[转]An overview of Openvswitch implementation
This is NOT a tutorial on how to use openvswitch, this is for developers who want to know the implementation details of openvswitch project, thus, I assume you at least know the basic concepts of openvswitch and know how to use it. If not, see www.openvswitch.org to get some documents or slides.
Let’s start from the user-space part. Openvswitch user-space contains several components: they are a few daemons which actually implements the switch and the flow table, the core of openvswitch, and several utilities to manage the switch, the database, and even talk to the kernel directly.
There are three daemons started by openvswitch service: ovs-vswitchd, which is the core implementation of the switch; ovsdb-server, which manipulates the database of the vswitch configuration and flows; and ovs-brcompatd which keeps the compatibility with the traditional bridges (that is the one you create with ‘brctl’ command) .
Their relationship is shown in the picture below:
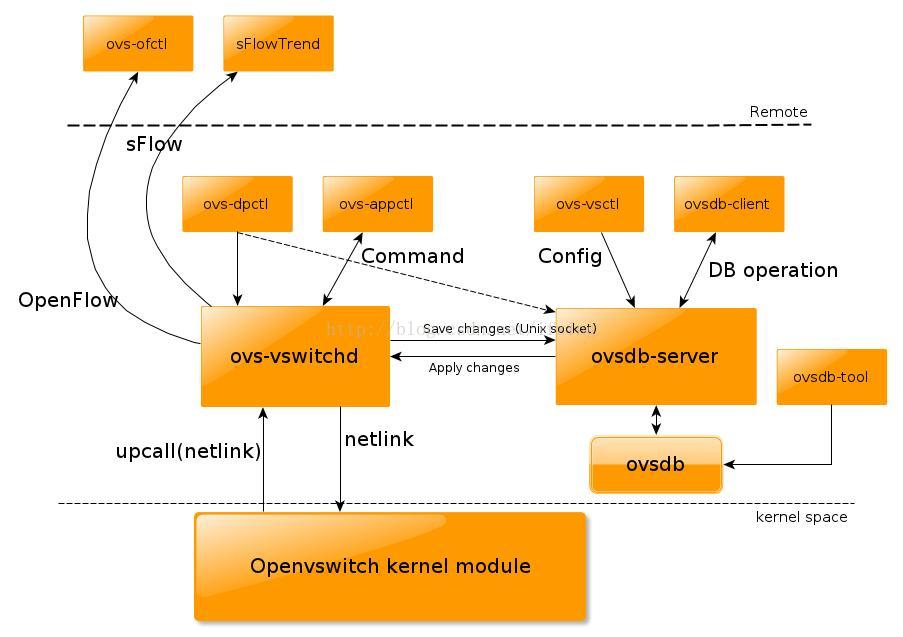
Obviously, the most important one is ovs-vswitchd, it implements the switch, it directly talks with kernel via netlink protocol (we will see the details later). And ovs-vsctl is the utility used primarily to manage the switch, which of course needs to talk with ovs-vswitchd. Ovs-vswitchd saves and changes the switch configuration into a database, which is directly managed by ovsdb-server, therefore, ovs-vswitchd will need to talk to ovsdb-server too, via Unix domain socket, in order to retrieve or save the configuration information. This is also why your openvswitch configuration could survive from reboot even you are not using ifcfg* files.
Ovs-brcompatd is omitted here, we are not very interested in it now.
Ovs-vsctl can do lots of things for you, so most of time, you will use ovs-vsctl to manage openvswitch. Ovs-appctl is also available to manage the ovs-vswitchd itself, it sends some internal commands to ovs-vswitchd daemon to change some configurations.
However, sometimes you may need to manage the datapath in the kernel directly by yourself, in this case, assume ovs-vswitchd is not running, you can invoke ovs-dpctl to let ovs-vswitchd to manage the datapath in the kernel space directly, without database.
And, when you need to talk with ovsdb-server directly, to do some database operation, you can run ovsdb-client, or you want to manipulate the database directly without ovsdb-server, ovsdb-tool is handy too.
What’s more, openvswitch can be also administered and monitored by a remote controller. This is why we could define the network by software! sFlow is a protocol for packet sampling and monitoring, while OpenFlow is a protocol to manage the flow table of a switch, bridge, or device. Openvswitch supports both OpenFlow and sFlow. With ovs-ofctl, you can use OpenFlow to connect to the switch and do some monitoring and administering in the remote. sFlowTrend, which is not a part of openvswitch package, is the one that is capable for sFlow.
Now, let’s take a look at the kernel part.
As mentioned previously, the user-space communicates with the kernel-space via netlink protocol, generic netlink is used in this case. So there are several groups of genl commands defined by the kernel, they are used to get/set/add/delete some datapath/flow/vport and execute some actions on a specific packet.
The ones used to control datapatch are:
enum ovs_datapath_cmd {
OVS_DP_CMD_UNSPEC,
OVS_DP_CMD_NEW,
OVS_DP_CMD_DEL,
OVS_DP_CMD_GET,
OVS_DP_CMD_SET
};
and there are corresponding kernel functions which does the job:
ovs_dp_cmd_new()
ovs_dp_cmd_del()
ovs_dp_cmd_get()
ovs_dp_cmd_set()
Similar functions are defined for vport and flow commands too.
Before we talk about the details of the data structures, let’s see how a packet is sent out or received from a port of an ovs bridge. When is packet is send out from the ovs bridge, an internal device defined by openvswitch module, which is viewed, by the kernel, as a struct vport too. The packet will be finally passed to internal_dev_xmit(), which in turn “receives” the packet. Now, the kernel needs to look at the flow table, to see if there is any “cache” for how to forward this packet. This is done by function ovs_flow_tbl_lookup(), which needs a key. The key is extracted by ovs_flow_extract() which briefly collects the details of the packet (L2~L4) and then constructs a unique key for this flow. Assume this is the first packet going out after we create the ovs bridge, so, there is no “cache” in the kernel, and the kernel doesn’t know how to handle this packet! Then it will pass it to the user-space with “upcall” which uses genl too. The user-space daemon, ovs-vswitchd, will check the database and see which is the destination port for this packet, and will response to the kernel with OVS_ACTION_ATTR_OUTPUT to tell kernel which is the port it should forward to, in this case let’s assume it is eth0. and finally a OVS_PACKET_CMD_EXECUTE command is to let the kernel execute the action we just set. That is, the kernel will execute this genl command in function do_execute_actions() and finally forward the packet to the port “eth0” with do_output(). Then it goes to outside!
The receiving side is similar. The openvswitch module registers an rx_handler for the underlying (non-internal) devices, it is netdev_frame_hook(), so once the underlying device receives packets on wire, openvswitch will forward it to user-space to check where it should goes, and what actions it needs to execute on it. For example, if this is a VLAN packet, the VLAN tag should be removed from the packet first, and then forwarded to a right port. The user-space could learn that which is the right port to forward a given packet.
The internal devices are special, when a packet is sent to an internal device, it is be immediately sent up to openvswitch to decide where it should go, instead of really sending it out. There is actually no way out of an internal device directly.
Besides OVS_ACTION_ATTR_OUTPUT, the kernel also defines some other actions:
OVS_ACTION_ATTR_USERSPACE, which tells the kernel to pass the packet to user-space
OVS_ACTION_ATTR_SET: Modify the header of the packet
OVS_ACTION_ATTR_PUSH_VLAN: Insert a vlan tag into the packet
OVS_ACTION_ATTR_POP_VLAN: Remove the vlan tag from the packet
OVS_ACTION_ATTR_SAMPLE: Do sampling
With these commands combined, the user-space could implement some different policies, like a bridge, a bond or a VLAN device etc. GRE tunnel is not currently in upstream, so we don’t care about it now.
So far, you already know how the packets are handled by openvswitch module. There are much more details, especially about the flow and datapath mentioned previously. A flow in kernel is represented as struct sw_flow, and datapath is defined as struct datapath, and the actions on a flow is defined as struct sw_flow_actions, and plus the one we mentioned, struct vport. These structures are the most important ones for openvswitch kernel module, their relationship is demonstrated in this picture:
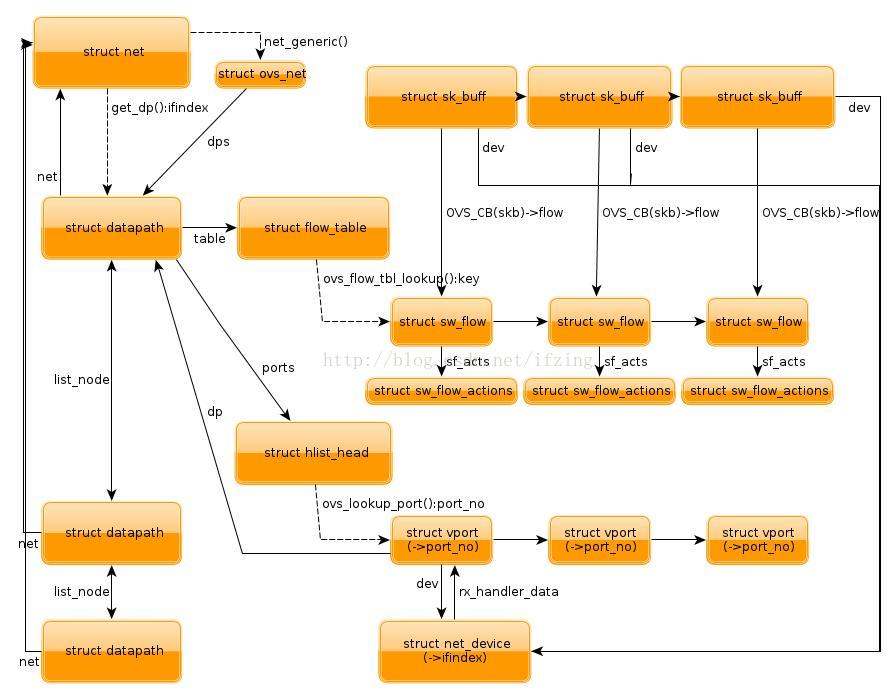
The most important one needs to mention is each struct sk_buff is associated with a struct sw_flow, which is via a pointer in ovs control block. And the above actions is associated with each flow, every time when a packet passed to openvswitch module, it first needs to lookup the flow table which is contained in a datapath which in turn either contains in a struct vport or in a global linked-list, with the key we mentioned. If a flow is found, the corresponding actions will be executed. Remember that datapath, flow, vport, all could be changed by the user-space with some specific genl command.
As you can see, the kernel part only implements a mechanism and the fast path (except the first packet), and the user-space implements different policies upon the mechanism provided by the kernel, the slow path. The user-space is much more complicated, so I will not cover its details here.
Update: Ben, one of the most active developers for openvswitch, pointed out some mistakes in the previous version, I updated this article as he suggested. Thanks to Ben!
[转]An overview of Openvswitch implementation的更多相关文章
- adb概览及协议參考
原文:https://github.com/android/platform_system_core/blob/master/adb/OVERVIEW.TXT) Implementation note ...
- 使Web Api 支持跨域资源共享(CORS)
Reference:http://www.asp.net/web-api/overview/security/enabling-cross-origin-requests-in-web-api Imp ...
- adb概览及协议参考
原文:https://github.com/android/platform_system_core/blob/master/adb/OVERVIEW.TXT) Implementation note ...
- Migrating Oracle on UNIX to SQL Server on Windows
Appendices Published: April 27, 2005 On This Page Appendix A: SQL Server for Oracle Professionals Ap ...
- wxpython wx.windows的API
wx.Window is the base class for all windows and represents any visible object on screen. All control ...
- Object Pascal中文手册 经典教程
Object Pascal 参考手册 (Ver 0.1)ezdelphi@hotmail.com OverviewOverview(概述)Using object pascal(使用 object p ...
- Method of address space layout randomization for windows operating systems
A system and method for address space layout randomization ("ASLR") for a Windows operatin ...
- Overview and Evaluation of Bluetooth Low Energy: An Emerging Low-Power Wireless Technology
转自:http://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220/12/9/11734/htm Sensors 2012, 12(9), 11734-11753; doi:10.3390/s12091 ...
- IMS Global Learning Tools Interoperability™ Implementation Guide
Final Version 1.1 Date Issued: 13 March 2012 Latest version: http://www.imsglobal ...
随机推荐
- Mysql引擎innodb_pool的作用
innodb_buffer_pool的简介: InnoDB主索引是聚簇索引,索引与数据共用表空间,对于InnoDB而言,数据就是索引,索引就是数据.InnoDB缓存机制和MyISAM缓存机制的最大区别 ...
- 028、HTML 标签2超链接,框架标签
内容:超链接,框架标签############################################################## <!-- 超链接 --> <a h ...
- SecureCRT Win免安装版本,简单好用
SecureCRT是一款支持SSH(SSH1和SSH2)的终端仿真程序,简单地说是Windows下登录UNIX或Linux服务器主机的软件. 这个简单好用,程序员必备. 下载地址:SecureCRT. ...
- C++的技术探究
C++深究 函数指针 double pam(int, double); // prototype double (*pf)(int, double); // declare function poin ...
- MetaMask/provider-engine-2-代码
package.json "main": "index.js", "scripts": { "test": " ...
- Centos7常见问题及解决方法
1,在Centos7中用MariaDB代替了mysql数据库 2,mysql报错:/usr/sbin/mysqld:unknown variable 'default-character-set=ut ...
- 利用存储过程来重命名SQL Server数据库
最近遇到一个需要在多用户模式下重新命名数据库的Case, 因为数据库可能被其他用户使用,所以直接修改可能会失败.对于此种情况,我们可以等所有用户结束使用数据库时修改,或者是将数据库切换到单用户模式下进 ...
- Grunt-jsdoc生成JS API文档
Grunt-jsdoc生成JS API文档 具体的请看官网 https://github.com/krampstudio/grunt-jsdoc 一:首先确保本机电脑上是否已经安装了nodejs和np ...
- JS输入框邮箱自动提示(带有demo和源码)
今天在javascriptQQ群里面 有童鞋问到 有没有 "JS输入框邮箱自动提示"插件,即说都找遍了github上源码 都没有看到这样类似的插件,然后我想了下 "JS输 ...
- Android Bundle传递对象
首先Android的Bundle是可以传递对象的.我们可以用Bundle b = new Bundle():b.putSerializable("key", 对象引用); 但是这样 ...
