后,跳转到sucess.jsp文件. (1)新建login.jsp文 ...
- vs 编译库文件
vs编译的库文件 静态库 debug和release版本 需要分开编译,我编译和实践的结果. 但是我也发现有的debug release都用同一个(搞不清楚). 然后添加到工程应用. 静态库 附件 ...
- numpy ndarray
>>> aarray([[1, 2], [3, 4]])>>> a.shape(2, 2)>>> barray([2, 3])>>&g ...
- ubuntu shell编程笔记
and 命令 if [ A -a B ] then else fi while [ ] do done set command set these are parameters $1 s ...
- 整数中1出现的次数(1~n)
题目描述 求出1~13的整数中1出现的次数,并算出100~1300的整数中1出现的次数?为此他特别数了一下1~13中包含1的数字有1.10.11.12.13因此共出现6次,但是对于后面问题他就没辙了. ...
- console.log()显示图片以及为文字加样式
有兴趣的同学可以文章最后的代码复制贴到控制台玩玩. Go for Code 在正常模式下,一般只能向console 控制台输出简单的文字信息.但为了把信息输出得更优雅更便于阅读,除了cosole.lo ...
- markdown语法模板
(GitHub-Flavored) Markdown Editor Basic useful feature list: Ctrl+S / Cmd+S to save the file Ctrl+Sh ...
- [POJ2985]The k-th Largest Group
Problem 刚开始,每个数一个块. 有两个操作:0 x y 合并x,y所在的块 1 x 查询第x大的块 Solution 用并查集合并时,把原来的大小删去,加上两个块的大小和. Notice 非旋 ...
- 【资料搜集】Python学习
python学习手册 | 演道网 http://dev.go2live.cn/python/python%e5%ad%a6%e4%b9%a0%e6%89%8b%e5%86%8c.html
