Android数据加密之Aes加密
前言:
项目中除了登陆,支付等接口采用rsa非对称加密,之外的采用aes对称加密,今天我们来认识一下aes加密。
其他几种加密方式:
什么是aes加密?
高级加密标准(英语:Advanced Encryption Standard,缩写:AES),在密码学中又称Rijndael加密法,是美国联邦政府采用的一种区块加密标准。这个标准用来替代原先的DES,已经被多方分析且广为全世界所使用。
接下来我们来实际看下具体怎么实现:
对于AesUtils类常量简介:
private final static String HEX = "0123456789ABCDEF";
private static final String CBC_PKCS5_PADDING = "AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding";//AES是加密方式 CBC是工作模式 PKCS5Padding是填充模式
private static final String AES = "AES";//AES 加密
private static final String SHA1PRNG="SHA1PRNG";//// SHA1PRNG 强随机种子算法, 要区别4.2以上版本的调用方法
如何生成一个随机Key?
/*
* 生成随机数,可以当做动态的密钥 加密和解密的密钥必须一致,不然将不能解密
*/
public static String generateKey() {
try {
SecureRandom localSecureRandom = SecureRandom.getInstance(SHA1PRNG);
byte[] bytes_key = new byte[20];
localSecureRandom.nextBytes(bytes_key);
String str_key = toHex(bytes_key);
return str_key;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
Aes密钥处理
// 对密钥进行处理
private static byte[] getRawKey(byte[] seed) throws Exception {
KeyGenerator kgen = KeyGenerator.getInstance(AES);
//for android
SecureRandom sr = null;
// 在4.2以上版本中,SecureRandom获取方式发生了改变
if (android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 17) {
sr = SecureRandom.getInstance(SHA1PRNG, "Crypto");
} else {
sr = SecureRandom.getInstance(SHA1PRNG);
}
// for Java
// secureRandom = SecureRandom.getInstance(SHA1PRNG);
sr.setSeed(seed);
kgen.init(128, sr); //256 bits or 128 bits,192bits
//AES中128位密钥版本有10个加密循环,192比特密钥版本有12个加密循环,256比特密钥版本则有14个加密循环。
SecretKey skey = kgen.generateKey();
byte[] raw = skey.getEncoded();
return raw;
}
Aes加密过程
/*
* 加密
*/
public static String encrypt(String key, String cleartext) {
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(cleartext)) {
return cleartext;
}
try {
byte[] result = encrypt(key, cleartext.getBytes());
return Base64Encoder.encode(result);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
} /*
* 加密
*/
private static byte[] encrypt(String key, byte[] clear) throws Exception {
byte[] raw = getRawKey(key.getBytes());
SecretKeySpec skeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(raw, AES);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(CBC_PKCS5_PADDING);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, skeySpec, new IvParameterSpec(new byte[cipher.getBlockSize()]));
byte[] encrypted = cipher.doFinal(clear);
return encrypted;
}
Aes解密过程
/*
* 解密
*/
public static String decrypt(String key, String encrypted) {
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(encrypted)) {
return encrypted;
}
try {
byte[] enc = Base64Decoder.decodeToBytes(encrypted);
byte[] result = decrypt(key, enc);
return new String(result);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
} /*
* 解密
*/
private static byte[] decrypt(String key, byte[] encrypted) throws Exception {
byte[] raw = getRawKey(key.getBytes());
SecretKeySpec skeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(raw, AES);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(CBC_PKCS5_PADDING);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, skeySpec, new IvParameterSpec(new byte[cipher.getBlockSize()]));
byte[] decrypted = cipher.doFinal(encrypted);
return decrypted;
}
二进制转字符
//二进制转字符
public static String toHex(byte[] buf) {
if (buf == null)
return "";
StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer(2 * buf.length);
for (int i = 0; i < buf.length; i++) {
appendHex(result, buf[i]);
}
return result.toString();
} private static void appendHex(StringBuffer sb, byte b) {
sb.append(HEX.charAt((b >> 4) & 0x0f)).append(HEX.charAt(b & 0x0f));
}
测试程序:
List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();
int testMaxCount = 1000;//测试的最大数据条数
//添加测试数据
for (int i = 0; i < testMaxCount; i++) {
Person person = new Person();
person.setAge(i);
person.setName(String.valueOf(i));
personList.add(person);
}
//FastJson生成json数据
String jsonData = JsonUtils.objectToJsonForFastJson(personList);
Log.e("MainActivity", "AES加密前json数据 ---->" + jsonData);
Log.e("MainActivity", "AES加密前json数据长度 ---->" + jsonData.length()); //生成一个动态key
String secretKey = AesUtils.generateKey();
Log.e("MainActivity", "AES动态secretKey ---->" + secretKey); //AES加密
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String encryStr = AesUtils.encrypt(secretKey, jsonData);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
Log.e("MainActivity", "AES加密耗时 cost time---->" + (end - start));
Log.e("MainActivity", "AES加密后json数据 ---->" + encryStr);
Log.e("MainActivity", "AES加密后json数据长度 ---->" + encryStr.length()); //AES解密
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String decryStr = AesUtils.decrypt(secretKey, encryStr);
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
Log.e("MainActivity", "AES解密耗时 cost time---->" + (end - start));
Log.e("MainActivity", "AES解密后json数据 ---->" + decryStr);
运行耗时:

数据前后变化:
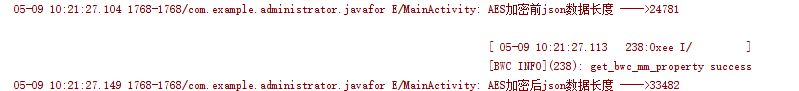
由此可见对称Aes效率还是比较高的
补充关于Base64Decoder类和Base64Encoder类
package com.whoislcj.testhttp.utils; import android.text.TextUtils; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.FilterInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream; public class Base64Decoder extends FilterInputStream { private static final char[] chars = { 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'O', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u',
'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z', '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '+', '/' }; // A mapping between char values and six-bit integers
private static final int[] ints = new int[128];
static {
for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) {
ints[chars[i]] = i;
}
} private int charCount;
private int carryOver; /***
* Constructs a new Base64 decoder that reads input from the given
* InputStream.
*
* @param in
* the input stream
*/
private Base64Decoder(InputStream in) {
super(in);
} /***
* Returns the next decoded character from the stream, or -1 if end of
* stream was reached.
*
* @return the decoded character, or -1 if the end of the input stream is
* reached
* @exception IOException
* if an I/O error occurs
*/
public int read() throws IOException {
// Read the next non-whitespace character
int x;
do {
x = in.read();
if (x == -1) {
return -1;
}
} while (Character.isWhitespace((char) x));
charCount++; // The '=' sign is just padding
if (x == '=') {
return -1; // effective end of stream
} // Convert from raw form to 6-bit form
x = ints[x]; // Calculate which character we're decoding now
int mode = (charCount - 1) % 4; // First char save all six bits, go for another
if (mode == 0) {
carryOver = x & 63;
return read();
}
// Second char use previous six bits and first two new bits,
// save last four bits
else if (mode == 1) {
int decoded = ((carryOver << 2) + (x >> 4)) & 255;
carryOver = x & 15;
return decoded;
}
// Third char use previous four bits and first four new bits,
// save last two bits
else if (mode == 2) {
int decoded = ((carryOver << 4) + (x >> 2)) & 255;
carryOver = x & 3;
return decoded;
}
// Fourth char use previous two bits and all six new bits
else if (mode == 3) {
int decoded = ((carryOver << 6) + x) & 255;
return decoded;
}
return -1; // can't actually reach this line
} /***
* Reads decoded data into an array of bytes and returns the actual number
* of bytes read, or -1 if end of stream was reached.
*
* @param buf
* the buffer into which the data is read
* @param off
* the start offset of the data
* @param len
* the maximum number of bytes to read
* @return the actual number of bytes read, or -1 if the end of the input
* stream is reached
* @exception IOException
* if an I/O error occurs
*/
public int read(byte[] buf, int off, int len) throws IOException {
if (buf.length < (len + off - 1)) {
throw new IOException("The input buffer is too small: " + len + " bytes requested starting at offset " + off + " while the buffer " + " is only " + buf.length + " bytes long.");
} // This could of course be optimized
int i;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
int x = read();
if (x == -1 && i == 0) { // an immediate -1 returns -1
return -1;
} else if (x == -1) { // a later -1 returns the chars read so far
break;
}
buf[off + i] = (byte) x;
}
return i;
} /***
* Returns the decoded form of the given encoded string, as a String. Note
* that not all binary data can be represented as a String, so this method
* should only be used for encoded String data. Use decodeToBytes()
* otherwise.
*
* @param encoded
* the string to decode
* @return the decoded form of the encoded string
*/
public static String decode(String encoded) {
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(encoded)) {
return "";
}
return new String(decodeToBytes(encoded));
} /***
* Returns the decoded form of the given encoded string, as bytes.
*
* @param encoded
* the string to decode
* @return the decoded form of the encoded string
*/
public static byte[] decodeToBytes(String encoded) {
byte[] bytes = encoded.getBytes();
Base64Decoder in = new Base64Decoder(new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes));
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream((int) (bytes.length * 0.75));
try {
byte[] buf = new byte[4 * 1024]; // 4K buffer
int bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = in.read(buf)) != -1) {
out.write(buf, 0, bytesRead);
}
return out.toByteArray();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
Base64Decoder
package com.whoislcj.testhttp.utils; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.FilterOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream; public class Base64Encoder extends FilterOutputStream { private static final char[] chars = { 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'O', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u',
'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z', '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '+', '/' }; private int charCount;
private int carryOver;
// 是否每76字节换行
private boolean isWrapBreak = true; /***
* Constructs a new Base64 encoder that writes output to the given
* OutputStream.
*
* @param out
* the output stream
*/
private Base64Encoder(OutputStream out) {
super(out);
} /***
* Constructs a new Base64 encoder that writes output to the given
* OutputStream.
*
* @param out
* the output stream
*/
private Base64Encoder(OutputStream out, boolean isWrapBreak) {
this(out);
this.isWrapBreak = isWrapBreak;
} /***
* Writes the given byte to the output stream in an encoded form.
*
* @exception IOException
* if an I/O error occurs
*/
public void write(int b) throws IOException {
// Take 24-bits from three octets, translate into four encoded chars
// Break lines at 76 chars
// If necessary, pad with 0 bits on the right at the end
// Use = signs as padding at the end to ensure encodedLength % 4 == 0 // Remove the sign bit,
// thanks to Christian Schweingruber <chrigu@lorraine.ch>
if (b < 0) {
b += 256;
} // First byte use first six bits, save last two bits
if (charCount % 3 == 0) {
int lookup = b >> 2;
carryOver = b & 3; // last two bits
out.write(chars[lookup]);
}
// Second byte use previous two bits and first four new bits,
// save last four bits
else if (charCount % 3 == 1) {
int lookup = ((carryOver << 4) + (b >> 4)) & 63;
carryOver = b & 15; // last four bits
out.write(chars[lookup]);
}
// Third byte use previous four bits and first two new bits,
// then use last six new bits
else if (charCount % 3 == 2) {
int lookup = ((carryOver << 2) + (b >> 6)) & 63;
out.write(chars[lookup]);
lookup = b & 63; // last six bits
out.write(chars[lookup]);
carryOver = 0;
}
charCount++; // Add newline every 76 output chars (that's 57 input chars)
if (this.isWrapBreak && charCount % 57 == 0) {
out.write('\n');
}
} /***
* Writes the given byte array to the output stream in an encoded form.
*
* @param buf
* the data to be written
* @param off
* the start offset of the data
* @param len
* the length of the data
* @exception IOException
* if an I/O error occurs
*/
public void write(byte[] buf, int off, int len) throws IOException {
// This could of course be optimized
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
write(buf[off + i]);
}
} /***
* Closes the stream, this MUST be called to ensure proper padding is
* written to the end of the output stream.
*
* @exception IOException
* if an I/O error occurs
*/
public void close() throws IOException {
// Handle leftover bytes
if (charCount % 3 == 1) { // one leftover
int lookup = (carryOver << 4) & 63;
out.write(chars[lookup]);
out.write('=');
out.write('=');
} else if (charCount % 3 == 2) { // two leftovers
int lookup = (carryOver << 2) & 63;
out.write(chars[lookup]);
out.write('=');
}
super.close();
} /***
* Returns the encoded form of the given unencoded string.<br>
* 默认是否每76字节换行
*
* @param bytes
* the bytes to encode
* @return the encoded form of the unencoded string
* @throws IOException
*/
public static String encode(byte[] bytes) {
return encode(bytes, true);
} /***
* Returns the encoded form of the given unencoded string.
*
* @param bytes
* the bytes to encode
* @param isWrapBreak
* 是否每76字节换行
* @return the encoded form of the unencoded string
* @throws IOException
*/
public static String encode(byte[] bytes, boolean isWrapBreak) {
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream((int) (bytes.length * 1.4));
Base64Encoder encodedOut = new Base64Encoder(out, isWrapBreak);
try {
encodedOut.write(bytes);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
encodedOut.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
return out.toString();
} // public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// if (args.length != 1) {
// System.err
// .println("Usage: java com.oreilly.servlet.Base64Encoder fileToEncode");
// return;
// }
// Base64Encoder encoder = null;
// BufferedInputStream in = null;
// try {
// encoder = new Base64Encoder(System.out);
// in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(args[0]));
//
// byte[] buf = new byte[4 * 1024]; // 4K buffer
// int bytesRead;
// while ((bytesRead = in.read(buf)) != -1) {
// encoder.write(buf, 0, bytesRead);
// }
// } finally {
// if (in != null)
// in.close();
// if (encoder != null)
// encoder.close();
// }
// }
}
Base64Encoder
Android数据加密之Aes加密的更多相关文章
- Android数据加密之MD5加密
前言: 项目中无论是密码的存储或者说判断文件是否是同一文件,都会用到MD5算法,今天来总结一下MD5加密算法. 什么是MD5加密? MD5英文全称“Message-Digest Algorithm 5 ...
- Android数据加密之Rsa加密
前言: 最近无意中和同事交流数据安全传输的问题,想起自己曾经使用过的Rsa非对称加密算法,闲下来总结一下. 其他几种加密方式: Android数据加密之Rsa加密 Android数据加密之Aes加密 ...
- Android数据加密之Des加密
前言: 端午节前有个同事咨询我有关Android DES加密的相关实现,简单的实现了一下,今天来总结一下. 其他几种加密方式: Android数据加密之Rsa加密 Android数据加密之Aes加密 ...
- android base64 和 aes 加密 解密
package pioneerbarcode.ccw.com.encryptanddecode;import android.os.Bundle;import android.support.v7.a ...
- iOS,Android,Jave后台AES加密解密
AES256 在iOS和Android上的相关代码: http://www.tuicool.com/articles/RVFbmmU 里面可以下载相关的代码. 我们遇到的问题是: 把Android的代 ...
- [android]DES/3DES/AES加密方式
DES 支持8位加密解密,3Des支持24位,Aes支持32位.3Des是Des算法做三次.位数的单位是字节byte.不是bits. 3Des是把24位分成3组.第一组八位用来加密,第二组8位用于解密 ...
- Android加密算法之AES加密和解密实现
<pre name="code" class="plain"><span style="font-family:Microsoft ...
- Android数据加密之异或加密算法
前言: 这几天被公司临时拉到去做Android IM即时通信协议实现,大致看了下他们定的协议,由于之前没有参与,据说因服务器性能限制,只达成非明文传递,具体原因我不太清楚,不过这里用的加密方式是采用异 ...
- Android数据加密之SHA安全散列算法
前言: 对于SHA安全散列算法,以前没怎么使用过,仅仅是停留在听说过的阶段,今天在看图片缓存框架Glide源码时发现其缓存的Key采用的不是MD5加密算法,而是SHA-256加密算法,这才勾起了我的好 ...
随机推荐
- 将表里的数据批量生成INSERT语句的存储过程 增强版
将表里的数据批量生成INSERT语句的存储过程 增强版 有时候,我们需要将某个表里的数据全部或者根据查询条件导出来,迁移到另一个相同结构的库中 目前SQL Server里面是没有相关的工具根据查询条件 ...
- Sublime的使用
1.一个可扩展性强的编辑工具 2.如何安装扩展 通过View->Show Console菜单打开命令行. 按图操作: 在控制台输入,然后回车: import urllib.request,os; ...
- webapi - 模型验证
本次要和大家分享的是webapi的模型验证,讲解的内容可能不单单是做验证,但都是围绕模型来说明的:首先来吐槽下,今天下午老板为自己买了套新办公家具,看起来挺好说明老板有钱,不好的是我们干技术的又成了搬 ...
- Javascript实用方法
这篇我主要记录一些在工作中常用的.实用的方法. String trim 字符串方法中的trim主要用来去空格使用,很多时候,在后台做参数处理的时候,我们都会使用该方法,比如在获取用户输入的账户时 va ...
- android 两种实现计时器时分秒的实现,把时间放在你的手中~
可能我们在开发中会时常用到计时器这玩意儿,比如在录像的时候,我们可能需要在右上角显示一个计时器.这个东西其实实现起来非常简单. 只需要用一个控件Chronometer,是的,就这么简单,我都不好意思讲 ...
- go语言:多个[]byte数组合并成一个[]byte
场景:在开发中,要将多个[]byte数组合并成一个[]byte,初步实现思路如下: 1.获取多个[]byte长度 2.构造一个二维码数组 3.循环将[]byte拷贝到二维数组中 package gst ...
- 6.在MVC中使用泛型仓储模式和依赖注入实现增删查改
原文链接:http://www.c-sharpcorner.com/UploadFile/3d39b4/crud-operations-using-the-generic-repository-pat ...
- C# BackgroundWorker 详解
在C#程序中,经常会有一些耗时较长的CPU密集型运算,如果直接在 UI 线程执行这样的运算就会出现UI不响应的问题.解决这类问题的主要途径是使用多线程,启动一个后台线程,把运算操作放在这个后台线程中完 ...
- eclipse如何添加Memory Analyzer
①启动Eclipse,并打开"Install New software..."对话框: ②点击Add,如图: ③点击OK,最后一直点next,完成
- Android之数据存储的五种方法
1.Android数据存储的五种方法 (1)SharedPreferences数据存储 详情介绍:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhangmiao14/p/6201900.html 优 ...
