ArrayList源代码深入剖析
第1部分 ArrayList介绍
ArrayList简介
Resizable-array implementation of the List interface. Implements all optional list operations, and permits all elements, including null. In addition to implementing the List interface, this class provides methods to manipulate the size of the array that is used internally to store the list. (This class is roughly equivalent to Vector, except that it is unsynchronized.) The size, isEmpty, get, set, iterator, and listIterator operations run in constant time. The add operation runs in amortized constant time, that is, adding n elements requires O(n) time. All of the other operations run in linear time (roughly speaking). The constant factor is low compared to that for the LinkedList implementation. Each ArrayList instance has a capacity. The capacity is the size of the array used to store the elements in the list. It is always at least as large as the list size. As elements are added to an ArrayList, its capacity grows automatically. The details of the growth policy are not specified beyond the fact that adding an element has constant amortized time cost. An application can increase the capacity of an ArrayList instance before adding a large number of elements using the ensureCapacity operation. This may reduce the amount of incremental reallocation. Note that this implementation is not synchronized. If multiple threads access an ArrayList instance concurrently, and at least one of the threads modifies the list structurally, it must be synchronized externally. (A structural modification is any operation that adds or deletes one or more elements, or explicitly resizes the backing array; merely setting the value of an element is not a structural modification.) This is typically accomplished by synchronizing on some object that naturally encapsulates the list. If no such object exists, the list should be "wrapped" using the Collections.synchronizedList method. This is best done at creation time, to prevent accidental unsynchronized access to the list: List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList(...)); The iterators returned by this class's iterator and listIterator methods are fail-fast: if the list is structurally modified at any time after the iterator is created, in any way except through the iterator's own remove or add methods, the iterator will throw a ConcurrentModificationException. Thus, in the face of concurrent modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather than risking arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at an undetermined time in the future. Note that the fail-fast behavior of an iterator cannot be guaranteed as it is, generally speaking, impossible to make any hard guarantees in the presence of unsynchronized concurrent modification. Fail-fast iterators throw ConcurrentModificationException on a best-effort basis. Therefore, it would be wrong to write a program that depended on this exception for its correctness: the fail-fast behavior of iterators should be used only to detect bugs.
ArrayList是一个动态数组容器类,会自动扩容。
以数组实现。节约空间,但数组有容量限制。超出限制时会增加50%容量(新容量是原来容量的1.5倍),用System.arraycopy()复制到新的数组,因此最好能给出数组大小的预估值(这个是好的编程习惯)。默认第一次插入元素时创建大小为10的数组。 按数组下标访问元素—get(i)/set(i,e) 的性能很高,这是数组的基本优势。 直接在数组末尾加入元素—add(e)的性能也高,但如果按下标插入、删除元素—add(i,e), remove(i), remove(e),则要用System.arraycopy()来移动部分受影响的元素,性能就变差了,这是基本劣势。
ArrayList中的操作不是线程安全的!在多线程中可以选择Vector或者CopyOnWriteArrayList。
来看一段简单的代码:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> strList = new ArrayList<String>();
strList.add("语文:99");
strList.add("数学:98");
strList.add("英语:100");
strList.remove(0);
}
}
在执行这四条语句时,是这么变化的:
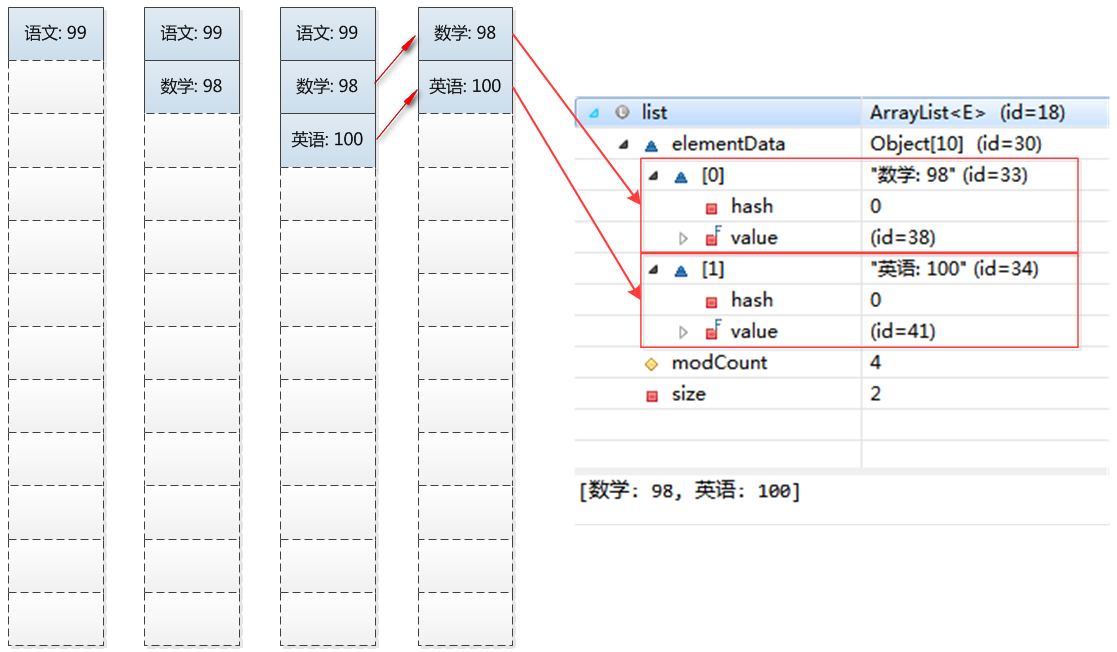
其中,add操作将元素放在数组的末尾,remove(0)操作可以理解为删除index为0的节点,并将后面元素移到0处。
第2部分 ArrayList数据结构
ArrayList包含了两个重要的对象:elementData和size。
(1)elementData是Object[]类型的数组,它保存了添加到ArrayList中的元素。
(2)size则是动态数组的实际元素大小。
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = ;
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
private int size;
第3部分 ArrayList源码api解析
3.1 add()
当我们在ArrayList中增加元素的时候,会使用add函数。他会将元素放到末尾。具体实现如下:
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.*/
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
我们可以看到他的实现其实最核心的内容就是ensureCapacityInternal。这个函数其实就是自动扩容机制的核心。我们依次来看一下他的具体实现
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 扩展为原来的1.5倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class)
? (T[]) new Object[newLength]
: (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength);
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
也就是说,当增加数据的时候,如果ArrayList的大小已经不满足需求时,那么就将数组变为原长度的1.5倍,之后的操作就是把老的数组拷到新的数组里面。例如,默认的数组大小是10,也就是说当我们add 10个元素之后,再进行一次add时,就会发生自动扩容,数组长度由10变为了15具体情况如下所示:
总结:
(01)ArrayList实际上是通过一个数组去保存数据的。当我们构造ArrayList时;若使用默认构造函数,则ArrayList的默认容量大小是10。
(02)当ArrayList容量不足以容纳全部元素时,ArrayList会重新设置容量:新的容量=原始容量x3/2。
3.2 set()和get()
ArrayList的set和get函数就比较简单了,先做index检查,然后执行赋值或访问操作:
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with
* the specified element.*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index); E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.*/
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index);
}
/**
* Checks if the given index is in range. If not, throws an appropriate
* runtime exception.
*/
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
3.3 remove()
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their
* indices).*/
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
// 把后面的往前移
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
// 把最后的置null
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue;
}
/**
* Removes all of the elements from this list. The list will
* be empty after this call returns.
*/
public void clear() {
modCount++; // clear to let GC do its work
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
elementData[i] = null; size = 0;
}
第4部分 ArrayList遍历方式
ArrayList支持3种遍历方式
(01)第一种,通过迭代器遍历。即通过Iterator去遍历。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(123);
list.add(456);
list.add(789);
Iterator iter = list.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Integer value = (Integer) iter.next();
System.out.println(value);
}
}
}
(02) 第二种,随机访问,通过索引值去遍历。
由于ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口,它支持通过索引值去随机访问元素。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(123);
list.add(456);
list.add(789);
int size = list.size();
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
Integer value = list.get(i);
System.out.println(value);
}
}
}
(03) 第三种,for循环遍历。如下:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(123);
list.add(456);
list.add(789);
for (Integer integer : list) {
Integer value = integer;
System.out.println(value);
}
}
}
第5部分 toArray()异常
当我们调用ArrayList中的toArray(),可能遇到过抛出"java.lang.ClassCastException"异常的情况。下面我们说说这是怎么回事。
ArrayList提供了2个toArray()函数:
Object[] toArray()
<T> T[] toArray(T[] contents)
调用toArray()函数会抛出"java.lang.ClassCastException"异常,但是调用toArray(T[] contents)能正常返回 T[]。
toArray()会抛出异常是因为 toArray() 返回的是Object[]数组,将Object[]转换为其它类型(如如,将Object[]转换为的Integer[])则会抛出"java.lang.ClassCastException"异常,因为Java不支持向下转型。具体的可以参考前面ArrayList.java的源码介绍部分的toArray()。
解决该问题的办法是调用<T> T[] toArray(T[] contents) , 而不是Object[] toArray()。
调用 toArray(T[] contents) 返回T[]的可以通过以下几种方式实现。
// toArray(T[] contents)调用方式一
public static Integer[] vectorToArray1(ArrayList<Integer> v) {
Integer[] newText = new Integer[v.size()];
v.toArray(newText);
return newText;
} // toArray(T[] contents)调用方式二。最常用!
public static Integer[] vectorToArray2(ArrayList<Integer> v) {
Integer[] newText = (Integer[])v.toArray(new Integer[0]);
return newText;
} // toArray(T[] contents)调用方式三
public static Integer[] vectorToArray3(ArrayList<Integer> v) {
Integer[] newText = new Integer[v.size()];
Integer[] newStrings = (Integer[])v.toArray(newText);
return newStrings;
}
参考:
http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3308556.html
Class ArrayList
ArrayList其实就那么一回事儿之源码浅析
关于ArrayList
ArrayList源代码深入剖析的更多相关文章
- 【Java集合源代码剖析】ArrayList源代码剖析
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主同意不得转载. https://blog.csdn.net/mmc_maodun/article/details/35568011 转载请注明出处:http:// ...
- ArrayList源码剖析与代码实测
ArrayList源码剖析与代码实测(基于OpenJdk14) 目录 ArrayList源码剖析与代码实测(基于OpenJdk14) 继承关系 从构造函数开始 从add方法深入 / 数组的扩容 其他的 ...
- [Java] List / ArrayList - 源代码学习笔记
在阅读 List / ArrayList 源代码过程中,做了下面的笔记. LinkedList 的笔记较多,放到了另一篇博文 LinkedList / Queue- 源代码学习笔记 List List ...
- ArrayList源码剖析
ArrayList简介 ArrayList是基于数组实现的,是一个动态数组,其容量能自动增长,类似于C语言中的动态申请内存,动态增长内存. ArrayList不是线程安全的,只能用在单线程环境下,多线 ...
- 转:【Java集合源码剖析】ArrayList源码剖析
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/ns_code/article/details/35568011 本篇博文参加了CSDN博文大赛,如果您觉得这篇博文不错,希望您能帮我投一 ...
- Java ArrayList源码剖析
转自: Java ArrayList源码剖析 总体介绍 ArrayList实现了List接口,是顺序容器,即元素存放的数据与放进去的顺序相同,允许放入null元素,底层通过数组实现.除该类未实现同步外 ...
- Java集合源码剖析——ArrayList源码剖析
ArrayList简介 ArrayList是基于数组实现的,是一个动态数组,其容量能自动增长,类似于C语言中的动态申请内存,动态增长内存. ArrayList不是线程安全的,只能用在单线程环境下,多线 ...
- Java 集合框架 ArrayList 源码剖析
总体介绍 ArrayList实现了List接口,是顺序容器,即元素存放的数据与放进去的顺序相同,允许放入null元素,底层通过数组实现.除该类未实现同步外,其余跟Vector大致相同.每个ArrayL ...
- javase基础回顾(一)ArrayList深入解析 解读ArrayList源代码(JDK1.8.0_92)
我们在学习这一块内容时需要注意的一个问题是 集合中存放的依然是对象的引用而不是对象本身. List接口扩展了Collection并声明存储一系列元素的类集的特性.使用一个基于零的下标,元素可以通过它们 ...
随机推荐
- hibernate的运行流程
首先了解什么是对象关系映射,ORM(Object/Relationship Mapping):对象关系映射.对象关系映射是一种为了解决面向对象与关系数据库存在的互不匹配的现象的技术.是通过使用描述对象 ...
- 创建型模式——Abstract Factory
1.意图 提供一个创建一系列相关或相互依赖的接口,而无需指定它们具体的类. 2.结构 3.参与者 AbstractFactory声明一个创建抽象产品对象的操作接口 ConcreteFactory实现创 ...
- MySQL忘记密码后重置密码(Mac )
安装好MySQL以后,系统给了个默认的的密码,然后说如果忘记了默认的密码......我复制了默认密码就走过了这一步,这一步就是我漫长旅程的开始.他给的密码太复杂了,当然我得换一个,而且我还要假装我不记 ...
- 编译安装php Cannot find MySQL header files under /usr/include/mysql.
编译php-5.5-6的mysql支持,出现Cannot find MySQL header files under /usr/include/mysql. Note that the MySQL c ...
- jQuery自己编写插件()
引言: 在项目中不同页面经常要用到已经写好的交互,比如弹窗,比如下拉菜单,比如选项卡,比如删除... 此时如果每次都把代码copy一份无疑是一件比较麻烦并且无趣的事情,而且个人认为有些low了,我们可 ...
- android studio引入第三方包记录
1.添加jar文件 将jar文件复制至app module目录下的libs文件夹下,然后打开app module目录下的build.gradle配置文件,在dependencies项中添加配置命令,这 ...
- PCB优化设计(二) 转载
PCB优化设计(二) 2011-04-25 11:41:05| 分类: PCB设计 目 前SMT技术已经非常成熟,并在电子产品上广泛应用,因此,电子产品设计师有必要了解SMT技术的常识和可制造性 ...
- 查看某一个点是否在某个多边形内 使用ST_Contains函数
查看某一个点是否在某个多边形内 使用ST_Contains函数 --LINESTRING ( 121.312350 30.971457 , 121.156783 31.092221 , 121.35 ...
- [译] ASP.NET 生命周期 – ASP.NET 上下文对象(六)
使用 HttpApplication 对象 ASP.NET 框架中的许多类都提供了许多很方便的属性可以直接映射到 HttpContext 类中定义的属性.这种交叠有一个很好的例子就是 HttpAppl ...
- C# 使用winForm的TreeView显示中国城镇四级联动
直接上代码吧,这里 MySql.Data.MySqlClient;需要到mysql官网下载mysql-connector-net-6.9.8-noinstall.zip 访问密码 6073 usi ...
