SpringMVC源码解读 - RequestMapping注解实现解读 - RequestCondition体系
一般我们开发时,使用最多的还是@RequestMapping注解方式.
@RequestMapping(value = "/", param = "role=guest", consumes = "!application/json")
public void myHtmlService() {
// ...
}
台前的是RequestMapping ,正经干活的却是RequestCondition,根据配置的不同条件匹配request.
@RequestMapping注解,请看<SpringMVC源码解读 - HandlerMapping - RequestMappingHandlerMapping初始化>
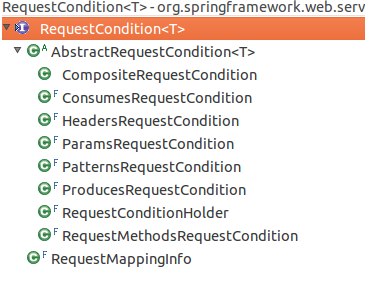
典型的接口+模板.一个接口ReqeustCondition,一个抽象类,定义基础,然后n多的具体实现.
实现中可以分为3类:基础实现,外观类和容器.
其中CompositeRequestCondition和RequestMappingInfo本身不带任何的匹配条件,只是用于包装其他的RequestCondition进行匹配
基础实现:
consumes对应request的提交内容类型content type,如application/json, text/html
headers 对应http request 的请求头
params对应http request parameter
Patterns对应url,就是注解value中的配置
produces指定返回的内容类型的content type,仅当request请求头中的(Accept)类型中包含该指定类型才返回
requestMethods对应 http method,如GET,POST,PUT,DELETE等
外观类:
RequestConditionHolder,用于不知道具体是RequestCondition哪个子类时.自定义的条件,使用的这个进行封装
容器:
CompositeRequestCondition封装基础实现,具体的匹配都委托给基础实现类.
RequestMappingInfo,对应@RequestMapping注解,一一对应注解内容与基础实现,使用时一一委托.
先来看看RequestCondition的接口定义
package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition;
/**
* The contract for request conditions.
*/
public interface RequestCondition<T> { /**
* 将不同的筛选条件合并
*/
T combine(T other); /**
* 根据request查找匹配到的筛选条件
*/
T getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request); /**
* 不同筛选条件比较,用于排序
*/
int compareTo(T other, HttpServletRequest request); }
}
老规矩,接下来得上抽象类AbstractRequestCondition
AbstractRequestCondition做的事不多,覆写equals,hashCode,toString.实现equals,hashCode,toString时预留模板方法getContent();实现toString时预留模板方法getToStringInfix().
package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition;
/**
* A base class for {@link RequestCondition} types providing implementations of
* {@link #equals(Object)}, {@link #hashCode()}, and {@link #toString()}.
*
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @since 3.1
*/
public abstract class AbstractRequestCondition<T extends AbstractRequestCondition<T>> implements RequestCondition<T> { /**
* Return the discrete items a request condition is composed of.
* For example URL patterns, HTTP request methods, param expressions, etc.
* @return a collection of objects, never {@code null}
*/
protected abstract Collection<?> getContent(); @Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o != null && getClass().equals(o.getClass())) {
AbstractRequestCondition<?> other = (AbstractRequestCondition<?>) o;
return getContent().equals(other.getContent());
}
return false;
} @Override
public int hashCode() {
return getContent().hashCode();
} @Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("[");
for (Iterator<?> iterator = getContent().iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
Object expression = iterator.next();
builder.append(expression.toString());
if (iterator.hasNext()) {
builder.append(getToStringInfix());
}
}
builder.append("]");
return builder.toString();
} /**
* The notation to use when printing discrete items of content.
* For example " || " for URL patterns or " && " for param expressions.
*/
protected abstract String getToStringInfix(); }
接下来得看具体实现了,捏不到软柿子,用ParamsRequestCondition简单说明下子类吧
// ParamsRequestCondition
// 保存解析出来的param匹配条件
private final Set<ParamExpression> expressions;
ParamExpression其实很简单,看父类AbstractNameValueExpression很清楚
// AbstractNameValueExpression
package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition;
abstract class AbstractNameValueExpression<T> implements NameValueExpression<T> {
// 参数的名字
protected final String name;
// 参数的值
protected final T value;
// 参数的匹配规则,是= 还是!=
protected final boolean isNegated;
}
到这里我们就可以看懂,使用ParamExpression保存param参数,这样可以任意多个.
combine的实现也就水到渠成,直接把expression拼接到一个集合里就行:
package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition;
public final class ParamsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ParamsRequestCondition> {
/**
* Returns a new instance with the union of the param expressions
* from "this" and the "other" instance.
*/
public ParamsRequestCondition combine(ParamsRequestCondition other) {
Set<ParamExpression> set = new LinkedHashSet<ParamExpression>(this.expressions);
set.addAll(other.expressions);
return new ParamsRequestCondition(set);
}
}
getMatchingCondition时,只要有一个不符合就判定条件不匹配
package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition;
public final class ParamsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ParamsRequestCondition> {
/**
* Returns "this" instance if the request matches all param expressions;
* or {@code null} otherwise.
*/
public ParamsRequestCondition getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) {
for (ParamExpression expression : expressions) {
if (!expression.match(request)) {
return null;
}
}
return this;
}
}
这边的match方法比较有意思,可以看下
package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition;
abstract class AbstractNameValueExpression<T> implements NameValueExpression<T> {
public final boolean match(HttpServletRequest request) {
boolean isMatch;
if (this.value != null) {
isMatch = matchValue(request);
}
else { // 没有value时,只要匹配name就好
isMatch = matchName(request);
}
return isNegated ? !isMatch : isMatch; // 这边需要看仔细,=与!=的处理
} protected abstract boolean matchName(HttpServletRequest request); protected abstract boolean matchValue(HttpServletRequest request);
}
ParamExpression中给出matchName与matchValue的实现.
ParamExpression这里又是接口+抽象实现+模板方法设计模式,偷个懒,暂时不去关心各层抽象的什么.
compareTo根据匹配条件的多少来判定顺序
// ParamsRequestCondition
public int compareTo(ParamsRequestCondition other, HttpServletRequest request) {
return other.expressions.size() - this.expressions.size();
}
记得还留有两个模板方法
getContent直接返回记录param的expressions
getToStringInfix则使用&&
// ParamsRequestCondition
@Override
protected Collection<ParamExpression> getContent() {
return expressions;
} @Override
protected String getToStringInfix() {
return " && ";
}
再看看是如何解析param的
// ParamsRequestCondition
/**
* Create a new instance from the given param expressions.
* @param params expressions with syntax defined in {@link RequestMapping#params()};
* if 0, the condition will match to every request.
*/
public ParamsRequestCondition(String... params) {
this(parseExpressions(params));
} private static Collection<ParamExpression> parseExpressions(String... params) {
Set<ParamExpression> expressions = new LinkedHashSet<ParamExpression>();
if (params != null) {
for (String param : params) {
expressions.add(new ParamExpression(param));
}
}
return expressions;
}
核心的代码还是在AbstractNameValueExpression
// AbstractNameValueExpression
逻辑不复杂,代码看着有点烦,是不是应该听Martin Fowler在<重构>中的建议,来个extract method?
AbstractNameValueExpression(String expression) {
int separator = expression.indexOf('=');
if (separator == -1) {
this.isNegated = expression.startsWith("!");
this.name = isNegated ? expression.substring(1) : expression;
this.value = null;
}
else {
this.isNegated = (separator > 0) && (expression.charAt(separator - 1) == '!');
this.name = isNegated ? expression.substring(0, separator - 1) : expression.substring(0, separator);
this.value = parseValue(expression.substring(separator + 1));
}
}
RequestCondition的解读未完,待续:
SpringMVC源码解读 - RequestMapping注解实现解读 - ConsumesRequestCondition
SpringMVC源码解读 - RequestMapping注解实现解读 - RequestMappingInfo
SpringMVC源码解读 - RequestMapping注解实现解读 - RequestCondition体系的更多相关文章
- SpringMVC源码解读 - RequestMapping注解实现解读 - RequestMappingInfo
使用@RequestMapping注解时,配置的信息最后都设置到了RequestMappingInfo中. RequestMappingInfo封装了PatternsRequestCondition, ...
- SpringMVC源码解读 - RequestMapping注解实现解读
SpringMVC源码解读 - RequestMapping注解实现解读 - RequestCondition体系 https://www.cnblogs.com/leftthen/p/520840 ...
- SpringMVC源码解读 - RequestMapping注解实现解读 - ConsumesRequestCondition
consumes 指定处理请求的提交内容类型(media-Type),例如application/json, text/html. 所以这边的ConsumesRequestCondition就是通过 ...
- SpringMVC源码阅读系列汇总
1.前言 1.1 导入 SpringMVC是基于Servlet和Spring框架设计的Web框架,做JavaWeb的同学应该都知道 本文基于Spring4.3.7源码分析,(不要被图片欺骗了,手动滑稽 ...
- SpringMVC源码解读 - HandlerMapping
SpringMVC在请求到handler处理器的分发这步是通过HandlerMapping模块解决的.handlerMapping 还处理拦截器. 先看看HandlerMapping的继承树吧 可以大 ...
- SpringMVC 源码深度解析<context:component-scan>(扫描和注冊的注解Bean)
我们在SpringMVC开发项目中,有的用注解和XML配置Bean,这两种都各有自己的优势,数据源配置比較经经常使用XML配置.控制层依赖的service比較经经常使用注解等(在部署时比較不会改变的) ...
- 7、SpringMVC源码分析(2):分析HandlerAdapter.handle方法,了解handler方法的调用细节以及@ModelAttribute注解
从上一篇 SpringMVC源码分析(1) 中我们了解到在DispatcherServlet.doDispatch方法中会通过 mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, res ...
- SpringMVC源码情操陶冶-AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser注解解析器
mvc:annotation-driven节点的解析器,是springmvc的核心解析器 官方注释 Open Declaration org.springframework.web.servlet.c ...
- SpringMVC源码剖析5:消息转换器HttpMessageConverter与@ResponseBody注解
转自 SpringMVC关于json.xml自动转换的原理研究[附带源码分析] 本系列文章首发于我的个人博客:https://h2pl.github.io/ 欢迎阅览我的CSDN专栏:Spring源码 ...
随机推荐
- IIS应用程序池频繁停止,任务管理器发现有多个w3wp.exe进程
网站其中的一个应用服务器最近频繁出现IIS应用程序池停止的问题,通过任务管理器查看发现有6个w3wp.exe进程,一般一个应用程序池只占有一个w3wp.exe进程,为什么会出现多个呢,通过查看其它服务 ...
- OD 实验(十八) - 简单注册机的编写
程序: 运行 这是一个注册机 随便输入点内容,点击 Check 弹出错误的对话框 逆向: 用 OD 载入程序 在文本框处下断点 按 Alt+B 查看断点 这个断点在动态链接库那里 跑一下程序,输入内容 ...
- nginx的下载和安装
安装 下载必要组件 nginx下载地址 http://nginx.org/en/download.html pcre库下载地址,nginx需要[解析正则] http://sourceforge.ne ...
- question?
- vue组件之echarts报表
vue组件之echarts报表 将echarts报表封装成组件,动态传入数据,显示图表. 1.饼状图 父组件: <MPie :datas="piedata"></ ...
- angular.module方法
关于module的定义为:angular.module(‘com.ngbook.demo’, []).关于module函数可以传递3个参数,它们分别为: name:模块定义的名称,它应该是一个唯一的必 ...
- vector(实现存图)
#include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<iostream> #i ...
- 【310】◀▶ Python 日期和时间
参考: python 时间日期计算 Python 日期和时间(菜鸟教程) 8.1. datetime — Basic date and time types python中datetime模块中dat ...
- nodejs开发工具
我选择的是Hbuilder作为node项目的开发工具. 先在Hbuilder 里面安装nodeEclipse插件,然后重启工具. 点击添加项目,选择其他选项,出现下图选项,然后选择圈住的选项点击下 ...
- 面试------Android 版本之前的差异(常见,欢迎补充)。
不管你技术如何,只要背点这个,能忽悠倒一片.. 1.WebView JS漏洞 ,Android4.2之前 ,解决办法,不用addJavascriptInterface,webchrome的onJsPr ...
