RUAL1519 Formula 1 【插头DP】
RUAL1519 Formula 1
Background
Regardless of the fact, that Vologda could not get rights to hold the Winter Olympic games of 20**, it is well-known, that the city will conduct one of the Formula 1 events. Surely, for such an important thing a new race circuit should be built as well as hotels, restaurants, international airport - everything for Formula 1 fans, who will flood the city soon. But when all the hotels and a half of the restaurants were built, it appeared, that at the site for the future circuit a lot of gophers lived in their holes. Since we like animals very much, ecologists will never allow to build the race circuit over the holes. So now the mayor is sitting sadly in his office and looking at the map of the circuit with all the holes plotted on it.
Problem
Who will be smart enough to draw a plan of the circuit and keep the city from inevitable disgrace? Of course, only true professionals - battle-hardened programmers from the first team of local technical university!.. But our heroes were not looking for easy life and set much more difficult problem: “Certainly, our mayor will be glad, if we find how many ways of building the circuit are there!” - they said.
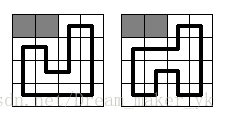
It should be said, that the circuit in Vologda is going to be rather simple. It will be a rectangle N*M cells in size with a single circuit segment built through each cell. Each segment should be parallel to one of rectangle’s sides, so only right-angled bends may be on the circuit. At the picture below two samples are given for N = M = 4 (gray squares mean gopher holes, and the bold black line means the race circuit). There are no other ways to build the circuit here.
Input
The first line contains the integer numbers N and M (2 ≤ N, M ≤ 12). Each of the next N lines contains M characters, which are the corresponding cells of the rectangle. Character “.” (full stop) means a cell, where a segment of the race circuit should be built, and character “*” (asterisk) - a cell, where a gopher hole is located. There are at least 4 cells without gopher holes.
Output
You should output the desired number of ways. It is guaranteed, that it does not exceed 263-1.
Samples
Input
4 4
**..
….
….
….
Output
2
Inpuut
4 4
….
….
….
….
Output
6
大概是插头DP的板子题
用Hash表储存状态
然后分别讨论当前的插头所对应的轮廓线上插头的情况
具体的在插头DP的总结里边写一些吧
然后根据已有的插头状态考虑当前位置的情况,大致分为连接,延长,新建三种
然后发现状态比较多,用四进制来进行储存,反正位运算快嘛
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define MAX 300010
#define N 20
int n,m,ind,endx,endy;
int mp[N][N],tot[2],bit[N];
LL dp[2][MAX],state[2][MAX],sum;
int head[MAX],Next[MAX],Hash[MAX],siz;
/*
tot 状态数
state 每个状态是什么
Hash hash表
*/
void init(){
memset(mp,0,sizeof(mp));
sum=ind=0;
tot[ind]=1;
dp[ind][1]=1;
state[ind][1]=0;
}
void Insert(LL s,LL num){
int pos=s%MAX;
for(int i=head[pos];~i;i=Next[i])
if(state[ind][Hash[i]]==s){dp[ind][Hash[i]]+=num;return;}
++tot[ind];
state[ind][tot[ind]]=s;
dp[ind][tot[ind]]=num;
Hash[siz]=tot[ind];
Next[siz]=head[pos];
head[pos]=siz++;
}
void DP(){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int k=1;k<=tot[ind];k++)state[ind][k]<<=2;
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));siz=0;
ind^=1;tot[ind]=0;
for(int k=1;k<=tot[ind^1];k++){
LL s=state[ind^1][k];
LL num=dp[ind^1][k];
int p=(s>>bit[j-1])%4;//左
int q=(s>>bit[j])%4;//上
if(!mp[i][j]){if(p+q==0)Insert(s,num);}
else if(p+q==0){//上左都没有插头
if((!mp[i+1][j])||(!mp[i][j+1]))continue;
s=s+(1<<bit[j-1])+2*(1<<bit[j]);
Insert(s,num);
}else if(p==0&&q){
if(mp[i][j+1])Insert(s,num);
if(mp[i+1][j]){
s=s+q*(1<<bit[j-1])-q*(1<<bit[j]);
Insert(s,num);
}
}else if(p&&q==0){
if(mp[i+1][j])Insert(s,num);
if(mp[i][j+1]){
s=s-p*(1<<bit[j-1])+p*(1<<bit[j]);
Insert(s,num);
}
}else if(p+q==2){
int b=1;
for(int t=j+1;t<=m;t++){
int v=(s>>bit[t])%4;
if(v==1)++b;
if(v==2)--b;
if(!b){s-=(1<<bit[t]);break;}
}
s=s-(1<<bit[j-1])-(1<<bit[j]);
Insert(s,num);
}else if(p+q==4){
int b=1;
for(int t=j-2;t>=0;--t){
int v=(s>>bit[t])%4;
if(v==2)++b;
if(v==1)--b;
if(!b){s+=(1<<bit[t]);break;}
}
s=s-2*(1<<bit[j-1])-2*(1<<bit[j]);
Insert(s,num);
}else if(p==1&&q==2){
if(i==endx&&j==endy)sum+=num;
}else if(p==2&&q==1){
s=s-2*(1<<bit[j-1])-(1<<bit[j]);
Insert(s,num);
}
}
}
}
}
int main(){
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)bit[i]=i<<1;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF){
init();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
getchar();char ch;
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
scanf("%c",&ch);
mp[i][j]=(ch=='.');
if(ch=='.')endx=i,endy=j;
}
}
DP();
printf("%lld\n",sum);
}
return 0;
}RUAL1519 Formula 1 【插头DP】的更多相关文章
- 【BZOJ1814】Ural 1519 Formula 1 插头DP
[BZOJ1814]Ural 1519 Formula 1 题意:一个 m * n 的棋盘,有的格子存在障碍,求经过所有非障碍格子的哈密顿回路个数.(n,m<=12) 题解:插头DP板子题,刷板 ...
- 【Ural】1519. Formula 1 插头DP
[题目]1519. Formula 1 [题意]给定n*m个方格图,有一些障碍格,求非障碍格的哈密顿回路数量.n,m<=12. [算法]插头DP [题解]<基于连通性状态压缩的动态规划问题 ...
- bzoj1814 Ural 1519 Formula 1(插头dp模板题)
1814: Ural 1519 Formula 1 Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 64 MBSubmit: 924 Solved: 351[Submit][Sta ...
- URAL1519 Formula 1 —— 插头DP
题目链接:https://vjudge.net/problem/URAL-1519 1519. Formula 1 Time limit: 1.0 secondMemory limit: 64 MB ...
- bzoj 1814 Ural 1519 Formula 1 ——插头DP
题目:https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=1814 普通的插头 DP .但是调了很久.注意如果合并两个 1 的话,不是 “把向右第一个 2 ...
- Ural 1519 Formula 1 插头DP
这是一道经典的插头DP单回路模板题. 用最小表示法来记录连通性,由于二进制的速度,考虑使用8进制. 1.当同时存在左.上插头的时候,需要判断两插头所在连通块是否相同,若相同,只能在最后一个非障碍点相连 ...
- [URAL1519] Formula 1 [插头dp入门]
题面: 传送门 思路: 插头dp基础教程 先理解一下题意:实际上就是要你求这个棋盘中的哈密顿回路个数,障碍不能走 看到这个数据范围,还有回路处理,就想到使用插头dp来做了 观察一下发现,这道题因为都是 ...
- URAL Formula 1 ——插头DP
[题目分析] 一直听说这是插头DP入门题目. 难到爆炸. 写了2h,各种大常数,ural垫底. [代码] #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> ...
- bzoj 1814 Ural 1519 Formula 1 插头DP
1814: Ural 1519 Formula 1 Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 64 MBSubmit: 942 Solved: 356[Submit][Sta ...
- BZOJ1814: Ural 1519 Formula 1(插头Dp)
Description Regardless of the fact, that Vologda could not get rights to hold the Winter Olympic gam ...
随机推荐
- POJ 3352 Road Construction(边—双连通分量)
http://poj.org/problem?id=3352 题意: 给出一个图,求最少要加多少条边,能把该图变成边—双连通. 思路:双连通分量是没有桥的,dfs一遍,计算出每个结点的low值,如果相 ...
- Build hadoop 2.5.2 with Java8
mvn clean package -Pdist,native -DskipTests -Dtar -Dmaven.javadoc.skip=true
- Interleaving String,交叉字符串,动态规划
问题描述: Given s1, s2, s3, find whether s3 is formed by the interleaving of s1 and s2. For example,Give ...
- 安装fcitx
设置好软件源后,终端执行: sudo apt-get install fcitx fcitx-ui-* fcitx-sunpinyin fcitx-googlepinyin fcitx-pinyin ...
- 1023: Pong’s Birds(概率)
1023: Pong’s Birds 时间限制: 1 Sec 内存限制: 128 MB提交: 94 解决: 21[提交][状态][讨论版] 题目描述 In order to train his b ...
- buffer与cache的区别
top命令中有两项与内存相关的东西:buffer和cache.这两项与页高速缓存相关.磁盘的操作有逻辑级(文件系统)和物理级(磁盘块),这两种Cache就是分别缓存逻辑和物理级数据的. 在linux内 ...
- day32 Python与金融量化分析(二)
第一部分:金融与量化投资 股票: 股票是股份公司发给出资人的一种凭证,股票的持有者就是股份公司的股东. 股票的面值与市值 面值表示票面金额 市值表示市场价值 上市/IPO: 企业通过证券交易所公开向社 ...
- log4j 日志详解
# 以下是rootLogger的配置,子类默认继承,但是子类重写下面配置=rootLogger+自己配置,我晕#输出到控制台 log4j.appender.console=org.apache.log ...
- 更改gitlab默认端口
若linux服务器的80和8080端口都已经被使用,则需修改gitlab监听的端口 修改路径文件:vim /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb 1.修改external_url 'http:// ...
- 【Seajs源码分析】3. 工具方法2
util-request.js 动态加载模块 /** * util-request.js - The utilities for requesting script and style files * ...