Calculate CAN bit timing parameters -- STM32
Calculate CAN bit timing parameters
Calculate CAN bit timing parameters
- typedef struct
- {
- //char name[ 16 ]; // Name of the CAN controller hardware
- //uint32_t ref_clk; // CAN system clock frequency in Hz
- //uint32_t sjw_max; // Synchronisation jump width
- uint32_t brp_min; // Bit-rate prescaler
- uint32_t brp_max;
- uint32_t brp_inc;
- uint32_t tseg1_min; // Time segement 1 = prop_seg + phase_seg1
- uint32_t tseg1_max;
- uint32_t tseg2_min; // Time segement 2 = phase_seg2
- uint32_t tseg2_max;
- } CAN_BitTimingConst_TypeDef;
- typedef struct
- {
- uint32_t ref_clk; // CAN system clock frequency in Hz
- uint32_t bitrate; // Bit-rate in bits/second
- uint32_t sample_point; // Sample point in one-tenth of a percent
- uint32_t brp; // Bit-rate prescaler
- uint32_t tq; // Time quanta (TQ) in nanoseconds
- uint32_t tseg1; // Time segement 1 = prop_seg + phase_seg1
- uint32_t tseg2; // Time segement 2 = phase_seg2
- uint32_t sjw; // Synchronisation jump width in TQs
- //uint32_t prop_seg; // Propagation segment in TQs
- //uint32_t phase_seg1; // Phase buffer segment 1 in TQs
- //uint32_t phase_seg2; // Phase buffer segment 2 in TQs
- } CAN_BitTiming_TypeDef;
- #define CAN_CALC_MAX_ERROR 50 // in one-tenth of a percent
- int32_t CAN_UpdateSamplePoint( CAN_BitTimingConst_TypeDef *btc,
- int32_t sampl_pt, int32_t tseg, int32_t *tseg1, int32_t *tseg2 )
- {
- *tseg2 = tseg + - ( sampl_pt * ( tseg + ) ) / ;
- if ( *tseg2 < btc->tseg2_min )
- *tseg2 = btc->tseg2_min;
- if ( *tseg2 > btc->tseg2_max )
- *tseg2 = btc->tseg2_max;
- *tseg1 = tseg - *tseg2;
- if ( *tseg1 > btc->tseg1_max )
- {
- *tseg1 = btc->tseg1_max;
- *tseg2 = tseg - *tseg1;
- }
- return * ( tseg + - *tseg2 ) / ( tseg + );
- }
- // CIA Sample Point : 75.0% : Speed > 800000
- // CIA Sample Point : 80.0% : Speed > 500000
- // CIA Sample Point : 87.5% : Speed <= 500000
- uint32_t CAN_CIA_SamplePoint( uint32_t bitrate )
- {
- uint32_t sampl_pt;
- if ( bitrate > )
- sampl_pt = ;
- else if ( bitrate > )
- sampl_pt = ;
- else
- sampl_pt = ;
- return sampl_pt;
- }
- int32_t CAN_CalcBitTiming( CAN_BitTimingConst_TypeDef *btc,
- CAN_BitTiming_TypeDef *bt )
- {
- uint64_t v64;
- int32_t rate = ;
- int32_t best_error = , error = ;
- int32_t best_tseg = , best_brp = , brp = ;
- int32_t tsegall, tseg = , tseg1 = , tseg2 = ;
- int32_t spt_error = , spt = , sampl_pt;
- // Use gived sample points
- if ( bt->sample_point )
- sampl_pt = bt->sample_point;
- else
- // Use CIA recommended sample points
- sampl_pt = CAN_CIA_SamplePoint( bt->bitrate );
- // tseg even = round down, odd = round up
- for ( tseg = ( btc->tseg1_max + btc->tseg2_max ) * + ;
- tseg >= ( btc->tseg1_min + btc->tseg2_min ) * ; tseg-- )
- {
- tsegall = + tseg / ;
- // Compute all possible tseg choices (tseg=tseg1+tseg2)
- brp = bt->ref_clk / ( tsegall * bt->bitrate ) + tseg % ;
- // chose brp step which is possible in system
- brp = ( brp / btc->brp_inc ) * btc->brp_inc;
- if ( ( brp < btc->brp_min ) || ( brp > btc->brp_max ) )
- continue;
- rate = bt->ref_clk / ( brp * tsegall );
- error = bt->bitrate - rate;
- // tseg brp biterror
- if ( error < )
- error = -error;
- if ( error > best_error )
- continue;
- best_error = error;
- if ( error == )
- {
- spt = CAN_UpdateSamplePoint( btc, sampl_pt, tseg / , &tseg1, &tseg2 );
- error = sampl_pt - spt;
- if ( error < )
- error = -error;
- if ( error > spt_error )
- continue;
- spt_error = error;
- }
- best_tseg = tseg / ;
- best_brp = brp;
- if ( error == )
- break;
- }
- if ( best_error )
- {
- /* Error in one-tenth of a percent */
- error = ( best_error * ) / bt->bitrate;
- if ( error > CAN_CALC_MAX_ERROR )
- {
- // error ( "bitrate error %ld.%ld%% too high\n", error / 10, error % 10 );
- return DRIVER_ERROR_PARAMETER;
- }
- else
- {
- // warn( "bitrate error %ld.%ld%%\n", error / 10, error % 10 );
- }
- }
- v64 = ( (uint64_t) best_brp * 1000000000UL ) / bt->ref_clk;
- bt->tq = (uint32_t) v64;
- bt->brp = best_brp;
- bt->tseg2 = tseg2;
- bt->tseg1 = tseg1;
- bt->sjw = ;
- // bt->prop_seg = tseg1 / 2;
- // bt->phase_seg1 = tseg1 - bt->prop_seg;
- // bt->phase_seg2 = tseg2;
- // real bit-rate
- bt->bitrate = bt->ref_clk / ( bt->brp * ( tseg1 + tseg2 + ) );
- // real sample point
- bt->sample_point = CAN_UpdateSamplePoint( btc, sampl_pt, best_tseg, &tseg1,
- &tseg2 );
- return DRIVER_OK;
- }
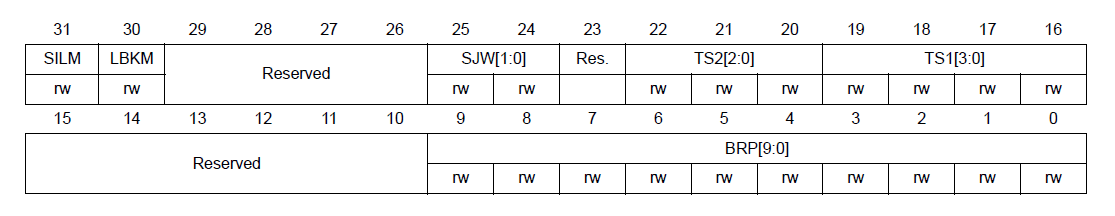
SJW[1:0]: Resynchronization jump width
These bits define the maximum number of time quanta the CAN hardware
is allowed to lengthen or shorten a bit to perform the resynchronization.
tRJW = tq x (SJW[1:0] + 1)
TS2[2:0]: Time segment 2
These bits define the number of time quanta in Time Segment 2.
tBS2 = tq x (TS2[2:0] + 1)
TS1[3:0]: Time segment 1
These bits define the number of time quanta in Time Segment 1
tBS1 = tq x (TS1[3:0] + 1)
BRP[9:0]: Baud rate prescaler
These bits define the length of a time quanta.
tq = (BRP[9:0]+1) x tPCLK
- const CAN_BitTimingConst_TypeDef CAN_BitTimingConst =
- { , // Bit-rate prescaler Min
- , // Bit-rate prescaler Max
- , // Bit-rate prescaler Inc
- , // Time segement 1 = prop_seg + phase_seg1 Min
- , // Time segement 1 = prop_seg + phase_seg1 Max
- , // Time segement 2 = phase_seg2 Min
- , // Time segement 2 = phase_seg2 Max
- };
- static int32_t CAN_SetSpeed( CAN_Controller_TypeDef *can, uint32_t speed )
- {
- int32_t RetValue = CAN_EnterInit( can );
- if ( RetValue != DRIVER_OK )
- return RetValue;
- uint32_t Freq = can->freq( );
- CAN_BitTiming_TypeDef CAN_BitTiming;
- CAN_BitTiming.ref_clk = Freq;
- CAN_BitTiming.bitrate = speed; // be updated to real speed
CAN_BitTiming.sample_point = 0; // be updated to real spt- RetValue = CAN_CalcBitTiming( &CAN_BitTimingConst, &CAN_BitTiming );
- if ( RetValue == DRIVER_OK )
- {
- can->info->speed = CAN_BitTiming.bitrate; // updated
- uint32_t BTR = can->reg->BTR & 0xC0000000; // SILM|LBKM
- BTR |= ( ( CAN_BitTiming.brp - ) << ) // BRP
- | ( ( CAN_BitTiming.tseg1 ) << ) // TS1
- | ( ( CAN_BitTiming.tseg2 - ) << ) // TS2
- | ( ( CAN_BitTiming.sjw - ) << ); // SJW
- can->reg->BTR = BTR;
- }
- return CAN_LeaveInit( can );
- /* BPR TSEG1 TSEG2 */
- /* 36 MHz 1 Mbps */ { , , }, // 75%
- /* 36 MHz 800 Kbps */ { , , }, // 80%
- /* 36 MHz 500 Kbps */ { , , }, // 83.3%
- /* 36 MHz 250 Kbps */ { , , }, // 87.5%
- /* 36 MHz 125 Kbps */ {, , }, // 87.5%
- /* 36 MHz 100 Kbps */ {, , }, // 86.6%
- /* 36 MHz 83.3 Kbps */ {, , }, // 83.3%
- /* 36 MHz 62.5 Kbps */ {, , }, // 87.5%
- /* 36 MHz 50 Kbps */ {, , }, // 87.5%
- /* 36 MHz 20 Kbps */ {,, }, // 86.6%
- /* 36 MHz 10 Kbps */ {,, }, // 87.5%
- /* 36 MHz 500 Kbps */ { , , } // 83.3%
Calculate CAN bit timing parameters -- STM32的更多相关文章
- Calculate CAN bit timing parameters
Calculate CAN bit timing parameters TSYNC_SEG === 1 TSEG1 = Prop_Seg + Phase_Seg1 TSEG2 = Phase_Seg2 ...
- 0xWS2812 STM32 driver for WS2812(B) RGB LEDs
0xWS2812 STM32 driver for WS2812(B) RGB LEDs 0xWS2812 pronounced "hex-WS2812" This code ai ...
- CRT/LCD/VGA Information and Timing
彩色阴极射线管的剖面图: 1. 电子QIANG Three Electron guns (for red, green, and blue phosphor dots)2. 电子束 Electron ...
- CRT/LCD/VGA Information and Timing【转】
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/shangdawei/p/4760933.html 彩色阴极射线管的剖面图: 1. 电子QIANG Three Electron guns (for ...
- CALayer之 customizing timing of an animation
customizing timing of an animation Timing is an important part of animations, and with Core Animatio ...
- RFID 读写器 Reader Writer Cloner
RFID读写器的工作原理 RFID的数据采集以读写器为主导,RFID读写器是一种通过无线通信,实现对标签识别和内存数据的读出和写入操作的装置. 读写器又称为阅读器或读头(Reader).查询器(Int ...
- RFID Reader 线路图收集
This 125 kHz RFID reader http://www.serasidis.gr/circuits/RFID_reader/125kHz_RFID_reader.htm http:// ...
- BlackArch-Tools
BlackArch-Tools 简介 安装在ArchLinux之上添加存储库从blackarch存储库安装工具替代安装方法BlackArch Linux Complete Tools List 简介 ...
- Timequest静态时序分析(STA)基础
Setup Slack Hold Slack Recovery&Removal Recovery: The minimum time an asynchronous signal must b ...
随机推荐
- 第11月第11天 avplayer循环播放
1. /* Setting actionAtItemEnd to None prevents the movie from getting paused at item end. A very sim ...
- 常用的C#编译命令
使用 csc.exe 实现命令行生成 作为一个半路出家的非计算机专业出身的前端码农,最近对C#很感兴趣,原因如下: 1.希望通过学习C#能熟悉一下windows系统和一些概念,例如:windows服务 ...
- Bug Bounty Reference
https://github.com/ngalongc/bug-bounty-reference/blob/master/README.md#remote-code-execution Bug Bou ...
- BAT获取FTP指定文件
以下两个文件放在同一目录下 getfile.bat文件内容如下: @echo offftp.exe -i -s:getfile.txt 192.168.1.2(更换成你的ip,参数之间有空格)paus ...
- MAC系统下Sublime Text3 配置Python3详细教程
MAC系统下Sublime Text3 配置Python3详细教程(亲测有效) https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41768008/article/details/798590 ...
- php的递归函数示例
递归函数太难理解了,写了一个示例放在这里方便没事的时候看一下. <?php /** *php递归函数示例 *(从1到100的累加和计算) * */ function summation($num ...
- 使用netperf测试网络性能
1.安装netperf 1)获取netperf安装包 netperf-2.7.0.tar.bz2 2)解压到本地目录 3)进入netperf-2.7.0,执行:./configure 4)编译执行:m ...
- CentOS下配置MySQL允许root用户远程登录
1.常用命令: 安装上传下载文件命令yum install lrzsz安装webget工具yum -y install wget ----------------------------------- ...
- 交换机NTP的MD5配置
1.ntp-service authentication enable 开启NTP身份验证功能 2.ntp-service source-interfer LoopBack0 指定本机发生NTP的端 ...
- IntelliJ IDEA 设置Output 窗口字体大小
Settings——>Editor——>Colors&Fonts——>Console Font 如图: 字体调好了以后使用起来眼睛就轻松多了
