【译】Spring 4 + Hibernate 4 + Mysql + Maven集成例子(注解 + XML)
前言
译文链接:http://websystique.com/spring/spring4-hibernate4-mysql-maven-integration-example-using-annotations/
本文将基于注解配置, 集成Spring 4和Hibernate 4,开发一个增删改查应用,涉及以下内容:
- 创建Hibernate实体
- 保存数据到mysql数据库中
- 在事务
transaction内部执行增删改查操作 - 典型企业应用中不同层之间的交互
- 基于注解配置
当然,我们也会给出XML配置作为对比。
如果你的应用是基于Spring MVC开发,那么可以参考该链接:Spring4 MVC Hibernate and MySQL integration.
涉及的技术及开发工具
- Spring 4.0.6.RELEASE
- Hibernate Core 4.3.6.Final
- MySQL Server 5.6
- Joda-time 2.3
- Maven 3
- JDK 1.6
- Eclipse JUNO Service Release 2
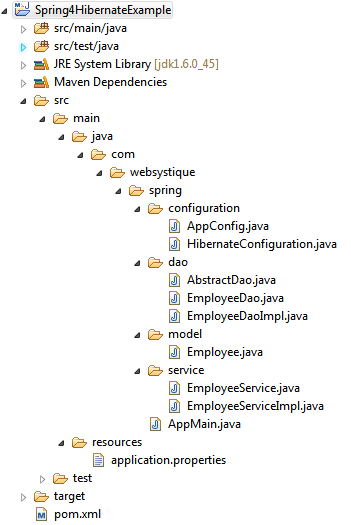
工程结构目录
步骤一:往pom.xml中添加依赖
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.websystique.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>Spring4HibernateExample</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging> <name>Spring4HibernateExample</name> <properties>
<springframework.version>4.0.6.RELEASE</springframework.version>
<hibernate.version>4.3.6.Final</hibernate.version>
<mysql.connector.version>5.1.31</mysql.connector.version>
<joda-time.version>2.3</joda-time.version>
</properties> <dependencies> <!-- Spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>${springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>${springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId>
<version>${springframework.version}</version>
</dependency> <!-- Hibernate -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>${hibernate.version}</version>
</dependency> <!-- MySQL -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>${mysql.connector.version}</version>
</dependency> <!-- Joda-Time -->
<dependency>
<groupId>joda-time</groupId>
<artifactId>joda-time</artifactId>
<version>${joda-time.version}</version>
</dependency> <!-- To map JodaTime with database type -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jadira.usertype</groupId>
<artifactId>usertype.core</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0.CR1</version>
</dependency> </dependencies>
<build>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.6</source>
<target>1.6</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build> </project>
很明显我们需要添加Spring、Hibernate和Mysql连接器相关依赖,另外,由于我们使用了joda-time库来处理时间,所以也引入了joda-time依赖。usertype-core库引入是为了提供数据库时间类型与joda-time LocalDate之间的映射。
步骤二:配置Hibernate
com.websystique.spring.configuration.HibernateConfiguration
package com.websystique.spring.configuration; import java.util.Properties; import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
import org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.HibernateTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.LocalSessionFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement; @Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
@ComponentScan({ "com.websystique.spring.configuration" })
@PropertySource(value = { "classpath:application.properties" })
public class HibernateConfiguration { @Autowired
private Environment environment; @Bean
public LocalSessionFactoryBean sessionFactory() {
LocalSessionFactoryBean sessionFactory = new LocalSessionFactoryBean();
sessionFactory.setDataSource(dataSource());
sessionFactory.setPackagesToScan(new String[] { "com.websystique.spring.model" });
sessionFactory.setHibernateProperties(hibernateProperties());
return sessionFactory;
} @Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(environment.getRequiredProperty("jdbc.driverClassName"));
dataSource.setUrl(environment.getRequiredProperty("jdbc.url"));
dataSource.setUsername(environment.getRequiredProperty("jdbc.username"));
dataSource.setPassword(environment.getRequiredProperty("jdbc.password"));
return dataSource;
} private Properties hibernateProperties() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("hibernate.dialect", environment.getRequiredProperty("hibernate.dialect"));
properties.put("hibernate.show_sql", environment.getRequiredProperty("hibernate.show_sql"));
properties.put("hibernate.format_sql", environment.getRequiredProperty("hibernate.format_sql"));
return properties;
} @Bean
@Autowired
public HibernateTransactionManager transactionManager(SessionFactory s) {
HibernateTransactionManager txManager = new HibernateTransactionManager();
txManager.setSessionFactory(s);
return txManager;
}
}
@Configuration注解表明该类包含了用@Bean标注的方法,这些被@Bean标注的方法可以生成bean并交由spring容器管理,在这里例子中,这个类代表了hibernate的配置。
@ComponentScan注解与xml配置中的“context:component-scan base-package="..."”等价,提供了扫描bean的包路径。
@EnableTransactionManagement注解与xml配置中Spring的tx:*命名空间等价,主要用于开启基于注解的事务管理。
@PropertySource注解用于在Spring运行时Environment中声明一组属性(在应用classpath路径下的properties文件中定义),可根据不同环境灵活改变属性值。
sessionFactory()方法创建了一个LocalSessionFactoryBean,与基于XML的配置类似,我们需要一个数据源dataSource和hibernate配置文件(如hibernate.properties)。
多亏了@PropertySource注解,我们可以从.properties文件中得到具体属性值,使用Spring的Environment接口获取对应项目的配置值。
一旦创建了SessionFactory,该bean将会被注入到transactionManager方法中,最终对sessionFactory创建的sessions提供事务支持功能。
如下是本文使用的属性配置文件:
/src/main/resources/application.properties
jdbc.driverClassName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/websystique
jdbc.username = myuser
jdbc.password = mypassword
hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
hibernate.show_sql = false
hibernate.format_sql = false
另外,对应的基于XML配置如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd"> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:application.properties" /> <context:component-scan base-package="com.websystique.spring" /> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </bean> <bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.LocalSessionFactoryBean" >
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="packagesToScan">
<list>
<value>com.websystique.spring.model</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="hibernateProperties">
<props>
<prop key="hibernate.dialect">${hibernate.dialect}</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.show_sql">${hibernate.show_sql:false}</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.format_sql">${hibernate.format_sql:false}</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" />
</bean> <bean id="persistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor"
class="org.springframework.dao.annotation.PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor"/> </beans>
步骤三:Spring配置
com.websystique.spring.configuration.AppConfig
package com.websystique.spring.configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.websystique.spring")
public class AppConfig { }
在我们这个示例中,即使该配置类内部是空的,但是使用了@ComponentScan注解,可以自动检测到对应包下所有的beans。
其实你可以完全去除以上的配置,将bean扫描功能放在application context级别去实现(main方法里)。
在成熟的应用里,你会发现使用配置类配置beans(如messageSource、PropertySourcesPlaceHolderConfigurer...)非常方便。
对应的基于XML的配置
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="com.websystique.spring" /> </beans>
以上就是关于本工程的所有配置了,现在,为了让工程能跑起来,我们还需要添加service、dao层,实体对象,数据库。
步骤四:DAO层
com.websystique.spring.dao.AbstractDao
package com.websystique.spring.dao; import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; public abstract class AbstractDao { @Autowired
private SessionFactory sessionFactory; protected Session getSession() {
return sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
} public void persist(Object entity) {
getSession().persist(entity);
} public void delete(Object entity) {
getSession().delete(entity);
}
}
注意,我们在步骤二创建的SessionFactory会被自动装配到这里,这个类将作为基类用于执行数据库相关操作。
com.websystique.spring.dao.EmployeeDao
package com.websystique.spring.dao;
import java.util.List;
import com.websystique.spring.model.Employee;
public interface EmployeeDao {
void saveEmployee(Employee employee);
List<Employee> findAllEmployees();
void deleteEmployeeBySsn(String ssn);
Employee findBySsn(String ssn);
void updateEmployee(Employee employee);
}
com.websystique.spring.dao.EmployeeDaoImpl
package com.websystique.spring.dao; import java.util.List; import org.hibernate.Criteria;
import org.hibernate.Query;
import org.hibernate.criterion.Restrictions;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import com.websystique.spring.model.Employee; @Repository("employeeDao")
public class EmployeeDaoImpl extends AbstractDao implements EmployeeDao{ public void saveEmployee(Employee employee) {
persist(employee);
} @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public List<Employee> findAllEmployees() {
Criteria criteria = getSession().createCriteria(Employee.class);
return (List<Employee>) criteria.list();
} public void deleteEmployeeBySsn(String ssn) {
Query query = getSession().createSQLQuery("delete from Employee where ssn = :ssn");
query.setString("ssn", ssn);
query.executeUpdate();
} public Employee findBySsn(String ssn){
Criteria criteria = getSession().createCriteria(Employee.class);
criteria.add(Restrictions.eq("ssn",ssn));
return (Employee) criteria.uniqueResult();
} public void updateEmployee(Employee employee){
getSession().update(employee);
} }
步骤五:添加Service层代码
com.websystique.spring.service.EmployeeService
package com.websystique.spring.service;
import java.util.List;
import com.websystique.spring.model.Employee;
public interface EmployeeService {
void saveEmployee(Employee employee);
List<Employee> findAllEmployees();
void deleteEmployeeBySsn(String ssn);
Employee findBySsn(String ssn);
void updateEmployee(Employee employee);
}
com.websystique.spring.service.EmployeeServiceImpl
package com.websystique.spring.service; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import com.websystique.spring.dao.EmployeeDao;
import com.websystique.spring.model.Employee; @Service("employeeService")
@Transactional
public class EmployeeServiceImpl implements EmployeeService{ @Autowired
private EmployeeDao dao; public void saveEmployee(Employee employee) {
dao.saveEmployee(employee);
} public List<Employee> findAllEmployees() {
return dao.findAllEmployees();
} public void deleteEmployeeBySsn(String ssn) {
dao.deleteEmployeeBySsn(ssn);
} public Employee findBySsn(String ssn) {
return dao.findBySsn(ssn);
} public void updateEmployee(Employee employee){
dao.updateEmployee(employee);
}
}
以上比较引人注目的部分是@Transactional注解,配置了该注解的类会在每个类方法开启事务,并在方法结束的时候提交事务(或者在方法内部出错时回滚事务)。
注意,由于以上事务范围是方法级别的,我们在方法内部使用DAO,DAO方法会在同样的事物内部执行。
步骤六:创建实体类(POJO)
com.websystique.spring.model.Employee
package com.websystique.spring.model; import java.math.BigDecimal; import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table; import org.hibernate.annotations.Type;
import org.joda.time.LocalDate; @Entity
@Table(name="EMPLOYEE")
public class Employee { @Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private int id; @Column(name = "NAME", nullable = false)
private String name; @Column(name = "JOINING_DATE", nullable = false)
@Type(type="org.jadira.usertype.dateandtime.joda.PersistentLocalDate")
private LocalDate joiningDate; @Column(name = "SALARY", nullable = false)
private BigDecimal salary; @Column(name = "SSN", unique=true, nullable = false)
private String ssn; public int getId() {
return id;
} public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public LocalDate getJoiningDate() {
return joiningDate;
} public void setJoiningDate(LocalDate joiningDate) {
this.joiningDate = joiningDate;
} public BigDecimal getSalary() {
return salary;
} public void setSalary(BigDecimal salary) {
this.salary = salary;
} public String getSsn() {
return ssn;
} public void setSsn(String ssn) {
this.ssn = ssn;
} @Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + id;
result = prime * result + ((ssn == null) ? 0 : ssn.hashCode());
return result;
} @Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (!(obj instanceof Employee))
return false;
Employee other = (Employee) obj;
if (id != other.id)
return false;
if (ssn == null) {
if (other.ssn != null)
return false;
} else if (!ssn.equals(other.ssn))
return false;
return true;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", joiningDate="
+ joiningDate + ", salary=" + salary + ", ssn=" + ssn + "]";
} }
这是一个标准的实体类,基于JPA注解@Entity, @Table, @Column以及hibernate注解@Type(用于提供数据库类型与Joda-Time LocalDate的映射)。
步骤七:在数据库里创建Schema
CREATE TABLE EMPLOYEE(
id INT NOT NULL auto_increment,
name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
joining_date DATE NOT NULL,
salary DOUBLE NOT NULL,
ssn VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
步骤八:创建main方法执行程序
package com.websystique.spring; import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.List; import org.joda.time.LocalDate;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext; import com.websystique.spring.configuration.AppConfig;
import com.websystique.spring.model.Employee;
import com.websystique.spring.service.EmployeeService; public class AppMain { public static void main(String args[]) {
AbstractApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class); EmployeeService service = (EmployeeService) context.getBean("employeeService"); /*
* Create Employee1
*/
Employee employee1 = new Employee();
employee1.setName("Han Yenn");
employee1.setJoiningDate(new LocalDate(2010, 10, 10));
employee1.setSalary(new BigDecimal(10000));
employee1.setSsn("ssn00000001"); /*
* Create Employee2
*/
Employee employee2 = new Employee();
employee2.setName("Dan Thomas");
employee2.setJoiningDate(new LocalDate(2012, 11, 11));
employee2.setSalary(new BigDecimal(20000));
employee2.setSsn("ssn00000002"); /*
* Persist both Employees
*/
service.saveEmployee(employee1);
service.saveEmployee(employee2); /*
* Get all employees list from database
*/
List<Employee> employees = service.findAllEmployees();
for (Employee emp : employees) {
System.out.println(emp);
} /*
* delete an employee
*/
service.deleteEmployeeBySsn("ssn00000002"); /*
* update an employee
*/ Employee employee = service.findBySsn("ssn00000001");
employee.setSalary(new BigDecimal(50000));
service.updateEmployee(employee); /*
* Get all employees list from database
*/
List<Employee> employeeList = service.findAllEmployees();
for (Employee emp : employeeList) {
System.out.println(emp);
} context.close();
}
}
注意,假如你想删除AppConfig文件,那么只需将
AbstractApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
替换为
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();context.scan("com.websystique.spring"); context.refresh();Employee [id=1, name=Han Yenn, joiningDate=2010-10-10, salary=10000, ssn=ssn00000001]
Employee [id=2, name=Dan Thomas, joiningDate=2012-11-11, salary=20000, ssn=ssn00000002]
Employee [id=1, name=Han Yenn, joiningDate=2010-10-10, salary=50000, ssn=ssn00000001]
工程代码
http://websystique.com/?smd_process_download=1&download_id=802
注:源码EmployeeDaoImpl类中有一处错误,将26行表名Employee改成EMPLOYEE即可。
【译】Spring 4 + Hibernate 4 + Mysql + Maven集成例子(注解 + XML)的更多相关文章
- Spring 4 MVC+Hibernate 4+MySQL+Maven使用注解集成实例
Spring 4 MVC+Hibernate 4+MySQL+Maven使用注解集成实例 转自:通过注解的方式集成Spring 4 MVC+Hibernate 4+MySQL+Maven,开发项目样例 ...
- Spring第12篇—— Spring对Hibernate的SessionFactory的集成功能
由于Spring和Hibernate处于不同的层次,Spring关心的是业务逻辑之间的组合关系,Spring提供了对他们的强大的管理能力, 而Hibernate完成了OR的映射,使开发人员不用再去关心 ...
- Spring3 + Spring MVC+ Mybatis 3+Mysql 项目整合(注解及源码)
Spring3 + Spring MVC+ Mybatis 3+Mysql 项目整合(注解及源码) 备注: 之前在Spring3 + Spring MVC+ Mybatis 3+Mysql 项目整合中 ...
- spring+struts2+hibernate框架搭建(Maven工程)
搭建Spring 1.porm.xml中添加jar包 <!-- spring3 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframew ...
- spring+springmvc+hibernate架构、maven分模块开发样例小项目案例
maven分模块开发样例小项目案例 spring+springmvc+hibernate架构 以用户管理做測试,分dao,sevices,web层,分模块开发測试!因时间关系.仅仅測查询成功.其它的准 ...
- Spring和Hibernate结合的一个小例子
1.新建一个SpringHibernate的maven项目 2.pom文件的依赖为 <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> &l ...
- Spring Boot (五)Spring Data JPA 操作 MySQL 8
一.Spring Data JPA 介绍 JPA(Java Persistence API)Java持久化API,是 Java 持久化的标准规范,Hibernate是持久化规范的技术实现,而Sprin ...
- Spring MVC Hibernate MySQL Integration(集成) CRUD Example Tutorial【摘】
Spring MVC Hibernate MySQL Integration(集成) CRUD Example Tutorial We learned how to integrate Spring ...
- Maven+Spring+Hibernate+Shiro+Mysql简单的demo框架(二)
然后是项目下的文件:完整的项目请看 上一篇 Maven+Spring+Hibernate+Shiro+Mysql简单的demo框架(一) 项目下的springmvc-servlet.xml配置文件: ...
随机推荐
- iOS开发系列文章(持续更新……)
iOS开发系列的文章,内容循序渐进,包含C语言.ObjC.iOS开发以及日后要写的游戏开发和Swift编程几部分内容.文章会持续更新,希望大家多多关注,如果文章对你有帮助请点赞支持,多谢! 为了方便大 ...
- C# - 缓存OutputCache(一)基础配置
本文是通过网上&个人总结的 1. 介绍 OutputCache输出缓存是复制ASP.NET页面,保存在内存的机制.这种行为有助于提高性能,通过返回的缓存达到网页及时响应的目的,减少客户机器需要 ...
- selenium自动化基础知识
什么是自动化测试? 自动化测试分为:功能自动化和性能自动化 功能自动化即使用计算机通过编码的方式来替代手工测试,完成一些重复性比较高的测试,解放测试人员的测试压力.同时,如果系统有不份模块更改后,只要 ...
- 列属性:RowGUIDCol、Identity 和 not for replication
Table Column有两个特殊的属性RowGUIDCol 和 Identity,用于标记数据列: $ROWGUID 用于引用被属性 RowGUIDCol 标识的UniqueIdentifier 类 ...
- 基于Caffe的Large Margin Softmax Loss的实现(上)
小喵的唠叨话:在写完上一次的博客之后,已经过去了2个月的时间,小喵在此期间,做了大量的实验工作,最终在使用的DeepID2的方法之后,取得了很不错的结果.这次呢,主要讲述一个比较新的论文中的方法,L- ...
- SVN:Previous operation has not finished; run 'cleanup' if it was interrupted
异常处理汇总-开发工具 http://www.cnblogs.com/dunitian/p/4522988.html cleanup failed to process the following ...
- 用枚举enum替代int常量
枚举的好处: 1. 类型安全性 2.使用方便性 public class EnumDemo { enum Color{ RED(3),BLUE(5),BLACK(8),YELLOW(13),GREEN ...
- c 进程间的通信
在上篇讲解了如何创建和调用进程 c 进程和系统调用 这篇文章就专门讲讲进程通信的问题 先来看一段下边的代码,这段代码的作用是根据关键字调用一个Python程序来检索RSS源,然后打开那个URL #in ...
- Oracle 故障处理总结
Oracle 故障处理总结(更新中..) 各类数据库问题描述模板 记录一则ORA-00054,ORA-00031解决过程 记录一则ORACLE MOVE操作后重建索引过程被强制中断导致的ORA-810 ...
- heart
好久没写博客了,不想废话,直接欣赏效果! 点击这里,查看完美效果! 附完整代码: <!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta ch ...
