关于作用域范围Scope
举个例子,如下:
public class C {
public int a = 2;
public void test(int b) {
int c = 3;
for (int d = 3; a < 6; a++) {
}
}
}
形成的Scope作用域如下图:

属性table中存储的具体数据如下截图:

关于Scope的定义如下:
/** A scope represents an area of visibility in a Java program. The
* Scope class is a container for symbols which provides
* efficient access to symbols given their names.
*
* Scopes are implemented as hash tables with "open addressing" and "double hashing".
* Scopes can be nested; the next field of a scope points
* to its next outer scope. Nested scopes can share their hash tables.
*
*/
public class Scope {
/** The number of scopes that share this scope's hash table.
*/
private int shared;
/** Next enclosing scope (with whom this scope may share a hashtable)
*
* 参考博文:https://www.cnblogs.com/extjs4/p/6386572.html
*/
public Scope next;
/** The scope's ownerSymbol.
*/
public Symbol ownerSymbol;
/** A hash table for the scope's entries.
*/
Entry[] table;
/** Mask for hash codes, always equal to (table.length - 1).
*/
int hashMask;
/** A linear list that also contains all entries in
* reverse order of appearance (i.e later entries are pushed on top).
*/
public Entry elems;
/** The number of elements in this scope.
* This includes deleted elements, whose value is the sentinel.
*/
int nelems = 0;
// ...
}
Scope是符号的容器,通过Scope来查找及决定符号的访问。创建Scope对象有三种途径:
(1)调用构造函数创建
/** The hash table's initial size.
*/
private static final int INITIAL_SIZE = 0x10;
/** A value for the empty scope.
*/
public static final Scope emptyScope = new Scope(null, null, new Entry[]{});
/** Construct a new scope, within scope next, with given owner, using
* given table. The table's length must be an exponent of 2.
*/
protected Scope(Scope next, Symbol owner, Entry[] table) {
this.next = next;
Assert.check(emptyScope == null || owner != null);
this.ownerSymbol = owner;
this.table = table;
this.hashMask = table.length - 1;
}
/** Construct a new scope, within scope next, with given owner,
* using a fresh table of length INITIAL_SIZE.
*/
public Scope(Symbol owner) {
this(null, owner, new Entry[INITIAL_SIZE]);
}
第一个为基本的构造函数,一般不对外开放调用,由于是protected权限,所以一般是子类通过super()方法来调用,而通过调用下面的构造函数来得到一个全新的Scope对象。
(2)调用dup()方法
/** Convenience constructor used for dup and dupUnshared. */
private Scope(Scope next, Symbol owner, Entry[] table, int nelems) {
this(next, owner, table);
this.nelems = nelems;
}
/** Construct a fresh scope within this scope, with same ownerSymbol,
* which shares its table with the outer scope. Used in connection with
* method leave if scope access is stack-like in order to avoid allocation
* of fresh tables.
*/
public Scope dup() {
return dup(this.ownerSymbol);
}
/** Construct a fresh scope within this scope, with new ownerSymbol,
* which shares its table with the outer scope. Used in connection with
* method leave if scope access is stack-like in order to avoid allocation
* of fresh tables.
* 如果范围访问是堆栈式的,则使用方法离开,以避免重新分配新表。
*/
public Scope dup(Symbol newOwner) {
Scope result = new Scope(this, newOwner, this.table, this.nelems);
shared++;
// System.out.println("====> duping scope " + this.hashCode() + " owned by " + newOwner + " to " + result.hashCode());
// new Error().printStackTrace(System.out);
return result;
}
共有几处调用这个dup()方法,如下截图:
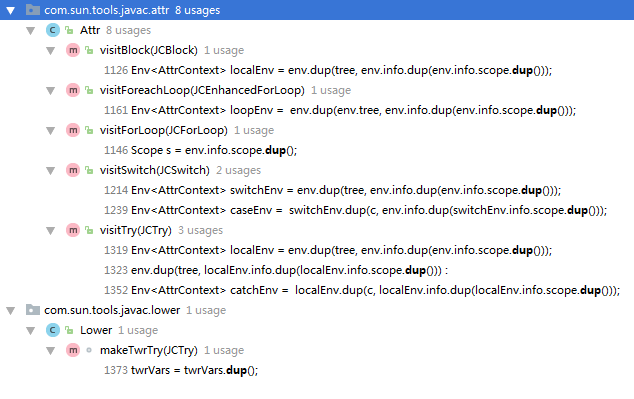
(3)调用dupUnshared()方法
/** Construct a fresh scope within this scope, with same ownerSymbol,
* with a new hash table, whose contents initially are those of
* the table of its outer scope.
*/
public Scope dupUnshared() {
return new Scope(this, this.ownerSymbol, this.table.clone(), this.nelems);
}
与dup()方法比起来,克隆了this.table的值,举个例子如下:
public class Test1 {
static class Entry{
int a = 0;
int[] arr = null;
public Entry(int a,int[] arr){
this.a = a;
this.arr = arr;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Entry [a=" + a + ", arr=" + Arrays.toString(arr) + "]";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Entry[] ens = new Entry[2];
ens[0] = new Entry(2,new int[]{2,3});
Entry[] ensC = ens.clone();
ensC[0].arr[0] = 33;
ensC[1] = new Entry(3,new int[]{2,3});
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ens));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ensC));
}
}
运行结果如下:
result: [Entry [a=2, arr=[33, 3]], null] [Entry [a=2, arr=[33, 3]], Entry [a=3, arr=[2, 3]]]
可以看到,调用了clone()方法后,往table中加入新的Entry,不会影响到原来table中的值。这就是所说的不共享。
GJC中调用dupUnshared()方法的地方如下图所示。

其中有些重要的属性如下:
1、属性next
/** Next enclosing scope (with whom this scope may share a hashtable)
*
*/
public Scope next;
从上面的例子可以清楚的看到next指向上一层作用域范围。作用域是通过块形成的,例如:
2、属性owner
/** The scope's owner.
*/
public Symbol owner;
表示的是这个作用域所属的符号。
3、属性table
/** A hash table for the scope's entries.
*/
Entry[] table;
这个属性比较重要,主要存储了这个Scope作用域内的符号,并且通过"open addressing"和"double hashing"来计算具体的某个Entry存储的位置。看一下Entry中除了存储符号Symbol还存储了哪些信息,定义如下:
/** A class for scope entries.
*
* shadowed指针指向桶中的下一个表项,shadowed意为隐蔽之义,sibling指针指向下一个填入哈希表中的表项,和符号的范围scope
*/
public class Entry {
/** The referenced symbol. 被引用的符号
* sym == null iff(if and only if 当且仅当) this == sentinel
*/
public Symbol sym;
/** An entry with the same hash code, or sentinel.
*/
public Entry shadowed;
/** Next entry in same scope.
*/
public Entry sibling;
/** The entry's scope.
* scope == null iff this == sentinel
* for an entry in an import scope, this is the scope where the entry came from (i.e. was imported from).
*/
public Scope scope;
...
}
由于table属性可以共享,也就是被enclosing封闭的作用域可以和外层的作用域共享table,从上面举的例子中就可以看出。如果要共享,那么还需要保证被封闭的作用域的符号不能
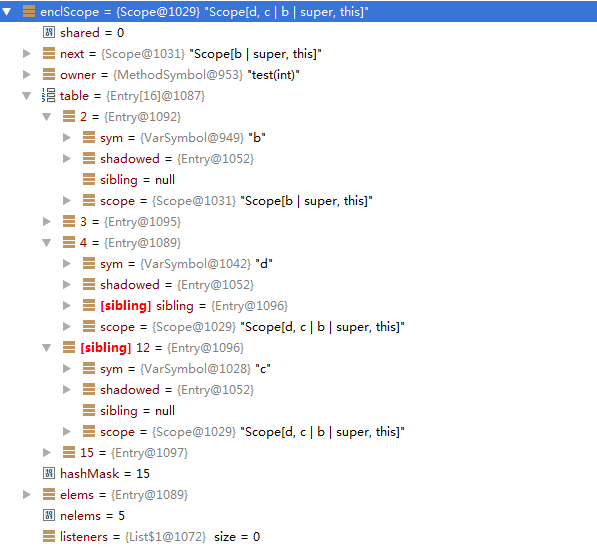
被外层作用域取到,所以必须在Entry中指定这个Symbol到底是属于哪个作用域Scope的。通过如下截图就可以清楚的看到各个Symbol是在哪个作用域内定义的。

sibling属性将Entry连接为单向链表,如同一个作用域内定义了3个Symbol,有3个Entry,按倒序链接起来,也就是后加入的在前面。先加入的在后面。
public class C {
public int a = 2;
public void test(int b) {
int c = 3;
int d = 4;
}
}
在方法内定义了两个变量c和d,通过如下截图可以清楚看到d的sibling指向c,因为c先定义的。
shadowed属性,举个例子,如下:
public class C {
public int a = 2;
public void test() {
int a = 2;
class a {}
}
}
截图如下:

可以看到,对于类名为a和变量名为a的符号存储到了同一个hash桶中,通过shadowed形成了链。
再看个例子,如下:
public class C {
public int a = 2;
class a {
}
public void a() {
}
}
截图如下:

关于作用域范围Scope的更多相关文章
- [译] 你该知道的javascript作用域 (javascript scope)(转)
javascript有一些对于初学者甚至是有经验的开发者都难以理解的概念. 这个部分是针对那些听到 : 作用域, 闭包, this, 命名空间, 函数作用域, 函数作用域, 全局作用域, 变量作用域( ...
- AngularJS 作用域(Scope)
AngularJS作用域(Scope) Scope作用域是应用在视图和控制器之间的纽带,Scope是一个对象包含可用的方法和属性,Scope可以应用在试图和控制器上. $scope是针对当前的cont ...
- JavaScript变量作用域(Variable Scope)和闭包(closure)的基础知识
在这篇文章中,我会试图讲解JavaScript变量的作用域和声明提升,以及许多隐隐藏的陷阱.为了确保我们不会碰到不可预见的问题,我们必须真正理解这些概念. 基本定义 作用范围是个“木桶”,里面装着变量 ...
- JavaScript 作用域(Scope)详解
先对需要用到的名词解释一下,再通过例子深入理解 一.什么是作用域(Scope) [[scope]]:每个javascript函数都是一个对象,对象中有些属性我们可以访问,但有些不可以,这些属性仅供ja ...
- 深入理解JavaScript系列(14):作用域链(Scope Chain)
前言 在第12章关于变量对象的描述中,我们已经知道一个执行上下文 的数据(变量.函数声明和函数的形参)作为属性存储在变量对象中. 同时我们也知道变量对象在每次进入上下文时创建,并填入初始值,值的更新出 ...
- JavaScript的作用域(Scope)和上下文(Context)
JavaScript对于作用域(Scope)和上下文(Context)的实现是这门语言的一个非常独到的地方,部分归功于其独特的灵活性. 函数可以接收不同的的上下文和作用域.这些概念为JavaScrip ...
- 依赖作用域之<scope>test</scope>
经常在代码中看到依赖的作用域为<scope>test</scope>,它的作用是,只能在test目录(通过右键->Make Directory as->Test S ...
- Spring中bean作用域属性scope
关键字: spring中属性scope的prototype是什么意思 默认情况下,从bean工厂所取得的实例为Singleton(bean的singleton属性) Singleton: Spri ...
- Mybatis笔记六:Mybatis中SqlSessionFactoryBuilder/SqlSessionFactory/SqlSession/映射器实例的作用域(Scope)和生命周期
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 这个类可以被实例化.使用和丢弃,一旦创建了 SqlSessionFactory,就不再需要它了.因此 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder ...
随机推荐
- MySQL Yum存储库 安装、升级、集群
添加MySQL Yum存储库 首先,将MySQL Yum存储库添加到系统的存储库列表中.按着这些次序: 在http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/repo/yum/上转到MySQ ...
- linux (centos 6.4)下编译安装git
是时候动手尝试下 Git 了,不过得先安装好它.有许多种安装方式,主要分为两种,一种是通过编译源代码来安装:另一种是使用为特定平台预编译好的安装包(yum install git). 若是条件允许,从 ...
- 从窗口句柄得到菜单句柄(从HWND得到HMENU)
1. 如果HWND是主窗口,可以使用API: GetMenu(...) 得到属于主窗口的句柄,原型如下: HMENU GetMenu(HWND hWnd); 在MFC中原型如下: CMenu* Get ...
- Lucene原理一
Lucene 是一个高效的,基于Java 的全文检索库. 所以在了解Lucene之前要费一番工夫了解一下全文检索. 那么什么叫做全文检索呢?这要从我们生活中的数据说起. 我们生活中的数据总体分为两种: ...
- Python学习-27.Python中的列表(list)
列表已经用了很多次了.使用中括号包含元素. list = ['a','b','c'] 获取元素使用[]. print(list[0]) 输出a 不过值得注意的是,[]只能是0到元素个数-1吗?在Pyt ...
- 统一登录中心SSO 单点登录系统的构想
什么是单点登录?我想肯定有一部分人“望文生义”的认为单点登录就是一个用户只能在一处登录,其实这是错误的理解.单点登录指的是多个子系统只需要登录一个,其他系统不需要登录了(一个浏览器内).一个子系统退出 ...
- C#通过rdp账密直接打开远程桌面
思路是首先新建一个vbs脚本,再创建一个bat脚本,再创建rdp文件,运行顺序是vbs->bat->rdp.rdp文件里面包含远程电脑的账密和其它信息,这样就可以不用再输入账密,而在程序里 ...
- map函数和reduce函数、filter函数的区别
①从参数方面来讲:map()函数: map()包含两个参数,第一个是参数是一个函数,第二个是序列(列表或元组).其中,函数(即map的第一个参数位置的函数)可以接收一个或多个参数.reduce()函数 ...
- 枚举类型内部函数 enumerate
enumerate()说明enumerate()是python的内置函数enumerate在字典上是枚举.列举的意思对于一个可迭代的(iterable)/可遍历的对象(如列表.字符串),enumera ...
- python scapy 网卡发包
from scapy.all import * pkt = Ether(src='11:22:33:44:55:77', dst='11:22:33:44:55:66')/ARP(op="w ...
