使用Patroni和HAProxy创建高可用的PostgreSQL集群
操作系统:CentOS Linux release 7.6.1810 (Core)
node1:192.168.216.130 master
node2:192.168.216.132 slave
node3:192.168.216.136 haproxy
这里仅测试,所以只部署了一主一丛,适用与测试环境,生产环境建议postgres至少1主2从,3个etcd节点,2个haproxy+keepalive组成
一、首先在两个节点上安装postgres,下面以postgres9.5.19为例
- 1、添加RPM
- yum install https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/9.5/redhat/rhel-7-x86_64/pgdg-centos95-9.5-3.noarch.rpm
- 2、安装PostgreSQL 9.5
- yum install postgresql95-server postgresql95-contrib
- 注意:本次实验我们这里只需要操作到第2步即可,初始化可以由patroni来替我们完成
- 3、初始化数据库
- /usr/pgsql-9.5/bin/postgresql95-setup initdb
- 4、设置开机自启动
- systemctl enable postgresql-9.5.service
- 5、启动服务
- systemctl start postgresql-9.5.service
- 6、查看版本
- psql --version
二、安装etcd服务
1、这里我只在node1单节点上安装,仅实验,未做分布式部署,如果集群部署可以参考博客etcd集群部署文章
- yum install etcd -y
- cp /etc/etcd/etcd.conf /etc/etcd/etcd.conf.bak
- cd /etc/etcd/
- [root@localhost etcd]# egrep ^[A-Z] ./etcd.conf
- ETCD_DATA_DIR="/var/lib/etcd/node1.etcd"
- ETCD_LISTEN_PEER_URLS="http://192.168.216.130:2380"
- ETCD_LISTEN_CLIENT_URLS="http://192.168.216.130:2379,http://127.0.0.1:2379"
- ETCD_NAME="node1"
- ETCD_INITIAL_ADVERTISE_PEER_URLS="http://192.168.216.130:2380"
- ETCD_ADVERTISE_CLIENT_URLS="http://192.168.216.130:2379"
- ETCD_INITIAL_CLUSTER="node1=http://192.168.216.130:2380"
- ETCD_INITIAL_CLUSTER_TOKEN="etcd-cluster"
- ETCD_INITIAL_CLUSTER_STATE="new"
2、保存文件,然后重启etcd服务
- systemctl restart etcd
3、查看ectd服务是否正常


三、安装patroni,分别在node1和node2节点安装
1、安装patroni用到依赖包,这里通过pip安装patroni
- yum install gcc
- yum install python-devel.x86_64
- curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py -o get-pip.py
- python get-pip.py
- pip install psycopg2-binary
- pip install --upgrade setuptools
- pip install patroni[etcd,consul]
2、验证patroni是否安装成功

3、配置patroni,以下操作在node1中进行
- mkdir /data/patroni/conf -p
- cd /data/patroni/conf
- yum install git
- git clone https://github.com/zalando/patroni.git
- cd /data/patroni/conf/patroni-master
- cp -r postgres0.yml ../conf/
4、编辑node1上的postgres0.yml文件
- scope: batman
- #namespace: /service/
- name: postgresql0
- restapi:
- listen: 192.168.216.130:8008
- connect_address: 192.168.216.130:8008
- # certfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
- # keyfile: /etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key
- # authentication:
- # username: username
- # password: password
- # ctl:
- # insecure: false # Allow connections to SSL sites without certs
- # certfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
- # cacert: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cacert-snakeoil.pem
- etcd:
- host: 192.168.216.130:2379
- bootstrap:
- # this section will be written into Etcd:/<namespace>/<scope>/config after initializing new cluster
- # and all other cluster members will use it as a `global configuration`
- dcs:
- ttl: 30
- loop_wait: 10
- retry_timeout: 10
- maximum_lag_on_failover: 1048576
- # master_start_timeout: 300
- synchronous_mode: false
- #standby_cluster:
- #host: 127.0.0.1
- #port: 1111
- #primary_slot_name: patroni
- postgresql:
- use_pg_rewind: true
- use_slots: true
- parameters:
- wal_level: logical
- hot_standby: "on"
- wal_keep_segments: 1000
- max_wal_senders: 10
- max_replication_slots: 10
- wal_log_hints: "on"
- archive_mode: "on"
- archive_timeout: 1800s
- archive_command: mkdir -p ../wal_archive && test ! -f ../wal_archive/%f && cp %p ../wal_archive/%f
- recovery_conf:
- restore_command: cp ../wal_archive/%f %p
- # some desired options for 'initdb'
- initdb: # Note: It needs to be a list (some options need values, others are switches)
- - encoding: UTF8
- - data-checksums
- pg_hba: # Add following lines to pg_hba.conf after running 'initdb'
- # For kerberos gss based connectivity (discard @.*$)
- #- host replication replicator 127.0.0.1/32 gss include_realm=0
- #- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 gss include_realm=0
- - host replication replicator 0.0.0.0/0 md5
- - host all admin 0.0.0.0/0 md5
- - host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
- # Additional script to be launched after initial cluster creation (will be passed the connection URL as parameter)
- # post_init: /usr/local/bin/setup_cluster.sh
- # Some additional users users which needs to be created after initializing new cluster
- users:
- admin:
- password: postgres
- options:
- - createrole
- - createdb
- replicator:
- password: replicator
- options:
- - replication
- postgresql:
- listen: 0.0.0.0:5432
- connect_address: 192.168.216.130:5432
- data_dir: /data/postgres
- bin_dir: /usr/pgsql-9.5/bin/
- # config_dir:
- # pgpass: /tmp/pgpass0
- authentication:
- replication:
- username: replicator
- password: replicator
- superuser:
- username: admin
- password: postgres
- # rewind: # Has no effect on postgres 10 and lower
- # username: rewind_user
- # password: rewind_password
- # Server side kerberos spn
- # krbsrvname: postgres
- parameters:
- # Fully qualified kerberos ticket file for the running user
- # same as KRB5CCNAME used by the GSS
- # krb_server_keyfile: /var/spool/keytabs/postgres
- unix_socket_directories: '.'
- #watchdog:
- # mode: automatic # Allowed values: off, automatic, required
- # device: /dev/watchdog
- # safety_margin: 5
- tags:
- nofailover: false
- noloadbalance: false
- clonefrom: false
- nosync: false
5、配置patroni,以下操作在node2中进行
- mkdir /data/patroni/conf -p
- cd /data/patroni/conf
- yum install git
- git clone https://github.com/zalando/patroni.git
- cd /data/patroni/conf/patroni-master
- cp -r postgres1.yml ../conf/
6、编辑node2上的postgres1.yml文件
- scope: batman
- #namespace: /service/
- name: postgresql1
- restapi:
- listen: 192.168.216.132:8008
- connect_address: 192.168.216.132:8008
- # certfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
- # keyfile: /etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key
- # authentication:
- # username: username
- # password: password
- # ctl:
- # insecure: false # Allow connections to SSL sites without certs
- # certfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
- # cacert: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cacert-snakeoil.pem
- etcd:
- host: 192.168.216.130:2379
- bootstrap:
- # this section will be written into Etcd:/<namespace>/<scope>/config after initializing new cluster
- # and all other cluster members will use it as a `global configuration`
- dcs:
- ttl: 30
- loop_wait: 10
- retry_timeout: 10
- maximum_lag_on_failover: 1048576
- # master_start_timeout: 300
- synchronous_mode: false
- #standby_cluster:
- #host: 127.0.0.1
- #port: 1111
- #primary_slot_name: patroni
- postgresql:
- use_pg_rewind: true
- use_slots: true
- parameters:
- wal_level: logical
- hot_standby: "on"
- wal_keep_segments: 1000
- max_wal_senders: 10
- max_replication_slots: 10
- wal_log_hints: "on"
- archive_mode: "on"
- archive_timeout: 1800s
- archive_command: mkdir -p ../wal_archive && test ! -f ../wal_archive/%f && cp %p ../wal_archive/%f
- recovery_conf:
- restore_command: cp ../wal_archive/%f %p
- # some desired options for 'initdb'
- initdb: # Note: It needs to be a list (some options need values, others are switches)
- - encoding: UTF8
- - data-checksums
- pg_hba: # Add following lines to pg_hba.conf after running 'initdb'
- # For kerberos gss based connectivity (discard @.*$)
- #- host replication replicator 127.0.0.1/32 gss include_realm=0
- #- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 gss include_realm=0
- - host replication replicator 0.0.0.0/0 md5
- - host all admin 0.0.0.0/0 md5
- - host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
- # Additional script to be launched after initial cluster creation (will be passed the connection URL as parameter)
- # post_init: /usr/local/bin/setup_cluster.sh
- # Some additional users users which needs to be created after initializing new cluster
- users:
- admin:
- password: postgres
- options:
- - createrole
- - createdb
- replicator:
- password: replicator
- options:
- - replication
- postgresql:
- listen: 0.0.0.0:5432
- connect_address: 192.168.216.132:5432
- data_dir: /data/postgres
- bin_dir: /usr/pgsql-9.5/bin/
- # config_dir:
- # pgpass: /tmp/pgpass0
- authentication:
- replication:
- username: replicator
- password: replicator
- superuser:
- username: admin
- password: postgres
- # rewind: # Has no effect on postgres 10 and lower
- # username: rewind_user
- # password: rewind_password
- # Server side kerberos spn
- # krbsrvname: postgres
- parameters:
- # Fully qualified kerberos ticket file for the running user
- # same as KRB5CCNAME used by the GSS
- # krb_server_keyfile: /var/spool/keytabs/postgres
- unix_socket_directories: '.'
- #watchdog:
- # mode: automatic # Allowed values: off, automatic, required
- # device: /dev/watchdog
- # safety_margin: 5
- tags:
- nofailover: false
- noloadbalance: false
- clonefrom: false
- nosync: false
7、记下data_dir上述yml配置文件中的值。该目录需要确保postgres用户具备写入的权限。如果此目录不存在,请创建它:在node1和node2节点分别进行如下操作
- mkdir /data/postgres -p
- chown -Rf postgres:postgres /data/postgres
- chmod 700 /data/postgres
8、在node1上切换到postgres用户,并启动patroni服务,这里patroni会帮我们自动初始化数据库并创建相应的角色
- chown -Rf postgres:postgres /data/patroni/conf
- su - postgres
- 启动patroni服务
- patroni /data/patroni/conf/postgres0.yml
此时如果服务正常启动可以打印以下日志信息

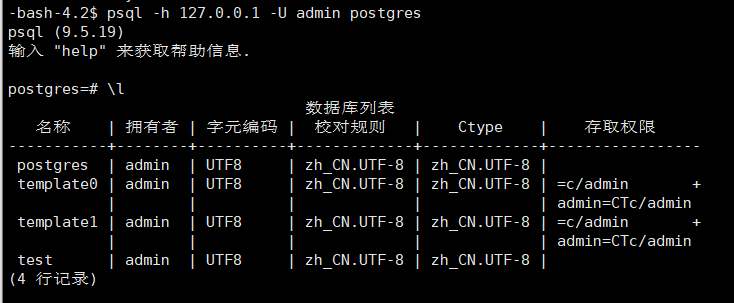
由于不是后台启动的服务,所以这里我们克隆一个窗口,切换到postgres用户下,并执行psql -h 127.0.0.1 -U admin postgres连接数据库,验证patroni是否正常托管postgres服务
9、在node2上切换到postgres用户,并启动patroni服务,这里和node1的操作一致
- chown -Rf postgres:postgres /data/patroni/conf
- su - postgres
- 启动patroni服务
- patroni /data/patroni/conf/postgres1.yml
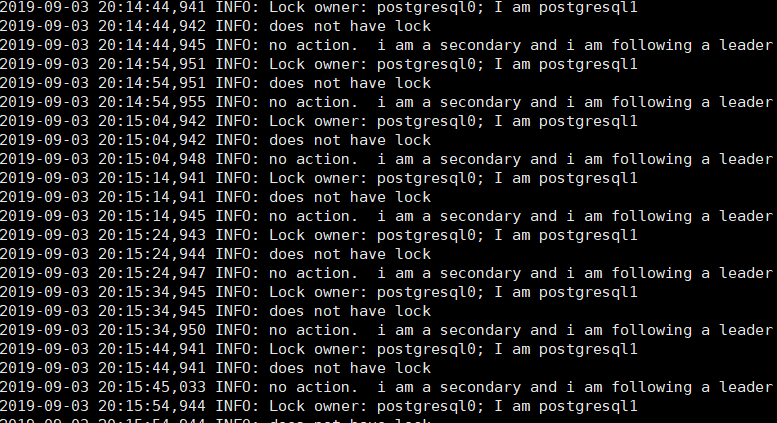
如果服务启动正常,可看到如下日志打印信息
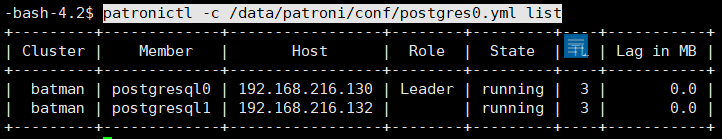
10、查询集群运行状态patronictl -c /data/patroni/conf/postgres0.yml list
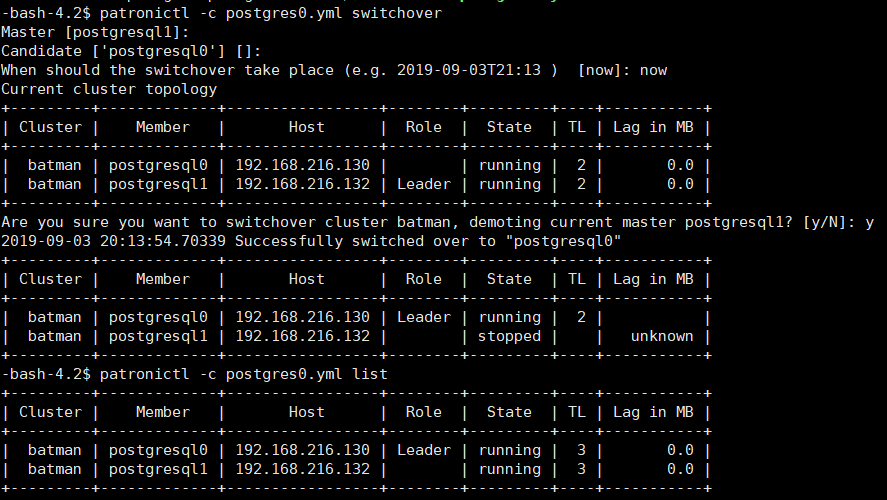
11、patronictl -c /data/patroni/conf/postgres0.yml switchover 手动切换master
12、可以后台启动来保持patroni服务不中断,也可以配置成systemd服务来管理保证开机自启
node1节点:
- nohup patroni /data/patroni/conf/postgres0.yml >
- /data/patroni/patroni_log 2>&1 &
node2节点:
- nohup patroni /data/patroni/conf/postgres1.yml >
- /data/patroni/patroni_log 2>&1 &
四、在node3节点安装haproxy
- yum install -y haproxy
- cp -r /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg_bak
编辑haproxy.cfg配置文件
- # vi /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
- #---------------------------------------------------------------------
- # 全局定义
- global
- # log语法:log [max_level_1]
- # 全局的日志配置,使用log关键字,指定使用127.0.0.1上的syslog服务中的local0日志设备,
- # 记录日志等级为info的日志
- # log 127.0.0.1 local0 info
- log 127.0.0.1 local1 notice
- chroot /var/lib/haproxy
- pidfile /var/run/haproxy.pid
- # 定义每个haproxy进程的最大连接数 ,由于每个连接包括一个客户端和一个服务器端,
- # 所以单个进程的TCP会话最大数目将是该值的两倍。
- maxconn 4096
- # 用户,组
- user haproxy
- group haproxy
- # 以守护进程的方式运行
- daemon
- # turn on stats unix socket
- stats socket /var/lib/haproxy/stats
- #---------------------------------------------------------------------
- # 默认部分的定义
- defaults
- # mode语法:mode {http|tcp|health} 。http是七层模式,tcp是四层模式,health是健康检测,返回OK
- mode tcp
- # 使用127.0.0.1上的syslog服务的local3设备记录错误信息
- log 127.0.0.1 local3 err
- #if you set mode to http,then you nust change tcplog into httplog
- option tcplog
- # 启用该项,日志中将不会记录空连接。所谓空连接就是在上游的负载均衡器或者监控系统为了
- #探测该服务是否存活可用时,需要定期的连接或者获取某一固定的组件或页面,或者探测扫描
- #端口是否在监听或开放等动作被称为空连接;官方文档中标注,如果该服务上游没有其他的负
- #载均衡器的话,建议不要使用该参数,因为互联网上的恶意扫描或其他动作就不会被记录下来
- option dontlognull
- # 定义连接后端服务器的失败重连次数,连接失败次数超过此值后将会将对应后端服务器标记为不可用
- retries 3
- # 当使用了cookie时,haproxy将会将其请求的后端服务器的serverID插入到cookie中,以保证
- #会话的SESSION持久性;而此时,如果后端的服务器宕掉了,但是客户端的cookie是不会刷新的
- #,如果设置此参数,将会将客户的请求强制定向到另外一个后端server上,以保证服务的正常
- option redispatch
- #等待最大时长 When a server's maxconn is reached, connections are left pending in a queue which may be server-specific or global to the backend.
- timeout queue 1m
- # 设置成功连接到一台服务器的最长等待时间,默认单位是毫秒
- timeout connect 10s
- # 客户端非活动状态的超时时长 The inactivity timeout applies when the client is expected to acknowledge or send data.
- timeout client 1m
- # Set the maximum inactivity time on the server side.The inactivity timeout applies when the server is expected to acknowledge or send data.
- timeout server 1m
- timeout check 5s
- maxconn 5120
- #---------------------------------------------------------------------
- # 配置haproxy web监控,查看统计信息
- listen status
- bind 0.0.0.0:1080
- mode http
- log global
- stats enable
- # stats是haproxy的一个统计页面的套接字,该参数设置统计页面的刷新间隔为30s
- stats refresh 30s
- stats uri /haproxy-stats
- # 设置统计页面认证时的提示内容
- stats realm Private lands
- # 设置统计页面认证的用户和密码,如果要设置多个,另起一行写入即可
- stats auth admin:passw0rd
- # 隐藏统计页面上的haproxy版本信息
- # stats hide-version
- #---------------------------------------------------------------------
- listen master
- bind *:5000
- mode tcp
- option tcplog
- balance roundrobin
- option httpchk OPTIONS /master
- http-check expect status 200
- default-server inter 3s fall 3 rise 2 on-marked-down shutdown-sessions
- server node1 192.168.216.130:5432 maxconn 1000 check port 8008 inter 5000 rise 2 fall 2
- server node2 192.168.216.132:5432 maxconn 1000 check port 8008 inter 5000 rise 2 fall 2
- listen replicas
- bind *:5001
- mode tcp
- option tcplog
- balance roundrobin
- option httpchk OPTIONS /replica
- http-check expect status 200
- default-server inter 3s fall 3 rise 2 on-marked-down shutdown-sessions
- server node1 192.168.216.130:5432 maxconn 1000 check port 8008 inter 5000 rise 2 fall 2
- server node2 192.168.216.132:5432 maxconn 1000 check port 8008 inter 5000 rise 2 fall 2
启动haproxy服务
- systemctl start haproxy
- systemctl status haproxy
浏览器访问http://192.168.216.136:1080/haproxy-stats输入用户名admin密码passw0rd
这里我们通过5000端口和5001端口分别来提供写服务和读服务,如果需要对数据库写入数据只需要对外提供192.168.216.136:5000即可,可以模拟主库故障,即关闭其中的master节点来验证是否会进行自动主从切换
https://www.linode.com/docs/databases/postgresql/create-a-highly-available-postgresql-cluster-using-patroni-and-haproxy/#configure-etcd
https://www.opsdash.com/blog/postgres-getting-started-patroni.html
使用Patroni和HAProxy创建高可用的PostgreSQL集群的更多相关文章
- 基于MySQL+MHA+Haproxy部署高可用负载均衡集群
一.MHA 概述 MHA(Master High Availability)是可以在MySQL上使用的一套高可用方案.所编写的语言为Perl 从名字上我们可以看到.MHA的目的就是为了维护Master ...
- docker下用keepalived+Haproxy实现高可用负载均衡集群
启动keepalived后宿主机无法ping通用keepalived,报错: [root@localhost ~]# ping 172.18.0.15 PING () bytes of data. F ...
- Haproxy+Keepalived搭建Weblogic高可用负载均衡集群
配置环境说明: KVM虚拟机配置 用途 数量 IP地址 机器名 虚拟IP地址 硬件 内存3G 系统盘20G cpu 4核 Haproxy keepalived 2台 192.168.1.10 192 ...
- Dubbo入门到精通学习笔记(二十):MyCat在MySQL主从复制的基础上实现读写分离、MyCat 集群部署(HAProxy + MyCat)、MyCat 高可用负载均衡集群Keepalived
文章目录 MyCat在MySQL主从复制的基础上实现读写分离 一.环境 二.依赖课程 三.MyCat 介绍 ( MyCat 官网:http://mycat.org.cn/ ) 四.MyCat 的安装 ...
- RabbitMQ(四):使用Docker构建RabbitMQ高可用负载均衡集群
本文使用Docker搭建RabbitMQ集群,然后使用HAProxy做负载均衡,最后使用KeepAlived实现集群高可用,从而搭建起来一个完成了RabbitMQ高可用负载均衡集群.受限于自身条件,本 ...
- 1.还不会部署高可用的kubernetes集群?看我手把手教你使用二进制部署v1.23.6的K8S集群实践(上)
公众号关注「WeiyiGeek」 设为「特别关注」,每天带你玩转网络安全运维.应用开发.物联网IOT学习! 本章目录: 0x00 前言简述 0x01 环境准备 主机规划 软件版本 网络规划 0x02 ...
- K8S 使用Kubeadm搭建高可用Kubernetes(K8S)集群 - 证书有效期100年
1.概述 Kubenetes集群的控制平面节点(即Master节点)由数据库服务(Etcd)+其他组件服务(Apiserver.Controller-manager.Scheduler...)组成. ...
- 企业运维实践-还不会部署高可用的kubernetes集群?使用kubeadm方式安装高可用k8s集群v1.23.7
关注「WeiyiGeek」公众号 设为「特别关注」每天带你玩转网络安全运维.应用开发.物联网IOT学习! 希望各位看友[关注.点赞.评论.收藏.投币],助力每一个梦想. 文章目录: 0x00 前言简述 ...
- keepalived工作原理和配置说明 腾讯云VPC内通过keepalived搭建高可用主备集群
keepalived工作原理和配置说明 腾讯云VPC内通过keepalived搭建高可用主备集群 内网路由都用mac地址 一个mac地址绑定多个ip一个网卡只能一个mac地址,而且mac地址无法改,但 ...
随机推荐
- nginx 进程问题
1 nginx的进程分为四种 master worker cacheLoader cacheManager. 实际接收请求的进程是 worker,master监控worker节点,之所以会多进程模式, ...
- [SourceTree] - 提交代码失败 "git -c diff.mnemonicprefix=false -c core.quotepath=false" 之解决
背景 使用 SourceTree 提交代码失败,尝试了重装 SourceTree 和 Git 问题依旧. 错误信息 git -c diff.mnemonicprefix=false -c core.q ...
- 用Scratch制作一个Hello World程序
网上出现了很多Hello World程序,看的小编心里也痒痒的,为此这次作为南京小码王Scratch培训机构的小编,就为大家来详细的了解下Scratch制作Hello World程序的过程,现在就和小 ...
- nmon2influxdb+grafana:服务监控可视化部署
在工作中,无论是定位线上问题,还是性能优化,都需要对前端.后台服务进行监控.而及时的获取监控数据,能更好的帮助技术人员排查定位问题. 前面的博客介绍过服务端监控工具:Nmon使用方法及利用easyNm ...
- Docker 四种网络模式
原文 https://www.cnblogs.com/gispathfinder/p/5871043.html 我们在使用docker run创建Docker容器时,可以用--net选项指定容器的网络 ...
- Lipo移除ORC架构
Lipo移除ORC架构 打包前检查链接 https://cloud.baidu.com/doc/OCR/OCR-iOS-SDK.html#FAQ cd /Users/guojun/JG-iOS/Pro ...
- 【开发工具】- 推荐一款好用的文本编辑器[Sublime Text]
作为一个程序员除了IDE外,文本编辑器也是必不可少的一个开发工具.之前一直在用的是NotePad++.EditPlus,这两款编辑器,但是总感觉差点什么,昨天在知乎上看到有人推荐Sublime Tex ...
- jQuery判断当前页面是APP内打开还是浏览器打开
一.代码如下: function check_useragent() { var browser = { versions: function() { var u = navigator.userAg ...
- GO执行shell命令
Golang执行shell命令主要依靠exec模块 代码为核心逻辑,并非全部 运行命令 cmd1 = exec.Command("ls") if err = cmd1.Run(); ...
- android ViewFlipper(翻转视图) 使用
1.布局文件 <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns ...
