MapReduce核心原理(下)
MapReduce 中的排序
MapTask 和 ReduceTask 都会对数据按key进行排序。该操作是 Hadoop 的默认行为,任何应用程序不管需不需要都会被排序。默认排序是字典顺序排序,排序方法是快速排序
下面介绍排序过程:
MapTask
- 它会将处理的结果暂时放到环形缓冲区中,当环形缓冲区使用率达到一定阈值后,再对缓冲区中的数据进行一次快速排序,并将这些有序数据溢写到磁盘
- 溢写完毕后,他会对磁盘所有文件进行归并排序
ReduceTask
- 当所有数据拷贝完后,会统一对内存和磁盘的所有数据进行一次归并排序。
排序方式
- 部分排序
MapReduce 根据输入记录的键值对数据集排序,保证输出的每个文件内部有序
- 全排序
最终输出结果只有一个文件,且文件内部有序。实现方式是只设置一个 ReduceTask,但是该方法在处理大型文件时效率极低。因为这样只有一台机器处理所有的文件,完全丧失了 MapReduce 所提供的并行架构
- 辅助排序(分组排序)
在 Reduce 端对 key 进行分组。应用于:在接受的 key 为 bean 对象时,想让一个或几个字段相同的 key 进入到同一个 reduce 方法时,可以采用分组排序。
- 二次排序
在自定义排序过程中,如果 compareTo 中的判断条件为两个即为二次排序。
排序接口 WritebleComparable
我们知道 MapReduce 过程是会对 key 进行排序的。那么如果我们将 Bean 对象作为 key 时,就需要实现 WritableComparable 接口并重写 compareTo 方法指定排序规则。
@Setter
@Getter
public class CustomSort implements WritableComparable<CustomSort> {
private Long orderId;
private String orderCode;
@Override
public int compareTo(CustomSort o) {
return orderId.compareTo(o.orderId);
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput dataOutput) throws IOException {
dataOutput.writeLong(orderId);
dataOutput.writeUTF(orderCode);
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput dataInput) throws IOException {
this.orderId = dataInput.readLong();
this.orderCode = dataInput.readUTF();
}
}
分组排序 GroupingComparator
GroupingComparator 是 Mapreduce 中 reduce 端的一个功能组件,主要的作用是决定哪些数据为一组,调用一次 reduce 逻辑。默认是每个不同的 key,作为不同的组。我们可以自定义 GroupingComparator 实现不同的 key 作为一个组,调用一次 reduce 逻辑。
案例实战:求出每一个订单中成交金额最大的一笔交易。下面的数据只给出了订单行的 id 和金额。订单行 id 中_前相等的算同一个订单
| 订单行 id | 商品金额 |
|---|---|
| order1_1 | 345 |
| order1_2 | 4325 |
| order1_3 | 44 |
| order2_1 | 33 |
| order2_2 | 11 |
| order2_3 | 55 |
实现思路
Mapper:
- 读取一行文本数据,切分每个字段
- 把订单行 id 和金额封装为一个 bean 对象,作为 key,排序规则是订单行 id“_”前面的订单 id 来排序,如果订单 id 相等再按金额降序排
- map 输出内容,key:bean 对象,value:NullWritable.get()
Shuffle:
- 自定义分区器,保证相同的订单 id 的数据去同一个分区
Reduce:
- 自定义 GroupingComparator,分组规则指定只要订单 id 相等则属于同一组
- 每个 reduce 方法写出同一组 key 的第一条数据就是最大金额的数据。
参考代码:
public class OrderBean implements WritableComparable<OrderBean> {
private String orderLineId;
private Double price;
@Override
public int compareTo(OrderBean o) {
String orderId = o.getOrderLineId().split("_")[0];
String orderId2 = orderLineId.split("_")[0];
int compare = orderId.compareTo(orderId2);
if(compare==0){
return o.price.compareTo(price);
}
return compare;
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput dataOutput) throws IOException {
dataOutput.writeUTF(orderLineId);
dataOutput.writeDouble(price);
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput dataInput) throws IOException {
this.orderLineId = dataInput.readUTF();
this.price = dataInput.readDouble();
}
}
public class OrderMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text,OrderBean, NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, OrderBean, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] split = value.toString().split(" ");
OrderBean orderBean=new OrderBean();
orderBean.setOrderLineId(split[0]);
orderBean.setPrice(Double.parseDouble(split[1]));
context.write(orderBean,NullWritable.get());
}
}
自定义分区:
public class OrderPartitioner extends Partitioner<OrderBean, NullWritable> {
@Override
public int getPartition(OrderBean orderBean, NullWritable nullWritable, int i) {
//相同订单id的发到同一个reduce中去
String orderId = orderBean.getOrderLineId().split("_")[0];
return (orderId.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % i;
}
}
组排序:
public class OrderGroupingComparator extends WritableComparator {
public OrderGroupingComparator() {
super(OrderBean.class,true);
}
@Override
public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
String aOrderId = ((OrderBean) a).getOrderLineId().split("_")[0];
String bOrderId = ((OrderBean) b).getOrderLineId().split("_")[0];
return aOrderId.compareTo(bOrderId);
}
}
public class OrderReducer extends Reducer<OrderBean, NullWritable,OrderBean,NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(OrderBean key, Iterable<NullWritable> values, Reducer<OrderBean, NullWritable, OrderBean, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
context.write(key,NullWritable.get());
}
}
driver 类:
public class OrderDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
// System.setProperty("java.library.path","d://");
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job=Job.getInstance(conf,"OrderDriver");
//指定本程序的jar包所在的路径
job.setJarByClass(OrderDriver.class);
//指定本业务job要使用的mapper/Reducer业务类
job.setMapperClass(OrderMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(OrderReducer.class);
//指定mapper输出数据的kv类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(OrderBean.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
//指定reduce输出数据的kv类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(OrderBean.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
//指定job的输入文件目录和输出目录
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job,new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path(args[1]));
job.setPartitionerClass(OrderPartitioner.class);
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(OrderGroupingComparator.class);
// job.setNumReduceTasks(2);
boolean result = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit( result ? 0: 1);
}
}
MapReduce 读取和输出数据
InputFormat
运行 MapReduce 程序时,输入的文件格式包括:基于行的日志文件、二进制格式文件、数据库表等。那么,针对不同的数据类型,MapReduce 是如何读取这些数据的呢?
InputFormat 是 MapReduce 框架用来读取数据的类。InputFormat 常用子类:
- TextInputFormat(普通文本文件,MR 框架默认的读取实现类)
- KeyValueTextInputFormat(读取一行文本数据按照指定分隔符,把数据封装为 kv 类型)
- NLineInputFormat(读取数据按照行数进行划分分片)
- CombineTextInputFormat(合并小文件,避免启动过多 MapTask 任务)
- 自定义 InputFormat
1. CombineTextInputFormat 案例
MR 框架默认的 TextInputFormat 切片机制按文件划分切片,文件无论多小,都是单独一个切片,然后由一个 MapTask 处理,如果有大量小文件,就对应生成并启动大量的 MapTask,就会浪费很多初始化资源、启动回收等阶段。
CombineTextInputFormat 用于小文件过多的场景,它可以将多个小文件从逻辑上划分成一个切片,这样多个小文件可以交给一个 MapTask 处理,提高资源利用率。
使用方式:
// 如果不设置InputFormat,它默认用的是TextInputFormat.class
job.setInputFormatClass(CombineTextInputFormat.class);
//虚拟存储切片最大值设置4m
CombineTextInputFormat.setMaxInputSplitSize(job, 4194304);
- CombineTextInputFormat 切片原理
假设设置 setMaxInputSplitSize 值为 4M,有四个小文件:1.txt -->2M ;2.txt-->7M;3.txt-->0.3M;4.txt--->8.2M
虚拟存储过程:
把输入目录下所有文件大小,依次和设置的 setMaxInputSplitSize 值进行比较,如果不大于设置的最大值,逻辑上划分一个块。如果输入文件大于设置的最大值且大于两倍,那么以最大值切割一块;当剩余数据大小超过设置的最大值且不大于最大值 2 倍,此时将文件均分成 2 个虚拟存储块(防止出现太小切片)。比如如 setMaxInputSplitSize 值为 4M,输入文件大小为 8.02M,则先逻辑上分出一个 4M 的块。剩余的大小为 4.02M,如果按照 4M 逻辑划分,就会出现 0.02M 的非常小的虚拟存储文件,所以将剩余的 4.02M 文件切分成(2.01M 和 2.01M)两个文件。
2M,一个块
7M,大于 4 但是不大于 4 的 2 倍,则分为两块,一块 3.5M
切片过程:
判断虚拟存储的文件大小是否大于 setMaxInputSplitSize 值,大于等于则单独形成一个切片
如果不大于则跟下一个虚拟存储文件进行合并,共同形成一个切片。
按照之前输入文件:那 4 个文件经过虚拟存储过程后,有 7 个文件块:2M、3.5M、3.5M、0.3M、4M、2.1M、2.1M
合并之后最终形成 3 个切片:(2+3.5)M、(3.5+0.3+4)M、(2.1+2.1)M
2. 自定义 InputFormat
无论 HDFS 还是 MapReduce,在处理小文件时效率都非常低,但又难免面临处理大量小文件的场景,此时,就需要有相应解决方案。可以自定义 InputFormat 实现小文件的合并。
案例实战
需求:
将多个小文件合并成一个 SequenceFile 文件(SequenceFile 文件是 Hadoop 用来存储二进制形式的 key-value 对的文件格式),SequenceFile 里面存储着多个文件,存储的形式为文件路径+名称为 key,文件内容为 value。
实现思路:
- 定义一个类继承 FileInputFormat
- 重写 isSplitable()指定为不可切分,重写 createRecordReader()方法,创建自己的 RecorderReader 对象
- 改变默认读取数据方式,实现一次读取一个完整文件作为 kv 输出
- Driver 指定使用自定义 InputFormat
代码参考:
public class CustomFileInputFormat extends FileInputFormat<Text, BytesWritable> {
@Override
protected boolean isSplitable(JobContext context, Path filename) {
return false;
}
@Override
public RecordReader<Text, BytesWritable> createRecordReader(InputSplit inputSplit, TaskAttemptContext taskAttemptContext) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
CustomRecordReader reader = new CustomRecordReader();
reader.initialize(inputSplit, taskAttemptContext);
return reader;
}
}
public class CustomRecordReader extends RecordReader <Text, BytesWritable> {
private Configuration conf;
private FileSplit split;
private boolean isProgress=true;
private BytesWritable value = new BytesWritable();
private Text key = new Text();
@Override
public void initialize(InputSplit inputSplit, TaskAttemptContext taskAttemptContext) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
this.split = (FileSplit) inputSplit;
this.conf = taskAttemptContext.getConfiguration();
}
@Override
public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
if(isProgress){
FSDataInputStream fis = null;
try {
//定义缓存区
byte[] contents = new byte[(int) split.getLength()];
//获取文件系统
Path path = split.getPath();
FileSystem fs = path.getFileSystem(conf);
//读取数据
fis = fs.open(path);
//读取文件内容到缓存区
IOUtils.readFully(fis,contents,0,contents.length);
//输出文件内容
value.set(contents,0,contents.length);
//获取文件路径
String name = split.getPath().toString();
key.set(name);
} finally {
IOUtils.closeStream(fis);
}
isProgress = false;
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public Text getCurrentKey() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
return key;
}
@Override
public BytesWritable getCurrentValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
return value;
}
@Override
public float getProgress() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void close() throws IOException {
}
}
在 driver 里设置 inputFormatclass
job.setInputFormatClass(CustomFileInputFormat.class);
OutputFormat
OutputFormat:是 MapReduce 输出数据的基类,所有 MapReduce 的数据输出都实现了 OutputFormat 抽象类。下面介绍几种常见的 OutputFormat 子类
- TextOutputFormat
默认的输出格式是 TextOutputFormat,它把每条记录写为文本行。
- SequenceFileOutputFormat
将 SequenceFileOutputFormat 输出作为后续 MapReduce 任务的输入,这是一种好的输出格式,因为它的格式紧凑,很容易被压缩。
自定义 OutputFormat
案例实战
需求:
需要一个 MapReduce 程序根据奇偶数把结果输出到不同目录。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
实现思路:
- 自定义一个类继承 FileOutPutFormat
- 改写 RecordWriter,重写 write 方法
代码参考:
public class CustomOutputFormat extends FileOutputFormat<Text, NullWritable> {
@Override
public RecordWriter<Text, NullWritable> getRecordWriter(TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(context.getConfiguration());
FSDataOutputStream oddOut = fs.create(new Path("e:/odd.log"));
FSDataOutputStream eventOut = fs.create(new Path("e:/event.log"));
return new CustomWriter(oddOut, eventOut);
}
}
public class CustomWriter extends RecordWriter<Text, NullWritable> {
private FSDataOutputStream oddOut;
private FSDataOutputStream evenOut;
public CustomWriter(FSDataOutputStream oddOut, FSDataOutputStream evenOut) {
this.oddOut = oddOut;
this.evenOut = evenOut;
}
@Override
public void write(Text text, NullWritable nullWritable) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Integer number = Integer.valueOf(text.toString());
System.out.println(text.toString());
if(number%2==0){
evenOut.write(text.toString().getBytes());
evenOut.write("\r\n".getBytes());
}else {
oddOut.write(text.toString().getBytes());
oddOut.write("\r\n".getBytes());
}
}
@Override
public void close(TaskAttemptContext taskAttemptContext) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
IOUtils.closeStream(oddOut);
IOUtils.closeStream(evenOut);
}
}
设置 outputFormat 类
job.setOutputFormatClass(CustomOutputFormat.class);
Shuffle 阶段数据的压缩机制
Hadoop 中支持的压缩算法
据压缩有两大好处,节约磁盘空间,加速数据在网络和磁盘上的传输!!
我们可以使用 bin/hadoop checknative 来查看我们编译之后的 hadoop 支持的各种压缩,如果出现 openssl 为 false,那么就在线安装一下依赖包!!

| 压缩格式 | hadoop 自带 | 算法 | 文件扩展名 | 是否可切分 | 换压缩格式后,原来的程序是否需要修改 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEFLATE | 是 | DEFLATE | .deflate | 否 | 不需要 |
| Gzip | 是 | DEFLATE | .gz | 否 | 不需要 |
| bzip2 | 是 | bzip2 | .bz2 | 是 | 不需要 |
| LZO | 否 | LZO | .lzo | 是 | 需要建索引,还需要指定输入格式 |
| Snappy | 否 | Snappy | .snappy | 否 | 不需要 |
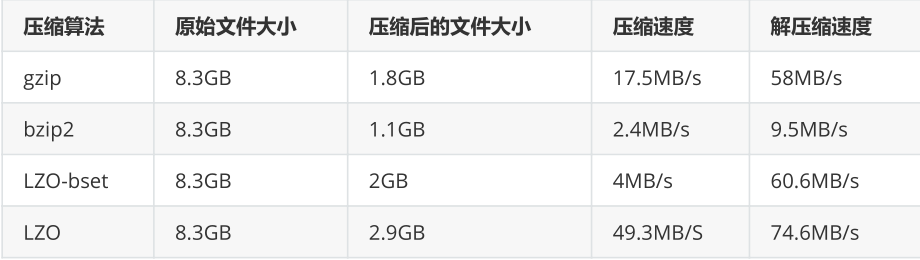
压缩效率对比:
压缩位置
- Map 输入端压缩
此处使用压缩文件作为 Map 的输入数据,无需显示指定编解码方式,Hadoop 会自动检查文件扩展名,如果压缩方式能够匹配,Hadoop 就会选择合适的编解码方式进行压缩和解压。
- Map 端输出压缩
Shuffle 是 MR 过程中资源消耗最多的阶段,如果有数据量过大造成网络传输速度缓慢,可以考虑使用压缩
- Reduce 端输出压缩
输出的结果数据使用压缩能够减少存储的数据量,降低所需磁盘的空间,并且作为第二个 MR 的输入时可以复用压缩
压缩配置方式
- 在驱动代码中通过 Configuration 设置。
设置map阶段压缩
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.set("mapreduce.map.output.compress","true");
configuration.set("mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec","org.apache.hadoop.i
o.compress.SnappyCodec");
设置reduce阶段的压缩
configuration.set("mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress","true");
configuration.set("mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.type","RECORD"
);
configuration.set("mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.codec","org.ap
ache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec");
- 配置 mapred-site.xml,这种方式是全局的,对所有 mr 任务生效
<property>
<name>mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.type</name>
<value>RECORD</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.codec</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec</value>
</property>
压缩实战
在驱动代码中添加即可
configuration.set("mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress","true");
configuration.set("mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.type","RECORD");
configuration.set("mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.codec","org.apache
.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec");
MapReduce核心原理(下)的更多相关文章
- mapreduce核心原理
1:第一阶段: 第一阶段的task每一个nodemanager并发运行程序,完全并发,各不影响.这就是map阶段 运行的task时maptask 2:第二个阶段的task并发实例互不相干,但是他们的数 ...
- 【算法】(查找你附近的人) GeoHash核心原理解析及代码实现
本文地址 原文地址 分享提纲: 0. 引子 1. 感性认识GeoHash 2. GeoHash算法的步骤 3. GeoHash Base32编码长度与精度 4. GeoHash算法 5. 使用注意点( ...
- docker核心原理
容器概念. docker是一种容器,应用沙箱机制实现虚拟化.能在一台宿主机里面独立多个虚拟环境,互不影响.在这个容器里面可以运行着我饿们的业务,输入输出.可以和宿主机交互. 使用方法. 拉取镜像 do ...
- MapReduce工作原理讲解
第一部分:MapReduce工作原理 MapReduce 角色•Client :作业提交发起者.•JobTracker: 初始化作业,分配作业,与TaskTracker通信,协调整个作业.•TaskT ...
- MapReduce工作原理
第一部分:MapReduce工作原理 MapReduce 角色•Client :作业提交发起者.•JobTracker: 初始化作业,分配作业,与TaskTracker通信,协调整个作业.•Tas ...
- MapReduce工作原理图文详解 (炼数成金)
MapReduce工作原理图文详解 1.Map-Reduce 工作机制剖析图: 1.首先,第一步,我们先编写好我们的map-reduce程序,然后在一个client 节点里面进行提交.(一般来说可以在 ...
- 高性能消息队列 CKafka 核心原理介绍(上)
欢迎大家前往腾讯云技术社区,获取更多腾讯海量技术实践干货哦~ 作者:闫燕飞 1.背景 Ckafka是基础架构部开发的高性能.高可用消息中间件,其主要用于消息传输.网站活动追踪.运营监控.日志聚合.流式 ...
- [转载] MapReduce工作原理讲解
转载自http://www.aboutyun.com/thread-6723-1-1.html 有时候我们在用,但是却不知道为什么.就像苹果砸到我们头上,这或许已经是很自然的事情了,但是牛顿却发现了地 ...
- 《大型网站技术架构:核心原理与案例分析》【PDF】下载
<大型网站技术架构:核心原理与案例分析>[PDF]下载链接: https://u253469.pipipan.com/fs/253469-230062557 内容简介 本书通过梳理大型网站 ...
随机推荐
- Dev C++编写C/C++程序 出现[Error] ld returned 1 exit status报错分析及解决
debug系列第一弹,不知道大家写程序的时候是不是都遇到过如题的报错. 我本人是经常遇到这行熟悉的令人不知所措的报错,可能是我太笨了 有时候百度无果也差不到原因,那就汇总一下目前我遇到的情况吧--持续 ...
- ExtJS 布局-Card 布局(Card layout)
更新记录: 2022年6月1日 开始. 2022年6月6日 发布. 1.说明 卡片布局类似牌堆,每次只有一个子组件可见,子组件几乎填满了整个容器.卡片布局常用于向导(Wizard)和选项卡(Tabs) ...
- HTML\Flex tips
相关文档 HTML:https://www.w3school.com.cn/html/index.asp bootstrap-css: https://v3.bootcss.com/css/#form ...
- Elasticsearch学习系列七(Es分布式集群)
核心概念 集群(Cluster) 一个Es集群由多个节点(Node)组成,每个集群都有一个共同的集群名称作为标识 节点(Node) 一个Es实例就是一个Node.Es的配置文件中可以通过node.ma ...
- 《AlignedReID:Surpassing Human-Level Performance in Person Re-Identification》理解
- File类创建删除功能的方法和File类遍历(文件夹)目录功能
File类创建删除功能的方法 -public boolean createNewFile():当且仅当具有该名称的文件尚不存在时,创建一个新的空文件 -public boolean delete(): ...
- docker快速安装openvas
项目地址 1.更换国内docker源 2.docker run -d -p 443:443 -e PUBLIC_HOSTNAME=此处填你宿主机IP --name openvas mikesplain ...
- C# MVCapi跨域问题
he 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header contains multiple values ', *', but only one is allowed. Or ...
- SQLZOO练习5--join(表的连接)
game表: id mdate stadium team1 team2 1001 8 June 2012 National Stadium, Warsaw POL GRE 1002 8 June 20 ...
- Spring知识点详解
1.Spring 概述 1.1.Spring 的概念和特点 Spring 是一个轻量级的控制反转(IoC)和面向切面(AOP)的开源容器框架,它是由 Rod Johnson(音乐学博士)所创建,其核心 ...
