Network Stack
OverviewThe network stack is a mostly single-threaded cross-platform library primarily for resource fetching. Its main interfaces are
URLRequest and URLRequestContext. URLRequest, as indicated by its name, represents the request for a URL. URLRequestContext contains all the associated context necessary to fulfill the URL request, such as cookies, host resolver, proxy resolver, cache, etc. Many URLRequest objects may share the same URLRequestContext. Most net objects are not threadsafe, although the disk cache can use a dedicated thread, and several components (host resolution, certificate verification, etc.) may use unjoined worker threads. Since it primarily runs on a single network thread, no operation on the network thread is allowed to block. Therefore we use non-blocking operations with asynchronous callbacks (typically CompletionCallback). The network stack code also logs most operations to NetLog, which allows the consumer to record said operations in memory and render it in a user-friendly format for debugging purposes.Chromium developers wrote the network stack in order to:
Code Layout
Anatomy of a Network Request (focused on HTTP)
URLRequestclass URLRequest { public: // Construct a URLRequest for |url|, notifying events to |delegate|. URLRequest(const GURL& url, Delegate* delegate); // Specify the shared state void set_context(URLRequestContext* context); // Start the request. Notifications will be sent to |delegate|. void Start(); // Read data from the request. bool Read(IOBuffer* buf, int max_bytes, int* bytes_read);}; class URLRequest::Delegate { public: // Called after the response has started coming in or an error occurred. virtual void OnResponseStarted(...) = 0; // Called when Read() calls complete. virtual void OnReadCompleted(...) = 0;};
When a
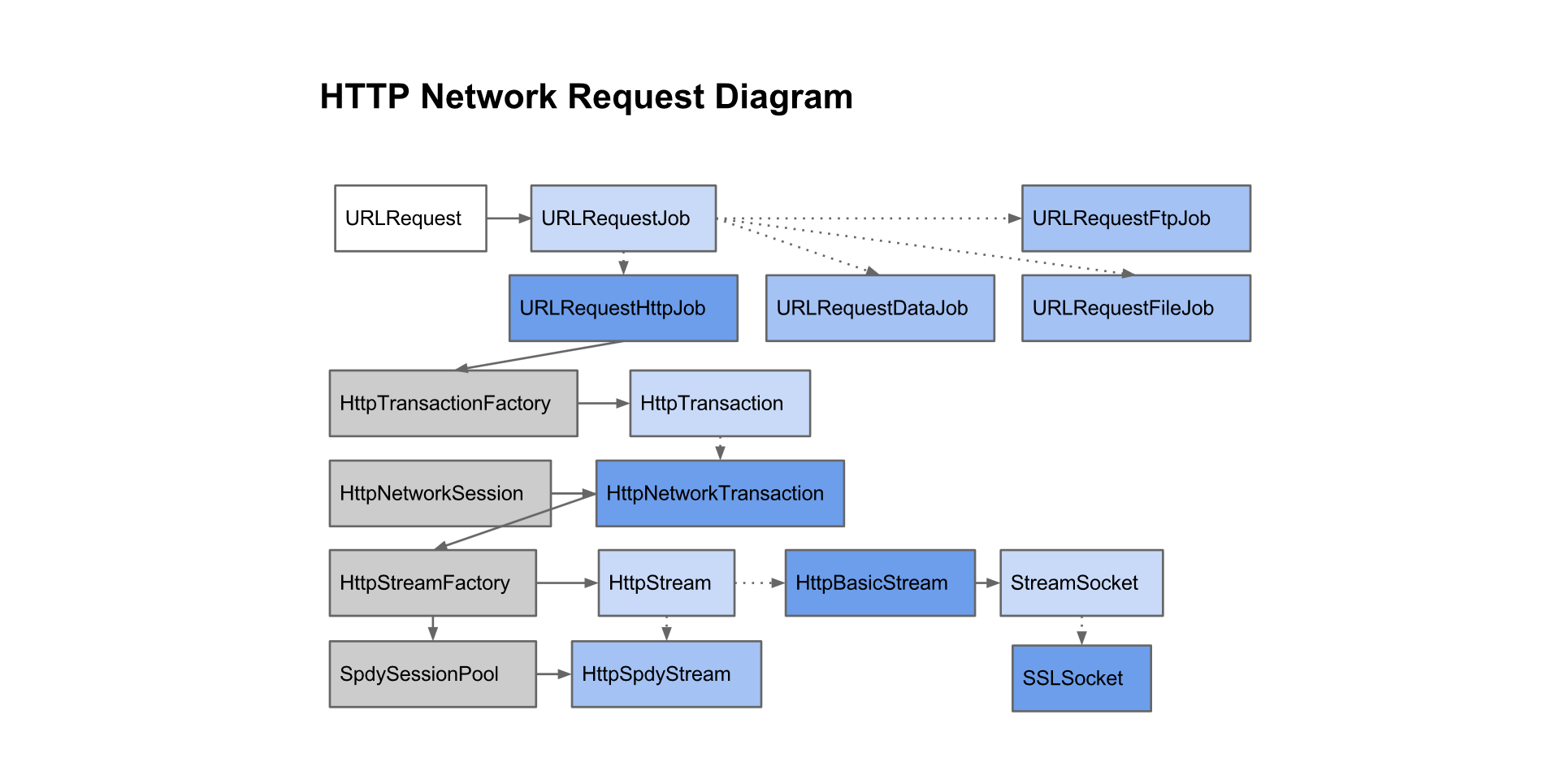
URLRequest is started, the first thing it does is decide what type of URLRequestJob to create. The main job type is the URLRequestHttpJob which is used to fulfill http:// requests. There are a variety of other jobs, such as URLRequestFileJob (file://), URLRequestFtpJob (ftp://), URLRequestDataJob (data://), and so on. The network stack will determine the appropriate job to fulfill the request, but it provides two ways for clients to customize the job creation: URLRequest::Interceptor and URLRequest::ProtocolFactory. These are fairly redundant, except that URLRequest::Interceptor's interface is more extensive. As the job progresses, it will notify the URLRequest which will notify the URLRequest::Delegate as needed.URLRequestHttpJobURLRequestHttpJob will first identify the cookies to set for the HTTP request, which requires querying the
CookieMonster in the request context. This can be asynchronous since the CookieMonster may be backed by an sqlitedatabase. After doing so, it will ask the request context's HttpTransactionFactory to create a HttpTransaction. Typically, the HttpCache will be specified as the HttpTransactionFactory. The HttpCache will create a HttpCache::Transaction to handle the HTTP request. The HttpCache::Transaction will first check the HttpCache (which checks the disk cache) to see if the cache entry already exists. If so, that means that the response was already cached, or a network transaction already exists for this cache entry, so just read from that entry. If the cache entry does not exist, then we create it and ask the HttpCache's HttpNetworkLayer to create a HttpNetworkTransaction to service the request. The HttpNetworkTransaction is given a HttpNetworkSession which contains the contextual state for performing HTTP requests. Some of this state comes from the URLRequestContext.HttpNetworkTransactionclass HttpNetworkSession { ... private: // Shim so we can mock out ClientSockets. ClientSocketFactory* const socket_factory_; // Pointer to URLRequestContext's HostResolver. HostResolver* const host_resolver_;
// Reference to URLRequestContext's ProxyService
scoped_refptr<ProxyService> proxy_service_; // Contains all the socket pools. ClientSocketPoolManager socket_pool_manager_;
// Contains the active SpdySessions.
scoped_ptr<SpdySessionPool> spdy_session_pool_;
// Handles HttpStream creation.
HttpStreamFactory http_stream_factory_;
};HttpNetworkTransaction asks the HttpStreamFactory to create a HttpStream. The HttpStreamFactory returns a HttpStreamRequest that is supposed to handle all the logic of figuring out how to establish the connection, and once the connection is established, wraps it with a HttpStream subclass that mediates talking directly to the network.class HttpStream { public: virtual int SendRequest(...) = 0; virtual int ReadResponseHeaders(...) = 0; virtual int ReadResponseBody(...) = 0; ...};Currently, there are only two main
HttpStream subclasses: HttpBasicStream and SpdyHttpStream, although we're planning on creating subclasses for HTTP pipelining. HttpBasicStream assumes it is reading/writing directly to a socket. SpdyHttpStream reads and writes to a SpdyStream. The network transaction will call methods on the stream, and on completion, will invoke callbacks back to the HttpCache::Transaction which will notify the URLRequestHttpJob and URLRequest as necessary. For the HTTP pathway, the generation and parsing of http requests and responses will be handled by the HttpStreamParser. For the SPDY pathway, request and response parsing are handled by SpdyStream and SpdySession. Based on the HTTP response, the HttpNetworkTransaction may need to perform HTTP authentication. This may involve restarting the network transaction.HttpStreamFactoryHttpStreamFactory first does proxy resolution to determine whether or not a proxy is needed. The endpoint is set to the URL host or the proxy server. HttpStreamFactory then checks the SpdySessionPool to see if we have an available SpdySession for this endpoint. If not, then the stream factory requests a "socket" (TCP/proxy/SSL/etc) from the appropriate pool. If the socket is an SSL socket, then it checks to see if NPN indicated a protocol (which may be SPDY), and if so, uses the specified protocol. For SPDY, we'll check to see if a SpdySession already exists and use that if so, otherwise we'll create a new SpdySession from this SSL socket, and create a SpdyStreamfrom the SpdySession, which we wrap a SpdyHttpStream around. For HTTP, we'll simply take the socket and wrap it in a HttpBasicStream.Proxy ResolutionHttpStreamFactory queries the ProxyService to return the ProxyInfo for the GURL. The proxy service first needs to check if it has an up-to-date proxy configuration. If not, it uses the ProxyConfigService to query the system for the current proxy settings. If the proxy settings are set to no proxy or a specific proxy, then proxy resolution is simple (we return no proxy or the specific proxy). Otherwise, we need to run a PAC script to determine the appropriate proxy (or lack thereof). If we don't already have the PAC script, then the proxy settings will indicate we're supposed to use WPAD auto-detection, or a custom PAC url will be specified, and we'll fetch the PAC script with the ProxyScriptFetcher. Once we have the PAC script, we'll execute it via the ProxyResolver. Note that we use a shim MultiThreadedProxyResolver object to dispatch the PAC script execution to threads, which run a ProxyResolverV8 instance. This is because PAC script execution may block on host resolution. Therefore, in order to prevent one stalled PAC script execution from blocking other proxy resolutions, we allow for executing multiple PAC scripts concurrently (caveat: V8 is not threadsafe, so we acquire locks for the javascript bindings, so while one V8 instance is blocked on host resolution, it releases the lock so another V8 instance can execute the PAC script to resolve the proxy for a different URL).Connection ManagementAfter the
HttpStreamRequest has determined the appropriate endpoint (URL endpoint or proxy endpoint), it needs to establish a connection. It does so by identifying the appropriate "socket" pool and requesting a socket from it. Note that "socket" here basically means something that we can read and write to, to send data over the network. An SSL socket is built on top of a transport (TCP) socket, and encrypts/decrypts the raw TCP data for the user. Different socket types also handle different connection setups, for HTTP/SOCKS proxies, SSL handshakes, etc. Socket pools are designed to be layered, so the various connection setups can be layered on top of other sockets. HttpStream can be agnostic of the actual underlying socket type, since it just needs to read and write to the socket. The socket pools perform a variety of functions-- They implement our connections per proxy, per host, and per process limits. Currently these are set to 32 sockets per proxy, 6 sockets per destination host, and 256 sockets per process (not implemented exactly correctly, but good enough). Socket pools also abstract the socket request from the fulfillment, thereby giving us "late binding" of sockets. A socket request can be fulfilled by a newly connected socket or an idle socket (reused from a previous http transaction).Host ResolutionNote that the connection setup for transport sockets not only requires the transport (TCP) handshake, but probably already requires host resolution.
HostResolverImpl uses getaddrinfo() to perform host resolutions, which is a blocking call, so the resolver invokes these calls on unjoined worker threads. Typically host resolution usually involves DNS resolution, but may involve non-DNS namespaces such as NetBIOS/WINS. Note that, as of time of writing, we cap the number of concurrent host resolutions to 8, but are looking to optimize this value. HostResolverImpl also contains a HostCache which caches up to 1000 hostnames.SSL/TLSSSL sockets require performing SSL connection setup as well as certificate verification. Currently, on all platforms, we use NSS's libssl to handle the SSL connection logic. However, we use platform specific APIs for certificate verification. We are moving towards using a certificate verification cache as well, which will consolidate multiple requests for certificate verification of the same certificate into a single certificate verification job and cache the results for a period of time.
SSLClientSocketNSS roughly follows this sequence of events (ignoring advanced features like Snap Start or DNSSEC based certificate verification):
Note that Chromium has its own NSS patches which support some advanced features which aren't necessarily in the system's NSS installation, such as support for NPN, False Start, Snap Start , OCSP stapling, etc.
TODO: talk about network change notifications
|
Network Stack的更多相关文章
- Queueing in the Linux Network Stack !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
https://www.coverfire.com/articles/queueing-in-the-linux-network-stack/ Queueing in the Linux Networ ...
- Contiki Network Stack
一.协议栈 主要有两大网络协议栈,uIP和Rime这两大协议栈(network stack): The uIP TCP/IP stack, which provides us with IPv4 ne ...
- Network Stack : HTTP authentication
HTTP authentication As specified in RFC 2617, HTTP supports authentication using the WWW-Authenticat ...
- Network Stack : HTTP Cache
HTTP Cache 目录 1 Operation 2 Sparse Entries 3 Truncated Entries 4 Byte-Range Requests 5 HttpCache::Tr ...
- Network Stack : CookieMonster
CookieMonster The CookieMonster is the class in Chromium which handles in-browser storage, managem ...
- Network Stack : Disk Cache
Disk Cache 目录 1 Overview 2 External Interface 3 Disk Structure 3.1 Cache Address 3.2 Index File Stru ...
- XV6学习(16)Lab net: Network stack
最后一个实验了,代码在Github上. 这一个实验其实挺简单的,就是要实现网卡的e1000_transmit和e1000_recv函数.不过看以前的实验好像还要实现上层socket相关的代码,今年就只 ...
- 【转】linux network namespace 学习
原文地址:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000004059167 介绍 在专业的网络世界中,经常使用到Virtual Routing and Forwarding(VR ...
- Monitoring and Tuning the Linux Networking Stack: Receiving Data
http://blog.packagecloud.io/eng/2016/06/22/monitoring-tuning-linux-networking-stack-receiving-data/ ...
随机推荐
- 05004_Linux的其他命令和权限命令
1.其他命令 (1)显示当前所在位置 命令:pwd (2)搜索命令 a.命令:grep 要搜索的字符串 要搜索的文件 示例:搜索/etc/sudu.conf文件中包含字符串to的行 b.搜索/etc/ ...
- 使用JMX透过防火墙远程监控tomcat服务
https://my.oschina.net/mye/blog/64879 http://blog.csdn.net/l1028386804/article/details/51547408 http ...
- flume 读取kafka 数据
本文介绍flume读取kafka数据的方法 代码: /************************************************************************* ...
- 破解APK注入代码大揭秘
点此了解详细的APK破解及二次打包过程揭秘: http://t.cn/RzEn7UK [HACK]破解APK并注入自己的代码 会破解是你的本事,但是请不要去干坏事! 使用工具: APKTool 提 ...
- MySQL 一台主机多实例root登录问题
假设在一台机子上起多个MySQL实例. 比方port号为 3306. 3307. 3308 登录时候要选择不同的 mysql.sock文件 mysql -uroot -p123456 这一句 登录的是 ...
- IIS预编译提升载入速度
当我们把站点部署在IIS7或IIS6S的时候,每当IIS或是ApplicationPool重新启动后,第一次请求站点反应总是非常慢.原因大家都知道(不知道能够參考这个动画说明ASP.NET网页第一个R ...
- html中隐藏一个元素的方法
display:none; 隐藏不占位 opacity:0; fliter:alpha(opa ...
- 机器学习(七) PCA与梯度上升法 (下)
五.高维数据映射为低维数据 换一个坐标轴.在新的坐标轴里面表示原来高维的数据. 低维 反向 映射为高维数据 PCA.py import numpy as np class PCA: def __ini ...
- 关于eclipse的注释和反注释的快捷键
使用eclipse那么久了额,对注释和反注释的快捷键一直很模糊,现在记下来,方便查看. 注释和反注释有两种方式.如对下面这段代码片段(①)进行注释: private String value; pri ...
- vue中使用console.log无效
webpack开发环境下,在vue中使用console.log无效,一直以为webpack出了问题. 使用window.console.log()就能够顺利在浏览器控制台输出了. 以及 在axios请 ...