Kerbernetes的Service资源管理
Kerbernetes的Service资源管理
作者:尹正杰
版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任。
一.Service概述
1>.为什么需要Service资源
我们知道在Kubernetes当中运行的基本单元是Pod,其它资源都是为了丰富Pod本身的应用而实现的,比如Service可以为Pod提供一个固定的访问接口,并且尝试着能够为Pod动态变动提供一个服务发现机制的基础单元。 在K8S之上服务就是指Service资源,而服务注册,服务发现都是借助于Service在K8S集群上所跑的CoreDNS服务实现的,因此CoreDNS也是围绕我们的基础服务构建的。 Pod对象的动态性会给客户端带来困扰:
Pod资源对象存在生命周期且不可重现,必要对仅能创建一个新的替代者。
Pod对象在其控制器进行应用规模进行伸缩时,同一个应用程序的Pod对象会增加或减少。
Service资源为动态管理的Pod对象添加一个有着固定访问入口的抽象层:
Service通过标签选择器关联至拥有相关标签的Pod对象。
客户端向Service进行请求,而非目标Pod对象。
2>.Service及Proxy Mode
简单来讲,一个Service对象就是工作节点上的一组iptables或者ipvs规则,用于将到达Service对象IP地址的流量调度转发至相应的Endpoint对象指向的IP地址和端口之上。 工作与每个工作节点的kube-proxy组件通过API service持续健康着各Service及其关联的Pod对象,并将其创建或变动实时反映至当前工作节点上相应的iptables或者ipvs规则。 kube-proxy把请求代理至相应端点的方式有三种:userspace(用户空间,目前已经被废弃),iptables和ipvs。
3>.Service的代理代理模型
userspace代理模型:
userspace是指Linux操作系统上的"用户空间"。
对于每个Service对象,kube-proxy会随机打开一个本地端口,任何到达此代理端口的连接请求都将被通过SNAT转发至当前Service资源对象的后端各Pod对象。
Kubernetes 1.1及之前版本的默认模型,默认调度算法是轮询(round-robin)
kube-proxy还会为此类的Service对象创建iptables规则以捕获达到ClusterIP和端口的流量。 iptables代理模型:
对于每个Service对象,kube-proxy会创建iptables规则直接捕获到达ClusterIP和Port的流量,并将其重定向至当前Service对象的后端Pod资源。
对于每个Endpoints对象,Service资源会为其创建iptables规则并关联至挑选的的后端Pod资源对象;
相对于用户空间模型来说,iptables模型无需将流量再用户空间和内核空间来回切换,因此也就更为高效和可靠。 ipvs代理模型:
Kubernetes字1.9-alpha起引入ipvs代理模式,且自1.11版本起成为默认设置。
kube-proxy跟踪API Server上Service和Endpoints对象的变动,据此来调用netlink接口创建ipvs规则,并确保与API Server中的变动保持同步。
它与iptables规则的不同之处仅在于其请求流量的调度功能由ipvs实现,余下的其它功能仍由iptables完成。
类似于iptable模型,ipvs构建与netfilter的钩子函数之上,但它使用hash表作为底层数据结构并工作于内核空间,因此具有流量转发速度快,规则同步性能好的特性;
另外,ipvs支持众多的调度算法,例如:rr,lc,dh,sh,sed和nq等。
二.定义Service资源案例
编写服务(Service)规范:
selector
ports 不带选择器的服务(Service):
服务通常抽象地访问Kubernetes Pods,但它们也可以抽象其他类型的后端。
您希望在生产中有一个外部数据库集群,但在测试中使用自己的数据库。
您要将服务指向另一个命名空间或另一个群集上的服务。
你把你的工作量导入了Kubernetes ,你的一些后端运行在Kubernetes 之外。
在这些场景中,您可以在不使用选择器的情况下定义服务:
由于此服务没有选择器,因此不会创建相应的Endpoints对象。
您可以手动将服务映射到自己的特定Endpoints对象。
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain service
KIND: Service
VERSION: v1 DESCRIPTION:
Service is a named abstraction of software service (for example, mysql)
consisting of local port (for example ) that the proxy listens on, and
the selector that determines which pods will answer requests sent through
the proxy. FIELDS:
apiVersion <string>
APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation of an
object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest internal
value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources kind <string>
Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this object
represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client submits
requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds metadata <Object>
Standard object's metadata. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata spec <Object>
Spec defines the behavior of a service.
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status status <Object>
Most recently observed status of the service. Populated by the system.
Read-only. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status [root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain service
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain service.apiVersion
KIND: Service
VERSION: v1 FIELD: apiVersion <string> DESCRIPTION:
APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation of an
object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest internal
value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain service.apiVersion
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain service.kind
KIND: Service
VERSION: v1 FIELD: kind <string> DESCRIPTION:
Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this object
represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client submits
requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain service.kind
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain service.metadata
KIND: Service
VERSION: v1 RESOURCE: metadata <Object> DESCRIPTION:
Standard object's metadata. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata ObjectMeta is metadata that all persisted resources must have, which
includes all objects users must create. FIELDS:
annotations <map[string]string>
Annotations is an unstructured key value map stored with a resource that
may be set by external tools to store and retrieve arbitrary metadata. They
are not queryable and should be preserved when modifying objects. More
info: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/annotations clusterName <string>
The name of the cluster which the object belongs to. This is used to
distinguish resources with same name and namespace in different clusters.
This field is not set anywhere right now and apiserver is going to ignore
it if set in create or update request. creationTimestamp <string>
CreationTimestamp is a timestamp representing the server time when this
object was created. It is not guaranteed to be set in happens-before order
across separate operations. Clients may not set this value. It is
represented in RFC3339 form and is in UTC. Populated by the system.
Read-only. Null for lists. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata deletionGracePeriodSeconds <integer>
Number of seconds allowed for this object to gracefully terminate before it
will be removed from the system. Only set when deletionTimestamp is also
set. May only be shortened. Read-only. deletionTimestamp <string>
DeletionTimestamp is RFC date and time at which this resource will be
deleted. This field is set by the server when a graceful deletion is
requested by the user, and is not directly settable by a client. The
resource is expected to be deleted (no longer visible from resource lists,
and not reachable by name) after the time in this field, once the
finalizers list is empty. As long as the finalizers list contains items,
deletion is blocked. Once the deletionTimestamp is set, this value may not
be unset or be set further into the future, although it may be shortened or
the resource may be deleted prior to this time. For example, a user may
request that a pod is deleted in seconds. The Kubelet will react by
sending a graceful termination signal to the containers in the pod. After
that seconds, the Kubelet will send a hard termination signal (SIGKILL)
to the container and after cleanup, remove the pod from the API. In the
presence of network partitions, this object may still exist after this
timestamp, until an administrator or automated process can determine the
resource is fully terminated. If not set, graceful deletion of the object
has not been requested. Populated by the system when a graceful deletion is
requested. Read-only. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata finalizers <[]string>
Must be empty before the object is deleted from the registry. Each entry is
an identifier for the responsible component that will remove the entry from
the list. If the deletionTimestamp of the object is non-nil, entries in
this list can only be removed. Finalizers may be processed and removed in
any order. Order is NOT enforced because it introduces significant risk of
stuck finalizers. finalizers is a shared field, any actor with permission
can reorder it. If the finalizer list is processed in order, then this can
lead to a situation in which the component responsible for the first
finalizer in the list is waiting for a signal (field value, external
system, or other) produced by a component responsible for a finalizer later
in the list, resulting in a deadlock. Without enforced ordering finalizers
are free to order amongst themselves and are not vulnerable to ordering
changes in the list. generateName <string>
GenerateName is an optional prefix, used by the server, to generate a
unique name ONLY IF the Name field has not been provided. If this field is
used, the name returned to the client will be different than the name
passed. This value will also be combined with a unique suffix. The provided
value has the same validation rules as the Name field, and may be truncated
by the length of the suffix required to make the value unique on the
server. If this field is specified and the generated name exists, the
server will NOT return a - instead, it will either return Created
or with Reason ServerTimeout indicating a unique name could not be
found in the time allotted, and the client should retry (optionally after
the time indicated in the Retry-After header). Applied only if Name is not
specified. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#idempotency generation <integer>
A sequence number representing a specific generation of the desired state.
Populated by the system. Read-only. labels <map[string]string>
Map of string keys and values that can be used to organize and categorize
(scope and select) objects. May match selectors of replication controllers
and services. More info: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/labels managedFields <[]Object>
ManagedFields maps workflow-id and version to the set of fields that are
managed by that workflow. This is mostly for internal housekeeping, and
users typically shouldn't need to set or understand this field. A workflow
can be the user's name, a controller's name, or the name of a specific
apply path like "ci-cd". The set of fields is always in the version that
the workflow used when modifying the object. name <string>
Name must be unique within a namespace. Is required when creating
resources, although some resources may allow a client to request the
generation of an appropriate name automatically. Name is primarily intended
for creation idempotence and configuration definition. Cannot be updated.
More info: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/identifiers#names namespace <string>
Namespace defines the space within each name must be unique. An empty
namespace is equivalent to the "default" namespace, but "default" is the
canonical representation. Not all objects are required to be scoped to a
namespace - the value of this field for those objects will be empty. Must
be a DNS_LABEL. Cannot be updated. More info:
http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/namespaces ownerReferences <[]Object>
List of objects depended by this object. If ALL objects in the list have
been deleted, this object will be garbage collected. If this object is
managed by a controller, then an entry in this list will point to this
controller, with the controller field set to true. There cannot be more
than one managing controller. resourceVersion <string>
An opaque value that represents the internal version of this object that
can be used by clients to determine when objects have changed. May be used
for optimistic concurrency, change detection, and the watch operation on a
resource or set of resources. Clients must treat these values as opaque and
passed unmodified back to the server. They may only be valid for a
particular resource or set of resources. Populated by the system.
Read-only. Value must be treated as opaque by clients and . More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#concurrency-control-and-consistency selfLink <string>
SelfLink is a URL representing this object. Populated by the system.
Read-only. DEPRECATED Kubernetes will stop propagating this field in 1.20
release and the field is planned to be removed in 1.21 release. uid <string>
UID is the unique in time and space value for this object. It is typically
generated by the server on successful creation of a resource and is not
allowed to change on PUT operations. Populated by the system. Read-only.
More info: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/identifiers#uids [root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain service.metadata
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain service.spec
KIND: Service
VERSION: v1 RESOURCE: spec <Object> DESCRIPTION:
Spec defines the behavior of a service.
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status ServiceSpec describes the attributes that a user creates on a service. FIELDS:
clusterIP <string>
clusterIP is the IP address of the service and is usually assigned randomly
by the master. If an address is specified manually and is not in use by
others, it will be allocated to the service; otherwise, creation of the
service will fail. This field can not be changed through updates. Valid
values are "None", empty string (""), or a valid IP address. "None" can be
specified for headless services when proxying is not required. Only applies
to types ClusterIP, NodePort, and LoadBalancer. Ignored if type is
ExternalName. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#virtual-ips-and-service-proxies externalIPs <[]string>
externalIPs is a list of IP addresses for which nodes in the cluster will
also accept traffic for this service. These IPs are not managed by
Kubernetes. The user is responsible for ensuring that traffic arrives at a
node with this IP. A common example is external load-balancers that are not
part of the Kubernetes system. externalName <string>
externalName is the external reference that kubedns or equivalent will
return as a CNAME record for this service. No proxying will be involved.
Must be a valid RFC- hostname (https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc1123) and
requires Type to be ExternalName. externalTrafficPolicy <string>
externalTrafficPolicy denotes if this Service desires to route external
traffic to node-local or cluster-wide endpoints. "Local" preserves the
client source IP and avoids a second hop for LoadBalancer and Nodeport type
services, but risks potentially imbalanced traffic spreading. "Cluster"
obscures the client source IP and may cause a second hop to another node,
but should have good overall load-spreading. healthCheckNodePort <integer>
healthCheckNodePort specifies the healthcheck nodePort for the service. If
not specified, HealthCheckNodePort is created by the service api backend
with the allocated nodePort. Will use user-specified nodePort value if
specified by the client. Only effects when Type is set to LoadBalancer and
ExternalTrafficPolicy is set to Local. ipFamily <string>
ipFamily specifies whether this Service has a preference for a particular
IP family (e.g. IPv4 vs. IPv6). If a specific IP family is requested, the
clusterIP field will be allocated from that family, if it is available in
the cluster. If no IP family is requested, the cluster's primary IP family
will be used. Other IP fields (loadBalancerIP, loadBalancerSourceRanges,
externalIPs) and controllers which allocate external load-balancers should
use the same IP family. Endpoints for this Service will be of this family.
This field is immutable after creation. Assigning a ServiceIPFamily not
available in the cluster (e.g. IPv6 in IPv4 only cluster) is an error
condition and will fail during clusterIP assignment. loadBalancerIP <string>
Only applies to Service Type: LoadBalancer LoadBalancer will get created
with the IP specified in this field. This feature depends on whether the
underlying cloud-provider supports specifying the loadBalancerIP when a
load balancer is created. This field will be ignored if the cloud-provider
does not support the feature. loadBalancerSourceRanges <[]string>
If specified and supported by the platform, this will restrict traffic
through the cloud-provider load-balancer will be restricted to the
specified client IPs. This field will be ignored if the cloud-provider does
not support the feature." More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/access-application-cluster/configure-cloud-provider-firewall/ ports <[]Object>
The list of ports that are exposed by this service. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#virtual-ips-and-service-proxies publishNotReadyAddresses <boolean>
publishNotReadyAddresses, when set to true, indicates that DNS
implementations must publish the notReadyAddresses of subsets for the
Endpoints associated with the Service. The default value is false. The
primary use case for setting this field is to use a StatefulSet's Headless
Service to propagate SRV records for its Pods without respect to their
readiness for purpose of peer discovery. selector <map[string]string>
Route service traffic to pods with label keys and values matching this
selector. If empty or not present, the service is assumed to have an
external process managing its endpoints, which Kubernetes will not modify.
Only applies to types ClusterIP, NodePort, and LoadBalancer. Ignored if
type is ExternalName. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/ sessionAffinity <string>
Supports "ClientIP" and "None". Used to maintain session affinity. Enable
client IP based session affinity. Must be ClientIP or None. Defaults to
None. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#virtual-ips-and-service-proxies sessionAffinityConfig <Object>
sessionAffinityConfig contains the configurations of session affinity. topologyKeys <[]string>
topologyKeys is a preference-order list of topology keys which
implementations of services should use to preferentially sort endpoints
when accessing this Service, it can not be used at the same time as
externalTrafficPolicy=Local. Topology keys must be valid label keys and at
most keys may be specified. Endpoints are chosen based on the first
topology key with available backends. If this field is specified and all
entries have no backends that match the topology of the client, the service
has no backends for that client and connections should fail. The special
value "*" may be used to mean "any topology". This catch-all value, if
used, only makes sense as the last value in the list. If this is not
specified or empty, no topology constraints will be applied. type <string>
type determines how the Service is exposed. Defaults to ClusterIP. Valid
options are ExternalName, ClusterIP, NodePort, and LoadBalancer.
"ExternalName" maps to the specified externalName. "ClusterIP" allocates a
cluster-internal IP address for load-balancing to endpoints. Endpoints are
determined by the selector or if that is not specified, by manual
construction of an Endpoints object. If clusterIP is "None", no virtual IP
is allocated and the endpoints are published as a set of endpoints rather
than a stable IP. "NodePort" builds on ClusterIP and allocates a port on
every node which routes to the clusterIP. "LoadBalancer" builds on NodePort
and creates an external load-balancer (if supported in the current cloud)
which routes to the clusterIP. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#publishing-services-service-types [root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain service.spec
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain service.status
KIND: Service
VERSION: v1 RESOURCE: status <Object> DESCRIPTION:
Most recently observed status of the service. Populated by the system.
Read-only. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status ServiceStatus represents the current status of a service. FIELDS:
loadBalancer <Object>
LoadBalancer contains the current status of the load-balancer, if one is
present. [root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain service.status
1>.创建pod
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# vim /yinzhengjie/data/k8s/manifests/basic/pod/mynginx-deploy.yaml
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# cat /yinzhengjie/data/k8s/manifests/basic/pod/mynginx-deploy.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: mynginx-deploy
namespace: myservice
spec:
replicas:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: mynginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: mynginx
spec:
containers:
- name: mynginx
image: nginx:1.14-alpine
ports:
- containerPort:
name: http
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# vim /yinzhengjie/data/k8s/manifests/basic/pod/mynginx-deploy.yaml
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl create namespace myservice
namespace/myservice created
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl apply -f /yinzhengjie/data/k8s/manifests/basic/pod/mynginx-deploy.yaml
deployment.apps/mynginx-deploy created
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get pod -n myservice -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
mynginx-deploy-55ffb645f8-cpjrf / Running 30s 10.244.1.11 node201.yinzhengjie.org.cn <none> <none>
mynginx-deploy-55ffb645f8-gbvdt / Running 30s 10.244.2.10 node202.yinzhengjie.org.cn <none> <none>
mynginx-deploy-55ffb645f8-ptm8h / Running 30s 10.244.3.4 node203.yinzhengjie.org.cn <none> <none>
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl apply -f /yinzhengjie/data/k8s/manifests/basic/pod/mynginx-deploy.yaml
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get pod -n myservice -o wide --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES LABELS
mynginx-deploy-55ffb645f8-cpjrf / Running 7m38s 10.244.1.11 node201.yinzhengjie.org.cn <none> <none> app=mynginx,pod-template-hash=55ffb645f8
mynginx-deploy-55ffb645f8-gbvdt / Running 7m38s 10.244.2.10 node202.yinzhengjie.org.cn <none> <none> app=mynginx,pod-template-hash=55ffb645f8
mynginx-deploy-55ffb645f8-ptm8h / Running 7m38s 10.244.3.4 node203.yinzhengjie.org.cn <none> <none> app=mynginx,pod-template-hash=55ffb645f8
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get pod -n myservice -o wide --show-labels
2>.定义service
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# vim /yinzhengjie/data/k8s/manifests/basic/service/mynginx-service.yaml
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# cat /yinzhengjie/data/k8s/manifests/basic/service/mynginx-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mynginx-service
namespace: myservice
spec:
ports:
- name: http
prot:
targetPort:
selector:
app: mynginx
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# vim /yinzhengjie/data/k8s/manifests/basic/service/mynginx-service.yaml
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get service -n myservice
No resources found in myservice namespace.
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl apply -f /yinzhengjie/data/k8s/manifests/basic/service/mynginx-service.yaml
service/mynginx-service created
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get service -n myservice
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
mynginx-service ClusterIP 10.102.60.144 <none> /TCP 3s
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl apply -f /yinzhengjie/data/k8s/manifests/basic/service/mynginx-service.yaml
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get service -n myservice
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
mynginx-service ClusterIP 10.102.60.144 <none> /TCP 3s
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl describe service mynginx-service -n myservice
Name: mynginx-service
Namespace: myservice
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration:
{"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Service","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"mynginx-service","namespace":"myservice"},"spec":{"ports":[{"name...
Selector: app=mynginx
Type: ClusterIP
IP: 10.102.60.144
Port: http /TCP
TargetPort: /TCP
Endpoints: 10.244.1.11:,10.244.2.10:,10.244.3.4:
Session Affinity: None
Events: <none>
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl describe service mynginx-service -n myservice
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl describe service mynginx-service -n myservice
Name: mynginx-service
Namespace: myservice
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration:
{"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Service","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"mynginx-service","namespace":"myservice"},"spec":{"ports":[{"name...
Selector: app=mynginx
Type: ClusterIP
IP: 10.102.60.144
Port: http /TCP
TargetPort: /TCP
Endpoints: 10.244.1.11:,10.244.2.10:,10.244.3.4:
Session Affinity: None
Events: <none>
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get endpoints -n myservice
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
mynginx-service 10.244.1.11:,10.244.2.10:,10.244.3.4: 3m52s
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get endpoints -n myservice
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get endpoints -n myservice
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
mynginx-service 10.244.1.11:,10.244.2.10:,10.244.3.4: 4m45s
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl describe endpoints -n myservice
Name: mynginx-service
Namespace: myservice
Labels: <none>
Annotations: endpoints.kubernetes.io/last-change-trigger-time: --08T01::51Z
Subsets:
Addresses: 10.244.1.11,10.244.2.10,10.244.3.4
NotReadyAddresses: <none>
Ports:
Name Port Protocol
---- ---- --------
http TCP Events: <none>
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl describe endpoints -n myservice
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get endpoints -n myservice -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
items:
- apiVersion: v1
kind: Endpoints
metadata:
annotations:
endpoints.kubernetes.io/last-change-trigger-time: "2020-02-08T01:26:51Z"
creationTimestamp: "2020-02-08T01:26:51Z"
name: mynginx-service
namespace: myservice
resourceVersion: ""
selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/myservice/endpoints/mynginx-service
uid: 07866fcb--4d8d-94f6-0af4d3324a5f
subsets:
- addresses:
- ip: 10.244.1.11
nodeName: node201.yinzhengjie.org.cn
targetRef:
kind: Pod
name: mynginx-deploy-55ffb645f8-cpjrf
namespace: myservice
resourceVersion: ""
uid: 938de275-fa19-4e66-95e0-a4afdf3b64c3
- ip: 10.244.2.10
nodeName: node202.yinzhengjie.org.cn
targetRef:
kind: Pod
name: mynginx-deploy-55ffb645f8-gbvdt
namespace: myservice
resourceVersion: ""
uid: 7cbac635-fae3--aae2-090a75b0b346
- ip: 10.244.3.4
nodeName: node203.yinzhengjie.org.cn
targetRef:
kind: Pod
name: mynginx-deploy-55ffb645f8-ptm8h
namespace: myservice
resourceVersion: ""
uid: 39eeaa6f-6d8a--a9e5-d2fed13091a0
ports:
- name: http
port:
protocol: TCP
kind: List
metadata:
resourceVersion: ""
selfLink: ""
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get endpoints -n myservice -o yaml
三.定义Service资源类型案例
使用"service.spec.type"确定服务的公开方式。默认为ClusterIP。有效选项包括ExternalName、ClusterIP、NodePort和LoadBalancer。
详情可参考官网:https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#publishing-services-service-types
1>.Service的类型概述
ClusterIP:
客户端Pod对象访问服务端Pod对象时不会进行源地址转换;换句话说,使用ClusterIP创建的IP地址只能在集群内部使用,在外部是无法访问的。
二者在同一主机时,源地址为客户端Pod地址。
二者在不同主机时,源地址为客户端Pod所在节点的flannel或cni接口的地址。 NodePort:
外部客户端的请求要发往某特定的节点的"<NodeIP>:<NodeOPort>"。
源地址转为当前节点的IP。
目标地址转换为Pod对象IP。 LoadBalancer:
为NodePort类型引入自动管理的外部负载均衡器,向底层cloud provider的API发送请求,由其按需创建(LBaas是需要收费的哟),有必要的话还得做高可用。
用户也可以手动提供负载均衡器,但他不再属于LoadBalancer类型。一般情况下使用这种类型相对较少,因为公有云是要收费的,大多数公司的运维工程师为了给公司节省成本可能得手动部署了,而且手动创建的可维护性更大。 ExternalName:
将集群外部Service引入几千年内容供各Pod客户端使用。
2>.配置NodePort案例
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# cat /yinzhengjie/data/k8s/manifests/basic/service/mynginx-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mynginx-service
namespace: myservice
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port:
nodePort:
targetPort:
selector:
app: mynginx
type: NodePort
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# cat /yinzhengjie/data/k8s/manifests/basic/service/mynginx-service.yaml
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl apply -f /yinzhengjie/data/k8s/manifests/basic/service/mynginx-service.yaml
service/mynginx-service created
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get service -n myservice
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
mynginx-service NodePort 10.102.98.128 <none> :/TCP 19s
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl apply -f /yinzhengjie/data/k8s/manifests/basic/service/mynginx-service.yaml

3>.创建endpoint资源
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain endpoints
KIND: Endpoints
VERSION: v1 DESCRIPTION:
Endpoints is a collection of endpoints that implement the actual service.
Example: Name: "mysvc", Subsets: [ { Addresses: [{"ip": "10.10.1.1"},
{"ip": "10.10.2.2"}], Ports: [{"name": "a", "port": }, {"name": "b",
"port": }] }, { Addresses: [{"ip": "10.10.3.3"}], Ports: [{"name": "a",
"port": }, {"name": "b", "port": }] }, ] FIELDS:
apiVersion <string>
APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation of an
object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest internal
value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources kind <string>
Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this object
represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client submits
requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds metadata <Object>
Standard object's metadata. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata subsets <[]Object>
The set of all endpoints is the union of all subsets. Addresses are placed
into subsets according to the IPs they share. A single address with
multiple ports, some of which are ready and some of which are not (because
they come from different containers) will result in the address being
displayed in different subsets for the different ports. No address will
appear in both Addresses and NotReadyAddresses in the same subset. Sets of
addresses and ports that comprise a service. [root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain endpoints
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain endpoints.apiVersion
KIND: Endpoints
VERSION: v1 FIELD: apiVersion <string> DESCRIPTION:
APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation of an
object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest internal
value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain endpoints.apiVersion
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain endpoints.kind
KIND: Endpoints
VERSION: v1 FIELD: kind <string> DESCRIPTION:
Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this object
represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client submits
requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain endpoints.kind
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain endpoints.metadata
KIND: Endpoints
VERSION: v1 RESOURCE: metadata <Object> DESCRIPTION:
Standard object's metadata. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata ObjectMeta is metadata that all persisted resources must have, which
includes all objects users must create. FIELDS:
annotations <map[string]string>
Annotations is an unstructured key value map stored with a resource that
may be set by external tools to store and retrieve arbitrary metadata. They
are not queryable and should be preserved when modifying objects. More
info: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/annotations clusterName <string>
The name of the cluster which the object belongs to. This is used to
distinguish resources with same name and namespace in different clusters.
This field is not set anywhere right now and apiserver is going to ignore
it if set in create or update request. creationTimestamp <string>
CreationTimestamp is a timestamp representing the server time when this
object was created. It is not guaranteed to be set in happens-before order
across separate operations. Clients may not set this value. It is
represented in RFC3339 form and is in UTC. Populated by the system.
Read-only. Null for lists. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata deletionGracePeriodSeconds <integer>
Number of seconds allowed for this object to gracefully terminate before it
will be removed from the system. Only set when deletionTimestamp is also
set. May only be shortened. Read-only. deletionTimestamp <string>
DeletionTimestamp is RFC date and time at which this resource will be
deleted. This field is set by the server when a graceful deletion is
requested by the user, and is not directly settable by a client. The
resource is expected to be deleted (no longer visible from resource lists,
and not reachable by name) after the time in this field, once the
finalizers list is empty. As long as the finalizers list contains items,
deletion is blocked. Once the deletionTimestamp is set, this value may not
be unset or be set further into the future, although it may be shortened or
the resource may be deleted prior to this time. For example, a user may
request that a pod is deleted in seconds. The Kubelet will react by
sending a graceful termination signal to the containers in the pod. After
that seconds, the Kubelet will send a hard termination signal (SIGKILL)
to the container and after cleanup, remove the pod from the API. In the
presence of network partitions, this object may still exist after this
timestamp, until an administrator or automated process can determine the
resource is fully terminated. If not set, graceful deletion of the object
has not been requested. Populated by the system when a graceful deletion is
requested. Read-only. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata finalizers <[]string>
Must be empty before the object is deleted from the registry. Each entry is
an identifier for the responsible component that will remove the entry from
the list. If the deletionTimestamp of the object is non-nil, entries in
this list can only be removed. Finalizers may be processed and removed in
any order. Order is NOT enforced because it introduces significant risk of
stuck finalizers. finalizers is a shared field, any actor with permission
can reorder it. If the finalizer list is processed in order, then this can
lead to a situation in which the component responsible for the first
finalizer in the list is waiting for a signal (field value, external
system, or other) produced by a component responsible for a finalizer later
in the list, resulting in a deadlock. Without enforced ordering finalizers
are free to order amongst themselves and are not vulnerable to ordering
changes in the list. generateName <string>
GenerateName is an optional prefix, used by the server, to generate a
unique name ONLY IF the Name field has not been provided. If this field is
used, the name returned to the client will be different than the name
passed. This value will also be combined with a unique suffix. The provided
value has the same validation rules as the Name field, and may be truncated
by the length of the suffix required to make the value unique on the
server. If this field is specified and the generated name exists, the
server will NOT return a - instead, it will either return Created
or with Reason ServerTimeout indicating a unique name could not be
found in the time allotted, and the client should retry (optionally after
the time indicated in the Retry-After header). Applied only if Name is not
specified. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#idempotency generation <integer>
A sequence number representing a specific generation of the desired state.
Populated by the system. Read-only. labels <map[string]string>
Map of string keys and values that can be used to organize and categorize
(scope and select) objects. May match selectors of replication controllers
and services. More info: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/labels managedFields <[]Object>
ManagedFields maps workflow-id and version to the set of fields that are
managed by that workflow. This is mostly for internal housekeeping, and
users typically shouldn't need to set or understand this field. A workflow
can be the user's name, a controller's name, or the name of a specific
apply path like "ci-cd". The set of fields is always in the version that
the workflow used when modifying the object. name <string>
Name must be unique within a namespace. Is required when creating
resources, although some resources may allow a client to request the
generation of an appropriate name automatically. Name is primarily intended
for creation idempotence and configuration definition. Cannot be updated.
More info: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/identifiers#names namespace <string>
Namespace defines the space within each name must be unique. An empty
namespace is equivalent to the "default" namespace, but "default" is the
canonical representation. Not all objects are required to be scoped to a
namespace - the value of this field for those objects will be empty. Must
be a DNS_LABEL. Cannot be updated. More info:
http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/namespaces ownerReferences <[]Object>
List of objects depended by this object. If ALL objects in the list have
been deleted, this object will be garbage collected. If this object is
managed by a controller, then an entry in this list will point to this
controller, with the controller field set to true. There cannot be more
than one managing controller. resourceVersion <string>
An opaque value that represents the internal version of this object that
can be used by clients to determine when objects have changed. May be used
for optimistic concurrency, change detection, and the watch operation on a
resource or set of resources. Clients must treat these values as opaque and
passed unmodified back to the server. They may only be valid for a
particular resource or set of resources. Populated by the system.
Read-only. Value must be treated as opaque by clients and . More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#concurrency-control-and-consistency selfLink <string>
SelfLink is a URL representing this object. Populated by the system.
Read-only. DEPRECATED Kubernetes will stop propagating this field in 1.20
release and the field is planned to be removed in 1.21 release. uid <string>
UID is the unique in time and space value for this object. It is typically
generated by the server on successful creation of a resource and is not
allowed to change on PUT operations. Populated by the system. Read-only.
More info: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/identifiers#uids [root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain endpoints.metadata
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain endpoints.subsets
KIND: Endpoints
VERSION: v1 RESOURCE: subsets <[]Object> DESCRIPTION:
The set of all endpoints is the union of all subsets. Addresses are placed
into subsets according to the IPs they share. A single address with
multiple ports, some of which are ready and some of which are not (because
they come from different containers) will result in the address being
displayed in different subsets for the different ports. No address will
appear in both Addresses and NotReadyAddresses in the same subset. Sets of
addresses and ports that comprise a service. EndpointSubset is a group of addresses with a common set of ports. The
expanded set of endpoints is the Cartesian product of Addresses x Ports.
For example, given: { Addresses: [{"ip": "10.10.1.1"}, {"ip":
"10.10.2.2"}], Ports: [{"name": "a", "port": }, {"name": "b", "port":
}] } The resulting set of endpoints can be viewed as: a: [
10.10.1.1:, 10.10.2.2: ], b: [ 10.10.1.1:, 10.10.2.2: ] FIELDS:
addresses <[]Object>
IP addresses which offer the related ports that are marked as ready. These
endpoints should be considered safe for load balancers and clients to
utilize. notReadyAddresses <[]Object>
IP addresses which offer the related ports but are not currently marked as
ready because they have not yet finished starting, have recently failed a
readiness check, or have recently failed a liveness check. ports <[]Object>
Port numbers available on the related IP addresses. [root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain endpoints.subsets
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain endpoints.subsets.addresses
KIND: Endpoints
VERSION: v1 RESOURCE: addresses <[]Object> DESCRIPTION:
IP addresses which offer the related ports that are marked as ready. These
endpoints should be considered safe for load balancers and clients to
utilize. EndpointAddress is a tuple that describes single IP address. FIELDS:
hostname <string>
The Hostname of this endpoint ip <string> -required-
The IP of this endpoint. May not be loopback (127.0.0.0/), link-local
(169.254.0.0/), or link-local multicast ((224.0.0.0/). IPv6 is also
accepted but not fully supported on all platforms. Also, certain kubernetes
components, like kube-proxy, are not IPv6 ready. nodeName <string>
Optional: Node hosting this endpoint. This can be used to determine
endpoints local to a node. targetRef <Object>
Reference to object providing the endpoint. [root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain endpoints.subsets.addresses
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain endpoints.subsets.ports
KIND: Endpoints
VERSION: v1 RESOURCE: ports <[]Object> DESCRIPTION:
Port numbers available on the related IP addresses. EndpointPort is a tuple that describes a single port. FIELDS:
name <string>
The name of this port. This must match the 'name' field in the
corresponding ServicePort. Must be a DNS_LABEL. Optional only if one port
is defined. port <integer> -required-
The port number of the endpoint. protocol <string>
The IP protocol for this port. Must be UDP, TCP, or SCTP. Default is TCP. [root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl explain endpoints.subsets.ports
4>.Headless Service(默认情况下会将ServiceName解析为Cluster-IP,如果Cluster-IP的值为None时会被解析为PodIP)
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get service -n myservice
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
mynginx-service NodePort 10.102.98.128 <none> :/TCP 45m
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get pods -n myservice
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
mynginx-deploy-55ffb645f8-cpjrf / Running 79m
mynginx-deploy-55ffb645f8-gbvdt / Running 79m
mynginx-deploy-55ffb645f8-ptm8h / Running 79m
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl exec -it mynginx-deploy-55ffb645f8-cpjrf -n myservice -- /bin/sh
/ #
/ # cat /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 10.96.0.10
search myservice.svc.cluster.local svc.cluster.local cluster.local localdomain org.cn
options ndots:
/ #
/ #
/ # nslookup mynginx-service
nslookup: can't resolve '(null)': Name does not resolve Name: mynginx-service
Address : 10.102.98.128 mynginx-service.myservice.svc.cluster.local
/ #
/ #
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl exec -it mynginx-deploy-55ffb645f8-cpjrf -n myservice -- /bin/sh
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl delete -f /yinzhengjie/data/k8s/manifests/basic/service/mynginx-service.yaml
service "mynginx-service" deleted
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# vim /yinzhengjie/data/k8s/manifests/basic/service/mynginx-service.yaml
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# cat /yinzhengjie/data/k8s/manifests/basic/service/mynginx-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mynginx-service
namespace: myservice
spec:
clusterIP: None
ports:
- name: http
port:
targetPort:
selector:
app: mynginx
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl apply -f /yinzhengjie/data/k8s/manifests/basic/service/mynginx-service.yaml
service/mynginx-service created
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get service -n myservice
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
mynginx-service ClusterIP None <none> /TCP 12s
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get pod -n myservice
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
mynginx-deploy-55ffb645f8-cpjrf / Running 93m
mynginx-deploy-55ffb645f8-gbvdt / Running 93m
mynginx-deploy-55ffb645f8-ptm8h / Running 93m
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl exec -it mynginx-deploy-55ffb645f8-cpjrf -n myservice -- /bin/sh
/ #
/ # cat /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 10.96.0.10
search myservice.svc.cluster.local svc.cluster.local cluster.local localdomain org.cn
options ndots:
/ #
/ # nslookup mynginx-service
nslookup: can't resolve '(null)': Name does not resolve Name: mynginx-service
Address : 10.244.1.11 mynginx-deploy-55ffb645f8-cpjrf
Address : 10.244.3.4 ---.mynginx-service.myservice.svc.cluster.local
Address : 10.244.2.10 ---.mynginx-service.myservice.svc.cluster.local
/ #
/ #
/ # nslookup mynginx-service

四.修改资源(修改K8S集群使用ipvs进行调度)
1>.编写启用ipvs内核模块脚本
如果是按照我之前的笔记部署的K8S集群,那么此步骤直接略过,因为我们在部署k8s集群时已经启用了ipvs内核相关模块。 博主推荐阅读:
https://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/p/12257108.html
2>.启用ipvs内核模块后,修改kube-proxy的配置文件并使之生效
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get cm -n kube-system
NAME DATA AGE
coredns 3d15h
extension-apiserver-authentication 3d15h
kube-flannel-cfg 3d15h
kube-proxy 3d15h
kubeadm-config 3d15h
kubelet-config-1.17 3d15h
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get cm -n kube-system
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get pods -n kube-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
coredns-6955765f44-455fh / Running 3d15h
coredns-6955765f44-q6zqj / Running 3d15h
etcd-master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn / Running 3d15h
kube-apiserver-master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn / Running 3d15h
kube-controller-manager-master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn / Running 3d15h
kube-flannel-ds-amd64-hnnhb / Running 3d15h
kube-flannel-ds-amd64-jhmh6 / Running 3d15h
kube-flannel-ds-amd64-lnldz / Running 3d15h
kube-flannel-ds-amd64-nwv2l / Running 3d15h
kube-proxy-2shb4 / Running 3d15h
kube-proxy-6r9dx / Running 3d15h
kube-proxy-cg2m6 / Running 3d15h
kube-proxy-lp5pr / Running 3d15h
kube-scheduler-master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn / Running 3d15h
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get pods -n kube-system
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get cm -n kube-system
NAME DATA AGE
coredns 3d15h
extension-apiserver-authentication 3d15h
kube-flannel-cfg 3d15h
kube-proxy 3d15h
kubeadm-config 3d15h
kubelet-config-1.17 3d15h
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get cm -n kube-system
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl edit cm kube-proxy -n kube-system
Edit cancelled, no changes made.
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl edit cm kube-proxy -n kube-system #边界kube-proxy的配置文件,将mode的值设置为"ipvs"
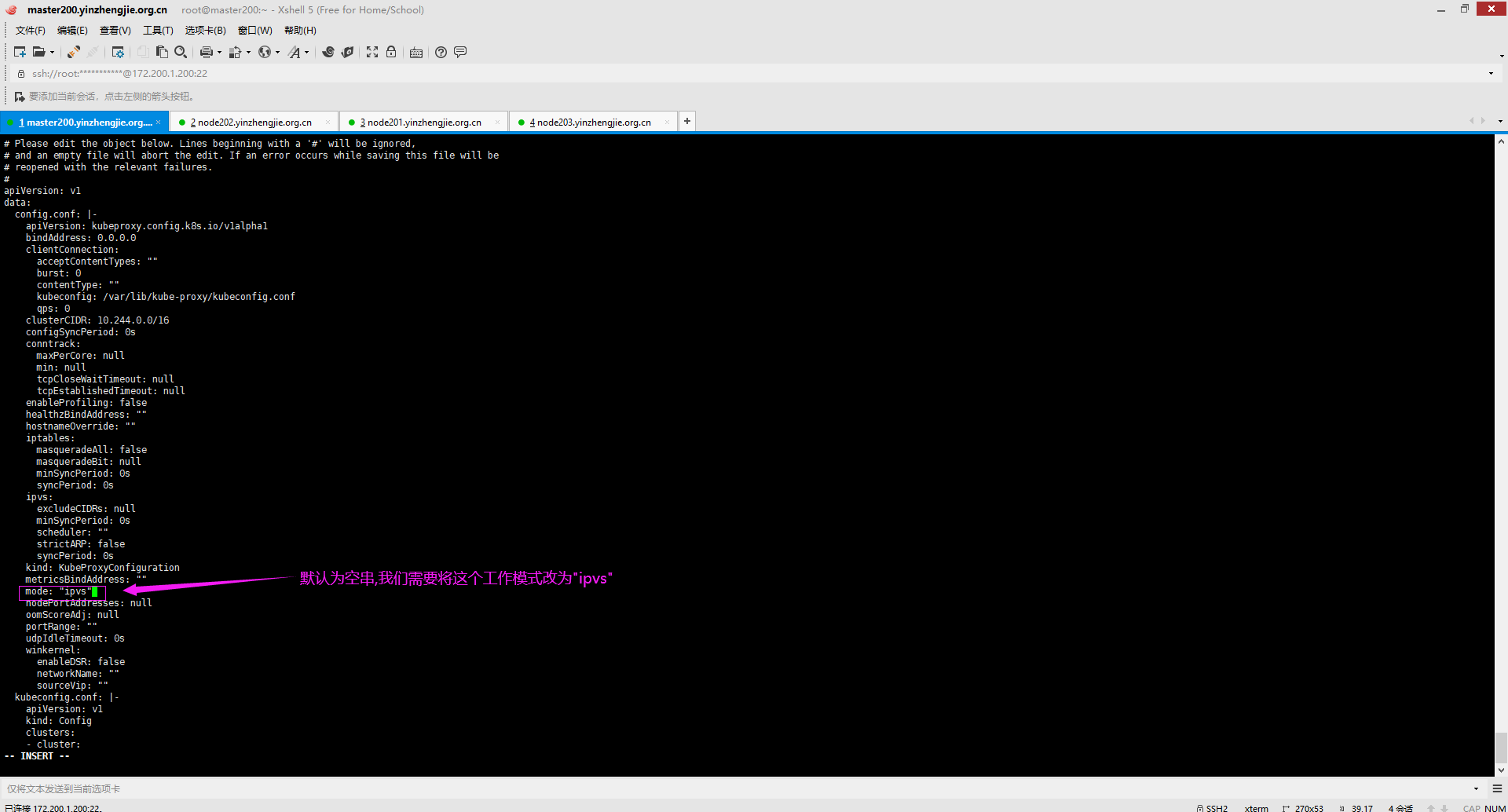
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get pods -n kube-system --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
coredns-6955765f44-455fh / Running 3d15h k8s-app=kube-dns,pod-template-hash=6955765f44
coredns-6955765f44-q6zqj / Running 3d15h k8s-app=kube-dns,pod-template-hash=6955765f44
etcd-master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn / Running 3d15h component=etcd,tier=control-plane
kube-apiserver-master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn / Running 3d15h component=kube-apiserver,tier=control-plane
kube-controller-manager-master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn / Running 3d15h component=kube-controller-manager,tier=control-plane
kube-flannel-ds-amd64-hnnhb / Running 3d15h app=flannel,controller-revision-hash=67f65bfbc7,pod-template-generation=,tier=node
kube-flannel-ds-amd64-jhmh6 / Running 3d15h app=flannel,controller-revision-hash=67f65bfbc7,pod-template-generation=,tier=node
kube-flannel-ds-amd64-lnldz / Running 3d15h app=flannel,controller-revision-hash=67f65bfbc7,pod-template-generation=,tier=node
kube-flannel-ds-amd64-nwv2l / Running 3d15h app=flannel,controller-revision-hash=67f65bfbc7,pod-template-generation=,tier=node
kube-proxy-2shb4 / Running 3d15h controller-revision-hash=844ff54b8,k8s-app=kube-proxy,pod-template-generation=
kube-proxy-6r9dx / Running 3d15h controller-revision-hash=844ff54b8,k8s-app=kube-proxy,pod-template-generation=
kube-proxy-cg2m6 / Running 3d15h controller-revision-hash=844ff54b8,k8s-app=kube-proxy,pod-template-generation=
kube-proxy-lp5pr / Running 3d15h controller-revision-hash=844ff54b8,k8s-app=kube-proxy,pod-template-generation=
kube-scheduler-master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn / Running 3d15h component=kube-scheduler,tier=control-plane
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl delete pods -l k8s-app=kube-proxy -n kube-system
pod "kube-proxy-2shb4" deleted
pod "kube-proxy-6r9dx" deleted
pod "kube-proxy-cg2m6" deleted
pod "kube-proxy-lp5pr" deleted
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl get pods -n kube-system --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
coredns-6955765f44-455fh / Running 3d15h k8s-app=kube-dns,pod-template-hash=6955765f44
coredns-6955765f44-q6zqj / Running 3d15h k8s-app=kube-dns,pod-template-hash=6955765f44
etcd-master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn / Running 3d15h component=etcd,tier=control-plane
kube-apiserver-master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn / Running 3d15h component=kube-apiserver,tier=control-plane
kube-controller-manager-master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn / Running 3d15h component=kube-controller-manager,tier=control-plane
kube-flannel-ds-amd64-hnnhb / Running 3d15h app=flannel,controller-revision-hash=67f65bfbc7,pod-template-generation=,tier=node
kube-flannel-ds-amd64-jhmh6 / Running 3d15h app=flannel,controller-revision-hash=67f65bfbc7,pod-template-generation=,tier=node
kube-flannel-ds-amd64-lnldz / Running 3d15h app=flannel,controller-revision-hash=67f65bfbc7,pod-template-generation=,tier=node
kube-flannel-ds-amd64-nwv2l / Running 3d15h app=flannel,controller-revision-hash=67f65bfbc7,pod-template-generation=,tier=node
kube-proxy-47pgb / Running 7s controller-revision-hash=844ff54b8,k8s-app=kube-proxy,pod-template-generation=
kube-proxy-bw85f / Running 8s controller-revision-hash=844ff54b8,k8s-app=kube-proxy,pod-template-generation=
kube-proxy-gdw7v / Running 14s controller-revision-hash=844ff54b8,k8s-app=kube-proxy,pod-template-generation=
kube-proxy-k4vhz / Running 16s controller-revision-hash=844ff54b8,k8s-app=kube-proxy,pod-template-generation=
kube-scheduler-master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn / Running 3d15h component=kube-scheduler,tier=control-plane
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# kubectl delete pods -l k8s-app=kube-proxy -n kube-system #我们将kube-proxy的Pod删除,删除后各node节点均会自动生成一个新的pod,此时会自动读取咱们上面修改的配置文件内容
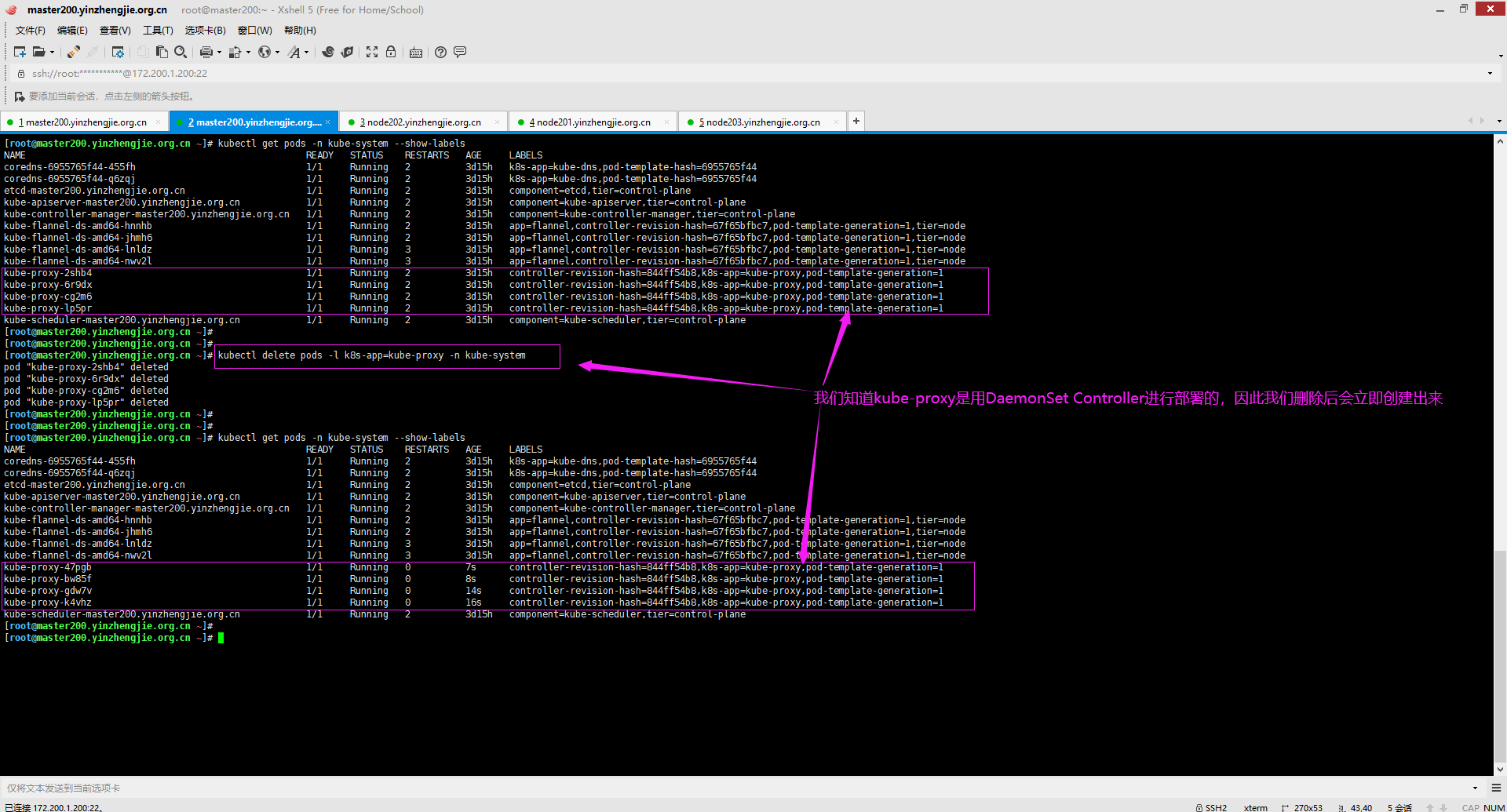
3>.验证ipvs是否生效
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# yum -y install ipvsadm
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirror.bit.edu.cn
* extras: mirror.bit.edu.cn
* updates: mirror.bit.edu.cn
base | 3.6 kB ::
docker-ce-stable | 3.5 kB ::
extras | 2.9 kB ::
kubernetes | 1.4 kB ::
updates | 2.9 kB ::
Resolving Dependencies
--> Running transaction check
---> Package ipvsadm.x86_64 :1.27-.el7 will be installed
--> Finished Dependency Resolution Dependencies Resolved ==============================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
==============================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================
Installing:
ipvsadm x86_64 1.27-.el7 base k Transaction Summary
==============================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================
Install Package Total download size: k
Installed size: k
Downloading packages:
ipvsadm-1.27-.el7.x86_64.rpm | kB ::
Running transaction check
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded
Running transaction
Installing : ipvsadm-1.27-.el7.x86_64 /
Verifying : ipvsadm-1.27-.el7.x86_64 / Installed:
ipvsadm.x86_64 :1.27-.el7 Complete!
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# yum -y install ipvsadm
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# ipvsadm -Ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2. (size=)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags
-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 10.96.0.1: rr
-> 172.200.1.200: Masq
TCP 10.96.0.10: rr
-> 10.244.0.6: Masq
-> 10.244.0.7: Masq
TCP 10.96.0.10: rr
-> 10.244.0.6: Masq
-> 10.244.0.7: Masq
UDP 10.96.0.10: rr
-> 10.244.0.6: Masq
-> 10.244.0.7: Masq
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@master200.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# ipvsadm -Ln
五.Ingress资源
通过上面的说明,k8s的Service资源无论是ipvs还是iptable,说到底都是四层调度(layer proxy)。但如果有多个Pod提供的是https服务,此时我们想要提供基于七层的调度的话,Server就有点爱莫能助了,但我们可以使用Ingress资源进行七层调度。 Ingress资源其实是一种七层流量的规则,它能将客户端对某个URL的访问转换为对当前机器上特定一个Pod的访问。 博主推荐阅读:
https://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/p/12271836.html
Kerbernetes的Service资源管理的更多相关文章
- K8S(02)管理核心资源的三种基本方法
系列文章说明 本系列文章,可以基本算是 老男孩2019年王硕的K8S周末班课程 笔记,根据视频来看本笔记最好,否则有些地方会看不明白 需要视频可以联系我 管理k8s核心资源的三种基本方法: 目录 系列 ...
- 学习k8s(四)
1.K8S核心组件 1.Master节点: etcd: 分布式键值对数据库,保存集群状态 api-server: 接受并响应用户的请求 controller: 控制器管理,控制容器的副本数,故障检测 ...
- 360安全卫士造成Sharepoint文档库”使用资源管理器打开“异常
备注:企业用户还是少用360为妙 有客户反馈:部门里的XP SP2环境客户机全部异常,使用资源管理器打开Sharepoint文档库,看到的界面样式很老土,跟本地文件夹不一样 ...
- web service 学习
是什么? 是一种远程调用技术,这种技术提供一些接口,这些接口实现让客户端和服务端进行通信和数据交换,并且让通信和交换与平台和开发语言无关.也可以说是提供了许多函数.客户端调用服务端的函数. 远程调用: ...
- Oracle资源管理器(二)-- 创建和使用数据库资源计划
(参考 http://blog.csdn.net/mrluoe/article/details/7969436 -- 整理并实践通过) 第1步,创建3个用户 SQL> create user s ...
- C#开发和调用Web Service
http://blog.csdn.net/h0322/article/details/4776819 1.1.Web Service基本概念 Web Service也叫XML Web Service ...
- 找不到类型“{x}.{x}”,它在 ServiceHost 指令中提供为 Service 特性值,或在配置元素 system.serviceModel/serviceHostingEnvironment/serviceActivations 中提供。
最近在搞一个WCF的项目... 刚开始在这条路上走... 各种崎岖... 网上搜到的一种解决方案(也是大多数情况的解决方案): 原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/Olive116/p ...
- C#利用Web Service实现短信发送(转)
通过编程方式实现短信息的发送对很多人来说是一件比较烦杂的事情,目前一般的解决方法是通过计算机和手机的连线,通过可对手机编程的语言编写相关的手机短信息程序来实现,而这种方法对于一般人来说是很难达到的,因 ...
- Azure开发者任务之六:使用WCF Service Web Role
在本文中,我们将会在local development fabric上创建一个WCF服务角色,然后在一个控制台应用程序中使用它. WCF服务角色可以让我们创建一个WCF服务,并且把它托管在Window ...
随机推荐
- Java多线程之Java内存模型
如果要了解Java内存模型,就得对多线程的三大特性有初步的了解. 1.原子性:独一无二.一个操作或者多个操作 要么全部执行并且执行的过程不会被任何因素打断,要么就都不执行.比如i = i+1:其中就包 ...
- 中文文本分类之CharCNN
文本分类是自然语言处理中一个非常经典的任务,可用的模型非常多,相关的开源代码也非常多了.这篇博客用一个CNN模型,对新闻文本进行分类. 全部代码有4个模块:1.数据处理模块(命名为:cnews_loa ...
- Local-Pref(本地优先属性)路由本地优先术
Local-Pref(本地优先属性)路由本地优先术: ①:抓取感兴趣流量——前缀与访问——prefix and access ②:创建路由地图——router-map ③:第一法则——permit 1 ...
- LCT(1)
LCT(Link-Cut Tree,动态树)是一个支持动态修改树的结构的数据结构,其基本操作有 \(\texttt{access}\) , \(\texttt{findroot}\) , \(\tex ...
- SpringMVC: Ajax技术
SpringMVC:Ajax技术 简介 AJAX = Asynchronous JavaScript and XML(异步的 JavaScript 和 XML). AJAX 是一种在无需重新加载整个网 ...
- Web基础之Maven
Web基础之Maven Maven是一个优秀的项目管理工具,可以很轻松的管理项目. POM和LifeCycle POM:Project Object Model.也就是项目模型,简单来说就是对项目进行 ...
- C++ 设置自动启动
WCHAR pFileName[MAX_PATH] = {}; //得到程序自身的全路径 DWORD dwRet = GetModuleFileName(NULL, pFileName, MAX_PA ...
- mongodb安装到配置问题
一.所有问题 Xshell 连接不上 报错类型:Could not connect to '192.168.122.1' (port 22): Connection failed.原因:IP地址未生成 ...
- spring+springMVC+mybatis , 项目启动遇坑
github上找的框架组合例子 结合自己的数据库作为新项目开发. 但是项目启动时,tomcat启动失败: 检查不出错误. 于是改换maven引入jetty插件来启动项目, 结果在未改动的任何代码的情况 ...
- mini2440 裸机程序,下载到nand 里面,复制到 sdram 中不运行
按照韦东山的视频中 sdram的裸机代码,写了一份,通过 minitools 下载到 0x30000000,然后烧录到 nand中,接过不能正常运行. 尝试过多种方法后,只有一种解决方法,就是不要用 ...
