c语言之学生管理系统
0x00 学生管理系统
说到学生管理系统,对于每一个初学c语言的人都是一道不得不过的砍。不过,学习c,我觉得我们都应该写一个学生管理系统,至于为什么,我想倘若连一个学生管理系统都写不好,哪么他的c是不过关的,当然,写出来也只是初步了解c而已。对于初学c,通过写一个简单的学生管理系统我们可以来练习和熟悉基本的语法,理解链表这种数据结构,查找、删除等操作,以及和数组的区别。
话不多说,这次写的学生管理系统是基于单向链表实现的,单向链表的内容可以查看之我前写的c语言之单向链表。
0x01 环境
我所有的代码都是在linux下编写的,编译器使用的是gcc,若移植到windows下,请做简单修改。
我的环境:
$ uname -a
Linux kali 4.19.0-kali5-amd64 #1 SMP Debian 4.19.37-5kali1 (2019-06-20) x86_64 GNU/Linux
$ gcc --version
gcc (Debian 9.2.1-30) 9.2.1 20200224
Copyright (C) 2019 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. There is NO
warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
0x02 定义数据结构
这里为了简化,使用的学生结构的成员仅有学号和姓名,由于我们使用list.h所以必须定义学生结构的比较、摧毁和打印函数。
点击查看list.h
#ifndef LINK_H
#define LINK_H
typedef struct node//链表元素的结构
{
void *data;//节点中的数据域,设置为无类型指针,数据类型大小由使用者定义
struct node *next;//指向下一节点的指针
}Node;
typedef struct list//链表的结构
{
int size;//链表中节点个数
void (*destroy)(void data);//由于链表节点中的数据是用户自定义的,故需要调用者提供释放空间的函数
void (print_data)(const void data);//同,由用户自定义打印数据的函数
int (match)(const void *key1, const void *key2);//同,由用户自定义数据的比较方式
Node *head;//记录链表的头部位置
Node *tail;//记录链表的尾部位置
}List;
extern void list_init(List list, void (destroy)(void data), void (print_data)(const void data),
int (match)(const void *key1, const void *key2));//初始化一个链表
extern int list_ins_head(List *list, const void *data);//链表的插入,将节点从头部插入
extern int list_ins_tail(List *list, const void *data);//链表的插入,将节点从尾部插入
extern int list_ins_sort(List *list, const void data);//链表的插入,插入后链表是一个有序的链表
extern void list_search(List *list, const void data);//在链表中查找指定数据,若找到返回数据的地址
extern void list_remove(List *list, const void *data);//在链表中删除指定数据,若找到删除节点并将数据地址返回
extern void list_reverse(List *list);//将链表逆置
extern void list_sort(List *list);//将链表按照一定方式排序
extern void print_list(List *list);//打印链表
extern void list_destroy(List *list);//删除整个链表
define list_size(list) (list->size) //返回链表节点个数
endif // LINK_H
/*这是一个学生结构体*/
typedef struct stu
{
int stu_id;//学生的id
char name[32];//学生的姓名
}STU;
/*学生信息的打印*/
void print_stu(const void *data)
{
STU *temp = (STU *)data;
printf("id = %d, name = %s\n", temp->stu_id, temp->name);
return;
}
/*学生之间的比较,此处以学生id做比较,若想使用其他字段比较,另行定义*/
int cmp_stu(const void *key1, const void *key2)
{
STU *stu1 = (STU *)key1;
STU *stu2 = (STU *)key2;
if(stu1->stu_id > stu2->stu_id)
return 1;
else if(stu1->stu_id < stu2->stu_id)
return -1;
else
return 0;
}
/*学生节点的摧毁,由于学生节点比较简单,直接对free函数简单封装一下*/
void destroy(void *data)
{
if(data != NULL)
{
free(data);
data = NULL;
}
return;
}
0x03 主菜单
/*打印菜单*/
void menu()
{
printf("------------------menu----------------------\n");
printf("|打印菜单: menu |\n");
printf("|打印列表: print |\n");
printf("|插入数据: insert |\n");
printf("|查找数据: search |\n");
printf("|删除数据: remove |\n");
printf("|逆置数据: reverse |\n");
printf("|排序数据: sort |\n");
printf("|清空屏幕: clear |\n");
printf("|退出程序: quit |\n");
printf("--------------------------------------------\n");
return;
}
运行效果:

0x04 主体逻辑
其实,剩下的极为简单,这些只是业务逻辑的处理,还有就是对链表接口的利用。
int main()
{
menu();//打印菜单
List list;//定义一个链表
list_init(&list, destroy, print_stu, cmp_stu);//初始化链表
while(1)
{
char cmd[32] = "";
printf("请输入你要执行的命令:\n");
printf("$ ");
scanf("%s", cmd);
if(strcmp(cmd, "print") == 0)//打印学生信息
{
print_list(&list);
}
else if(strcmp(cmd, "insert") == 0)//插入学生信息
{
STU *temp = (STU *)calloc(1, sizeof (STU));//初始化一个学生信息
printf("请输入需要插入的数据:\n");
printf("-> ");
scanf("%d %s",&temp->stu_id, temp->name);
list_ins_head(&list, temp); //使用链表的头部插入
//list_ins_tail(&list, temp); //使用链表的尾部插入
//list_ins_sort(&list, temp); //使用链表的有序插入
}
else if(strcmp(cmd, "search") == 0)//查找学生信息
{
printf("请输入查找学员的学号:\n");
printf("-> ");
STU *temp = (STU *)calloc(1, sizeof (STU));//感觉此处极为丑陋,为了查找学号,还必须分配一个完整的学生信息空间,可是若不分配,及必须破坏链表,无法单独的抽象出链表结构
scanf("%d", &temp->stu_id);
strcpy(temp->name, "");
STU *ret = (STU *)list_search(&list, temp);
if(ret != NULL)
printf("id = %d, name = %s\n", ret->stu_id, ret->name);
else
printf("not found\n");
destroy(temp);//由于仅仅是比较,学生信息只是临时的,所以要释放堆空间
}
else if(strcmp(cmd, "remove") == 0)//删除学生信息
{
printf("请输入删除学员的学号:\n");
printf("-> ");
STU *temp = (STU *)calloc(1, sizeof (STU));
scanf("%d", &temp->stu_id);
strcpy(temp->name, "");
STU *ret = (STU *)list_remove(&list, temp);//由于返回值是一个指向学生信息的空间,并且已经被删除,所以需要手动释放
if(ret != NULL)
{
printf("removed:id = %d, name = %s\n", ret->stu_id, ret->name);
list.destroy(ret);//释放掉返回的空间
}
else
printf("not found\n");
destroy(temp);
}
else if(strcmp(cmd, "reverse") == 0)//逆置链表
{
list_reverse(&list);
}
else if(strcmp(cmd, "sort") == 0)//对学生信息排序
{
list_sort(&list);
}
else if(strcmp(cmd, "clear") == 0)//使用系统调用,对控制台清屏
{
system("clear");//windows下使用system("cls");
}
else if(strcmp(cmd, "menu") == 0)
{
menu();
}
else if(strcmp(cmd, "quit") == 0)//退出程序
{
list_destroy(&list);//在程序退出前,清理链表内存
printf("byebye!\n");
break;
}
else
{
printf("请输入正确指令!\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
0x05 运行结果


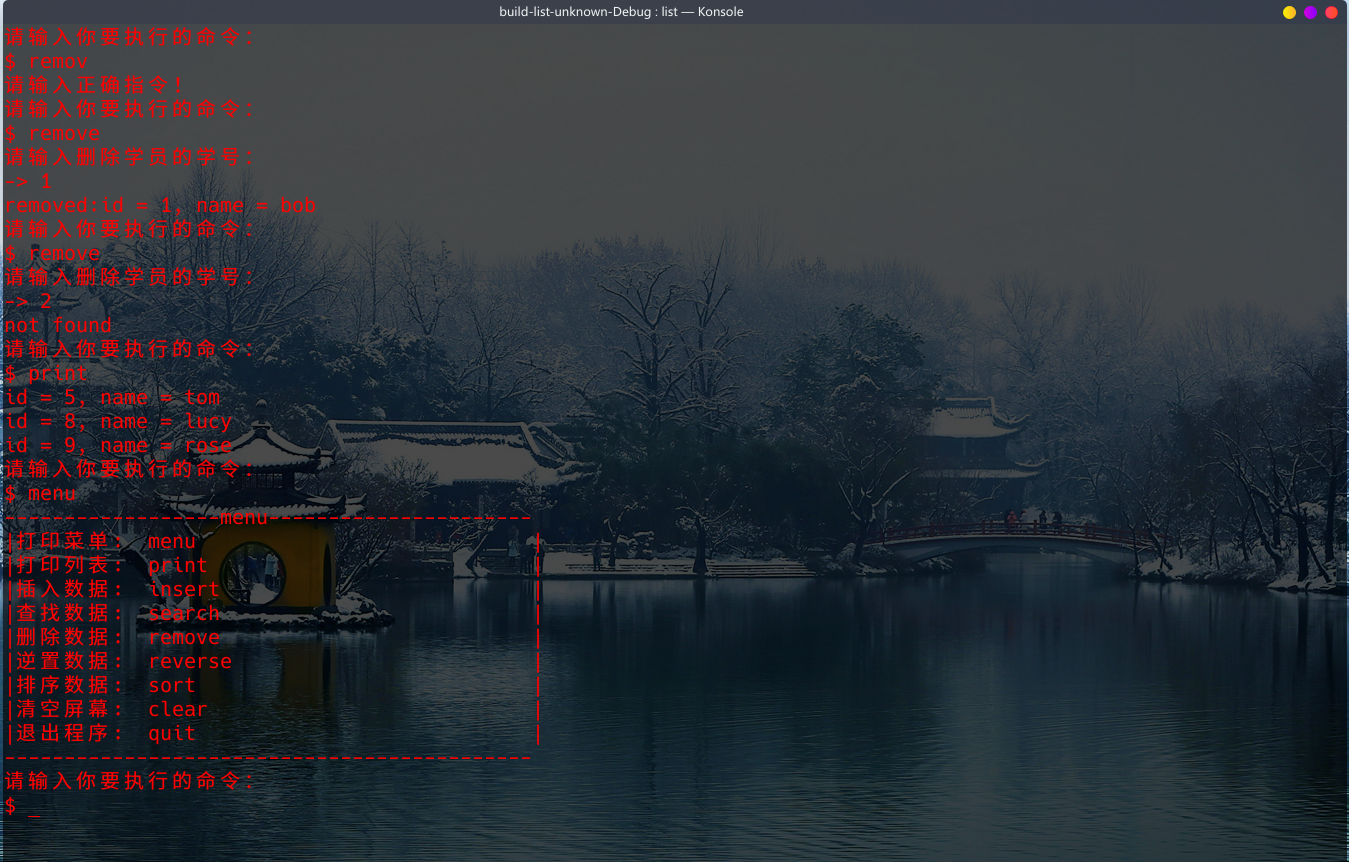
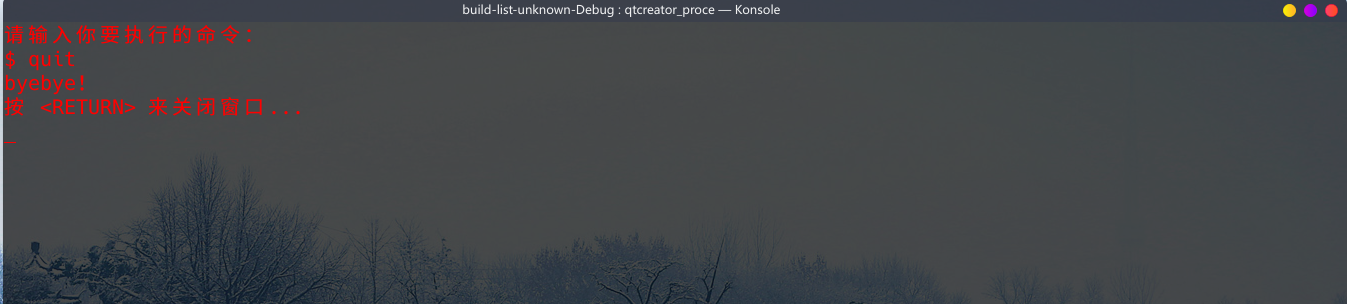
0x06 总结
学生管理系统还不是很完善,有很多细节可以扣,容错方面是肯定不够的,另外我们没有对学生信息存储,可以使用文件或数据库。
其实,学生管理系统只是形式,我们只要学会链表的增删改查,可以随意更改,可以是书籍管理系统、电影管理系统等。
附,源码:
#ifndef LINK_H
#define LINK_H
typedef struct node//链表元素的结构
{
void *data;//节点中的数据域,设置为无类型指针,数据类型大小由使用者定义
struct node *next;//指向下一节点的指针
}Node;
typedef struct list//链表的结构
{
int size;//链表中节点个数
void (*destroy)(void *data);//由于链表节点中的数据是用户自定义的,故需要调用者提供释放空间的函数
void (*print_data)(const void *data);//同,由用户自定义打印数据的函数
int (*match)(const void *key1, const void *key2);//同,由用户自定义数据的比较方式
Node *head;//记录链表的头部位置
Node *tail;//记录链表的尾部位置
}List;
extern void list_init(List *list, void (*destroy)(void *data), void (*print_data)(const void *data), \
int (*match)(const void *key1, const void *key2));//初始化一个链表
extern int list_ins_head(List *list, const void *data);//链表的插入,将节点从头部插入
extern int list_ins_tail(List *list, const void *data);//链表的插入,将节点从尾部插入
extern int list_ins_sort(List *list, const void *data);//链表的插入,插入后链表是一个有序的链表
extern void* list_search(List *list, const void *data);//在链表中查找指定数据,若找到返回数据的地址
extern void* list_remove(List *list, const void *data);//在链表中删除指定数据,若找到删除节点并将数据地址返回
extern void list_reverse(List *list);//将链表逆置
extern void list_sort(List *list);//将链表按照一定方式排序
extern void print_list(List *list);//打印链表
extern void list_destroy(List *list);//删除整个链表
#define list_size(list) (list->size) //返回链表节点个数
#endif // LINK_H
#include "list.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
void list_init(List *list, void (*destroy)(void *data), void (*print_data)(const void *data), \
int (*match)(const void *key1, const void *key2))
{
list->size = 0;
list->head = NULL;
list->tail = NULL;
list->match = match;
list->destroy = destroy;
list->print_data = print_data;
return;
}
void print_list(List *list)
{
if(list->head == NULL)//链表为空
{
printf("list is empty\n");
}
else //链表非空
{
Node * p_cur = list->head;
while (p_cur)
{
list->print_data(p_cur->data);
p_cur = p_cur->next;
}
}
return;
}
/*在链表的头部插入数据*/
int list_ins_head(List *list, const void *data)
{
Node *new_node = (Node *)calloc(1, sizeof (Node)); //创建插入的节点
if(new_node == NULL)
return -1;
new_node->data = (void *)data;//关联节点与数据
/*
if(list_size(list) == 0)//链表为空时,插入节点
{
list->tail = new_node;
new_node->next = NULL;
list->head = new_node;
}
else //链表非空时将节点插入头部
{
new_node->next = list->head;
list->head = new_node;
}
*/
if(list_size(list) == 0)//链表为空时,插入节点
list->tail = new_node;
new_node->next = list->head;
list->head = new_node;
list->size ++;
return 0;
}
/*在链表的尾部插入数据*/
int list_ins_tail(List *list, const void *data)
{
Node *new_node = (Node *)calloc(1, sizeof (Node)); //创建插入的节点
if(new_node == NULL)
return -1;
new_node->data = (void *)data;//关联节点与数据
if(list_size(list) == 0)
list->head = new_node;
else
list->tail->next = new_node;
list->tail = new_node;
new_node->next = NULL;
list->size ++;
return 0;
}
/*在链表的有序插入数据*/
int list_ins_sort(List *list, const void *data)
{
Node *new_node = (Node *)calloc(1, sizeof (Node)); //创建插入的节点
if(new_node == NULL)
return -1;
new_node->data = (void *)data;//关联节点与数据
if(list_size(list) == 0)//链表为空时,插入节点
{
list->tail = new_node;
new_node->next = NULL;
list->head = new_node;
}
else//链表非空时
{
Node *p_cur = list->head;
Node *p_pre = list->head;
while(p_cur != NULL && list->match(new_node->data, p_cur->data) > 0)//查找链表的插入位置
{
p_pre = p_cur;
p_cur = p_cur->next;
}
if(p_cur != NULL)//插入位置在头部和中间时
{
if(p_cur == list->head)//插入位置在头部
{
new_node->next = list->head;
list->head = new_node;
}
else//位置在链表中间
{
new_node->next = p_pre->next;
p_pre->next = new_node;
}
}
else//插入位置在链表尾部
{
list->tail->next = new_node;
list->tail = new_node;
new_node = NULL;
}
}
list->size ++;
return 0;
}
/*查找链表中与数据匹配的节点,并返回节点指针*/
void* list_search(List *list, const void *data)
{
if(list_size(list) == 0)
{
printf("list is empty\n");
return NULL;
}
else
{
Node *p_cur = list->head;
while(p_cur != NULL && list->match(p_cur->data, data) != 0)//查找数据在链表中的位置
p_cur = p_cur->next;
if(p_cur != NULL)//找到返回数据地址,否则返回NULL
return p_cur->data;
else
return NULL;
}
}
/*删除指定数据的节点*/
void* list_remove(List *list, const void *data)
{
void *old_data = NULL;
Node *p_cur = list->head;
Node *p_pre = list->head;
while (p_cur != NULL && list->match(p_cur->data, data) !=0)
{
p_pre = p_cur;
p_cur = p_cur->next;
}
if(p_cur != NULL && list->match(p_cur->data, data) ==0)//删除位置在头部和中间时
{
if(p_cur == list->head)//删除位置在头部
{
list->head = p_cur->next;
if(p_cur->next == NULL)
list->tail = NULL;
}
else//中部时或尾部
{
p_pre->next = p_cur->next;
if(p_cur->next == NULL)
list->tail = p_pre;
}
old_data = p_cur->data;
free(p_cur);
list->size --;
}
return old_data;
}
void list_reverse(List *list)
{
if(list_size(list) != 0)
{
Node *p_pre = list->head;
Node *p_cur = list->head->next;
list->head->next = NULL;
list->tail = list->head;
while(p_cur!= NULL)
{
p_pre = p_cur;
p_cur = p_cur->next;
p_pre->next = list->head;
list->head = p_pre;
}
}
return;
}
void list_sort(List *list)
{
if(list_size(list) != 0)
{
Node *p_i = list->head;
while(p_i->next != NULL)
{
Node *p_min = p_i;
Node *p_j = p_min->next;
while (p_j != NULL)
{
if(list->match(p_min->data, p_j->data) > 0)
p_min = p_j;
p_j = p_j->next;
}
if(p_min != p_i)
{
void *data = p_i->data;
p_i->data = p_min->data;
p_min->data = data;
}
p_i = p_i->next;
}
}
return;
}
void list_destroy(List *list)
{
Node *p_cur = list->head;
while (p_cur != NULL)
{
list->head = list->head->next;
list->destroy(p_cur->data);//释放节点中的数据
free(p_cur);//释放节点
p_cur = list->head;
}
memset(list, 0, sizeof (List));
return;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "list.h"
typedef struct stu
{
int stu_id;
char name[32];
}STU;
void print_stu(const void *data)
{
STU *temp = (STU *)data;
printf("id = %d, name = %s\n", temp->stu_id, temp->name);
return;
}
int cmp_stu(const void *key1, const void *key2)
{
STU *stu1 = (STU *)key1;
STU *stu2 = (STU *)key2;
if(stu1->stu_id > stu2->stu_id)
return 1;
else if(stu1->stu_id < stu2->stu_id)
return -1;
else
return 0;
}
void destroy(void *data)
{
if(data != NULL)
{
free(data);
data = NULL;
}
return;
}
void menu()
{
printf("------------------menu----------------------\n");
printf("|打印菜单: menu |\n");
printf("|打印列表: print |\n");
printf("|插入数据: insert |\n");
printf("|查找数据: search |\n");
printf("|删除数据: remove |\n");
printf("|逆置数据: reverse |\n");
printf("|排序数据: sort |\n");
printf("|清空屏幕: clear |\n");
printf("|退出程序: quit |\n");
printf("--------------------------------------------\n");
return;
}
int main()
{
menu();
List list;
list_init(&list, destroy, print_stu, cmp_stu);
while(1)
{
char cmd[32] = "";
printf("请输入你要执行的命令:\n");
printf("$ ");
scanf("%s", cmd);
if(strcmp(cmd, "print") == 0)
{
print_list(&list);
}
else if(strcmp(cmd, "insert") == 0)
{
STU *temp = (STU *)calloc(1, sizeof (STU));
printf("请输入需要插入的数据:\n");
printf("-> ");
scanf("%d %s",&temp->stu_id, temp->name);
list_ins_head(&list, temp);
//list_ins_tail(&list, temp);
//list_ins_sort(&list, temp);
}
else if(strcmp(cmd, "search") == 0)
{
printf("请输入查找学员的学号:\n");
printf("-> ");
STU *temp = (STU *)calloc(1, sizeof (STU));
scanf("%d", &temp->stu_id);
strcpy(temp->name, "");
STU *ret = (STU *)list_search(&list, temp);
if(ret != NULL)
printf("id = %d, name = %s\n", ret->stu_id, ret->name);
else
printf("not found\n");
destroy(temp);
}
else if(strcmp(cmd, "remove") == 0)
{
printf("请输入删除学员的学号:\n");
printf("-> ");
STU *temp = (STU *)calloc(1, sizeof (STU));
scanf("%d", &temp->stu_id);
strcpy(temp->name, "");
STU *ret = (STU *)list_remove(&list, temp);
if(ret != NULL)
{
printf("removed:id = %d, name = %s\n", ret->stu_id, ret->name);
list.destroy(ret);
}
else
printf("not found\n");
destroy(temp);
}
else if(strcmp(cmd, "reverse") == 0)
{
list_reverse(&list);
}
else if(strcmp(cmd, "sort") == 0)
{
list_sort(&list);
}
else if(strcmp(cmd, "clear") == 0)
{
system("clear");
}
else if(strcmp(cmd, "menu") == 0)
{
menu();
}
else if(strcmp(cmd, "quit") == 0)
{
list_destroy(&list);
printf("byebye!\n");
break;
}
else
{
printf("请输入正确指令!\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
c语言之学生管理系统的更多相关文章
- C语言强化——学生管理系统
系统模块设计 a.预处理模块 系统在启动时会根据配置文件里的内容去相应文件里去加载账户信息和学生信息. b.登陆模块 输入用户名和密码,输密码的时候用"*" 代表用户当前输入的内容 ...
- 用C语言关于学生管理系统的几种实现方法(一位数组,二维数组,指针,结构体)
一位数组: #include <stdio.h> #include<string.h> #define N 5 void luru(float s[],int n); void ...
- 学生管理系统-火车订票系统 c语言课程设计
概要: C 语言课程设计一---学生管理系统 使使用 C 语言实现学生管理系统.系统实现对学生的基本信息和考试成绩的 管理.采用终端命令界面,作为系统的输入输出界面.采用文件作为信息存储介质. 功能描 ...
- #006 C语言大作业学生管理系统第三天
还差最后两部分 读取文件 恢复删除的学生信息 先学会处理文件的 知识点,再继续跟着视频做这个作业. 应该明天周六能把视频里手把手教的学生管理系统敲完 第二周尽量自己能完成C语言课本最后面那道学生管理系 ...
- 学生管理系统(C语言简单实现)
仅供借鉴.仅供借鉴.仅供借鉴(整理了一下大一C语言每个章节的练习题.没得题目.只有程序了) 文章目录 1 .实训名称 2.实训目的及要求 3. 源码 4.实验小结 1 .实训名称 实训12:文件 2. ...
- #007 C语言大作业学生管理系统第四天
第四天还差恢复已删除学生功能 对于我来说,已经开始很复杂了. 小细节太重要了,边写边出错 1 #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #inc ...
- #004 C语言大作业学生管理系统试着做
链表不会用 文件不会使 在这种情况下就边写边做 希望这个月能做完这个作业 #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<st ...
- 学生管理系统 Python语言
def show_student(): print(('*'*20).center(55)) print('1.添加学生信息'.center(50)) print('2.修改学生信息'.center( ...
- C语言版本学生信息管理系统
仍然有一些小bug,后续会发布OC完善版的图书馆管理系统,欢迎批评指正. #include <stdio.h> void menu_choose(); typedef struct { i ...
随机推荐
- 吴裕雄--天生自然C语言开发: 输入 & 输出
#include <stdio.h> int main() { ; printf("Number = %d", testInteger); ; } #include & ...
- ODT(区间覆盖问题)
解释:先留坑 题目:https://www.cometoj.com/contest/73/problem/D?problem_id=4120 #include<bits/stdc++.h> ...
- pycharm打印出的汉字显示乱码
pycharm未配置时,默认配置为: 打印汉字时显示乱码 简单设置即可 这下以后就没有问题了.
- centos jdk
yum list java* yum install xxx -y java -version /* 可省略 */ vi /etc/profile export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/ ...
- hdu5452
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5452 题意:给个图T(图G的最小生成树),然后再给定图G的剩余边,问你从图T中当且割一条边的情况再割图G中不属于 ...
- cs231n spring 2017 lecture2 Image Classification
1. 相比于传统的人工提取特征(边.角等),深度学习是一种Data-Driven Approach.深度学习有统一的框架,喂不同的数据集,可以训练识别不同的物体.而人工提取特征的方式很脆弱,换一个物体 ...
- spring事务管理(xml配置)与spring自带连接数据库JdbcTemplate
什么是事务,很通俗的话来说就是,我们日常生活中总会出现在银行转账的业务,加入A向B转账100元,此时A的账户中应该减少100元,B的账户中增加100元,但是如果在A转完账B还没有接受的时候,服务器出现 ...
- Warning: $HADOOP_HOME is deprecated. hadoop解决方法补充版
下面的解决方案我亲自试了没有问题:可行,但是对于初学者来说肯定会有一个疑问:这个.bash_profile文件到底在哪呢:其实很简单: 当前用户的.bash_profile在/home/用户/下,系统 ...
- Java IO: 管道
原文链接 作者: Jakob Jenkov 译者: 李璟(jlee381344197@gmail.com) Java IO中的管道为运行在同一个JVM中的两个线程提供了通信的能力.所以管道也可以作为 ...
- excel中ppmt/pmt/ipmt的计算方式
参考来源: https://www.experts-exchange.com/articles/1948/A-Guide-to-the-PMT-FV-IPMT-and-PPMT-Functions.h ...
