Tomcat session的实现:线程安全与管理
本文所说的session是单机版本的session, 事实上在当前的互联网实践中已经不太存在这种定义了。我们主要讨论的是其安全共享的实现,只从理论上来讨论,不必太过在意实用性问题。
1. session 的意义简说
大概就是一个会话的的定义,客户端有cookie记录,服务端session定义。用于确定你就是你的一个东西。
每个用户在一定范围内共享某个session信息,以实现登录状态,操作的鉴权保持等。
我们将会借助tomcat的实现,剖析session管理的一些实现原理。
2. tomcat 中 session 什么时候创建?
session 信息会在两个地方调用,一是每次请求进来时,框架会尝试去加载原有对应的session信息(不会新建)。二是应用自己调用getSession()时,此时如果不存在session信息,则创建一个新的session对象,代表应用后续会使用此功能。即框架不会自动支持session相关功能,只是在你需要的时候进行辅助操作。
// case1. 框架自行调用session信息,不会主动创建session
// org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager#retrieveFlashMaps
/**
* Retrieves saved FlashMap instances from the HTTP session, if any.
*/
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected List<FlashMap> retrieveFlashMaps(HttpServletRequest request) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
return (session != null ? (List<FlashMap>) session.getAttribute(FLASH_MAPS_SESSION_ATTRIBUTE) : null);
}
// case2. 应用主动调用session信息,不存在时会创建新的session, 以满足业务连续性需要
@GetMapping("sessionTest")
public Object sessionTest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
// 主动获取session信息
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
String sid = session.getId();
System.out.println("sessionId:" + sid);
return ResponseInfoBuilderUtil.success(sid);
}
在tomcat中,HttpServletRequest的实际类都是 RequestFacade, 所以获取session信息也是以其为入口进行。
// org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade#getSession()
@Override
public HttpSession getSession() { if (request == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
sm.getString("requestFacade.nullRequest"));
}
// 如果不存在session则创建一个
// session 的实现有两种:一是基于内存的实现,二是基于文件的实现。
return getSession(true);
}
@Override
public HttpSession getSession(boolean create) { if (request == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
sm.getString("requestFacade.nullRequest"));
} if (SecurityUtil.isPackageProtectionEnabled()){
return AccessController.
doPrivileged(new GetSessionPrivilegedAction(create));
} else {
// RequestFacade 是个外观模式实现,核心请求还是会传递给 Request处理的
// org.apache.catalina.connector.Request
return request.getSession(create);
}
} // org.apache.catalina.connector.Request#getSession(boolean)
/**
* @return the session associated with this Request, creating one
* if necessary and requested.
*
* @param create Create a new session if one does not exist
*/
@Override
public HttpSession getSession(boolean create) {
// 由 create 字段决定是否需要创建新的session, 如果不存在的话。
// Session 是tomcat的一个会话实现类,并非对接规范接口类,其会包装一个HttpSession,以便统一交互
// 因为只有 HttpSession 才是 Servlet 的接口规范,在tomcat中会以 StandardSessionFacade 实现接口,其也是一个外观模式的实现,具体工作由 StandardSession 处理。
Session session = doGetSession(create);
if (session == null) {
return null;
}
// 包装 Session 为 HttpSession 规范返回
return session.getSession();
}
// org.apache.catalina.connector.Request#doGetSession
protected Session doGetSession(boolean create) { // There cannot be a session if no context has been assigned yet
// mappingData.context;
Context context = getContext();
if (context == null) {
return (null);
} // Return the current session if it exists and is valid
// 此处检查session有效性时,也会做部分清理工作
if ((session != null) && !session.isValid()) {
session = null;
}
if (session != null) {
return (session);
} // Return the requested session if it exists and is valid
// 获取manager 实例,即真正进行 Session 管理的类,其实主要分两种:1. 基于内存;2. 基于文件的持久化;
Manager manager = context.getManager();
if (manager == null) {
return (null); // Sessions are not supported
}
if (requestedSessionId != null) {
try {
// 如果不是第一次请求,则会带上服务返回的 sessionId, 就会主动查找原来的session
// 从 sessions 中查找即可
session = manager.findSession(requestedSessionId);
} catch (IOException e) {
session = null;
}
if ((session != null) && !session.isValid()) {
session = null;
}
// 后续请求,每次请求都会更新有效时间
if (session != null) {
session.access();
return (session);
}
} // Create a new session if requested and the response is not committed
// 主动请求session时,才会继续后续逻辑
if (!create) {
return (null);
}
if (response != null
&& context.getServletContext()
.getEffectiveSessionTrackingModes()
.contains(SessionTrackingMode.COOKIE)
&& response.getResponse().isCommitted()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
sm.getString("coyoteRequest.sessionCreateCommitted"));
} // Re-use session IDs provided by the client in very limited
// circumstances.
String sessionId = getRequestedSessionId();
if (requestedSessionSSL) {
// If the session ID has been obtained from the SSL handshake then
// use it.
} else if (("/".equals(context.getSessionCookiePath())
&& isRequestedSessionIdFromCookie())) {
/* This is the common(ish) use case: using the same session ID with
* multiple web applications on the same host. Typically this is
* used by Portlet implementations. It only works if sessions are
* tracked via cookies. The cookie must have a path of "/" else it
* won't be provided for requests to all web applications.
*
* Any session ID provided by the client should be for a session
* that already exists somewhere on the host. Check if the context
* is configured for this to be confirmed.
*/
if (context.getValidateClientProvidedNewSessionId()) {
boolean found = false;
for (Container container : getHost().findChildren()) {
Manager m = ((Context) container).getManager();
if (m != null) {
try {
if (m.findSession(sessionId) != null) {
found = true;
break;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore. Problems with this manager will be
// handled elsewhere.
}
}
}
if (!found) {
sessionId = null;
}
}
} else {
// 当session无效时,需要将原来的seesionId置空,删除并新创建一个使用
sessionId = null;
}
// 创建session, StandardManager -> ManagerBase
session = manager.createSession(sessionId); // Creating a new session cookie based on that session
if (session != null
&& context.getServletContext()
.getEffectiveSessionTrackingModes()
.contains(SessionTrackingMode.COOKIE)) {
// 创建cookie信息,与session对应
Cookie cookie =
ApplicationSessionCookieConfig.createSessionCookie(
context, session.getIdInternal(), isSecure());
// 添加到response中,在响应结果一起返回给客户端
response.addSessionCookieInternal(cookie);
} if (session == null) {
return null;
}
// 每次请求session时,必然刷新激活时间,以便判定会话是否超时
session.access();
return session;
}
从上面我们可以看到,session的流程大概是这样的:
1. 先查找是否有session信息存在,如果有则判断是否失效;
2. 如果不存在session或已失效,则使用一个新的sessionId(非必须)创建一个session实例;
3. session创建成功,则将sessionId写入到cookie信息中,以便客户端后续使用;
4. 每次请求完session,必定刷新下访问时间以续期;
session的管理主要有两种实现方式,类图如下:
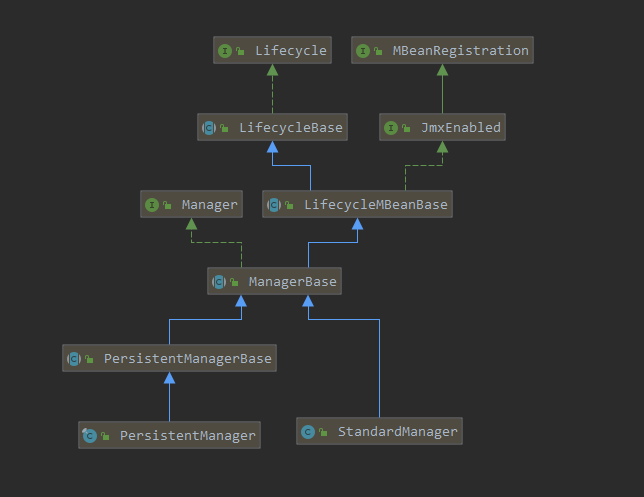
我们先主要以基于内存的实现来理解下session的管理过程。实际上StandardManager基本就依托于 ManagerBase 就实现了Session管理功能,下面我们来看一下其创建session如何?
// org.apache.catalina.session.ManagerBase#createSession
@Override
public Session createSession(String sessionId) {
// 首先来个安全限制,允许同时存在多少会话
// 这个会话实际上代表的是一段时间的有效性,并非真正的用户有效使用在线,所以该值一般要求比预计的数量大些才好
if ((maxActiveSessions >= 0) &&
(getActiveSessions() >= maxActiveSessions)) {
rejectedSessions++;
throw new TooManyActiveSessionsException(
sm.getString("managerBase.createSession.ise"),
maxActiveSessions);
} // Recycle or create a Session instance
// 创建空的session 容器 return new StandardSession(this);
Session session = createEmptySession(); // Initialize the properties of the new session and return it
// 默认30分钟有效期
session.setNew(true);
session.setValid(true);
session.setCreationTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
session.setMaxInactiveInterval(getContext().getSessionTimeout() * 60);
String id = sessionId;
if (id == null) {
// sessionId 为空时,生成一个,随机id
id = generateSessionId();
}
// 设置sessionId, 注意此处不仅仅是set这么简单,其同时会将自身session注册到全局session管理器中.如下文
session.setId(id);
sessionCounter++; SessionTiming timing = new SessionTiming(session.getCreationTime(), 0);
synchronized (sessionCreationTiming) {
// LinkedList, 添加一个,删除一个?
sessionCreationTiming.add(timing);
sessionCreationTiming.poll();
}
return (session); }
// org.apache.catalina.session.StandardSession#setId
/**
* Set the session identifier for this session.
*
* @param id The new session identifier
*/
@Override
public void setId(String id) {
setId(id, true);
}
@Override
public void setId(String id, boolean notify) {
// 如果原来的id不为空,则先删除原有的
if ((this.id != null) && (manager != null))
manager.remove(this); this.id = id;
// 再将自身会话注册到 manager 中,即 sessions 中
if (manager != null)
manager.add(this);
// 通知监听者,这是框架该做好的事(扩展点),不过不是本文的方向,忽略
if (notify) {
tellNew();
}
}
// org.apache.catalina.session.ManagerBase#add
@Override
public void add(Session session) {
// 取出 sessionId, 添加到 sessions 容器,统一管理
sessions.put(session.getIdInternal(), session);
int size = getActiveSessions();
// 刷新最大活跃数,使用双重锁优化更新该值
if( size > maxActive ) {
synchronized(maxActiveUpdateLock) {
if( size > maxActive ) {
maxActive = size;
}
}
}
}
// 查找session也是异常简单,只管从 ConcurrentHashMap 中查找即可
// org.apache.catalina.session.ManagerBase#findSession
@Override
public Session findSession(String id) throws IOException {
if (id == null) {
return null;
}
return sessions.get(id);
}
有兴趣的同学可以看一下sessionId的生成算法:主要保证两点:1. 随机性;2.不可重复性;
// org.apache.catalina.session.ManagerBase#generateSessionId
/**
* Generate and return a new session identifier.
* @return a new session id
*/
protected String generateSessionId() { String result = null; do {
if (result != null) {
// Not thread-safe but if one of multiple increments is lost
// that is not a big deal since the fact that there was any
// duplicate is a much bigger issue.
duplicates++;
}
// 使用 sessionIdGenerator 生成sessionId
result = sessionIdGenerator.generateSessionId();
// 如果已经存在该sessionId, 则重新生成一个
// session 是一个 ConcurrentHashMap 结构数据
} while (sessions.containsKey(result)); return result;
}
// org.apache.catalina.util.SessionIdGeneratorBase#generateSessionId
/**
* Generate and return a new session identifier.
*/
@Override
public String generateSessionId() {
return generateSessionId(jvmRoute);
}
// org.apache.catalina.util.StandardSessionIdGenerator#generateSessionId
@Override
public String generateSessionId(String route) { byte random[] = new byte[16];
// 默认16
int sessionIdLength = getSessionIdLength(); // Render the result as a String of hexadecimal digits
// Start with enough space for sessionIdLength and medium route size
// 创建双倍大小的stringBuilder, 容纳sessionId
StringBuilder buffer = new StringBuilder(2 * sessionIdLength + 20); int resultLenBytes = 0;
//
while (resultLenBytes < sessionIdLength) {
getRandomBytes(random);
for (int j = 0;
j < random.length && resultLenBytes < sessionIdLength;
j++) {
// 转换为16进制
byte b1 = (byte) ((random[j] & 0xf0) >> 4);
byte b2 = (byte) (random[j] & 0x0f);
if (b1 < 10)
buffer.append((char) ('0' + b1));
else
buffer.append((char) ('A' + (b1 - 10)));
if (b2 < 10)
buffer.append((char) ('0' + b2));
else
buffer.append((char) ('A' + (b2 - 10)));
resultLenBytes++;
}
} if (route != null && route.length() > 0) {
buffer.append('.').append(route);
} else {
String jvmRoute = getJvmRoute();
if (jvmRoute != null && jvmRoute.length() > 0) {
buffer.append('.').append(jvmRoute);
}
} return buffer.toString();
}
// org.apache.catalina.util.SessionIdGeneratorBase#getRandomBytes
protected void getRandomBytes(byte bytes[]) {
// 使用 random.nextBytes(), 预生成 random
SecureRandom random = randoms.poll();
if (random == null) {
random = createSecureRandom();
}
random.nextBytes(bytes);
// 添加到 ConcurrentLinkedQueue 队列中,事实上该 random 将会被反复循环使用, poll->add
randoms.add(random);
}
创建好session后,需要进行随时的维护:我们看下tomcat是如何刷新访问时间的?可能比预想的简单,其仅是更新一个访问时间字段,再无其他。
// org.apache.catalina.session.StandardSession#access
/**
* Update the accessed time information for this session. This method
* should be called by the context when a request comes in for a particular
* session, even if the application does not reference it.
*/
@Override
public void access() {
// 更新访问时间
this.thisAccessedTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 访问次数统计,默认不启用
if (ACTIVITY_CHECK) {
accessCount.incrementAndGet();
} }
最后,还需要看下 HttpSession 是如何被包装返回的?
// org.apache.catalina.session.StandardSession#getSession
/**
* Return the <code>HttpSession</code> for which this object
* is the facade.
*/
@Override
public HttpSession getSession() { if (facade == null){
if (SecurityUtil.isPackageProtectionEnabled()){
final StandardSession fsession = this;
facade = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction<StandardSessionFacade>(){
@Override
public StandardSessionFacade run(){
return new StandardSessionFacade(fsession);
}
});
} else {
// 直接使用 StandardSessionFacade 包装即可
facade = new StandardSessionFacade(this);
}
}
return (facade); }
再最后,要说明的是,整个sessions的管理使用一个 ConcurrentHashMap 来存放全局会话信息,sessionId->session实例。
对于同一次http请求中,该session会被存储在当前的Request栈org.apache.catalina.connector.Request#session字段中,从而无需每次深入获取。每个请求进来后,会将session保存在当前的request信息中。
3. 过期session清理?
会话不可能不过期,不过期的也不叫会话了。
会话过期的触发时机主要有三个:1. 每次进行会话调用时,会主动有效性isValid()验证,此时如果发现过期可以主动清理: 2. 后台定时任务触发清理; 3. 启动或停止应用的时候清理;(这对于非内存式的存储会更有用些)
// case1. 请求时验证,如前面所述
// org.apache.catalina.connector.Request#doGetSession
protected Session doGetSession(boolean create) {
...
// Return the current session if it exists and is valid
if ((session != null) && !session.isValid()) {
session = null;
}
if (session != null) {
return (session);
}
...
} // case2. 后台定时任务清理
// org.apache.catalina.session.ManagerBase#backgroundProcess
@Override
public void backgroundProcess() {
// 并非每次定时任务到达时都会进行清理,而是要根据其清理频率设置来运行
// 默认是 6
count = (count + 1) % processExpiresFrequency;
if (count == 0)
processExpires();
}
/**
* Invalidate all sessions that have expired.
*/
public void processExpires() { long timeNow = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 找出所有的sessions, 转化为数组遍历
Session sessions[] = findSessions();
int expireHere = 0 ; if(log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Start expire sessions " + getName() + " at " + timeNow + " sessioncount " + sessions.length);
for (int i = 0; i < sessions.length; i++) {
// 事实上后台任务也是调用 isValid() 方法 进行过期任务清理的
if (sessions[i]!=null && !sessions[i].isValid()) {
expireHere++;
}
}
long timeEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();
if(log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("End expire sessions " + getName() + " processingTime " + (timeEnd - timeNow) + " expired sessions: " + expireHere);
processingTime += ( timeEnd - timeNow ); } //case3. start/stop 时触发过期清理(生命周期事件)
// org.apache.catalina.session.StandardManager#startInternal
/**
* Start this component and implement the requirements
* of {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error
* that prevents this component from being used
*/
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException { super.startInternal(); // Load unloaded sessions, if any
try {
// doLoad() 调用
load();
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error(sm.getString("standardManager.managerLoad"), t);
} setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
} /**
* Load any currently active sessions that were previously unloaded
* to the appropriate persistence mechanism, if any. If persistence is not
* supported, this method returns without doing anything.
*
* @exception ClassNotFoundException if a serialized class cannot be
* found during the reload
* @exception IOException if an input/output error occurs
*/
protected void doLoad() throws ClassNotFoundException, IOException {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Start: Loading persisted sessions");
} // Initialize our internal data structures
sessions.clear(); // Open an input stream to the specified pathname, if any
File file = file();
if (file == null) {
return;
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("standardManager.loading", pathname));
}
Loader loader = null;
ClassLoader classLoader = null;
Log logger = null;
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file.getAbsolutePath());
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis)) {
Context c = getContext();
loader = c.getLoader();
logger = c.getLogger();
if (loader != null) {
classLoader = loader.getClassLoader();
}
if (classLoader == null) {
classLoader = getClass().getClassLoader();
} // Load the previously unloaded active sessions
synchronized (sessions) {
try (ObjectInputStream ois = new CustomObjectInputStream(bis, classLoader, logger,
getSessionAttributeValueClassNamePattern(),
getWarnOnSessionAttributeFilterFailure())) {
Integer count = (Integer) ois.readObject();
int n = count.intValue();
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Loading " + n + " persisted sessions");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
StandardSession session = getNewSession();
session.readObjectData(ois);
session.setManager(this);
sessions.put(session.getIdInternal(), session);
session.activate();
if (!session.isValidInternal()) {
// If session is already invalid,
// expire session to prevent memory leak.
// 主动调用 expire
session.setValid(true);
session.expire();
}
sessionCounter++;
}
} finally {
// Delete the persistent storage file
if (file.exists()) {
file.delete();
}
}
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("No persisted data file found");
}
return;
} if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Finish: Loading persisted sessions");
}
}
// stopInternal() 事件到达时清理 sessions
/**
* Save any currently active sessions in the appropriate persistence
* mechanism, if any. If persistence is not supported, this method
* returns without doing anything.
*
* @exception IOException if an input/output error occurs
*/
protected void doUnload() throws IOException { if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug(sm.getString("standardManager.unloading.debug")); if (sessions.isEmpty()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("standardManager.unloading.nosessions"));
return; // nothing to do
} // Open an output stream to the specified pathname, if any
File file = file();
if (file == null) {
return;
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("standardManager.unloading", pathname));
} // Keep a note of sessions that are expired
ArrayList<StandardSession> list = new ArrayList<>(); try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file.getAbsolutePath());
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos)) { synchronized (sessions) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Unloading " + sessions.size() + " sessions");
}
// Write the number of active sessions, followed by the details
oos.writeObject(Integer.valueOf(sessions.size()));
for (Session s : sessions.values()) {
StandardSession session = (StandardSession) s;
list.add(session);
session.passivate();
session.writeObjectData(oos);
}
}
} // Expire all the sessions we just wrote
// 将所有session失效,实际上应用即将关闭,失不失效的应该也无所谓了
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Expiring " + list.size() + " persisted sessions");
}
for (StandardSession session : list) {
try {
session.expire(false);
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
} finally {
session.recycle();
}
} if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Unloading complete");
}
}
接下来我们看下具体如何清理过期的会话?实际应该就是一个remove的事。
// org.apache.catalina.session.StandardSession#isValid
/**
* Return the <code>isValid</code> flag for this session.
*/
@Override
public boolean isValid() { if (!this.isValid) {
return false;
} if (this.expiring) {
return true;
} if (ACTIVITY_CHECK && accessCount.get() > 0) {
return true;
}
// 超过有效期,主动触发清理
if (maxInactiveInterval > 0) {
int timeIdle = (int) (getIdleTimeInternal() / 1000L);
if (timeIdle >= maxInactiveInterval) {
expire(true);
}
} return this.isValid;
} // org.apache.catalina.session.StandardSession#expire(boolean)
/**
* Perform the internal processing required to invalidate this session,
* without triggering an exception if the session has already expired.
*
* @param notify Should we notify listeners about the demise of
* this session?
*/
public void expire(boolean notify) { // Check to see if session has already been invalidated.
// Do not check expiring at this point as expire should not return until
// isValid is false
if (!isValid)
return;
// 上锁保证线程安全
synchronized (this) {
// Check again, now we are inside the sync so this code only runs once
// Double check locking - isValid needs to be volatile
// The check of expiring is to ensure that an infinite loop is not
// entered as per bug 56339
if (expiring || !isValid)
return; if (manager == null)
return; // Mark this session as "being expired"
expiring = true; // Notify interested application event listeners
// FIXME - Assumes we call listeners in reverse order
Context context = manager.getContext(); // The call to expire() may not have been triggered by the webapp.
// Make sure the webapp's class loader is set when calling the
// listeners
if (notify) {
ClassLoader oldContextClassLoader = null;
try {
oldContextClassLoader = context.bind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, null);
Object listeners[] = context.getApplicationLifecycleListeners();
if (listeners != null && listeners.length > 0) {
HttpSessionEvent event =
new HttpSessionEvent(getSession());
for (int i = 0; i < listeners.length; i++) {
int j = (listeners.length - 1) - i;
if (!(listeners[j] instanceof HttpSessionListener))
continue;
HttpSessionListener listener =
(HttpSessionListener) listeners[j];
try {
context.fireContainerEvent("beforeSessionDestroyed",
listener);
listener.sessionDestroyed(event);
context.fireContainerEvent("afterSessionDestroyed",
listener);
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
try {
context.fireContainerEvent(
"afterSessionDestroyed", listener);
} catch (Exception e) {
// Ignore
}
manager.getContext().getLogger().error
(sm.getString("standardSession.sessionEvent"), t);
}
}
}
} finally {
context.unbind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, oldContextClassLoader);
}
} if (ACTIVITY_CHECK) {
accessCount.set(0);
} // Remove this session from our manager's active sessions
// 从ManagerBase 中删除
manager.remove(this, true); // Notify interested session event listeners
if (notify) {
fireSessionEvent(Session.SESSION_DESTROYED_EVENT, null);
} // Call the logout method
if (principal instanceof TomcatPrincipal) {
TomcatPrincipal gp = (TomcatPrincipal) principal;
try {
gp.logout();
} catch (Exception e) {
manager.getContext().getLogger().error(
sm.getString("standardSession.logoutfail"),
e);
}
} // We have completed expire of this session
setValid(false);
expiring = false; // Unbind any objects associated with this session
String keys[] = keys();
ClassLoader oldContextClassLoader = null;
try {
oldContextClassLoader = context.bind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, null);
for (int i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
removeAttributeInternal(keys[i], notify);
}
} finally {
context.unbind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, oldContextClassLoader);
}
} } // org.apache.catalina.session.ManagerBase#remove(org.apache.catalina.Session, boolean)
@Override
public void remove(Session session, boolean update) {
// If the session has expired - as opposed to just being removed from
// the manager because it is being persisted - update the expired stats
if (update) {
long timeNow = System.currentTimeMillis();
int timeAlive =
(int) (timeNow - session.getCreationTimeInternal())/1000;
updateSessionMaxAliveTime(timeAlive);
expiredSessions.incrementAndGet();
SessionTiming timing = new SessionTiming(timeNow, timeAlive);
synchronized (sessionExpirationTiming) {
sessionExpirationTiming.add(timing);
sessionExpirationTiming.poll();
}
}
// 从sessions中移除session
if (session.getIdInternal() != null) {
sessions.remove(session.getIdInternal());
}
}
清理工作的核心任务没猜错,还是进行remove对应的session, 但作为框架必然会设置很多的扩展点,为各监听器接入的机会。这些点的设计,直接关系到整个功能的好坏了。
4. session如何保证线程安全?
实际是废话,前面已经明显看出,其使用一个 ConcurrentHashMap 作为session的管理容器,而ConcurrentHashMap本身就是线程安全的,自然也就保证了线程安全了。
不过需要注意的是,上面的线程安全是指的不同客户端间的数据是互不影响的。然而对于同一个客户端的重复请求,以上实现并未处理,即可能会生成一次session,也可能生成n次session,不过实际影响不大,因为客户端的状态与服务端的状态都是一致的。
5. 使用持久化方案的session管理实现
默认情况使用内存作为session管理工具,一是方便,二是速度相当快。但是最大的缺点是,其无法实现持久化,即可能停机后信息就丢失了(虽然上面有在停机时做了持久化操作,但仍然是不可靠的)。
所以就有了与之相对的存储方案了:Persistent,它有一个基类 PersistentManagerBase 继承了 ManagerBase,做了些特别的实现:
// 1. session的添加
// 复用 ManagerBase // 2. session的查找
// org.apache.catalina.session.PersistentManagerBase#findSession
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* <p>
* This method checks the persistence store if persistence is enabled,
* otherwise just uses the functionality from ManagerBase.
*/
@Override
public Session findSession(String id) throws IOException {
// 复用ManagerBase, 获取Session实例
Session session = super.findSession(id);
// OK, at this point, we're not sure if another thread is trying to
// remove the session or not so the only way around this is to lock it
// (or attempt to) and then try to get it by this session id again. If
// the other code ran swapOut, then we should get a null back during
// this run, and if not, we lock it out so we can access the session
// safely.
if(session != null) {
synchronized(session){
session = super.findSession(session.getIdInternal());
if(session != null){
// To keep any external calling code from messing up the
// concurrency.
session.access();
session.endAccess();
}
}
}
if (session != null)
return session; // See if the Session is in the Store
// 如果内存中找不到会话信息,从存储中查找,这是主要的区别
session = swapIn(id);
return session;
}
// org.apache.catalina.session.PersistentManagerBase#swapIn
/**
* Look for a session in the Store and, if found, restore
* it in the Manager's list of active sessions if appropriate.
* The session will be removed from the Store after swapping
* in, but will not be added to the active session list if it
* is invalid or past its expiration.
*
* @param id The id of the session that should be swapped in
* @return restored session, or {@code null}, if none is found
* @throws IOException an IO error occurred
*/
protected Session swapIn(String id) throws IOException { if (store == null)
return null; Object swapInLock = null; /*
* The purpose of this sync and these locks is to make sure that a
* session is only loaded once. It doesn't matter if the lock is removed
* and then another thread enters this method and tries to load the same
* session. That thread will re-create a swapIn lock for that session,
* quickly find that the session is already in sessions, use it and
* carry on.
*/
// 额,总之就是有点复杂
synchronized (this) {
swapInLock = sessionSwapInLocks.get(id);
if (swapInLock == null) {
swapInLock = new Object();
sessionSwapInLocks.put(id, swapInLock);
}
} Session session = null; synchronized (swapInLock) {
// First check to see if another thread has loaded the session into
// the manager
session = sessions.get(id); if (session == null) {
Session currentSwapInSession = sessionToSwapIn.get();
try {
if (currentSwapInSession == null || !id.equals(currentSwapInSession.getId())) {
// 从存储中查找session
session = loadSessionFromStore(id);
sessionToSwapIn.set(session); if (session != null && !session.isValid()) {
log.error(sm.getString("persistentManager.swapInInvalid", id));
session.expire();
removeSession(id);
session = null;
}
// 重新加入到内存 sessions 中
if (session != null) {
reactivateLoadedSession(id, session);
}
}
} finally {
sessionToSwapIn.remove();
}
}
} // Make sure the lock is removed
synchronized (this) {
sessionSwapInLocks.remove(id);
} return session; }
private Session loadSessionFromStore(String id) throws IOException {
try {
if (SecurityUtil.isPackageProtectionEnabled()){
return securedStoreLoad(id);
} else {
// 依赖于store的实现了,比如 file, jdbc...
return store.load(id);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
String msg = sm.getString(
"persistentManager.deserializeError", id);
log.error(msg, e);
throw new IllegalStateException(msg, e);
}
}
// store 实现样例: fileStore
// org.apache.catalina.session.FileStore#load
/**
* Load and return the Session associated with the specified session
* identifier from this Store, without removing it. If there is no
* such stored Session, return <code>null</code>.
*
* @param id Session identifier of the session to load
*
* @exception ClassNotFoundException if a deserialization error occurs
* @exception IOException if an input/output error occurs
*/
@Override
public Session load(String id) throws ClassNotFoundException, IOException {
// Open an input stream to the specified pathname, if any
File file = file(id);
if (file == null) {
return null;
} if (!file.exists()) {
return null;
} Context context = getManager().getContext();
Log contextLog = context.getLogger(); if (contextLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
contextLog.debug(sm.getString(getStoreName()+".loading", id, file.getAbsolutePath()));
} ClassLoader oldThreadContextCL = context.bind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, null); try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file.getAbsolutePath());
ObjectInputStream ois = getObjectInputStream(fis)) { StandardSession session = (StandardSession) manager.createEmptySession();
session.readObjectData(ois);
session.setManager(manager);
return session;
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
if (contextLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
contextLog.debug("No persisted data file found");
}
return null;
} finally {
context.unbind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, oldThreadContextCL);
}
} private void reactivateLoadedSession(String id, Session session) {
if(log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug(sm.getString("persistentManager.swapIn", id)); session.setManager(this);
// make sure the listeners know about it.
((StandardSession)session).tellNew();
// 添加回sessions
add(session);
((StandardSession)session).activate();
// endAccess() to ensure timeouts happen correctly.
// access() to keep access count correct or it will end up
// negative
session.access();
session.endAccess();
}
// 3. session 的移除
@Override
public void remove(Session session, boolean update) { super.remove (session, update);
// 和内存的实现差别就是,还要多一个对外部存储的管理维护
if (store != null){
removeSession(session.getIdInternal());
}
}
可以看到, PersistentManager 的实现还是有点复杂的,主要是在安全性和性能之间的平衡,它和 StandardManager 基本是一种包含关系,即除了要维护内存session外,还要维护外部存储的状态。
而现实情况是,既然已经需要自行维护外部状态了,为何还要去使用tomcat自带的session管理呢?而如果站在框架session管理的设计者的角度,这可能也是无可奈何的事。
而在我们自己的session管理实现中,一般的思路还是相通的,创建 -> 查找 -> 维持 -> 删除 。 可以基于数据库,缓存,或者其他,而且相信也不是件难事。
Tomcat session的实现:线程安全与管理的更多相关文章
- Tomcat session集群
author:JevonWei 版权声明:原创作品 环境 tomcatA 172.16.253.108 tomcatB 172.16.253.105 代理服务器 172.16.253.191 Tomc ...
- 关于tomcat session机制梳理
一道题目引起的思考:"tomcat里怎样禁止服务端自己主动创建session". 1背景知识: 要说tomcat的机制.先从session说起. http是无状态协议(http详 ...
- Redis+Tomcat+Nginx集群实现Session共享,Tomcat Session共享
Redis+Tomcat+Nginx集群实现Session共享,Tomcat Session共享 ============================= 蕃薯耀 2017年11月27日 http: ...
- Session会话保持机制的原理与Tomcat Session共享的几种实现方式(Session Cluster、memcached+MSM)
一.Session的定义 在计算机科学中,特别是在网络中,session是两个或更多个通信设备之间或计算机和用户之间的临时和交互式信息交换.session在某个时间点建立,然后在之后的某一时间点拆除. ...
- Java应用服务器之tomcat session server msm搭建配置
在上一篇博客中,我们介绍了tomcat自带的cluster组件配置session replication cluster,回顾请参考https://www.cnblogs.com/qiuhom-187 ...
- .NET组件程序设计之线程、并发管理(二)
.Net组件程序设计之线程.并发管理(二) 2.同步线程 手动同步 监视器 互斥 可等待事件 同步线程 所有的.NET组件都支持在多线程的环境中运行,可以被多个线程并发访问,如果没有线程同步,这样的后 ...
- .Net组件程序设计之线程、并发管理(一)
.Net组件程序设计之线程.并发管理(一) 1.线程 线程 线程的创建 线程的阻塞 线程挂起 线程睡眠 加入线程 线程中止 现在几乎所有的应用程序都是多线程的,给用户看来就是一个应用程序界面(应用程序 ...
- tomcat session cluster
Session的生命周期 以前在学习的时候没怎么注意,今天又回过头来仔细研究研究了一下Session的生命周期. Session存储在服务器端,一般为了防止在服务器的内存中(为了高速存取),Sessi ...
- 【Tomcat】Tomcat Session在Redis共享
参考的优秀文章 Redis-backed non-sticky session store for Apache Tomcat 简单地配置Tomcat Session在Redis共享 我使用的是现有的 ...
随机推荐
- 用pip install不能成功安装时的处理方法
解决办法: pip install pymysql -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple --trusted-host pypi.douban.com
- 0day学习笔记(3)Windows定位API引起的惨案(原理)
段选择器FS与TEB WinNT内核下内存采用保护模式,段寄存器的意义与实模式汇编下的意义不同.另外,FS存的是段选择子,而不是实模式下的高16位基地址. FS寄存器指向当前活动线程的TEB结构(线程 ...
- JavaScript--'data-'的用法(1)
HTML5为我们提供了一个强大的功能,前段也也能实现后台数据库的效果,例如data-xxx <a href="#myModal" data-industry_id=" ...
- linux--配置开发环境 --Nginx篇
安装: 安装好了话,我们的nginx的目录在: /etc/nginx 启动: sudo service nginx start 然后访问我们的页面就可以看到了我们的界面 然后我们配置我们的域名: 我 ...
- 解决laravel5.4视图不生效的坑
遇到这种坑,主要是路由的问题 1.看看是不是单词拼错了 Route::get('/posts/{post}','\App\Http\Controllers\PostController@show'); ...
- java list随机截取(洗牌)
public void solution(){ List<Integer> givenList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3,4,5,6); Collections.sh ...
- Springboot以Tomcat为容器实现http重定向到https的两种方式
1 简介 本文将介绍在Springboot中如何通过代码实现Http到Https的重定向,本文仅讲解Tomcat作为容器的情况,其它容器将在以后一一道来. 建议阅读之前的相关文章: (1) Sprin ...
- 听说你在从事前端开发?那这10个JavaScript的优化问题你不得不知道!
JavaScript的高效优化一直都是我们前端开发中非常重要的工作,也是很多开发人员无法做好的一部分内容,今天我总结了10个优化问题,大家可以参考来做优化,这其中很多问题都是大家经常遇到的哦. ==和 ...
- Python 正则表达式——re模块介绍
Python 正则表达式 re 模块使 Python 语言拥有全部的正则表达式功能,re模块常用方法: re.match函数 re.match从字符串的起始位置匹配,如果起始位置匹配不成功,则matc ...
- laravel 5.5 ajax返回错误信息
前段ajax发送请求 $('#reg_reg').click(function () { var formData = new FormData($( "#reg_form" )[ ...
