Spark GraphX图计算简单案例【代码实现,源码分析】
一.简介
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/yszd/p/10186556.html
二.代码实现
package big.data.analyse.graphx
import org.apache.log4j.{Level, Logger}
import org.apache.spark.graphx._
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession
class VertexProperty()
case class UserProperty(val name: String) extends VertexProperty
case class ProductProperty(val name: String, val price: Double) extends VertexProperty
/*class Graph[VD, ED]{
val vertices: VertexRDD[VD]
val edges: EdgeRDD[ED]
}*/
/**
* Created by zhen on 2019/10/4.
*/
object GraphXTest {
/**
* 设置日志级别
*/
Logger.getLogger("org").setLevel(Level.WARN)
def main(args: Array[String]) {
val spark = SparkSession.builder().appName("GraphXTest").master("local[2]").getOrCreate()
val sc = spark.sparkContext
/**
* 创建vertices的RDD
*/
val users : RDD[(VertexId, (String, String))] = sc.parallelize(
Array((3L, ("Spark", "GraphX")), (7L, ("Hadoop", "Java")),
(5L, ("HBase", "Mysql")), (2L, ("Hive", "Mysql"))))
/**
* 创建edges的RDD
*/
val relationships: RDD[Edge[String]] = sc.parallelize(
Array(Edge(3L, 7L, "Fast"), Edge(5L, 3L, "Relation"),
Edge(2L, 5L, "colleague"), Edge(5L, 7L, "colleague")))
/**
* 定义默认用户
*/
val defualtUser = ("Machical", "Missing")
/**
* 构建初始化图
*/
val graph = Graph(users, relationships, defualtUser)
/**
* 使用三元组视图呈现顶点之间关系
*/
val facts : RDD[String] = graph.triplets.map(triplet =>
triplet.srcAttr._1 + " is the " + triplet.attr + " with " + triplet.dstAttr._1)
facts.collect().foreach(println)
graph.vertices.foreach(println) //顶点
graph.edges.foreach(println) //边
graph.ops.degrees.foreach(println) // 各顶点的度
graph.triplets.foreach(println) // 顶点,边,关系
println(graph.ops.numEdges) // 边的数量
println(graph.ops.numVertices) // 顶点的数量
}
}
三.结果
1.三元组视图

2.顶点

3.边
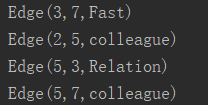
4.各顶点的度

5.三元组视图

6.边/顶点数量

四.源码分析
class Graph[VD, ED] {
// Information about the Graph
val numEdges: Long
val numVertices:Long
val inDegrees: VertexRDD[Int]
val outDegrees: VertexRDD[Int]
val degrees: VertexRDD[Int]
// Views of the graph as collections
val vertices: VertexRDD[VD]
val edges: EdgeRDD[ED]
val triplets: RDD[EdgeTriplet[VD,ED]]
//Functions for caching graphs
def persist(newLevel1:StorageLevel = StorageLevel.MEMORY_ONLY): Graph[VD, ED]//默认存储级别为MEMORY_ONLY
def cache(): Graph[VD, ED]
def unpersistVertices(blocking: Boolean = true): Graph[VD, ED]
// Change the partitioning heuristic
def partitionBy(partitionStrategy: PartitionStrategy)
// Transform vertex and edge attributes
def mapVertices[VD2](map: (VertexId, VD) => VD2): Graph[VD2, ED]
def mapEdges[ED2](map: Edge[ED] => ED2): Graph[VD, ED2]
def mapEdges[ED2](map: (PartitionID, Iterator[Edge[ED]]) => Iterator[ED2]): Graph[VD, ED2]
def mapTriplets[ED2](map: EdgeTriplet[VD, ED] => ED2): Graph[VD, ED2]
def mapTriplets[ED2](map: (PartitionID, Iterator[EdgeTriplet[VD, ED]]) => Iterator[ED2]): Graph[VD, ED2]
// Modify the graph structure
def reverse: Graph[VD, ED]
def subgraph(epred: EdgeTriplet[VD,ED] => Boolean,vpred: (VertexId, VD) => Boolean): Graph[VD, ED]
def mask[VD2, ED2](other: Graph[VD2, ED2]): Graph[VD, ED] // 返回当前图和其它图的公共子图
def groupEdges(merge: (ED, ED) => ED): Graph[VD,ED]
// Join RDDs with the graph
def joinVertices[U](table: RDD[(VertexId, U)])(mapFunc: (VertexId, VD, U) => VD): Graph[VD, ED]
def outerJoinVertices[U, VD2](other: RDD[(VertexId, U)])(mapFunc: (VertexId, VD, Option[U]))
// Aggregate information about adjacent triplets
def collectNeighborIds(edgeDirection: EdgeDirection): VertexRDD[Array[VertexId]]
def collectNeighbors(edgeDirection: EdgeDirection): VertexRDD[Array[(VertexId, VD)]]
def aggregateMessages[Msg: ClassTag](sendMsg: EdgeContext[VD, ED, Msg] => Unit, merageMsg: (Msg, Msg) => Msg, tripletFields: TripletFields: TripletFields = TripletFields.All): VertexRDD[A]
//Iterative graph-parallel computation
def pregel[A](initialMsg: A, maxIterations: Int, activeDirection: EdgeDiection)(vprog: (VertexId, VD, A) => VD, sendMsg: EdgeTriplet[VD, ED] => Iterator[(VertexId, A)], mergeMsg: (A, A) => A): Graph[VD, ED]
// Basic graph algorithms
def pageRank(tol: Double, resetProb: Double = 0.15): Graph[Double, Double]
def connectedComponents(): Graph[VertexId, ED]
def triangleCount(): Graph[Int, ED]
def stronglyConnectedComponents(numIter: Int): Graph[VertexId, ED]
}
Spark GraphX图计算简单案例【代码实现,源码分析】的更多相关文章
- Spark GraphX图计算核心源码分析【图构建器、顶点、边】
一.图构建器 GraphX提供了几种从RDD或磁盘上的顶点和边的集合构建图形的方法.默认情况下,没有图构建器会重新划分图的边:相反,边保留在默认分区中.Graph.groupEdges要求对图进行重新 ...
- Spark技术内幕:Stage划分及提交源码分析
http://blog.csdn.net/anzhsoft/article/details/39859463 当触发一个RDD的action后,以count为例,调用关系如下: org.apache. ...
- 5.Spark Streaming流计算框架的运行流程源码分析2
1 spark streaming 程序代码实例 代码如下: object OnlineTheTop3ItemForEachCategory2DB { def main(args: Array[Str ...
- 仿爱奇艺视频,腾讯视频,搜狐视频首页推荐位轮播图(二)之SuperIndicator源码分析
转载请把头部出处链接和尾部二维码一起转载,本文出自逆流的鱼:http://blog.csdn.net/hejjunlin/article/details/52510431 背景:仿爱奇艺视频,腾讯视频 ...
- Spark大师之路:广播变量(Broadcast)源码分析
概述 最近工作上忙死了……广播变量这一块其实早就看过了,一直没有贴出来. 本文基于Spark 1.0源码分析,主要探讨广播变量的初始化.创建.读取以及清除. 类关系 BroadcastManager类 ...
- 史上最简单的的HashTable源码分析
HashTable源码分析 1.前言 Hashtable 一个元老级的集合类,早在 JDK 1.0 就诞生了 1.1.摘要 在集合系列的第一章,咱们了解到,Map 的实现类有 HashMap.Link ...
- 65、Spark Streaming:数据接收原理剖析与源码分析
一.数据接收原理 二.源码分析 入口包org.apache.spark.streaming.receiver下ReceiverSupervisorImpl类的onStart()方法 ### overr ...
- struts2 paramsPrepareParamsStack拦截器简化代码(源码分析)
目录 一.在讲 paramsPrepareParamsStack 之前,先看一个增删改查的例子. 1. Dao.java准备数据和提供增删改查 2. Employee.java 为model 3. E ...
- Spark GraphX图计算核心算子实战【AggreagteMessage】
一.简介 参考博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/yszd/p/10186556.html 二.代码实现 package graphx import org.apache.log4j ...
随机推荐
- CentOS 8 正式发布!
CentOS 8 正式发布! CentOS 8 和 RedHat Enterprise Linux 8 发行的版本是一致的,都是基于 Fedora 28 和 内核 4.18.支持传统的.新兴的工作负载 ...
- Java8——jdk——java.time包
public class TestLocalDateTime { //6.ZonedDate.ZonedTime.ZonedDateTime : 带时区的时间或日期 @Test public void ...
- luoguP3312 [SDOI2014]数表
题意 默认\(n\leqslant m\). 设\(f(i)\)表示\(i\)的约数和,因为是积性函数,可以用线性筛求. 先不考虑\(a\)的限制,我们推下式子: \(\sum\limits_{i=1 ...
- HttpRequest对象
在面向对象的语言中,有种“万物皆对象”的说法.在上篇文章中介绍了HttpRuntime类,在该类收到请求之后,立即通过HttpWorkerRequest工作者对象对传递的参数进行分析和分解,创建方便网 ...
- Java解决方案
1.新建模板类提示版本太低 Syntax error, type parameters are only available if source level is 1.5 当我的eclipse使用jd ...
- [ Python入门教程 ] Python基础语法
Python的语法非常简练,因此用Python编写的程序可读性强.容易理解.本章将介绍Python的基本语法和概念. Python文件类型 1.源代码.Python的源代码的扩展名以py结尾,可直接运 ...
- [BJOI2019]奥术神杖(AC自动机,DP,分数规划)
题目大意: 给出一个长度 $n$ 的字符串 $T$,只由数字和点组成.你可以把每个点替换成一个任意的数字.再给出 $m$ 个数字串 $S_i$,第 $i$ 个权值为 $t_i$. 对于一个替换方案,这 ...
- [LeetCode] 161. One Edit Distance 一个编辑距离
Given two strings s and t, determine if they are both one edit distance apart. Note: There are 3 pos ...
- CentOS6.9安装MySQL5.6
1 检查系统是否自带MySQL 检查系统是否自带MySQL yum list installed | grep mysql 下面结果说明系统自带MySQL 卸载系统自带MySQL yum -y rem ...
- 一步步从零开始用 webpack 搭建一个大型项目
开篇 很多人都或多或少使用过 webpack,但是很少有人能够系统的学习 webpack 配置,遇到错误的时候就会一脸懵,不知道从哪查起?性能优化时也不知道能做什么,网上的优化教程是不是符合自己的项目 ...
