Spring Boot实践——基础和常用配置
借鉴:https://blog.csdn.net/j903829182/article/details/74906948
一、Spring Boot 启动注解说明
@SpringBootApplication开启了Spring的组件扫描和Spring Boot的自动配置功能。实际上, @SpringBootApplication将三个有用的注解组合在了一起。
- Spring的@Configuration:标明该类使用Spring基于Java的配置。虽然本书不会写太多配置,但我们会更倾向于使用基于Java而不是XML的配置。
- Spring的@ComponentScan:启用组件扫描,这样你写的Web控制器类和其他组件才能被自动发现并注册为Spring应用程序上下文里的Bean。默认扫描
@SpringBootApplication所在类的同级目录以及它的子目录。本章稍后会写一个简单的Spring MVC控制器,使用@Controller进行注解,这样组件扫描才能找到它。 - Spring Boot 的 @EnableAutoConfiguration: 这 个 不 起 眼 的 小 注 解 也 可 以 称 为@Abracadabra①,就是这一行配置开启了Spring Boot自动配置的魔力,让你不用再写成篇的配置了。
在Spring Boot的早期版本中,你需要在ReadingListApplication类上同时标上这三个注解,但从Spring Boot 1.2.0开始,有@SpringBootApplication就行了。
二、Bean的scope
scope描述了spring容器如何新建bena的实例,spring的scope有以下几种,通过@Scope注解来实现
- Singleton:一个spring容器中只有一个bena的实例,此为spring的默认配置,全容器共享一个实例的bean。
- Prototype:每次调用新建一个bean的实例。
- Request:web项目中,给每一个http request新建一个Bean实例。
- Session :web项目中,给每一个http session新建一个实例。
- GlobalSession:这个只在portal应用中有用,给每一个global http session新建一个bean实例。
另外,在spring batch中还有一个Scope是使用@StepScope,用在批处理中。
实例:
定义一个Single的Bean
/**
* @Description: 自定义Single实例
* @ClassName: CustomSingleService
* @author OnlyMate
* @Date 2018年9月13日 上午10:34:36
*
*/
@Service
//默认为Sinleton,相当于@Scope("singleton")
@Scope(value="singleton")
public class CustomSingleService { }
定义一个Prototype的Bean
/**
* @Description: 自定义Prototype实例
* @ClassName: CustomPrototypeService
* @author OnlyMate
* @Date 2018年9月13日 上午10:34:36
*
*/
@Service
@Scope(value="prototype")
public class CustomPrototypeService { }
Bean的Scope配置
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; /**
* @Description: 自定义Bean的Scope配置类
* @ClassName: CustomScopConfig
* @author OnlyMate
* @Date 2018年9月13日 上午10:59:54
*
*/
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value="com.only.mate.springboot.basic.scope")
public class CustomScopConfig { }
测试类
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import com.only.mate.springboot.configure.basic.CustomScopConfig; public class CustomScopeMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// AnnotationConfigApplicationContext作为spring容器,接受一个配置类作为参数
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(CustomScopConfig.class);
CustomSingleService cs1 = context.getBean(CustomSingleService.class);
CustomPrototypeService cp1 = context.getBean(CustomPrototypeService.class); CustomSingleService cs2 = context.getBean(CustomSingleService.class);
CustomPrototypeService cp2 = context.getBean(CustomPrototypeService.class);
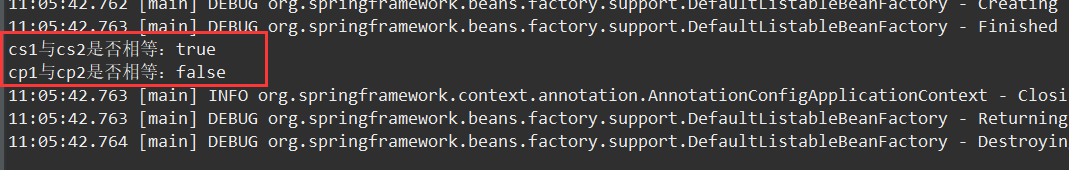
System.out.println("cs1与cs2是否相等:" + cs1.equals(cs2));
System.out.println("cp1与cp2是否相等:" + cp1.equals(cp2));
context.close(); }
}
结果:
三、Bean的初始化和销毁
在我们实际开发的时候,经常会遇到在bean使用之前或者之后做一些必要的操作,spring 对bean的生命周期的操作提供了支持。在使用java配置和注解配置下提供如下两种方式:
- java配置方式:使用@Bean的initMethod和destroyMethod(相当于xml配置的init-method和destory-method)
- 注解方式:利用JSR-250的@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy
1、增加JSR250支持
<!--增加JSR250支持-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>jsr250-api</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
</dependency>
2、使用@Bean形式的bean
/**
* @Description: 自定义@Bean方式的初始化和销毁方法
* @ClassName: CustomBeanWay
* @author OnlyMate
* @Date 2018年9月13日 上午11:15:41
*
*/
public class CustomBeanWay {
public CustomBeanWay() {
super();
System.out.println("@Bean初始化构造方法 ==> CustomBeanWay method");
} public void init() {
System.out.println("@Bean初始化方法 ==> init method");
} public void destroy() {
System.out.println("@Bean销毁方法 ==> destroy method");
}
}
3、使用JSR250形式的bean
/**
* @Description: 自定义JSR250方式的初始化和销毁方法
* @ClassName: CustomJSR250Way
* @author OnlyMate
* @Date 2018年9月13日 上午11:15:41
*
*/
public class CustomJSR250Way {
public CustomJSR250Way() {
super();
System.out.println("JSR250初始化构造方法 ==> CustomJSR250Way method");
} @PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("JSR250初始化方法 ==> init method");
} @PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("JSR250销毁方法 ==> destroy method");
}
}
4、配置
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import com.only.mate.springboot.basic.lifecycle.CustomBeanWay;
import com.only.mate.springboot.basic.lifecycle.CustomJSR250Way; @Configuration
@ComponentScan(value="com.only.mate.springboot.basic.lifecycle")
public class CustomLifeCycleConfig { @Bean(initMethod = "init",destroyMethod = "destroy")
public CustomBeanWay customBeanWay(){
return new CustomBeanWay();
} @Bean
public CustomJSR250Way customJSR250Way(){
return new CustomJSR250Way();
} }
5、启动
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import com.only.mate.springboot.configure.lifecycle.CustomLifeCycleConfig;
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public class CustomLifeCycleMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// AnnotationConfigApplicationContext作为spring容器,接受一个配置类作为参数
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(CustomLifeCycleConfig.class);
CustomBeanWay customBeanWay = context.getBean(CustomBeanWay.class);
CustomJSR250Way customJSR250Way = context.getBean(CustomJSR250Way.class);
context.close();
}
}
6、效果图
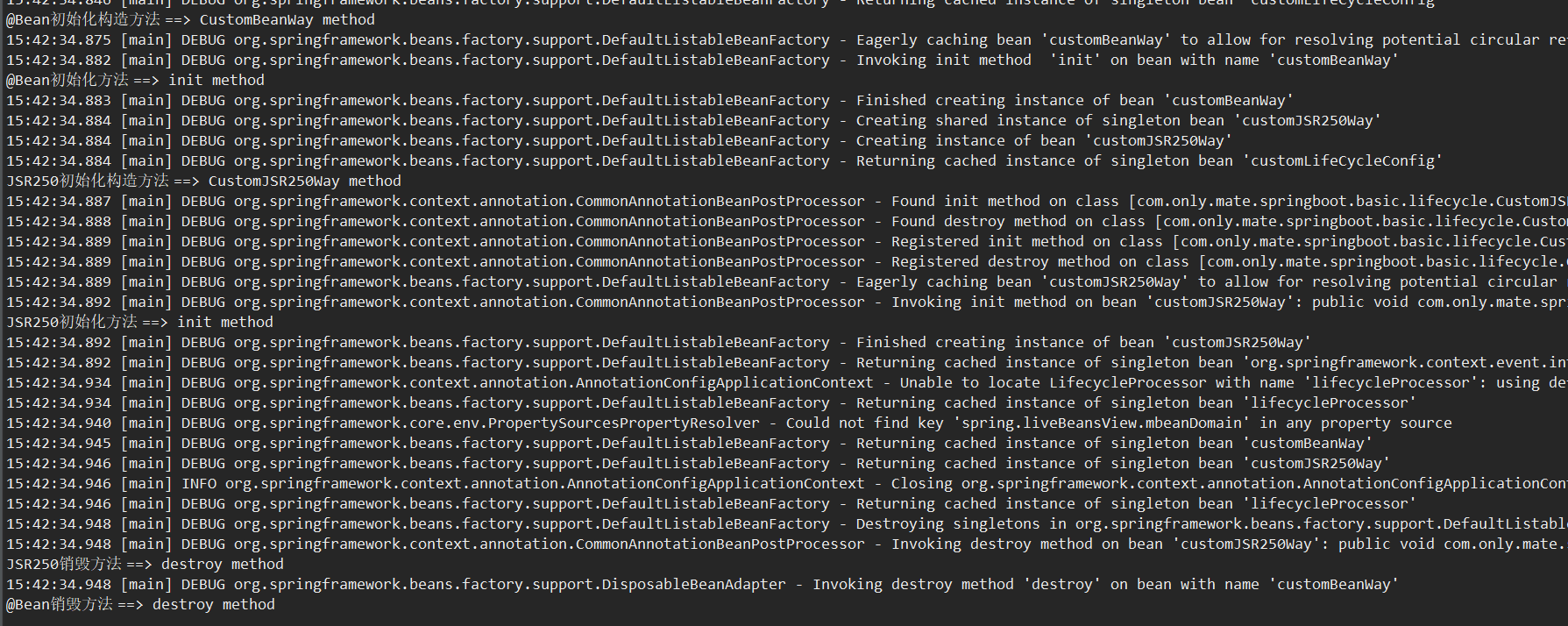
可见init方法和destory方法在构造方法之后,bean销毁之前执行。
四、Spring EL和资源调用
spring EL-Spring表达式语言,支持在xml和注解中使用表达式,类似于jsp的EL表达式语言。
spring开发中经常涉及调用各种资源的情况,包含普通文件,网址,配置文件,系统环境变量等,我们可以使用 spring表达式语言实现资源的注入。
spring主要在注解@Vavle的参数中使用表达式。
下面演示一下几种情况:
- 注入普通字符串
- 注入操作系统属性
- 注入表达式运算结果
- 注入其他Bean的属性
- 注入文件内容
- 注入网址内容
- 注入属性文件
1、准备,增加commons-io可简化文件相关的操作,本例使用commons-io将file转换成字符串。
<!--增加commons-io可简化文件相关操作-->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.3</version>
</dependency>
2、创建文件
在resources下简历files文件夹,并创建el.properties和test.txt文件
内容如下:
el.properties
book.author=onlymate
book.name=Java is s magic
test.txt
这是test.txt里面的内容,很高兴认识大家
3、需被注入的bean
@Component
public class CustomElBean {
//注入普通字符串
@Value("其他类属性")
private String another; public String getAnother() {
return another;
} public void setAnother(String another) {
this.another = another;
}
}
4、配置类
import java.nio.charset.Charset; import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; /**
* @Description: 自定义el配置类
* @ClassName: CustomElConfig
* @author OnlyMate
* @Date 2018年9月13日 上午10:59:54
*
*/
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages="com.only.mate.springboot.basic.el")
//注入配置文件需要使用@PropertySource指定文件地址,若使用@Value注入,则要配置一个PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer的bean
//注意,@ @Value("${book.name}")使用的是$而不是#
//注入Properties还可以从Environment中获得
@PropertySource("classpath:files/el.properties")
public class CustomElConfig {
//注入普通字符串
@Value("I Love YOU!")
private String normal;
//注入操作系统属性
@Value("#{systemProperties['os.name']}")
private String osName;
//注入表达式结果
@Value("#{T(java.lang.Math).random()*100.0}")
private double randomNumber;
//注入其他的bean属性
@Value("#{customElBean.another}")
private String fromAnother;
//注入文件资源
@Value("classpath:files/test.txt")
private Resource testFile;
//注入网址资源
@Value("http://www.baidu.com")
private Resource testUrl;
//注入配置文件
@Value("${book.name}")
private String bookNmame; //注入环境
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
@Bean
public static PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer propertyConfigure(){
return new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer();
} public void outputResource(){
try {
System.out.println(normal);
System.out.println(osName);
System.out.println(randomNumber);
System.out.println(fromAnother);
System.out.println(IOUtils.toString(testFile.getInputStream(), Charset.defaultCharset()));
System.out.println(IOUtils.toString(testUrl.getInputStream(), Charset.defaultCharset()));
System.out.println(bookNmame);
System.out.println(environment.getProperty("book.author")); }catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(e);
}
} }
5、启动运行
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import com.only.mate.springboot.configure.el.CustomElConfig; public class CustomElMain { public static void main(String [] args){
//AnnotationConfigApplicationContext作为spring容器,接受一个配置类作为参数
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(CustomElConfig.class);
CustomElConfig elConfig = context.getBean(CustomElConfig.class);
elConfig.outputResource();
context.close();
} }
6、效果图
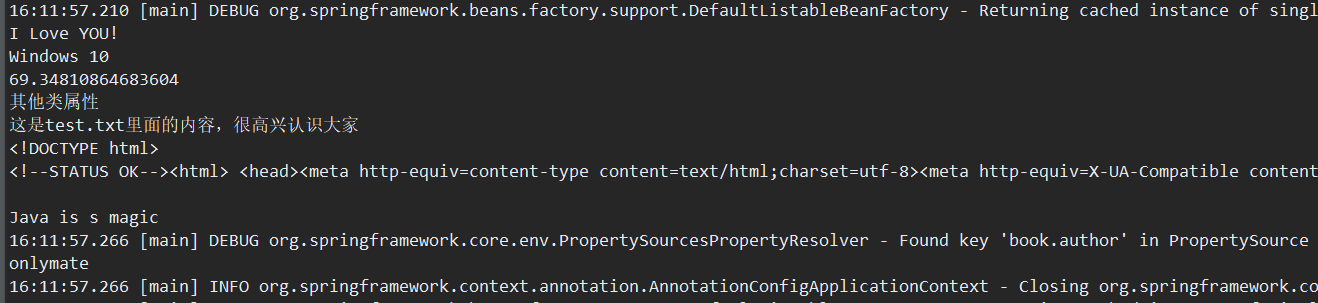
五、Profile
1、基础练习
Profile为在不同环境下使用不同的配置提供了支持(开发环境下的配置和生产环境下的配置不同,比如数据库)
- 通过设定Enviroment的ActiveProfiles来设定当前context需要使用的配置环境。在开发中使用@Profile注解类或者方法,达到在不同情况下选择实例化不同的Bean
- 通过设定jvm的spring.profiles.active参数来设置配置环境
- Web项目设置在Servlet的context parameter中
1、定义一个bean
/**
* @Description: 定义一个bean
* @ClassName: CustomProfileBean
* @author OnlyMate
* @Date 2018年9月13日 下午4:26:22
*
*/
public class CustomProfileBean {
private String content; public CustomProfileBean(String content) {
super();
this.content = content;
} public String getContent() {
return content;
} public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
}
2、配置
/**
* @Description: 自定义Profile的配置类
* @ClassName: CustomProfileConfig
* @author OnlyMate
* @Date 2018年9月13日 下午4:27:17
*
*/
@Configuration
public class CustomProfileConfig {
@Bean
@Profile("dev")//Profile为dev时实例化devCustomProfileBean
public CustomProfileBean devCustomProfileBean(){
return new CustomProfileBean("from development pfofile");
} @Bean
@Profile("prod")//Profile为prod时实例化prodCustomProfileBean
public CustomProfileBean prodCustomProfileBean(){
return new CustomProfileBean("from production profile");
} }
3、启动运行
/**
* @Description:
* @ClassName: CustomProfileMain
* @author OnlyMate
* @Date 2018年9月13日 下午4:26:22
*
*/
public class CustomProfileMain { public static void main(String [] args){
//AnnotationConfigApplicationContext作为spring容器,接受一个配置类作为参数
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
//先将活动的Profile设置为prod
context.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("prod");
//后置注册Bean配置类,不然会报bean未定义的错误
context.register(CustomProfileConfig.class);
//刷新容器
context.refresh();
CustomProfileBean demoBean = context.getBean(CustomProfileBean.class);
System.out.println(demoBean.getContent());
context.close();
}
}
4、效果图
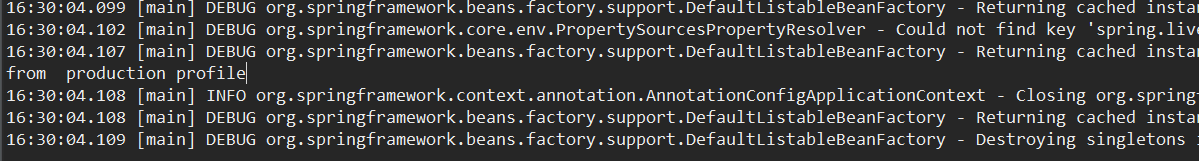
2、日志信息的配置
logback-spring.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration debug="true"><!-- debug="true"设置调试模式 -->
<!--定义日志文件的存储地址 勿在 LogBack 的配置中使用相对路径,文件要以logback-spring.xml命名-->
<springProfile name="test">
<property name="catalina.base" value="/home/webapp/logs/spring-boot" />
</springProfile>
<springProfile name="prod">
<property name="catalina.base" value="/app/webapp/logs/spring-boot" />
</springProfile>
<springProfile name="dev">
<property name="catalina.base" value="H:/logs/spring-boot" />
</springProfile> <!--<springProperty scope="context" name="catalina.base" source="catalina.base"/>--> <!-- 日志地址 -->
<!--<property name="catalina.base" value="H:/logs"></property>--> <!-- 控制台输出 -->
<appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder class="ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder">
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} 耗时:%r 日志来自:%logger{50} 日志类型: %-5p 日志内容:%m%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!-- 按照每天生成日志文件 -->
<appender name="DEFAULT-APPENDER" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<File>${catalina.base}/logs/common-default.log</File>
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<!--日志文件输出的文件名 -->
<FileNamePattern>${catalina.base}/logs/common-default-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log</FileNamePattern>
<!--日志文件保留天数 -->
<MaxHistory>30</MaxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
<encoder class="ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder">
<!--格式化输出:%d表示日期,%thread表示线程名,%-5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度%msg:日志消息,%n是换行符 -->
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
<!--日志文件最大的大小 -->
<triggeringPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy">
<MaxFileSize>10MB</MaxFileSize>
</triggeringPolicy>
</appender>
<!-- 按照每天生成日志文件 -->
<appender name="INFO-APPENDER" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<File>${catalina.base}/logs/info-log.log</File>
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<!--日志文件输出的文件名 -->
<FileNamePattern>${catalina.base}/logs/info-log-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log</FileNamePattern>
<!--日志文件保留天数 -->
<MaxHistory>30</MaxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
<encoder class="ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder">
<!-- 格式化输出:%d表示日期,%thread表示线程名,%-5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度%msg:日志消息,%n是换行符 -->
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
<!--日志文件最大的大小 -->
<triggeringPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy">
<MaxFileSize>10MB</MaxFileSize>
</triggeringPolicy>
</appender> <logger name="com.google.code.yanf4j" level="ERROR" /> <!-- show parameters for hibernate sql 专为 Hibernate 定制 -->
<logger name="org.hibernate.type.descriptor.sql.BasicBinder" level="TRACE" />
<logger name="org.hibernate.type.descriptor.sql.BasicExtractor" level="DEBUG" />
<logger name="org.hibernate.SQL" level="DEBUG" />
<logger name="org.hibernate.engine.QueryParameters" level="DEBUG" />
<logger name="org.hibernate.engine.query.HQLQueryPlan" level="DEBUG" /> <!--myibatis log configure-->
<logger name="org.apache.ibatis" level="DEBUG"/>
<logger name="java.sql.Connection" level="DEBUG"/>
<logger name="java.sql.Statement" level="DEBUG"/>
<logger name="java.sql.PreparedStatement" level="DEBUG"/> <logger name="net.rubyeye.xmemcached" level="INFO"/>
<logger name="org.springframework" level="INFO"/>
<logger name="net.sf.ehcache" level="INFO"/> <logger name="org.apache.zookeeper" level="INFO" /> <!-- 指定某一个包或者某一个类的打印级别以及是否传入root进行打印 -->
<!-- addtivity:是否向上级loger传递打印信息。默认是true。-->
<!-- <loger>可以包含零个或多个<appender-ref>元素,标识这个appender将会添加到这个loger。-->
<!-- name:用来指定受此loger约束的某一个包或者具体的某一个类。-->
<!-- level:
用来设置打印级别,大小写无关:TRACE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR, ALL 和 OFF,还有一个特俗值INHERITED或者同义词NULL,代表强制执行上级的级别。
如果未设置此属性,那么当前loger将会继承上级的级别。-->
<!-- 为所有开头为dao的类打印sql语句 -->
<!-- <logger name="dao" level="DEBUG">
<appender-ref ref="INFO-APPENDER" />
</logger> -->
<logger name="com.only.mate" level="DEBUG" additivity="true">
<appender-ref ref="INFO-APPENDER" />
</logger>
<!-- 也是<loger>元素,但是它是根loger。只有一个level属性,应为已经被命名为"root". -->
<root level="DEBUG">
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
<appender-ref ref="DEFAULT-APPENDER"/>
</root> </configuration>
这里有兴趣的自己自己尝试。
3、Java代码中根据系统环境处理逻辑
创建一个服务,实现ApplicationContextAware接口
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service
public class CustomProfileService implements ApplicationContextAware{
private ApplicationContext applicationContext = null; @Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
} public void doSomething() {
//获取当前系统环境
String[] springActives = applicationContext.getEnvironment().getActiveProfiles();
String springActive = "";
if(springActives.length > 0) {
springActive = springActives[0];
}else {
springActive = applicationContext.getEnvironment().getDefaultProfiles()[0];
}
System.out.println("当前的开发环境:"+ springActive);
}
}
配置类
/**
* @Description: 自定义Profile的配置类
* @ClassName: CustomProfileConfig
* @author OnlyMate
* @Date 2018年9月13日 下午4:27:17
*
*/
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages="com.only.mate.springboot.basic.profile")
public class CustomProfileConfig {
@Bean
@Profile("dev")//Profile为dev时实例化devCustomProfileBean
public CustomProfileBean devCustomProfileBean(){
return new CustomProfileBean("from development pfofile");
} @Bean
@Profile("prod")//Profile为prod时实例化prodCustomProfileBean
public CustomProfileBean prodCustomProfileBean(){
return new CustomProfileBean("from production profile");
} }
启动类
/**
* @Description:
* @ClassName: CustomProfileMain
* @author OnlyMate
* @Date 2018年9月13日 下午4:26:22
*
*/
public class CustomProfileMain { public static void main(String [] args){
//AnnotationConfigApplicationContext作为spring容器,接受一个配置类作为参数
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
//先将活动的Profile设置为prod
context.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("prod");
//后置注册Bean配置类,不然会报bean未定义的错误
context.register(CustomProfileConfig.class);
//刷新容器
context.refresh();
CustomProfileBean customProfileBean = context.getBean(CustomProfileBean.class);
System.out.println(customProfileBean.getContent()); CustomProfileService customProfileService = context.getBean(CustomProfileService.class);
customProfileService.doSomething(); context.close();
}
}
效果图

Spring Boot实践——基础和常用配置的更多相关文章
- Spring Boot项目简单上手+swagger配置+项目发布(可能是史上最详细的)
Spring Boot项目简单上手+swagger配置 1.项目实践 项目结构图 项目整体分为四部分:1.source code 2.sql-mapper 3.application.properti ...
- Spring Boot实践——Spring Boot 2.0 新特性和发展方向
出自:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/EWmuzsgHueHcSB0WH-3AQw 以Java 8 为基准 Spring Boot 2.0 要求Java 版本必须8以上, Jav ...
- Spring Boot实践——Spring AOP实现之动态代理
Spring AOP 介绍 AOP的介绍可以查看 Spring Boot实践——AOP实现 与AspectJ的静态代理不同,Spring AOP使用的动态代理,所谓的动态代理就是说AOP框架不会去修改 ...
- Spring Boot实践——AOP实现
借鉴:http://www.cnblogs.com/xrq730/p/4919025.html https://blog.csdn.net/zhaokejin521/article/detai ...
- 自定义的Spring Boot starter如何设置自动配置注解
本文首发于个人网站: 在Spring Boot实战之定制自己的starter一文最后提到,触发Spring Boot的配置过程有两种方法: spring.factories:由Spring Boot触 ...
- Spring Boot应用的后台运行配置
酱油一篇,整理一下关于Spring Boot后台运行的一些配置方式.在介绍后台运行配置之前,我们先回顾一下Spring Boot应用的几种运行方式: 运行Spring Boot的应用主类 使用Mave ...
- Spring boot 的 properties 属性值配置 application.properties 与 自定义properties
配置属性值application.properties 文件直接配置: com.ieen.super.name="MDD" 自定义properties文件配置:src/main/r ...
- Spring Boot 启动(二) 配置详解
Spring Boot 启动(二) 配置详解 Spring 系列目录(https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/10198698.html) Spring Boot 配置 ...
- JAR(Spring Boot)应用的后台运行配置
酱油一篇,整理一下关于Spring Boot后台运行的一些配置方式.在介绍后台运行配置之前,我们先回顾一下Spring Boot应用的几种运行方式: 运行Spring Boot的应用主类 使用Mave ...
随机推荐
- LTE空口协议——是空口3GPP协议 不是网络IP协议
[LTE基础知识]LTE空口协议分析 from:https://www.mscbsc.com/viewnews-102038.html控制面协议 控制面协议结构如下图所示. PDCP在网络侧终止于eN ...
- 使用springfox+swagger2书写API文档(十八)
使用springfox+swagger2书写API文档 springfox是通过注解的形式自动生成API文档,利用它,可以很方便的书写restful API,swagger主要用于展示springfo ...
- POJ 1426 Find the Multiple 思路,线性同余,搜索 难度:2
http://poj.org/problem?id=1426 测试了一番,从1-200的所有值都有long long下的解,所以可以直接用long long 存储 从1出发,每次向10*s和10*s+ ...
- Thinking in Java之衍生类和基础类的初始化顺序
<Thinking in Java>书里的例子,我又稍微修改了下代码: class Real{ public Real(String index) { // TODO Auto-gener ...
- Lucene Scoring 评分机制
原文出处:http://blog.chenlb.com/2009/08/lucene-scoring-architecture.html Lucene 评分体系/机制(lucene scoring)是 ...
- 在Google Maps中导出KML文件
教你一招:在Google Maps中导出KML文件 2011-07-11 15:24:49 4819 人阅读 作者:上方文Q 编辑:上方文Q [复制链接] [爆料] Google Earth的一大乐趣 ...
- 201621123005《Java程序设计》第六次学习总结
201621123005<java程序设计>第六周学习总结 1.本周学习总结 1.1 面向对象学习暂告一段落,请使用思维导图,以封装.继承.多态为核心概念画一张思维导图或相关笔记,对面向对 ...
- 五种开源协议的比较(BSD,Apache,GPL,LGPL,MIT)
本篇博客比较了常见的5种开源协议的异同,大家在为自己的代码选择协议的时候可以参考.现今存在的开源协议很多,而经过Open Source Initiative组织通过批准的开源协议目前有58种(http ...
- Oracle(一)安装
一.到官网或者哪里去下载Oracle,我下的是winX64的11g版本 官网:https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/database/enterprise-editio ...
- OPENQUERY用法以及使用需要注意的地方
对给定的链接服务器执行指定的传递查询.该服务器是 OLE DB 数据源.OPENQUERY 可以在查询的 FROM 子句中引用,就好象它是一个表名.OPENQUERY 也可以作为 INSERT.UPD ...
