Java并发编程 (六) 线程安全策略
个人博客网:https://wushaopei.github.io/ (你想要这里多有)
一、不可变对象-1
有一种安全的发布对象,即不可变对象。1、不可变对象需要满足的条件
① 对象创建以后其状态就不能修改
② 对象所有域都是final类型
③ 对象是正确创建的(在对象创建期间,this引用没有逸出)
2、final关键字:
final 关键字可以用来修饰:类、方法、变量
修饰类:不能被继承,final类中的成员方法都会被隐式的指定为final方法
修饰方法:1、锁定方法不被继承类修改;2、效率
注意:一个类的private方法会被隐式的指定为final方法
修饰变量:基本数据类型变量、引用类型变量
被final修饰的数值不能再被修改;被final修饰的引用类型不能再指向另一个对象。
重点:fianl修饰数据类型变量和引用类型变量的区别
3、fianl的使用代码演示:
@Slf4j
@NoThreadSafe
public class immutableExample1 {
private final static Integer a = 1;
private final static String b = "2";
private final static Map<Integer,Integer> map = Maps.newHashMap();
static {
map.put(1,2);
map.put(3,4);
map.put(5,6);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// a = 2;
// b = "3";
// map = Maps.newHashMap();
map.put(1,3);
log.info("{}",map.get(1));
}
private void test(final int a ){
// a = 1;
}
}执行结果:
17:13:54.256 [main] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.immutable.immutableExample1 - 3
分析:由图中可知,被final修饰的变量无法被重新赋值,被final修饰的map引用类型变量也不能指向新的内存引用。
又由代码执行结果可知,被final修饰的引用数据类型如map的值是可以改变的。
4、常见不可变对象
Collections.unmodifiableXXX : Collection 、List、Set、Map ..,
Guava : ImmutableXXX : Collection 、List、Set、Map....
注意:
使用Collections的unmodifiableXXX生成的引用变量就不能再被修改了;
使用Guava的ImmutableXXX生成的引用变量就不能再被修改了;
5、 Collections.unmodifiableXXX :代码演示:
@Slf4j
@NoThreadSafe
public class immutableExample2 {
private static Map<Integer,Integer> map = Maps.newHashMap();
static {
map.put(1,2);
map.put(3,4);
map.put(5,6);
map = Collections.unmodifiableMap(map);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
map.put(1,3);
log.info("{}",map.get(1));
}
}
执行结果:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException
at java.util.Collections$UnmodifiableMap.put(Collections.java:1457)
at com.mmall.concurrency.example.immutable.immutableExample2.main(immutableExample2.java:31)
Process finished with exit code 1由执行结果可知,被Collections.unmodifiableMap()修改过的map不能再被重新赋值,虽然声明时没有报错,但是编译运行时却抛出了异常。
二、不可变对象-2
1、从源码对原因进行分析:
unmodifiableMap调用了UnmodifiableMap方法;
public static <K,V> Map<K,V> unmodifiableMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
return new UnmodifiableMap<>(m);
}在UnmodifiableMap方法中,进行了序列化已经使用final对传入参数m进行修饰:
private static final long serialVersionUID = -1034234728574286014L;
private final Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m;相当于將原本的map使用另一个map进行替代,并将所有的更新方法在操作时进行异常的抛出,相关源码如下:
@Override
public void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public boolean remove(Object key, Object value) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public V replace(K key, V value) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
.............当第一次声明值时,会对引用变量的长度和数据进行副本备份,如果有第二次修改时,会进行校验,发现传入参数和底层取出的值不同时,抛出异常。
2、ImmutableXXX代码演示:
@Slf4j
@ThreadSafe
public class immutableExample3 {
private final static ImmutableList list = ImmutableList.of(1,2,3);
private final static ImmutableSet set = ImmutableSet.copyOf(list);
private final static ImmutableMap<Integer,Integer> map = ImmutableMap.of(1,2,3,4);
private final static ImmutableMap<Integer,Integer> map2 = ImmutableMap.<Integer,Integer>builder().put(1,2).put(3,4).put(5,6).build();
public static void main(String[] args) {
// list.add(4);
// map.put(1,4);
System.out.println(map.get(3));
}
}ImmutableList 重新赋值测试结果:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException
at com.google.common.collect.ImmutableCollection.add(ImmutableCollection.java:221)
at com.mmall.concurrency.example.immutable.immutableExample3.main(immutableExample3.java:33)
Process finished with exit code 1ImmutableMap重新赋值测试结果:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException
at com.google.common.collect.ImmutableMap.put(ImmutableMap.java:495)
at com.mmall.concurrency.example.immutable.immutableExample3.main(immutableExample3.java:35)
Process finished with exit code 1查询ImmutableMap的value值:
4
Process finished with exit code 0由结果可知,ImmutableXXX声明的对象为不可变对象,是线程安全的,同时不影响值的获取。
三、线程封闭-1
避免并发,除了设置不可变对象,还有线程封闭。
1、什么是线程封闭
所谓线程封闭,就是把对象锁定到一个线程里,只有这个线程可以看到对象,那么,这个对象就算不是线程安全的,也不会出现线程安全的问题了。因为它只能在一个线程内访问。
2、线程封闭共有三种:
第一种线程封闭:
Ad-hoc 线程封闭 : 程序控制实现,最糟糕,忽略
第二种线程封闭:
堆栈封闭:局部变量,无并发问题
多个线程访问一个方法的时候,局部变量都会被拷贝一份到线程的栈中,所以局部变量是不会被多个线程所共享的,因此也就不会出现并发问题。
全局的变量容易出现并发问题。
在一个方法内定义局部变量来完成各种操作,就是属于堆栈封闭的范畴。第三种线程封闭:
ThreadLocal线程封闭:特别好的封闭方法
原因:
ThreadLocal内部维护了一个map,map的key是每一个线程的名称,而map的值就是我们要封闭的对象,每个map中的对象都对应了一个线程中的值,也就是ThreadLocal利用map实现了线程封闭。
3、ThreadLocal线程封闭——代码演示:
package com.mmall.concurrency.example.threadLocal;
import com.mmall.concurrency.annoations.ThreadSafe;
/**
* @ClassName RequestHolder
* @Description TODO
* @Author wushaopei
* @Date 2019/11/1 11:12
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class RequestHolder {
private final static ThreadLocal<Long> requestHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();
//在接口未实际处理之前,在filter中将值添加到ThreadLocal中,等到url被调用处理时,再从ThreadLocal中取出相应的值
public static void add(Long id){
requestHolder.set(id);
}
public static Long getId(){
return requestHolder.get();
}
//在接口真正处理完之后进行处理
public static void remove(){
requestHolder.remove();
}
}Fitler :
package com.mmall.concurrency;
import com.mmall.concurrency.example.threadLocal.RequestHolder;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @ClassName HttpFilter
* @Description TODO
* @Author wushaopei
* @Date 2019/11/1 11:18
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class HttpFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
RequestHolder.add(Thread.currentThread().getId());
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
四、线程封闭-2
1、HttpFilter.java
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
log.info("do filter,{} - {}",Thread.currentThread().getId(),request.getServletPath());
RequestHolder.add(Thread.currentThread().getId());
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);
}2、配置Filter,将HttpFilter添加到容器
@SpringBootApplication
public class ConcurrencyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConcurrencyApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean httpFilter(){
FilterRegistrationBean<Filter> registrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean<>();
registrationBean.setFilter(new HttpFilter());
registrationBean.addUrlPatterns("/threadLocal/*");
return registrationBean;
}
}3、Handler适配器实现接口实现前后的拦截、过滤操作:
package com.mmall.concurrency;
import com.mmall.concurrency.example.threadLocal.RequestHolder;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.HandlerInterceptorAdapter;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
* @ClassName HttpInterceptor
* @Description TODO
* @Author wushaopei
* @Date 2019/11/1 11:25
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j
public class HttpInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
log.info("preHandle");
return true;
}
//接口执行完成后删除ThreadLocal线程变量
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, @Nullable Exception ex) throws Exception {
RequestHolder.remove();
log.info("afterCompletion");
return ;
}
}4、在启动器中将HttpInterceptor 的Bean配置到容器中:
@SpringBootApplication
public class ConcurrencyApplication extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter{
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new HttpInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**");
}
创建ThreadLocal测试接口:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/threadLocal")
public class ThreadLocalController {
@RequestMapping("/test")
@ResponseBody
public Long test(){
return RequestHolder.getId();
}
}启动并执行测试接口:
2019-11-01 12:19:08.757 INFO 23868 --- [p-nio-80-exec-2] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Initializing Servlet 'dispatcherServlet'
2019-11-01 12:19:08.763 INFO 23868 --- [p-nio-80-exec-2] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Completed initialization in 6 ms
2019-11-01 12:19:08.769 INFO 23868 --- [p-nio-80-exec-2] com.mmall.concurrency.HttpFilter : do filter,30 , /threadLocal/test
2019-11-01 12:19:08.779 INFO 23868 --- [p-nio-80-exec-2] com.mmall.concurrency.HttpInterceptor : preHandle
2019-11-01 12:19:08.852 INFO 23868 --- [p-nio-80-exec-2] com.mmall.concurrency.HttpInterceptor : afterCompletio由执行结果可知,使用ThreadLocal实现了线程封闭,以为着ThreadLocal是线程安全的。
5、分析:
实现流程:
当请求进来的时候,通过Filter将线程ID存储到了ThreadLocal里面,当接口被处理调用的时候,就可以从ThreadLocal里去取出线程ID,当接口处理完后,再通过HttpInterception适配器中的afterCompletion方法将线程ID给移除掉。
分析:
这里在使用ThreadLocal的时候,定义了三个方法,分别是从ThreaadLocal里面放数据、移除数据、获取数据,放数据一般是通过Filter来放数据,先拦截住接口,在拦截器里面把数据放进去,数据处理完之后在Interceptor里面将数据移除出去,避免内存泄露。
扩展:
线程封闭技术的常见应用:
数据库连接对应JDBC的Connection对象,Connection对象在实现时并没有对线程安全做太多的处理,在相应的JDBC规范里也没有要求Connection对象一定是线程安全的,实际上在服务器应用程序中线程从连接池获取了一个Connection对象,使用完之后再将对象返回给连接池,由于大多数请求都是采用单线程同步的方式处理的,在Connection对象返回之前,连接池不会将它分配给其他线程,因此这种管理模式在请求时隐含的将对象封闭在线程里面。我们使用Connnection对象虽然本身不是线程安全的,但是通过线程封闭也做到了线程安全。
五、线程不安全类与写法-1
线程不安全的类:如果一个类的对象同时可以被多个线程访问,如果你不做特殊的同步处理。那么,它就容易表现出线程不安全的现象。
如:抛出异常、逻辑处理错误等等。
这种类就成为线程不安全的类。
1、字符串拼接
StringBuilder - > StringBuffer
1) StringBuilder 线程安全代码演示:
package com.mmall.concurrency.example.commonUnsafe;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
/**
* @ClassName StringExample1
* @Description TODO
* @Author wushaopei
* @Date 2019/11/1 12:45
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j
@NoThreadSafe
public class StringExample1 {
//请求总数
public static int clientTotal = 5000;
// 同时并发执行的线程数
public static int threadTotal = 200;
public static StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for (int i = 0 ; i < clientTotal ; i++){
executorService.execute(()->{
try {
semaphore.acquire();
update();
semaphore.release();
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("exception",e);
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executorService.shutdown();
log.info("size:{}",stringBuilder.length());
}
private static void update(){
stringBuilder.append("1");
}
}如果线程安全的话,打印结果应该为5000!
执行打印结果:
12:48:15.598 [main] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.commonUnsafe.StringExample1 - size:4937
Process finished with exit code 0由打印结果可知,size的值小于5000,意味着StringBuilder是线程不安全的类。
2) StringBuffer 线程安全代码演示:
public static StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();执行打印结果:
12:51:06.859 [main] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.commonUnsafe.StringExample2 - size:5000
Process finished with exit code 0由打印结果可知,size的值等于5000,意味着StringBuffer是线程安全的类。
3) StringBuffer和StringBuilder线程分析:

由截图可知,StringBuffer的底层实现方法都添加synchronized同步锁,是线程安全的。

而StringBuilder底层的方法没有添加synchronized同步锁,存在线程安全的问题。
4)为什么java要同时提供StringBuilder和StringBuffer两个类?
之所以java同时提供StringBuilder和StringBuffer两个线程安全和不安全的类,是因为在StringBuffer中,使用synchronized锁机制会导致同时只有一个线程可以操作该对象,对性能和效率有损耗。StringBuffer只有在多线程并发且声明为成员变量时使用就可以保证线程的安全;而在业务层逻辑方法中声明StringBuilder局部变量时,由于存在堆栈封闭的关系,同一时间内只会有一个线程调用该类变量,所以不存在线程安全的问题。
2、日期转换的类
SimpleDateFormat - > JodaTimie
1)SimpleDateFormat类线程安全测试:
@Slf4j
@NoThreadSafe
public class DateFormatExample1 {
//请求总数
public static int clientTotal = 5000;
// 同时并发执行的线程数
public static int threadTotal = 200;
private static SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd");
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for (int i = 0 ; i < clientTotal ; i++){
executorService.execute(()->{
try {
semaphore.acquire();
update();
semaphore.release();
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("exception",e);
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executorService.shutdown();
}
private static void update(){
try {
simpleDateFormat.parse("20191101");
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("parse exception",e);
}
}
}执行结果:
14:25:08.453 [pool-1-thread-162] ERROR com.mmall.concurrency.example.commonUnsafe.DateFormatExample1 - parse exception
java.lang.NumberFormatException: multiple points
at sun.misc.FloatingDecimal.readJavaFormatString(FloatingDecimal.java:1890)
at sun.misc.FloatingDecimal.parseDouble(FloatingDecimal.java:110)
....................
at com.mmall.concurrency.example.commonUnsafe.DateFormatExample1.update(DateFormatExample1.java:51)
at com.mmall.concurrency.example.commonUnsafe.DateFormatExample1.lambda$main$0(DateFormatExample1.java:37)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1142)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:617)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:745)
14:25:08.446 [pool-1-thread-74] ERROR com.mmall.concurrency.example.commonUnsafe.DateFormatExample1 - parse exception
java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: ".20192019E"
at java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(NumberFormatException.java:65)
at java.lang.Long.parseLong(Long.java:578)
..........
at com.mmall.concurrency.example.commonUnsafe.DateFormatExample1.update(DateFormatExample1.java:51)
at com.mmall.concurrency.example.commonUnsafe.DateFormatExample1.lambda$main$0(DateFormatExample1.java:37)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1142)
............由执行结果可知,SimpleDateFormat在进行并发执行时抛出了大量异常,这说明了SimpleDateFormat类的线程是不安全的。SimpleDateFormat声明的实例不能直接以成员变量的形式声明来被多线程使用。
正确使用SimpleDateFormat类,应该以局部变量的方式声明该类的实例:
代码如下:
private static void update(){
try {
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd");
simpleDateFormat.parse("20191101");
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("parse exception",e);
}
}执行结果没有抛出异常:
//空行
Process finished with exit code 0注意:多线程并发使用SimpleDateFormat类时,一定要在方法中以局部变量的方式声明该类的实例。从而避免线程安全的问题。
2)JodaTimie类线程安全测试:
导入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>joda-time</groupId>
<artifactId>joda-time</artifactId>
<version>2.10.5</version>
</dependency>代码段:
//声明DateTimeFormatter实例
private static DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormat.forPattern("yyyyMMdd");
//获取当前线程次序
final int count = i;
//传递线程次序
update(count);
//update方法中日志输出线程执行结果
log.info("{}, {}",i,DateTime.parse("20191101",dateTimeFormatter).toDate());

由执行结果可知,虽然DateTimeFormatter 实例结果是乱序输出的,但是执行线程总数是完全符合要求的,所以DateTimeFormatter的线程是安全的。
六、线程不安全类与写法-2
ArrayList , HashSet , HashMap 等 Collections
1、ArrayList线程安全测试:
public class ArrayListExample {
//请求总数
public static int clientTotal = 5000;
// 同时并发执行的线程数
public static int threadTotal = 200;
private static List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for (int i = 0 ; i < clientTotal ; i++){
int count = i;
executorService.execute(()->{
try {
semaphore.acquire();
update(count);
semaphore.release();
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("exception",e);
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executorService.shutdown();
log.info("size:{}",list.size());
}
private static void update(int i){
list.add(i);
}
}执行并打印结果:
15:02:53.644 [main] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.commonUnsafe.ArrayListExample - size:4892
Process finished with exit code 0由结果可知,size的长度不为5000,说明了ArrayList的add操作在多线程并发环境下是线程不安全的。
2、HashSet线程安全测试:
private static Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
//获取当前线程次序
final int count = i;
//传递线程次序
update(count);
//update方法中日志输出线程执行结果
log.info("size:{}",set.size());
private static void update(int i){
set.add(i);
}执行并打印结果:
15:08:23.554 [main] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.commonUnsafe.HashSetExample - size:4864
Process finished with exit code 0由结果可知,size的长度不为5000,说明了HashSet的add操作在多线程并发环境下也是线程不安全的。
3、HashMap线程安全测试:
private static Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>();
//获取当前线程次序
final int count = i;
//传递线程次序
update(count);
//update方法中日志输出线程执行结果
log.info("size:{}",map.size());private static void update(int i){
map.put(i,i);
}执行并打印结果:
15:16:26.117 [main] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.commonUnsafe.HashMapExample - size:4870
Process finished with exit code 0由结果可知,size的长度不为5000,说明了HashMap的add操作在多线程并发环境下也是线程不安全的。
4、扩展
先检查再执行: if(condition(a)) { handle(a) ; }
七、同步容器-1
线程安全的同步容器:
ArrayList - > Vecotr , Stack
HashMap - > HashTable (key 、value 不能为 null)
Collections.synchronizedXXX(List、Set、Map)
在多线程环境下,要使用ArrayList时,可以使用Vector、Stack替代
在多线程环境下,要使用HashMap时,可以使用HashTable替代
HashTable底层实现使用synchronized进行修饰,同步锁的存在保证了线程的安全。
1、Vector线程安全测试:
@Slf4j
public class VectorExample1 {
//请求总数
public static int clientTotal = 5000;
// 同时并发执行的线程数
public static int threadTotal = 200;
private static Vector<Integer> list = new Vector<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for (int i = 0 ; i < clientTotal ; i++){
int count = i;
executorService.execute(()->{
try {
semaphore.acquire();
update(count);
semaphore.release();
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("exception",e);
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executorService.shutdown();
log.info("size:{}",list.size());
}
private static void update(int i){
list.add(i);
}
}
测试执行结果:
15:35:31.360 [main] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.syncContainer.VectorExample1 - size:5000
Process finished with exit code 0由结果可知,size的长度为5000,说明了Vector的add操作在多线程并发环境下是线程安全的。
注意:即使是线程安全的Vector也可能发生线程不安全的情况,如下演示
@Slf4j
@NoThreadSafe
public class VectorExample2 {
private static Vector<Integer> vector = new Vector<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
while (true){
for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++ ){
vector.add(i);
}
Thread thread1 = new Thread(){
public void run (){
for (int i = 0 ; i < vector.size() ; i++){
vector.remove(i);
}
}
};
Thread thread2 = new Thread(){
public void run (){
for (int i = 0 ; i < vector.size() ; i++){
vector.get(i);
}
}
};
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
}执行结果:
如图,vector的多线程操作发生了异常,全都集中在执行get()操作时,一直发生数组索引越界的异常问题。
原因分析:vector 是一个线程同步容器,所有的remove操作都是有synchronized修饰的,get操作也是有synchronized修饰的,如图:
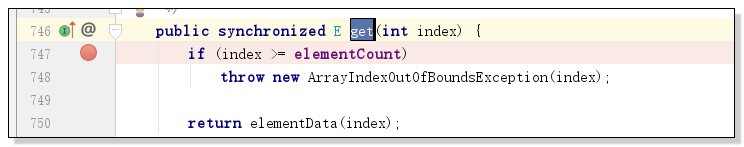

在Vector中由于有synchronized同步锁机制,保证了当前两个线程即thread1 和 thread2 是属于两个独立的同步线程;但是,在实际执行代码的过程中,当thread1执行了remove()删除操作时,thread2正好也执行到了get()方法,两者由于相对独立且同步,所以当thread1删除了某个索引的值时,thread2依旧会去get()获取那个索引位的值,但这时候对应的值已经被删除了,所以java会抛出索引越界的异常来提示用户,当前所要get()的值是不存在的。
2、将HashMap替换成Hashtable实现线程安全:
代码演示:
@Slf4j
@ThreadSafe
public class HashTableExample {
//请求总数
public static int clientTotal = 5000;
// 同时并发执行的线程数
public static int threadTotal = 200;
private static Map<Integer,Integer> map = new Hashtable<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for (int i = 0 ; i < clientTotal ; i++){
int count = i;
executorService.execute(()->{
try {
semaphore.acquire();
update(count);
semaphore.release();
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("exception",e);
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executorService.shutdown();
log.info("size:{}",map.size());
}
private static void update(int i){
map.put(i,i);
}
}
执行结果:
16:07:08.814 [main] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.syncContainer.HashTableExample - size:5000
Process finished with exit code 0由结果可知:size的长度为5000,说明了HashTable的put操作在多线程并发环境下是线程安全的。
源码查看:

由上图可知,HashTable的put、remove等方法的底层实现都是使用synchronized修饰的,是线程安全的。
八、同步容器-2
1、synchronizedList测试线程安全:
@Slf4j
@ThreadSafe
public class CollectionsExample1 {
//请求总数
public static int clientTotal = 5000;
// 同时并发执行的线程数
public static int threadTotal = 200;
private static List<Integer> list = Collections.synchronizedList(Lists.newArrayList());
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for (int i = 0 ; i < clientTotal ; i++){
int count = i;
executorService.execute(()->{
try {
semaphore.acquire();
update(count);
semaphore.release();
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("exception",e);
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executorService.shutdown();
log.info("size:{}",list.size());
}
private static void update(int i){
list.add(i);
}
}
执行测试打印结果:
16:17:49.852 [main] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.syncContainer.CollectionsExample1 - size:5000
Process finished with exit code 0由结果可知:size的长度为5000,说明了synchronizedList的add操作在多线程并发环境下是线程安全的。
2、synchronizedSet测试线程安全:
@Slf4j
@ThreadSafe
public class CollectionsExample2 {
//请求总数
public static int clientTotal = 5000;
// 同时并发执行的线程数
public static int threadTotal = 200;
private static Set<Integer> set = Collections.synchronizedSet(Sets.newHashSet());
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for (int i = 0 ; i < clientTotal ; i++){
int count = i;
executorService.execute(()->{
try {
semaphore.acquire();
update(count);
semaphore.release();
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("exception",e);
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executorService.shutdown();
log.info("size:{}",set.size());
}
private static void update(int i){
set.add(i);
}
}
执行测试打印结果:
16:20:59.015 [main] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.syncContainer.CollectionsExample2 - size:5000
Process finished with exit code 0由结果可知:size的长度为5000,说明了synchronizedSet的add操作在多线程并发环境下是线程安全的。
3、synchronizedMap测试线程安全:
@Slf4j
@NoThreadSafe
public class HashMapExample {
//请求总数
public static int clientTotal = 5000;
// 同时并发执行的线程数
public static int threadTotal = 200;
private static Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for (int i = 0 ; i < clientTotal ; i++){
int count = i;
executorService.execute(()->{
try {
semaphore.acquire();
update(count);
semaphore.release();
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("exception",e);
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executorService.shutdown();
log.info("size:{}",map.size());
}
private static void update(int i){
map.put(i,i);
}
}
执行测试打印结果:
16:23:13.660 [main] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.syncContainer.CollectionsExample13 - size:5000
Process finished with exit code 0由结果可知:size的长度为5000,说明了synchronizedMap的put操作在多线程并发环境下是线程安全的。
九、并发容器及安全共享策略总结
ArrayList - > CopyOnWriteArrayList
HashSet 、TreeSet - > CopyOnWriteArraySet ConcurrentSkipListSet
HashMap 、 TreeMap - > ConcurrentHashMap ConcurrentSkipListMap
1、用CopyOnWriteArrayList 替代ArrayList
1) 使用原理:
写操作时复制,当有新元素添加到CopyOnWriteArrayList时,会从原有数组里面拷贝一份出来,在新的数组上用写操作,写完之后把原来的数组指向新的数组,CopyOnWriteArrayList的整个add()操作都是在锁的保护下进行的,主要是为了避免在多线程情况下复制出多个副本出来把数据搞乱,导致最终返回的数据结果不是我们所期待的。
2) 适用场景:
CopyOnWriteArrayList适合读多写少的场景。3) CopyOnWriteArrayList的设计思想:
第一点:读写分离,让读和写分开;
第二点:最终一致性,因为在copy的过程需要一些时间,而最终一致性保证了数据是对的;
第三点:使用时另外开辟空间,通过这种方式解决掉并发冲突。
CopyOnWriteArrayList读操作时是在原数组上读的,不需要加锁;而写操作的时候需要加锁,以避免产生多个副本出来,影响最终的数据结果。
4) 代码演示验证CopyOnWriteArrayList的写操作线程安全性:
@Slf4j
public class CopyOnWriteArrayListExample {
//请求总数
public static int clientTotal = 5000;
// 同时并发执行的线程数
public static int threadTotal = 200;
private static List<Integer> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for (int i = 0 ; i < clientTotal ; i++){
int count = i;
executorService.execute(()->{
try {
semaphore.acquire();
update(count);
semaphore.release();
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("exception",e);
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executorService.shutdown();
log.info("size:{}",list.size());
}
private static void update(int i){
list.add(i);
}
}
执行测试打印结果:
16:50:23.972 [main] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.CopyOnWriteArrayListExample - size:5000
Process finished with exit code 0由结果可知:size的长度为5000,说明了CopyOnWriteArrayList的add操作在多线程并发环境下是线程安全的。
2、HashSet 、TreeSet - > CopyOnWriteArraySet ConcurrentSkipListSet
1) 代码演示验证CopyOnWriteArraySet的写操作线程安全性:
@Slf4j
public class CopyOnWriteArraySetExample {
//请求总数
public static int clientTotal = 5000;
// 同时并发执行的线程数
public static int threadTotal = 200;
private static Set<Integer> set = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for (int i = 0 ; i < clientTotal ; i++){
int count = i;
executorService.execute(()->{
try {
semaphore.acquire();
update(count);
semaphore.release();
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("exception",e);
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executorService.shutdown();
log.info("size:{}",set.size());
}
private static void update(int i){
set.add(i);
}
}
执行测试打印结果:
16:56:40.047 [main] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArraySetExample - size:5000
Process finished with exit code 0
由结果可知:size的长度为5000,说明了CopyOnWriteArraySet的add操作在多线程并发环境下是线程安全的。
2) 代码演示验证ConcurrentSkipListSet的写操作线程安全性:
@Slf4j
public class ConcurrentSkipListSetExample {
//请求总数
public static int clientTotal = 5000;
// 同时并发执行的线程数
public static int threadTotal = 200;
private static Set<Integer> set = new ConcurrentSkipListSet<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for (int i = 0 ; i < clientTotal ; i++){
int count = i;
executorService.execute(()->{
try {
semaphore.acquire();
update(count);
semaphore.release();
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("exception",e);
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executorService.shutdown();
log.info("size:{}",set.size());
}
private static void update(int i){
set.add(i);
}
}
执行测试打印结果:
16:58:05.936 [main] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.concurrent.ConcurrentSkipListSetExample - size:5000
Process finished with exit code 0由结果可知:size的长度为5000,说明了ConcurrentSkipListSet的add操作在多线程并发环境下是线程安全的。
这里的线程安全仅限于做add操作时,如果是做remove操作,还需要其他锁机制保障线程安全。
3、HashMap 、 TreeMap - > ConcurrentHashMap ConcurrentSkipListMap
对并发要求比较高的时候,建议使用ConcurrentSkipListMap
1) 代码演示验证ConcurrentHashMap的写操作线程安全性:
@Slf4j
public class ConcurrentHashMapExample {
//请求总数
public static int clientTotal = 5000;
// 同时并发执行的线程数
public static int threadTotal = 200;
private static Map<Integer,Integer> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for (int i = 0 ; i < clientTotal ; i++){
int count = i;
executorService.execute(()->{
try {
semaphore.acquire();
update(count);
semaphore.release();
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("exception",e);
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executorService.shutdown();
log.info("size:{}",map.size());
}
private static void update(int i){
map.put(i,i);
}
}
执行测试打印结果:
17:04:16.524 [main] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMapExample - size:5000
Process finished with exit code 0由结果可知:size的长度为5000,说明了ConcurrentHashMap的add操作在多线程并发环境下是线程安全的。
2) 代码演示验证ConcurrentSkipListMap的写操作线程安全性:
@Slf4j
public class ConcurrentSkipListMapExample {
//请求总数
public static int clientTotal = 5000;
// 同时并发执行的线程数
public static int threadTotal = 200;
private static Map<Integer,Integer> map = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for (int i = 0 ; i < clientTotal ; i++){
int count = i;
executorService.execute(()->{
try {
semaphore.acquire();
update(count);
semaphore.release();
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("exception",e);
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executorService.shutdown();
log.info("size:{}",map.size());
}
private static void update(int i){
map.put(i,i);
}
}
执行测试打印结果:
17:06:13.842 [main] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.concurrent.ConcurrentSkipListMapExample - size:5000
Process finished with exit code 0由结果可知:size的长度为5000,说明了ConcurrentSkipListMap的add操作在多线程并发环境下是线程安全的。
总结:

安全共享对象策略 - 总结:
线程限制:一个被线程限制的对象,由线程独占,并且只能被占有它的线程修改
共享只读:一个共享只读的对象,在没有额外同步的情况下,可以被多个线程并发访问,但是任何线程都不能修改它
线程安全对象:一个线程安全的对象或者容器,在内部通过同步机制来保证线程安全,所以其他线程无需额外的同步就可以通过公共接口随意访问它
被守护对象:被守护对象只能通过获取特定的锁来访问
Java并发编程 (六) 线程安全策略的更多相关文章
- Java并发编程:线程控制
在上一篇文章中(Java并发编程:线程的基本状态)我们介绍了线程状态的 5 种基本状态以及线程的声明周期.这篇文章将深入讲解Java如何对线程进行状态控制,比如:如何将一个线程从一个状态转到另一个状态 ...
- Java并发编程:线程池的使用
Java并发编程:线程池的使用 在前面的文章中,我们使用线程的时候就去创建一个线程,这样实现起来非常简便,但是就会有一个问题: 如果并发的线程数量很多,并且每个线程都是执行一个时间很短的任务就结束了, ...
- Java并发编程:线程间协作的两种方式:wait、notify、notifyAll和Condition
Java并发编程:线程间协作的两种方式:wait.notify.notifyAll和Condition 在前面我们将了很多关于同步的问题,然而在现实中,需要线程之间的协作.比如说最经典的生产者-消费者 ...
- Java并发编程:线程池的使用(转)
Java并发编程:线程池的使用 在前面的文章中,我们使用线程的时候就去创建一个线程,这样实现起来非常简便,但是就会有一个问题: 如果并发的线程数量很多,并且每个线程都是执行一个时间很短的任务就结束了, ...
- Java 并发编程:线程间的协作(wait/notify/sleep/yield/join)
Java并发编程系列: Java 并发编程:核心理论 Java并发编程:Synchronized及其实现原理 Java并发编程:Synchronized底层优化(轻量级锁.偏向锁) Java 并发编程 ...
- (转)Java并发编程:线程池的使用
背景:线程池在面试时候经常遇到,反复出现的问题就是理解不深入,不能做到游刃有余.所以这篇博客是要深入总结线程池的使用. ThreadPoolExecutor的继承关系 线程池的原理 1.线程池状态(4 ...
- Java并发编程:线程池的使用(转载)
转载自:https://www.cnblogs.com/dolphin0520/p/3932921.html Java并发编程:线程池的使用 在前面的文章中,我们使用线程的时候就去创建一个线程,这样实 ...
- Java并发编程:线程池的使用(转载)
文章出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/dolphin0520/p/3932921.html Java并发编程:线程池的使用 在前面的文章中,我们使用线程的时候就去创建一个线程,这样实 ...
- [转]Java并发编程:线程池的使用
Java并发编程:线程池的使用 在前面的文章中,我们使用线程的时候就去创建一个线程,这样实现起来非常简便,但是就会有一个问题: 如果并发的线程数量很多,并且每个线程都是执行一个时间很短的任务就结束了, ...
随机推荐
- 整型和浮点型与QByteArray的转换
目录 QByteArray 整型 QByteArray 浮点型 QByteArray QByteArray The QByteArray class provides an array of byte ...
- [hdu1847]博弈,推理
题意:一堆石子,有n个,两个人轮流取,每次都只能取2的幂次方个数,不能取的人输 思路:首先0是必败态,2的所有幂次都是必胜态.由于选的数模3只能是1或2,恰好又都是2的幂次,0,.3都为必败态,猜想3 ...
- python100例 11-20
011 兔子问题 题目:古典问题:有一对兔子,从出生后第3个月起每个月都生一对兔子,小兔子长到第三个月后每个月又生一对兔子,假如兔子都不死,问每个月的兔子总数为多少? f1=1 f2=1 for i ...
- POI 导入excel数据自动封装成model对象--介绍
1.项目开发中,导入输入应该是常用的基本功能.我们经常会使用excel将数据导入到数据库,在导入之前必须得将excel数据转换成javaBean对象 2.由于此功能经常使用,所以开发此工具类方便日后轻 ...
- React:form
表单控件: input 文档在介绍控件之前,先提到了react组件自身的一个特点:状态由state掌控,改变组件状态只能用setState方法. 而在html的表单里,input.radio.chec ...
- 适配器模式C++实现
目录 类适配器 对象适配器 类适配器 #include <iostream> using namespace std; // Target class Target { public: v ...
- Django之form表单常用字段与插件
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse from django import forms from app01 import models f ...
- STM32 Keil 软件仿真设置
设置 Dialog.DLL 分别为:DARMSTM.DLL和TARMSTM.DLL, Parameter 均为:-pSTM32F103RC,用于设置支持芯片的软硬件仿真
- Spring 基于 Java 的配置
前面已经学习如何使用 XML 配置文件来配置 Spring bean. 基于 Java 的配置可以达到基于XML配置的相同效果. 基于 Java 的配置选项,可以使你在不用配置 XML 的情况下编写大 ...
- Spring 由构造函数自动装配
Spring 由构造函数自动装配,这种模式与 byType 非常相似,但它应用于构造器参数. Spring 容器看作 beans,在 XML 配置文件中 beans 的 autowire 属性设置为 ...
