堆溢出---glibc malloc
成功从来没有捷径。如果你只关注CVE/NVD的动态以及google专家泄露的POC,那你只是一个脚本小子。能够自己写有效POC,那就证明你已经是一名安全专家了。今天我需要复习一下glibc中内存的相关知识,以巩固我对堆溢出的理解和分析。带着以下问题去阅读本章:
- dlmalloc – General purpose allocator
- ptmalloc2 – glibc
- jemalloc – FreeBSD and Firefox
- tcmalloc – Google
- libumem – Solaris
我们以glibc为例探讨堆的运行机制,主要是因为服务器绝大部分都和glibc有关,研究glibc有广泛意义。
系统调用:malloc本身需要调用brk或mmap完成内存分配操作
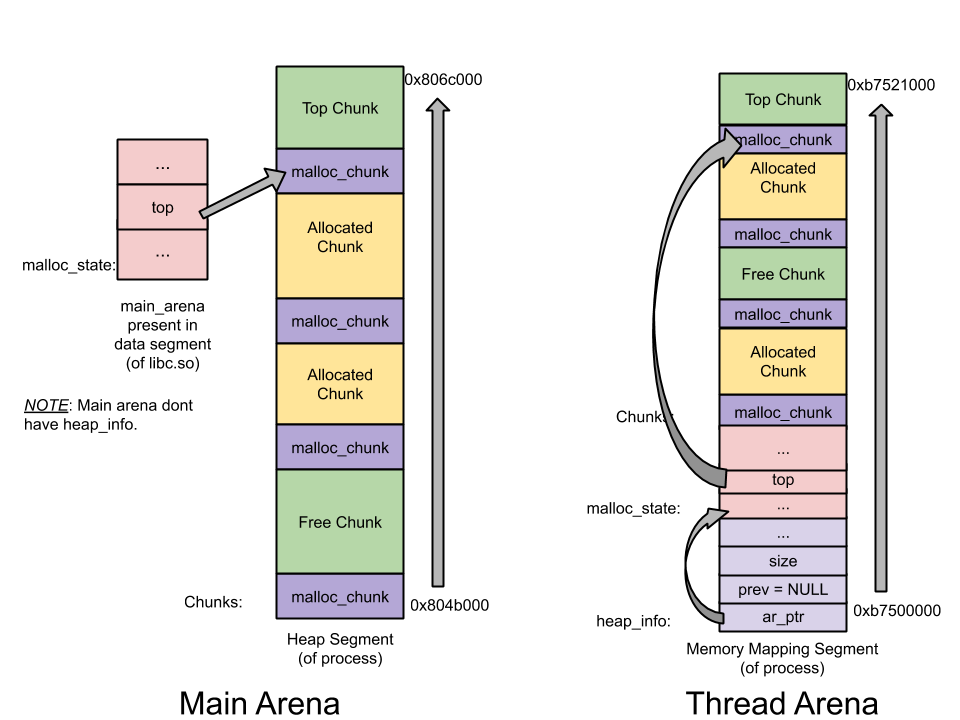
线程:ptmalloc2的前身是dlmalloc,它们最大的区别是ptmalloc2支持线程,它提升了内存分配的效率。在dlmalloc中,如果有2个线程同时调用 malloc,只有一个线程可以进入关键区,线程之间共享同一个freelist数据结构。在ptmaloc2中,每一个线程都拥有单独的堆区段,也就意味着每个线程都有自己的freelist结构体。没有线程之间的共享和争用,性能自然提高不少。Per thread arena用来特指为每个线程维护独立的堆区段和freelist结构体的方式。
- /* Per thread arena example. */
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <pthread.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <sys/types.h>
- void* threadFunc(void* arg) {
- printf("Before malloc in thread 1\n");
- getchar();
- char* addr = (char*) malloc();
- printf("After malloc and before free in thread 1\n");
- getchar();
- free(addr);
- printf("After free in thread 1\n");
- getchar();
- }
- int main() {
- pthread_t t1;
- void* s;
- int ret;
- char* addr;
- printf("Welcome to per thread arena example::%d\n",getpid());
- printf("Before malloc in main thread\n");
- getchar();
- addr = (char*) malloc();
- printf("After malloc and before free in main thread\n");
- getchar();
- free(addr);
- printf("After free in main thread\n");
- getchar();
- ret = pthread_create(&t1, NULL, threadFunc, NULL);
- if(ret)
- {
- printf("Thread creation error\n");
- return -;
- }
- ret = pthread_join(t1, &s);
- if(ret)
- {
- printf("Thread join error\n");
- return -;
- }
- return ;
- }
分析:主线程在malloc调用之前,没有任何堆区和栈区被分配
- sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ ./mthread
- Welcome to per thread arena example::
- Before malloc in main thread
- ...
- sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ cat /proc//maps
- - r-xp : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
- -0804a000 r--p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
- 0804a000-0804b000 rw-p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
- b7e05000-b7e07000 rw-p :
- ...
- sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$
主线程在调用malloc之后,从下图中我们可以看出堆区域被分配在0804b000-0806c000区域,这是通过调用brk调整内存中止点来建立堆。此外,尽管申请了1000字节,但分配了132KB的堆内存。这个连续区域被称为Arena。主线程建立的就称为Main Arena。未来分配内存的请求会持续使用Arena区域直到用尽。如果用尽,可以调整内存中止点来扩大Top trunk。相似的,也可以相应的收缩以防止top chunk有太多的空间。(Top trunk是Arena最顶部的chunk)
- sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ ./mthread
- Welcome to per thread arena example::
- Before malloc in main thread
- After malloc and before free in main thread
- ...
- sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/lsploits/hof/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ cat /proc//maps
- - r-xp : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
- -0804a000 r--p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
- 0804a000-0804b000 rw-p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
- 0804b000-0806c000 rw-p : [heap]
- b7e05000-b7e07000 rw-p :
- ...
- sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$
主线程 Free之后,内存并未归还给OS,而是交由glibc malloc管理,放在Main Arena的bin中。(freelist数据结构体就是bin)之后所有的空间申请,都会在bin中寻求满足。无法满足时才再次向内核获得空间。
- sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ ./mthread
- Welcome to per thread arena example::
- Before malloc in main thread
- After malloc and before free in main thread
- After free in main thread
- ...
- sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/lsploits/hof/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ cat /proc//maps
- - r-xp : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
- -0804a000 r--p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
- 0804a000-0804b000 rw-p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
- 0804b000-0806c000 rw-p : [heap]
- b7e05000-b7e07000 rw-p :
- ...
- sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$
在调用thread1中malloc之前,thread1的堆区域并未建立,但线程栈已建立。
- sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ ./mthread
- Welcome to per thread arena example::
- Before malloc in main thread
- After malloc and before free in main thread
- After free in main thread
- Before malloc in thread
- ...
- sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ cat /proc//maps
- - r-xp : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
- -0804a000 r--p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
- 0804a000-0804b000 rw-p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
- 0804b000-0806c000 rw-p : [heap]
- b7604000-b7605000 ---p :
- b7605000-b7e07000 rw-p : [stack:]
- ...
- sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$
在thread1中malloc调用之后,线程堆区段建立了。位于b7500000-b7521000,大小132KB。这显示和主线程不同,线程malloc调用的是mmap系统调用,而非sbrk。尽管用户请求1000字节,1M的堆内存被映射到了进程地址空间。但只有132KB被设置为可读写权限,并被设置为该线程的堆空间。这个连续的内存空间是Thread Arena。
当用户内存请求大小超过128KB时,不论请求是从主线程还是子线程,内存分配都是由mmap系统调用来完成的。
- sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ ./mthread
- Welcome to per thread arena example::
- Before malloc in main thread
- After malloc and before free in main thread
- After free in main thread
- Before malloc in thread
- After malloc and before free in thread
- ...
- sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ cat /proc//maps
- - r-xp : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
- -0804a000 r--p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
- 0804a000-0804b000 rw-p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
- 0804b000-0806c000 rw-p : [heap]
- b7500000-b7521000 rw-p :
- b7521000-b7600000 ---p :
- b7604000-b7605000 ---p :
- b7605000-b7e07000 rw-p : [stack:]
- ...
- sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$
Thread1在free之后,被分配的内存区并未交还给操作系统,而是归还给glicbc分配器,实际上它交给了线程Arena bin.
- sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ ./mthread
- Welcome to per thread arena example::
- Before malloc in main thread
- After malloc and before free in main thread
- After free in main thread
- Before malloc in thread
- After malloc and before free in thread
- After free in thread
- ...
- sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ cat /proc//maps
- - r-xp : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
- -0804a000 r--p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
- 0804a000-0804b000 rw-p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
- 0804b000-0806c000 rw-p : [heap]
- b7500000-b7521000 rw-p :
- b7521000-b7600000 ---p :
- b7604000-b7605000 ---p :
- b7605000-b7e07000 rw-p : [stack:]
- ...
- sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$
Arena:
在上面的例子中,主线程对应的是Main Arena,子线程对应的是Thread Arena。那线程和Arena是否是一一对应的呢?不是。实际上线程数可以多于核数,因此,让一个线程拥有一个Arena有些奢侈。应用程序Arena的数量是和核数相关的,具体如下:
- For bit systems:
- Number of arena = * number of cores.
- For bit systems:
- Number of arena = * number of cores.
Multiple Arena:
举例说明:一个单核32位系统有4个线程(1主3子)。那4个线程只有2个Arena。Glibc内存分配器确保Multiple Arena在线程之间共享
- 主线程首次调用malloc时一定是创建了Main Arena
- 当子线程1和子线程2首次调用malloc时,会给它们都建立一个新的Arena。此时Arena和线程是一一对应的
- 当子线程3首次调用 malloc,此时会计算Arena的限制。已超出Arena数量限制,要重用Main Arena, Thread1 Arena或Thread2 Arena
- 重用:
- 遍历存在的Arena,找到一个后试图去lock它
- 成功lock,比如是Main Arena,给用户返回Arena
- 没有空闲的Arena,就排队等待
- 当Thread3二次调用 malloc时,malloc将使用最近访问的Arena(可能是main arena)。如果main arena是空闲的就使用它,如果忙时就Block等待。
多堆:
Heap_info: 堆头。一个线程Arena拥有多个堆,每个堆有它自己的头。之所以有多个堆,是因为开始的时候只有一个堆,但随着堆区空间用尽,新堆会由mmap重新建立,而且地址空间是不连续的,新旧堆无法合并
malloc_state: Arena Header - 一个线程Arena有多个堆,但那些堆只有一个Arena头。Arena头包含了bins,top chunk和last remainder chunk等信息
malloc_chunk: Chunk Header - 一个堆被分为很多chunks,多个用户请求导致多个chunk。每个chunk有它自己的头部信息
注意:
- Main Arena没有多个堆,因此没有heap_info结构。当main arena空间耗尽,sbrk的堆区被延展
- 和线程Arena不同,Main Arena的Arena头并非由sbrk调用而产生的堆区的一部分。它是全局变量,存在于libc.so的数据区



Chunk的类型:
- Allocated chunk
- Free chunk
- Top chunk
- Last Remainder chunk
Allocated Trunk:

prev_size: 前一个chunk为空闲区,则该区域包含前一区域的大小。如果非空闲,则该域包含前一区域的用户数据
size: 被分配空间的大小 。后三比特域包含标志位
- PREV_INUSE (P) – 前一个chunk是否被占用
- IS_MMAPPED (M) – 是否是mmap分配
- NON_MAIN_ARENA (N) – 是否属于thread arena
注意:
- 对于allocated chunk, 其他域如 fd, bk不被使用. 这里只存储用户数据
- 用户请求的内存空间包含了malloc_chunk信息,因此实际使用的空间会小于用户请求大小。
Free Trunk:

prev_size: 两个空闲区不能毗邻,当两个chunk空闲豕毗邻,则会合并为一个空闲区。因此通常前一个chunk是非空闲的,prev_size是前一个chunk的用户数据
size: 空间大小
fd: Forward pointer – 同一bin中的下一个chunk(非物理空间)
bk: Backward pointer – 同一bin中的前一个chunk(非物理空间)
Bins: 根据大小不同,有如下bin
- Fast bin
- Unsorted bin
- Small bin
- Large bin
fastbinsY: 这个array是fastbin列表
bins: 共有126 个bins
- Bin 1 – Unsorted bin
- Bin 2 to Bin 63 – Small bin
- Bin 64 to Bin 126 – Large bin
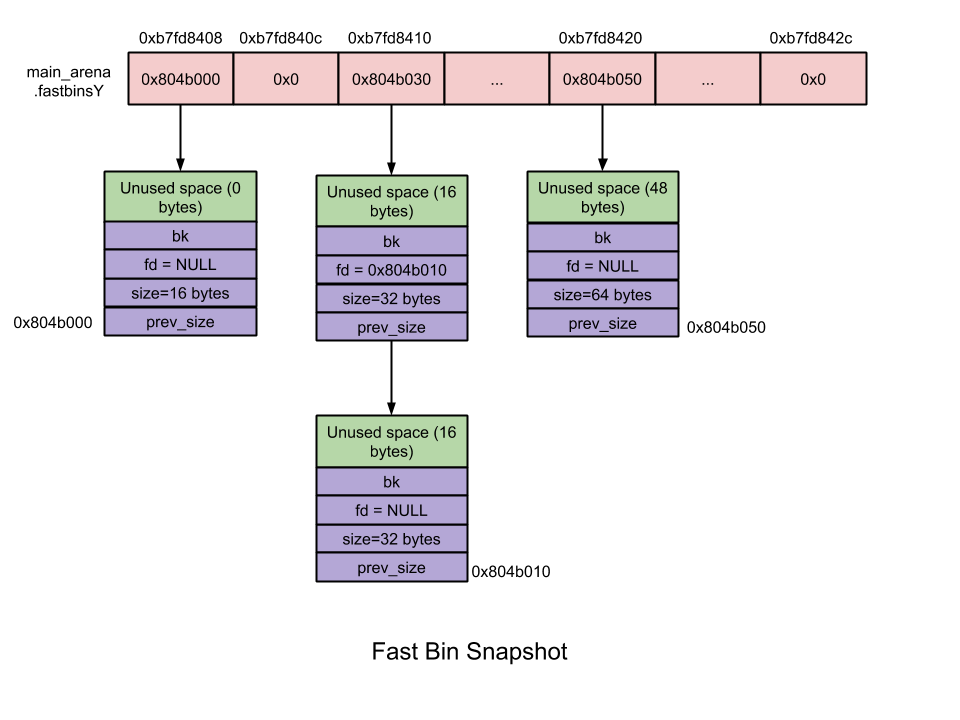
Fast Bin: 大小在16~80字节之间.
- 数量 – 10
- 每个fastbin有一个空闲chunk的单链表. 之所以用单链表是因为在链表中没有删除操作。添加和删除都在表的顶部 – LIFO.
- Chunk大小 – 8字节对齐
- 首个fastbin包含16字节的binlist, 第2个fastbin包含24 bytes的binlist,以此类推
- 同一fastbin中的chunk大小是一致的
- 在malloc初始化时, 最大的fast bin 大小设置为64比特,而非80比特.
- 不合并 – 毗邻chunk不合并. 不合并会导致碎片,但效率提高
- malloc(fast chunk) –
- 初始态 fast bin max size 和 fast bin indices 为空,因此尽管用户请求fast chunk,是small bin code提供服务而非fast bin code。
- 之后当fastbin不为空,fast bin index通过计算激活相应的binlist
- 激活后的binlist中可以给用户提供内存
- free(fast chunk) –
- 计算Fast bin index以激活相应binlist
- 释放后的chunk被放入刚才激活的binlist 中
Unsorted Bin: 当small chunk 或 large chunk被释放,不是将其归还给相应的bin中,而是添加至unsorted bin。这对性能有所提升
- 数量 – 1
- 循环双链表
- Chunk 大小 – 大小无限制
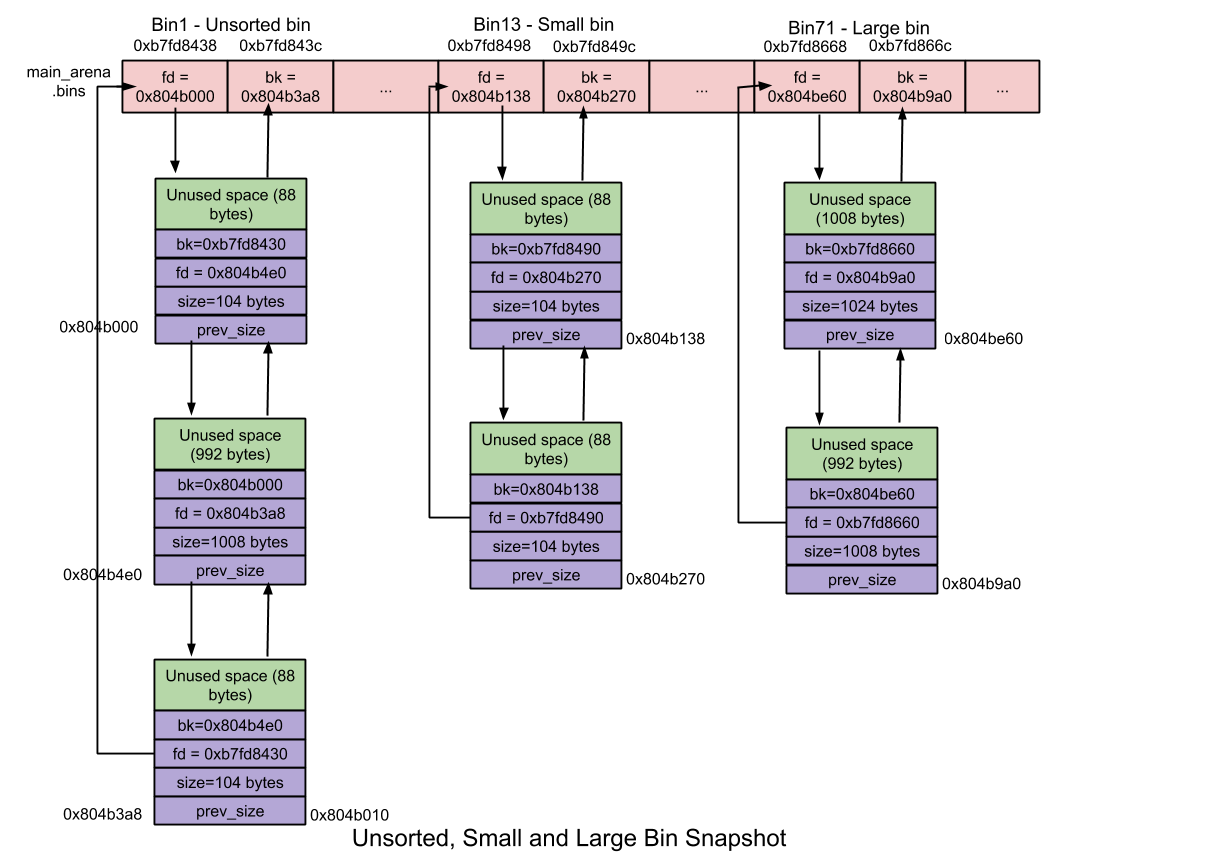
Small Bin:大小小于512字节的块称为小块。small bins在内存分配和释放方面比large bins快(但比fast bins慢)。
- 数量– 62
- 每个small bin都包含一个循环的空闲块的双向链接列表(又称垃圾箱列表)。使用双链表是因为在小垃圾箱链接的中间可能会发生块移除的操作。FIFO。
- 块大小 – 8字节对齐:
- 小bin包含大小为8个字节的块的binlist。first small bin包含大小为16个字节的块,second small bin包含大小为24个字节的块,依此类推……
- small bin 内的块大小相同
- 合并– 两个空闲的chunk不能彼此相邻,将它们合并为一个空闲的块。合并消除了外部碎片,但它放慢了速度!!
- malloc(small chunk)–
- 初始,所有small bin都将为NULL,尽管用户请求一个small chunk, unsorted bin code 会为其服务,而不是smll bin code
- 同样,第一次调用malloc的过程中,将初始化malloc_state中发现的small bin和large bin数据结构(bin),即,bin指向自身,表示它们为空。
- 稍后,当small bin不为空时,将删除其对应的binlist 中的last chunk并将其返回给用户。
- free (small chunk) –
- 释放该块时,请检查其上一个或下一个块是否空闲,如果有,则将它们从各自的链接列表中取消链接,然后将新合并的块添加到未排序的bin链接列表的开头
Large Bin:大小大于512的块称为大块。存放大块的垃圾箱称为大垃圾箱。大存储区在内存分配和释放方面比小存储区慢。
垃圾箱数量– 63
每个大垃圾箱都包含一个循环的空闲块的双向链接列表(又称垃圾箱)。使用双链表是因为在大仓中,可以在任何位置(前,中或后)添加和删除块。
在这63个垃圾箱中:
32个bin包含大小为64个字节的块的binlist。即)第一个大容器(Bin 65)包含大小为512字节至568字节的块的binlist,第二个大容器(Bin 66)包含大小为576字节至632字节的块的binlist,依此类推…
16个bin包含大小为512字节的块的binlist。
8个bin包含大小为4096字节的块的binlist。
4个bin包含大小为32768字节的块的binlist。
2个bin包含大小为262144个字节的块的binlist。
1箱包含一块剩余的大小。
与小垃圾箱不同,大垃圾箱中的块大小不相同。因此,它们以降序存储。最大的块存储在前端,而最小的块存储在其binlist的后端。
合并–两个空闲的块不能彼此相邻,将它们合并为一个空闲的块。
malloc(大块)–
最初,所有大容器都将为NULL,因此即使用户请求了大块而不是大容器代码,下一个最大的容器代码也会尝试为其服务。
同样在第一次调用malloc的过程中,将初始化malloc_state中发现的小bin和大bin数据结构(bin),即,bin指向自身,表示它们为空。
稍后,当大容器为非空时,如果最大的块大小(在其Binlist中)大于用户请求的大小,则将Binlist从后端移动到前端,以找到大小接近/等于用户请求的大小的合适块。一旦找到,该块将分为两个块
用户块(具有用户请求的大小)–返回给用户。
剩余块(剩余大小)–添加到未排序的垃圾箱。
如果最大的块大小(在其binlist中)小于用户请求的大小,请尝试使用下一个最大的(非空)容器来满足用户请求。下一个最大的bin代码扫描binmap,以查找不为空的下一个最大的bin,如果找到任何这样的bin,则从该binlist中检索合适的块并将其拆分并返回给用户。如果找不到,请尝试使用顶部块满足用户请求。
free(大块)–其过程类似于free(小块)
TOP Chunk: Arena顶部的chunk称为top chunk. 它不属于任何bin。它在当用户需求无法满足时使用。如果top chunk size 比用户请求大小大,那top chunk被分为两个
- 用户块
- 剩下的块
剩下的块成为新的top chunk。如果top chunk 大小小于用户请求大小,则top chunk调用sbrk(Main arena)或mmap(thread arena)系统调用进行延展
Last Remainder Chunk: 即最近一次切割后剩下的那个chunk. Last remainder chunk 可帮助提升性能。连续的small chunk请求可能会导致分配的位置相近。
在很多arena的chunk中,哪个能够成为last reminder chunk?
当一个用户请求small chunk,small bin和unsorted bin都无法满足,就会扫描binmaps进而找寻next largest bin. 正如较早提及的,找到the next largest bin,它将会分为2个chunk,user chunk返回给用户,remainder chunk 添加至unsorted bin. 除此之外,它成为最新的last remainder chunk.
堆溢出---glibc malloc的更多相关文章
- Linux堆溢出漏洞利用之unlink
Linux堆溢出漏洞利用之unlink 作者:走位@阿里聚安全 0 前言 之前我们深入了解了glibc malloc的运行机制(文章链接请看文末▼),下面就让我们开始真正的堆溢出漏洞利用学习吧.说实话 ...
- linux下堆溢出unlink的一个简单例子及利用
最近认真学习了下linux下堆的管理及堆溢出利用,做下笔记:作者作为初学者,如果有什么写的不对的地方而您又碰巧看到,欢迎指正. 本文用到的例子下载链接https://github.com/ctfs/w ...
- 堆溢出学习笔记(linux)
本文主要是linux下堆的数据结构及堆调试.堆溢出利用的一些基础知识 首先,linux下堆的数据结构如下 /* This struct declaration is misleading (but a ...
- stm32 堆溢出
STM32 堆溢出 遇到的问题 最近在给旧项目添加了段代码,程序经常到某个状态就突然崩溃了,也不一定是在运行新代码的时候崩溃.检查了几遍代码,数组越界访问,除数为0,内存泄露等常见的问题都不存在. 原 ...
- Linux 堆溢出原理分析
堆溢出与堆的内存布局有关,要搞明白堆溢出,首先要清楚的是malloc()分配的堆内存布局是什么样子,free()操作后又变成什么样子. 解决第一个问题:通过malloc()分配的堆内存,如何布局? 上 ...
- 【转载】利用一个堆溢出漏洞实现 VMware 虚拟机逃逸
1. 介绍 2017年3月,长亭安全研究实验室(Chaitin Security Research Lab)参加了 Pwn2Own 黑客大赛,我作为团队的一员,一直专注于 VMware Worksta ...
- vmware漏洞之一——转:利用一个堆溢出漏洞实现VMware虚拟机逃逸
转:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/27733895?utm_source=tuicool&utm_medium=referral 小结: vmware通过Backd ...
- 理解 glibc malloc:主流用户态内存分配器实现原理
https://blog.csdn.net/maokelong95/article/details/51989081 Understanding glibc malloc 修订日志: 2017-03- ...
- 由STL map调用clear后,内存不返还给操作系统的问题出发,探讨glibc malloc/free行为(转)
1. 问题 我们的程序有几十个线程,每个线程拥有一个std::map,每个线程都要向自己的std::map中插入大量的数据,但每个数据只有几十字节:当使用完std::map,调用map.clear() ...
随机推荐
- Oracle 10g客户端的安装和配置
1.双击Oracle11g_database安装目录下的Setup.exe. 2.选择“基本安装”,设置“安装位置”,填写“数据库名”和“口令”,点击“下一步”. 3.点击“下一步”. 4.一般会出现 ...
- Web Scraper 性能测试 (-_-)
刚在研究 Python 爬虫的时候,看到了个小白工具,叫 Web Scraper,于是来测试下好不好用. Web Scraper 是什么? 它是一个谷歌浏览器的插件, 用于批量抓取网页信息, 主要特点 ...
- coding++:SpringBoot 处理前台字符串日期自动转换成后台date类型的三种办法
第(1)种: 使用@DateTimeFormat(pattern = “yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss”)注解在实体字段上. 这种方式的优点是:可以灵活的定义接收的类型 缺点很明显:不能全局统 ...
- docker 搭建keepalived+nginx高可用
前言 最近工作 中 有用到keepalived,就想着 在 本地 搭建一套环境验证一下相关的功能.因为创建虚拟机比较麻烦,就借助 docker来搭建这样 一套 环境 ,顺带学习 巩固下docker的 ...
- D - D 分糖果HDU - 1059(完全背包+二进制优化)
有两个小朋友想要平分一大堆糖果,但他们不知道如何平分需要你的帮助,由于没有spj我们只需回答能否平分即可. 糖果大小有6种分别是1.2.3.4.5.6,每种若干颗,现在需要知道能不能将这些糖果分成等额 ...
- D - Expanding Rods POJ - 1905(二分)
D - Expanding Rods POJ - 1905 When a thin rod of length L is heated n degrees, it expands to a new l ...
- 从头捋捋jvm(-java虚拟机)
jvm 是Java Virtual Machine(Java虚拟机)的缩写,java 虚拟机作为一种跨平台的软件是作用于操作系统之上的,那么认识并了解它的底层运行逻辑对于java开发人员来说很有必要! ...
- JQ前端上传图片显示在页面以及发送到后端服务器
// 单张上传照片 html: <div class="azwoo"></div> <div class="azwot"& ...
- 逍遥云天 H5外部浏览器直接调起微信——通过url协议 weixin:// 判断是否安装微信及启动微信
h5分享到微信,h5使用微信支付这些功能,都需要先判断是否安装微信客户端,如果已安装就启动微信,如果没有安装微信,就提示用户前去安装. 我们可以通过访问微信提供的URL协议(weixin://)来实现 ...
- django自定义实现登录验证-更新版
django自定义实现登录验证 django内置的登录验证必须让开发者使用django内置的User模块,这会让开发者再某些方面被限制住 下面的模块是我自己自定义实现的django验证,使用方式和dj ...
