Python-Day11 RabbitMQ/redis
写在前面:
好久不写了,实在是不想写,坚持果然是一件不容易的事情。
我喜欢玩,我更爱学习,然而喜欢是放肆,爱是克制,哈哈。每天上班有些忙就不想动,只想在床上翻滚或者鏖战召唤师峡谷。上班闲着时想了想,一是不方便写,二是忘了很多了---------经过铺垫可以明确的说了:前面都是借口。
白天自己承诺自己晚上要写,虽然没人知道,自己答应自己的事也不能不做啊,晚上复习了一个多小时,现在是实践的时候了:Come on baby,不逼自己一把,你永远不知道自己有多优秀。So anyway,鸡汤香否,哈哈哈,就喜欢转折转的措手不及,这是一种乐观的生活态度。历千劫万险,纵使魂飞魄散,我灵识依在,战百世轮回,纵使六道无常,我依然相信你可以在下面点个赞。
一、RabbitMQ队列
1.RabbitMQ介绍
MQ全称为Message Queue, 消息队列(MQ)是一种应用程序对应用程序的通信方法。应用程序通过读写出入队列的消息(针对应用程序的数据)来通信,而无需专用连接来链接它们。
消息传递指的是程序之间通过在消息中发送数据进行通信,而不是通过直接调用彼此来通信。
MQ是消费-生产者模型的一个典型的代表,一端往消息队列中不断写入消息,而另一端则可以读取或者订阅队列中的消息。
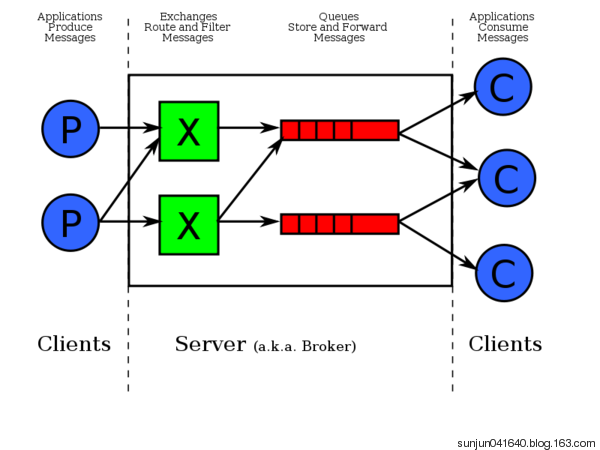
2.RabbitMQ安装(Windows)
http://www.rabbitmq.com/install-windows.html
安装python rabbitMQ module
#windows在cmd里执行即可
#(如果不能找不到命令是Python没有设置好环境变量,手动找pip命令)
pip install pika
or
easy_install pika
or
源码
https://pypi.python.org/pypi/pika
3.实现最简单的队列通信
send端
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters('localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
#声明queue
channel.queue_declare(queue='hello')
#n RabbitMQ a message can never be sent directly to the queue, it always needs to go through an exchange.
channel.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key='hello', #routing_key 就是queue名
body='Hello World!',
)
print(" [x] Sent 'Hello World!'")
connection.close()
receive端
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
'localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
#You may ask why we declare the queue again ‒ we have already declared it in our previous code.
#We could avoid that if we were sure that the queue already exists. For example if send.py program
#was run before. But we're not yet sure which program to run first. In such cases it's a good
#practice to repeat declaring the queue in both programs.
channel.queue_declare(queue='hello')
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(ch,method,properties)
#ch <pika.adapters.blocking_connection.BlockingChannel object at 0x00000000029A5C50> 管理内存对象地址
#method <Basic.Deliver(['consumer_tag=ctag1.aef832e45baf4745af94ab1b2b75ff22', 'delivery_tag=1', 'exchange=', 'redelivered=False', 'routing_key=hello'])> 具体信息
#properties:<BasicProperties>
print(" --> Received %r" % body)
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag=method.delivery_tag)
channel.basic_qos(prefetch_count=1)
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue='hello'
no_ack=True)
print(' [*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C')
channel.start_consuming()
4.RabbitMQ消息分发轮询
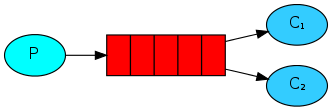
在这种模式下,RabbitMQ会默认把p发的消息依次分发给各个消费者(c),跟负载均衡差不多
import pika connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
'localhost'))
channel = connection.channel() #声明queue
channel.queue_declare(queue='task_queue') #n RabbitMQ a message can never be sent directly to the queue, it always needs to go through an exchange.
import sys message = ' '.join(sys.argv[1:]) or "Hello World!"
channel.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key='task_queue',
body=message,
properties=pika.BasicProperties(
delivery_mode = 2, # make message persistent
))
print(" [x] Sent %r" % message)
connection.close()
发送消息端
import pika,time connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
'localhost'))
channel = connection.channel() def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] Received %r" % body)
time.sleep(body.count(b'.'))
print(" [x] Done")
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag = method.delivery_tag) channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue='task_queue',
) print(' [*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C')
channel.start_consuming()
接收消息端
此时,先启动消息生产者,然后再分别启动3个消费者,通过生产者多发送几条消息,你会发现,这几条消息会被依次分配到各个消费者身上
加上时间参数,延迟程序的执行时间,这时候如果消息没有执行完关闭就不会再有了,接收端里的no_ack=True去掉之后并在callback函数里面添加ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag = method.delivery_tag,就可以实现消息不被处理完不能在队列里清除。
import pika,time
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
'localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.queue_declare(queue='hello')
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(ch,method,properties)
#ch <pika.adapters.blocking_connection.BlockingChannel object at 0x00000000029A5C50> 管理内存对象地址
#method <Basic.Deliver(['consumer_tag=ctag1.aef832e45baf4745af94ab1b2b75ff22', 'delivery_tag=1', 'exchange=', 'redelivered=False', 'routing_key=hello'])> 具体信息
#properties:<BasicProperties>
time.sleep(20)
print(" --> Received %r" % body)
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag=method.delivery_tag)
channel.basic_qos(prefetch_count=1)
channel.basic_consume(callback,#如果收到消息,就调用callback函数处理消息
queue='hello')#,
#no_ack=True)
print(' [*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C')
channel.start_consuming()
5.RabbitMQ消息持久化
查看消息队列:

如果消息在传输过程中rabbitMQ服务器宕机了,会发现之前的消息队列就不存在了,这时我们就要用到队列持久化,会让队列不随着服务器宕机而消失,会永久的保存下去消息,发送接收端都需要设置消息持久化,不持久化的接收端接收持久化的发送端会错误。
发送端:
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters('localhost'))
channel = connection.channel() #声明一个管道(管道内发消息)
channel.queue_declare(queue='hi',durable=True) #队列持久化
channel.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key='hi', #routing_key 就是queue名
body='Hello World!',
properties=pika.BasicProperties(
delivery_mode = 2 #消息持久化
)
)
print("Sent 'Hello,World!'")
connection.close() #关闭
接收端:
import pika,time
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters('localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.queue_declare(queue='hi',durable=True)
def callback(ch,method,properties,body):
print("->>",ch,method,properties)
time.sleep(15) # 模拟处理时间
print("Received %r"%body)
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag=method.delivery_tag)
channel.basic_consume(callback, #如果收到消息,就调用callback函数处理消息
queue="hi",
)
print(' [*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C')
channel.start_consuming() #开始收消息
6.RabbitMQ消息公平分发
如果Rabbit只管按顺序把消息发到各个消费者身上,不考虑消费者负载的话,很可能出现,一个机器配置不高的消费者那里堆积了很多消息处理不完,同时配置高的消费者却一直很轻松。为解决此问题,可以在各个消费者端,配置perfetch=1,意思就是告诉RabbitMQ在我这个消费者当前消息还没处理完的时候就不要再给我发新消息了。
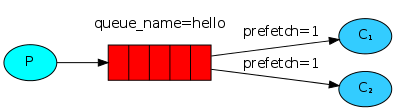
带消息持久化+公平分发的完整代码
生产者端:
import pika
import sys connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel() channel.queue_declare(queue='task_queue', durable=True) message = ' '.join(sys.argv[1:]) or "Hello World!"
channel.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key='task_queue',
body=message,
properties=pika.BasicProperties(
delivery_mode = 2, # make message persistent
))
print(" [x] Sent %r" % message)
connection.close()
消费者端:
import pika
import time connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel() channel.queue_declare(queue='task_queue', durable=True)
print(' [*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C') def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] Received %r" % body)
time.sleep(body.count(b'.'))
print(" [x] Done")
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag = method.delivery_tag) channel.basic_qos(prefetch_count=1)
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue='task_queue') channel.start_consuming()
7.Publish\Subscribe(消息发布\订阅)
之前的例子都基本都是1对1的消息发送和接收,即消息只能发送到指定的queue里,但有些时候你想让你的消息被所有的Queue收到,类似广播的效果,这时候就要用到exchange了,
An exchange is a very simple thing. On one side it receives messages from producers and the other side it pushes them to queues. The exchange must know exactly what to do with a message it receives. Should it be appended to a particular queue? Should it be appended to many queues? Or should it get discarded. The rules for that are defined by the exchange type.
Exchange在定义的时候是有类型的,以决定到底是哪些Queue符合条件,可以接收消息
fanout: 所有bind到此exchange的queue都可以接收消息
direct: 通过routingKey和exchange决定的那个唯一的queue可以接收消息
topic:所有符合routingKey(此时可以是一个表达式)的routingKey所bind的queue可以接收消息
表达式符号说明:#代表一个或多个字符,*代表任何字符
例:#.a会匹配a.a,aa.a,aaa.a等
*.a会匹配a.a,b.a,c.a等
注:使用RoutingKey为#,Exchange Type为topic的时候相当于使用fanout
headers: 通过headers 来决定把消息发给哪些queue

消息publisher
import pika
import sys connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel() channel.exchange_declare(exchange='logs',
type='fanout') message = ' '.join(sys.argv[1:]) or "info: Hello World!"
channel.basic_publish(exchange='logs',
routing_key='',
body=message)
print(" [x] Sent %r" % message)
connection.close()
消息publisher
import pika connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel() channel.exchange_declare(exchange='logs',
type='fanout') result = channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True) #不指定queue名字,rabbit会随机分配一个名字,exclusive=True会在使用此queue的消费者断开后,自动将queue删除
queue_name = result.method.queue channel.queue_bind(exchange='logs',
queue=queue_name) print(' [*] Waiting for logs. To exit press CTRL+C') def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] %r" % body) channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue=queue_name,
no_ack=True) channel.start_consuming()
8.有选择的接收消息(exchange type=direct)
RabbitMQ还支持根据关键字发送,即:队列绑定关键字,发送者将数据根据关键字发送到消息exchange,exchange根据 关键字 判定应该将数据发送至指定队列。
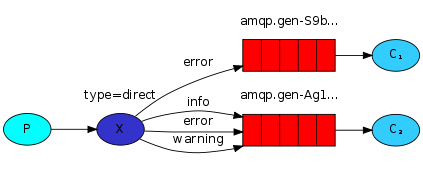
publisher
import pika
import sys connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel() channel.exchange_declare(exchange='direct_logs',
type='direct') severity = sys.argv[1] if len(sys.argv) > 1 else 'info'
message = ' '.join(sys.argv[2:]) or 'Hello World!'
channel.basic_publish(exchange='direct_logs',
routing_key=severity,
body=message)
print(" [x] Sent %r:%r" % (severity, message))
connection.close()
publisher
subscriber
import pika
import sys connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel() channel.exchange_declare(exchange='direct_logs',
type='direct') result = channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True)
queue_name = result.method.queue severities = sys.argv[1:]
if not severities:
sys.stderr.write("Usage: %s [info] [warning] [error]\n" % sys.argv[0])
sys.exit(1) for severity in severities:
channel.queue_bind(exchange='direct_logs',
queue=queue_name,
routing_key=severity) print(' [*] Waiting for logs. To exit press CTRL+C') def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] %r:%r" % (method.routing_key, body)) channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue=queue_name,
no_ack=True) channel.start_consuming()
subscriber
9.更细致的消息过滤
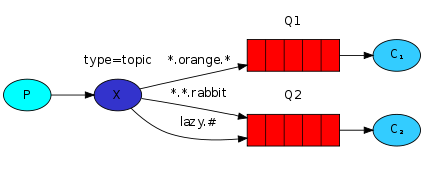
import pika
import sys connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel() channel.exchange_declare(exchange='topic_logs',
type='topic') routing_key = sys.argv[1] if len(sys.argv) > 1 else 'anonymous.info'
message = ' '.join(sys.argv[2:]) or 'Hello World!'
channel.basic_publish(exchange='topic_logs',
routing_key=routing_key,
body=message)
print(" [x] Sent %r:%r" % (routing_key, message))
connection.close()
publisher
import pika
import sys connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel() channel.exchange_declare(exchange='topic_logs',
type='topic') result = channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True)
queue_name = result.method.queue binding_keys = sys.argv[1:]
if not binding_keys:
sys.stderr.write("Usage: %s [binding_key]...\n" % sys.argv[0])
sys.exit(1) for binding_key in binding_keys:
channel.queue_bind(exchange='topic_logs',
queue=queue_name,
routing_key=binding_key) print(' [*] Waiting for logs. To exit press CTRL+C') def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] %r:%r" % (method.routing_key, body)) channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue=queue_name,
no_ack=True) channel.start_consuming()
subscriber
10.Remote procedure call (RPC)
二、Redis(linux)
1.Redis的基本安装和使用
wget http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-3.0.6.tar.gz
tar xzf redis-3.0.6.tar.gz
cd redis-3.0.6
make
2.启动
#启动服务端
src/redis-server
#启动客户端
src/redis-cli
redis> set foo bar
OK
redis> get foo
"bar"
3.Python操作Redis
sudo pip install redis
or
sudo easy_install redis
or
源码安装
详见:https://github.com/WoLpH/redis-py
API使用
redis-py 的API的使用可以分类为:
- 连接方式
- 连接池
- 操作
- String 操作
- Hash 操作
- List 操作
- Set 操作
- Sort Set 操作
- 管道
- 发布订阅
1、操作模式
redis-py提供两个类Redis和StrictRedis用于实现Redis的命令,StrictRedis用于实现大部分官方的命令,并使用官方的语法和命令,Redis是StrictRedis的子类,用于向后兼容旧版本的redis-py。
import redis r = redis.Redis(host='127.0.0.1', port=)
r.set('foo', 'Bar')
print r.get('foo')
2、连接池
redis-py使用connection pool来管理对一个redis server的所有连接,避免每次建立、释放连接的开销。默认,每个Redis实例都会维护一个自己的连接池。可以直接建立一个连接池,然后作为参数Redis,这样就可以实现多个Redis实例共享一个连接池。
import redis pool = redis.ConnectionPool(host='127.0.0.1', port=) r = redis.Redis(connection_pool=pool)
r.set('foo', 'Bar')
print r.get('foo')
3、操作
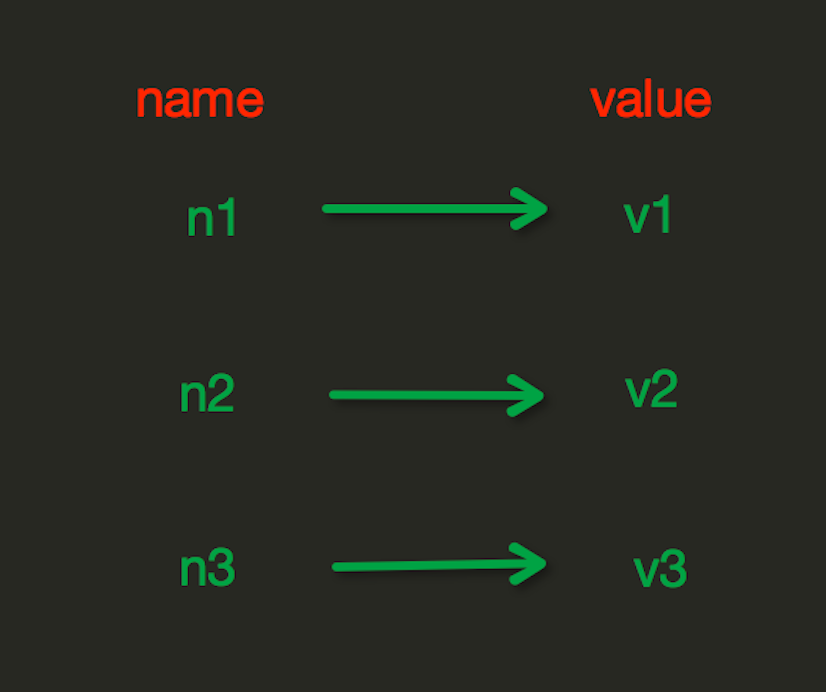
String操作,redis中的String在在内存中按照一个name对应一个value来存储。如图:
http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/5132791.html
Python-Day11 RabbitMQ/redis的更多相关文章
- Python学习-day11 RabbitMQ Redis
这次文章包含两个内容: 1.RabbitMQ使用 2.Redis基础操作 代码部分为练习笔记和作业 概念部分转自Alex老师 RabbitMQ 安装 http://www.rabbitmq.com/i ...
- 使用python操作RabbitMQ,Redis,Memcache,SQLAlchemy 其二
一.概念 1.Memcached Memcached 是一个高性能的分布式内存对象缓存系统,用于动态Web应用以减轻数据库负载.它通过在内存中缓存数据和对象来减少读取数据库的次数,从而提高动态 ...
- 使用python操作RabbitMQ,Redis,Memcache,SQLAlchemy 其一
一.概念 1.Memcached Memcached 是一个高性能的分布式内存对象缓存系统,用于动态Web应用以减轻数据库负载.它通过在内存中缓存数据和对象来减少读取数据库的次数,从而提高动态 ...
- Python之路【第九篇】:Python操作 RabbitMQ、Redis、Memcache、SQLAlchemy
Python之路[第九篇]:Python操作 RabbitMQ.Redis.Memcache.SQLAlchemy Memcached Memcached 是一个高性能的分布式内存对象缓存系统,用 ...
- 文成小盆友python-num12 Redis发布与订阅补充,python操作rabbitMQ
本篇主要内容: redis发布与订阅补充 python操作rabbitMQ 一,redis 发布与订阅补充 如下一个简单的监控模型,通过这个模式所有的收听者都能收听到一份数据. 用代码来实现一个red ...
- Python之异步IO&RabbitMQ&Redis
协程: 1.单线程运行,无法实现多线程. 2.修改数据时不需要加锁(单线程运行),子程序切换是线程内部的切换,耗时少. 3.一个cpu可支持上万协程,适合高并发处理. 4.无法利用多核资源,因为协程只 ...
- Python 之路:Python操作 RabbitMQ、Redis、Memcache、SQLAlchemy
一.Memcached Memcached是一个高性能的分布式内存对象缓存系统,用于动态Web应用以减轻数据库负债.它通过在内存中缓存数据和对象来减少读取数据库的次数,从而提高动态.数据库驱动网站的速 ...
- Python操作 RabbitMQ、Redis、Memcache
Python操作 RabbitMQ.Redis.Memcache Memcached Memcached 是一个高性能的分布式内存对象缓存系统,用于动态Web应用以减轻数据库负载.它通过在内存中缓存数 ...
- python - 操作RabbitMQ
python - 操作RabbitMQ 介绍 RabbitMQ是一个在AMQP基础上完整的,可复用的企业消息系统.他遵循Mozilla Public License开源协议.MQ全称为Mess ...
- Python之RabbitMQ的使用
今天总结一下Python关于Rabbitmq的使用 RabbitMQ官网说明,其实也是一种队列,那和前面说的线程queue和进程queue有什么区别呢? 线程queue只能在同一个进程下进行数据交互 ...
随机推荐
- Hadoop概念学习系列之分布式数据集的容错性(二十七)
一般来说,分布式数据集的容错性有两种方式: 1.数据检查点 2.记录数据的更新 我们面向的是大规模数据分析,数据检查点操作成本很高:需要通过数据中心的网络连接在机器之间复制庞大的数据集,而网络带宽往往 ...
- Cocos2d-x项目移植到WP8小记
Cocos2d-x项目移植到WP8小记 作者: K.C. 日期: 10/24/2013 Date: 2013-10-24 00:33 Title: Cocos2d-x项目移植到WP8小记 Tags: ...
- Java反射机制(Class类的使用)
1:通过无参构造实例化对象 package cn.itcast; /* * 通过无参构造实例化对象 * 通过Class类本身实例化对象,使用newInstance方法 * 需要注意的是:实例化类中存在 ...
- 显示MYSQL数据库信息
显示所有的数据库:show databases 显示一个数据库所有表用:show tables from DatabaseName SELECT table_name FROM information ...
- ADT下开发环境的配置--个人配置啦 Eclipse Color Themes
一. Eclipse Color Themes的安装 首先 这个ADT没有Marketplace Client 需要装一个, 节选自: http://blog.csdn.net/liu37226700 ...
- android 简易定时器
定时器 1.在android 应用开发当中,很多时候都要用到定时器,而要实现定时器更多的时候要用到两个类:Timer,和TimerTask 2.API对Timer的解释是:
- 不需要JAVAScript完成分页查询功能
分页查询之前已经说过,现在用另一种方法实现,换汤不换药.但是更简单. view层代码: 控制层代码: 业务逻辑层,主要看一下方法count1()的代码: count1()方法的功能就是控制翻页,如果传 ...
- 《Secrets of the JavaScript Ninja》:JavaScript 之运行时代码
最近,在阅读 jQuery 之父 John Resig 力作:Secrets of the JavaScript Ninja(JavaScript忍者秘籍).关于第九章提及的 JavaScript 之 ...
- BOM(制造数据管理)
--工艺路线 DECLARE -- API input variables l_operation_tbl bom_rtg_pub.operation_tbl_type := bom_rtg_pub. ...
- 组合View Controller时遇到的一点问题
View Controller的组合应用其实很常见了,比如说Tab bar controller和Navigation view controller的组合使用,像这种一般都是Navigation v ...
