数据结构------------------二叉查找树(BST)的java实现
数据结构------------------二叉查找树(BST)的java实现
二叉查找树(BST)是一种能够将链表插入的灵活性和有序数组查找的高效性相结合的一种数据结构。它的定义如下:
二叉查找树是一种二叉树,它的每个节点的key都大于它左子树中的任意节点的key小于它右子树中的所有节点的key。
本文对二叉树查找树的基本功能进行了实现,包括添加元素、查找元素、删除元素、遍历元素等等,具体API请看下图及后续详细介绍:
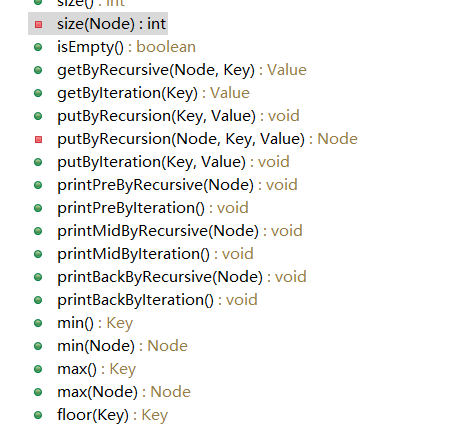

1. 二叉树的节点Node
二叉树的节点包括一个键、值,以及左右子树的链接,是BST的一个内部类。
private class Node {
private Key key;//键
private Value value;//值
private Node left;//左子树链接
private Node right;//右子树链接
public Node(Key key, Value value, BST<Key, Value>.Node left, BST<Key, Value>.Node right) {
super();
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [key=" + key + ", value=" + value + "]";
}
}
2. 添加元素
本文对二叉查找树的添加提供了两种实现:递归添加和迭代添加
/**
* 递归添加
* @param key
* @param value
*/
public void putByRecursion(Key key,Value value) {
root = putByRecursion(root, key,value);
} private Node putByRecursion(Node x, Key key, Value value) {
//1. 如果x为null,返回新添加的节点
if(x == null) {
return new Node(key,value,null,null);
} if(key.compareTo(x.key) < 0) {//要添加的key<当前key,往其左子树添加
x.left = putByRecursion(x.left,key,value);
}else if(key.compareTo(x.key) == 0){//如果相等,替换value值
x.value = value;
}else {
x.right = putByRecursion(x.right,key,value);//要添加的key>当前key,往其右子树添加
}
//2. 如果不为null的返回值为当前节点
return x;
} /**
* 迭代添加
* @param key
* @param value
*/
public void putByIteration(Key key,Value value) {
//如果根节点为null,添加根节点
if(root == null) {
root = new Node(key,value,null,null);
return;
} Node current = root;
Node parent = null;//记录要添加节点的父节点
while(current != null) {
parent = current;
if(key.compareTo(current.key) < 0) {
current = current.left;
}else if(key.compareTo(current.key) == 0) {
current.value = value;
return;
}else {
current = current.right;
}
}
//判断要添加的节点是其父节点的做节点还是右节点
if(key.compareTo(parent.key) < 0) {
parent.left = new Node(key,value,null,null);
}else {
parent.right = new Node(key,value,null,null);
}
}
3. 查找
(1)返回BST的总节点数、判断BST是否为空
//返回二叉查找树的节点总数
public int size() {
return size(root);
}
/**
* 返回以node为根节点的子树中的节点总数
* @param node
* @return
*/
public int size(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return 0;
} return 1 + size(node.left) + size(node.right);//1 + 左子树数量 + 右子树数量 } /**
* 判断二叉树是否为空
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return root == null;
}
(2) 查找指定Key的递归实现和迭代实现
public Value getByRecursive(Key key) {
return getByRecursive(root,key);
}
/**
* 递归实现查找
* @param x
* @param key
* @return
*/
public Value getByRecursive(Node x,Key key) {
if(x == null) {
return null;
}
if(key.compareTo(x.key) == 0) {
return x.value;
}else if(key.compareTo(x.key) < 0) {//查找左树
return getByRecursive(x.left, key);
}else {//查找右树
return getByRecursive(x.right, key);
}
}
/**
* 迭代查找(循环遍历)
* @return
*/
public Value getByIteration(Key key) {
if(root == null) {
return null;
}
Node current = root;
while(current != null) {
int cmp = key.compareTo(current.key);
if(cmp < 0) {//左节点
current = current.left;
}else if(cmp == 0) {//返回
return current.value;
}else {//右节点
current = current.right;
}
} return null;
}
4.遍历
(1)前序遍历
前序遍历:先遍历当前节点,之后遍历当前节点的左子树,最后遍历当前节点的右子树
/**
* 前序遍历:先打印当前节点,再打印当前节点的左左子树和右子树
* @param x
*/
public void printPreByRecursive(Node x) {
if(x == null) {
return;
}
System.out.println(x);//打印当前节点
printPreByRecursive(x.left);//遍历左子树
printPreByRecursive(x.right);//遍历右子树
} /**
* 迭代前序遍历:
* 借助于一个栈数据结构
*/
public void printPreByIteration() {
if(root == null) {
return;
}
LinkedList<Node> stack = new LinkedList<>();
Node current = root;
while(current != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if(current != null) {//一直遍历左子树,添加节点,并打印
stack.push(current);
System.out.println(current);
current = current.left;
}else {//遇到空节点,就谈一个节点,然后指向右节点
current = stack.pop();
current = current.right;
} } }
(2)中序遍历
中序遍历:在遍历当前节点前,先遍历当前节点的左子树,然后再打印当前节点,最后遍历当前节点的右子树
/**
* 中序遍历递归实现:要打印当前节点前,先打印当前节点的左子树,再打印当前节点,最后打印当前节点的右子树
* @param x
*/
public void printMidByRecursive(Node x) {
if(x == null) {
return;
}
printMidByRecursive(x.left);
System.out.println(x);
printMidByRecursive(x.right);
}
/**
* 中序遍历迭代实现:
* 借助于栈数据结构
*/
public void printMidByIteration() {
if(root == null) {
return;
} Node current = root;
LinkedList<Node> stack = new LinkedList<>();
while(current != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if(current != null) {
stack.push(current);
current = current.left;
}else {
current = stack.pop();
System.out.println(current);
current = current.right;
}
}
}
(3)后序遍历
后序遍历:先遍历当前节点的左右子树,再打印当前节点:
/**
* 后序遍历:要输出当前节点前,先输出当前节点的左右节点
* @param x
*/
public void printBackByRecursive(Node x) {
if(x == null) {
return;
}
printBackByRecursive(x.left);
printBackByRecursive(x.right);
System.out.println(x);
} /**
* 后续遍历的迭代实现
*/
public void printBackByIteration() {
if(root == null) {
return;
} LinkedList<Node> stack = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<Node> output = new LinkedList<>();
stack.push(root); //存放数据
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node current = stack.pop();
output.push(current);
if(current.left != null) {
stack.push(current.left);
}
if(current.right != null) {
stack.push(current.right);
} } //遍历数据
while(!output.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(output.pop());
}
}
5. 最小键和最大键的获取
/**
* 获取最小key
* @return
*/
public Key min() {
return min(root).key;
} public Node min(Node x) {
if(x.left == null) {
return x;
}
return min(x.left);
} /**
* 返回最大Key
* @return
*/
public Key max() {
return max(root).key;
} public Node max(Node x) {
if(x.right == null) {
return x;
}
return max(x.right);
}
6. 向上取整、向下取整
public Key floor(Key key) {
Node node = floor(root,key);
if(node != null) {
return node.key;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 查找小于等于指定键的最大键:
* 思想:
* 1.如果给定的键小于根节点的键,那么要查找的键肯定在二叉树的左侧。
* 2.如果给定的键等于根节点的键,自然返回根节点的键
* 3.如果给定的键大于根节点的键,那么只有当根节点的右子树中存在小于等于key的节点时,小于等于key的最大键才会出现在右子树,否则就是根节点
* @param node
* @param key
* @return
*/
public Node floor(Node node, Key key) {
if(node == null) return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(node.key);
if(cmp == 0) return node;
if(cmp < 0) {
return floor(node.left,key);
}
Node t = floor(node.right,key);
if(t != null) {
return t;
}else {
return node;
}
}
public Key ceil(Key key) {
Node x = ceil(root,key);
if(x != null) {
return x.key;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 查找大于等于指定键的最小键
* 1. 如果给定的键大于根节点的键,那么要查找的键肯定在根节点的右子树
* 2. 如果给定的键等于根节点的键,那么要查找的键就是该键
* 3. 如果给定的键小于等于根节点的键,那么当且仅当根节点的左子树中存在大于等于给定键的节点时,才会出现在左子树中,否则就是根节点
* @param root2
* @param key
* @return
*/
private Node ceil(Node node, Key key) {
if(node == null) {
return null;
}
int cmp = key.compareTo(node.key);
if(cmp > 0) {
return ceil(node.right,key);
}
if(cmp == 0) return node;
Node x = ceil(node.left,key);
if(x != null) {
return x;
}
return null;
}
7. 键的排名
/**
* 返回排名为k的节点:
* 思想:通过判断以根节点左子树的数量来判断
* @param node
* @param k
* @return
*/
private Node select(Node node, int k) {
if(node == null) return null;
int size = size(node.left);
if(size > k) {
return select(node.left,k);
}else if(size < k) {
return select(node.right,k-size-1);
}else {
return node;
}
} public int rank(Key key) {
return rank(root,key);
} /**
* 返回以node为根节点的子树中小于x.key的键的数量
* @param node
* @param key
* @return
*/
private int rank(Node node, Key key) {
if(node == null) {
return 0;
}
int cmp = key.compareTo(node.key);
if(cmp < 0) {
return rank(node.left,key);
}else if(cmp > 0) {
return size(node.left) + 1 + rank(node.right,key);
}else {
return size(node.left);
}
}
8. 节点删除
(1)删除最大、最小节点
public void deleteMin() {
root = deleteMin(root);
}
/**
* 删除最小key
*
* 如果node.left == null 返回node.right;
* 否则,将当前节点的做节点的做节点指向delete(node.left)
* @param node
* @return 返回值有分为两种情况,要么是当前节点的右节点,或者是本身
*/
private Node deleteMin(Node node) {
if(node.left == null) {
return node.right;
}
node.left = deleteMin(root.left);
return node;
}
public void deleteMax() {
root = deleteMax(root);
}
/**
* 删除最大节点
* @param node
* @return
*/
public Node deleteMax(Node node) {
if(node.right == null) {
return node.left;
}
node.right = deleteMax(node.right);
return node;
}
(2)删除指定节点
public void delete(Key key) {
root = delete(root,key);
}
public Node delete(Node node, Key key) {
//1. 如果node为null,返回null
if(node == null) {
return null;
}
int cmp = key.compareTo(node.key);
if(cmp < 0) {
node.left = delete(node.left,key);
}else if(cmp > 0) {
node.right = delete(node.right,key);
}else {
if(node.left == null) {
return node.right;
}
if(node.right == null) {
return node.left;
}
//取出要删除节点右子树的最小节点替换当前节点
Node t = node;
node = min(node.right);
node.right = deleteMin(t.right);
node.left = t.left;
}
//2. 否则返回当前节点
return node;
}
9. 范围查找
/**
* 遍历所有的key
* @return
*/
public Iterable<Key> keys() {
return keys(min(),max());
} /**
* 遍历指定范围内的key
* @param lo
* @param hi
* @return
*/
public Iterable<Key> keys(Key lo, Key hi) { Queue<Key> queue = new LinkedList<>();
keys(root,queue,lo,hi);
return queue;
} private void keys(Node node, Queue<Key> queue, Key lo, Key hi) {
if(node == null) {
return;
} int cmplo = lo.compareTo(node.key);
int cmphi = hi.compareTo(node.key);
//如果最小键比当前键小,遍历左树
if(cmplo < 0) {
keys(node.left,queue,lo,hi);
}
//如果最小键 <= 当前键 <= 最大键,添加到队列
if(cmplo <= 0 && cmphi >= 0) {
queue.add(node.key);
}
//如果最大键比当前键大,遍历其右树
if(cmplo > 0) {
keys(node.left,queue,lo,hi);
} }
数据结构------------------二叉查找树(BST)的java实现的更多相关文章
- 二叉查找树(三)之 Java的实现
概要 在前面分别介绍了"二叉查找树的相关理论知识,然后给出了二叉查找树的C和C++实现版本".这一章写一写二叉查找树的Java实现版本. 目录 1. 二叉树查找树2. 二叉查找树的 ...
- 查找系列合集-二叉查找树BST
一. 二叉树 1. 什么是二叉树? 在计算机科学中,二叉树是每个结点最多有两个子树的树结构. 通常子树被称作“左子树”(left subtree)和“右子树”(right subtree). 二叉树常 ...
- [学习笔记] 二叉查找树/BST
平衡树前传之BST 二叉查找树(\(BST\)),是一个类似于堆的数据结构, 并且,它也是平衡树的基础. 因此,让我们来了解一下二叉查找树吧. (其实本篇是作为放在平衡树前的前置知识的,但为了避免重复 ...
- 数据结构与算法【Java】08---树结构的实际应用
前言 数据 data 结构(structure)是一门 研究组织数据方式的学科,有了编程语言也就有了数据结构.学好数据结构才可以编写出更加漂亮,更加有效率的代码. 要学习好数据结构就要多多考虑如何将生 ...
- 二叉查找树(BST)
二叉查找树(BST):使用中序遍历可以得到一个有序的序列
- 【图数据结构的遍历】java实现广度优先和深度优先遍历
[图数据结构的遍历]java实现广度优先和深度优先遍历 宽度优先搜索(BFS)遍历图需要使用队列queue数据结构: 深度优先搜索(DFS, Depth First Search)的实现 需要使用到栈 ...
- 二叉查找树BST 模板
二叉查找树BST 就是二叉搜索树 二叉排序树. 就是满足 左儿子<父节点<右儿子 的一颗树,插入和查询复杂度最好情况都是logN的,写起来很简单. 根据BST的性质可以很好的解决这些东 ...
- 数据结构与算法【Java】02---链表
前言 数据 data 结构(structure)是一门 研究组织数据方式的学科,有了编程语言也就有了数据结构.学好数据结构才可以编写出更加漂亮,更加有效率的代码. 要学习好数据结构就要多多考虑如何将生 ...
- 数据结构与算法【Java】03---栈
前言 数据 data 结构(structure)是一门 研究组织数据方式的学科,有了编程语言也就有了数据结构.学好数据结构才可以编写出更加漂亮,更加有效率的代码. 要学习好数据结构就要多多考虑如何将生 ...
随机推荐
- 网络流之Dinic算法
初学网络流.存一下Dinic板子. 复杂度O(n^2*m) UVA - 1515 Pool construction 把每个草地与 S 相连,花费为dig,每个洞与 T 相连,花费为 然后对于每个两个 ...
- ACM-ICPC 2017 Asia Urumqi A. Coins
Alice and Bob are playing a simple game. They line up a row of n identical coins, all with the heads ...
- re--参考手册
表达式全集 字符 描述 \ 将下一个字符标记为一个特殊字符.或一个原义字符.或一个向后引用.或一个八进制转义符.例如,“n”匹配字符“n”.“\n”匹配一个换行符.串行“\\”匹配“\”而“\(”则匹 ...
- 笔记-python-urllib
笔记-python-urllib 1. 简介 PYTHON3中将urllib,urllib2整合到URLLIB中 包括以下模块 urllib.request 请求模块(核心) urllib. ...
- cygwin的使用
参考资料: 对话 UNIX: 在 Windows 上使用 Cygwin Cygwin使用指南
- 系统测试过程截获SQL方法
1 摘要 测试过程中,经常会遇到莫名的各种问题,可能从开发同学的日志无法发现具体出现问题的原因,本着测试同学深入分析.定位问题的目的,经常需要一些额外的手段获得更多的错误异常信息. 我们涉及 ...
- 04_ThreadLocal整合事务操作
文章导读: 本文主要讲解了如何在没有框架情况下如何解决Dao的事务问题, 重点理解Connection存放到WeakReference中为什么垃圾回收的时候Connection不回收 视频与源码下载: ...
- python-网络编程-03
首先我们可以看下可以最简单的交互性的服务端和客户端程序 server import socket def main(): sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,soc ...
- Linux进程间通信(IPC)
linux下的进程通信手段基本上是从Unix平台上的进程通信手段继承而来的.而对Unix发展做出重大贡献的两大主力AT&T的贝尔实验室及BSD(加州大学伯克利分校的伯克利软件发布中心)在进程间 ...
- wordpress 获取站点的所有链接
<?php include "wp-load.php"; $posts = new WP_Query('post_type=any&posts_per_page=-1 ...
