【requireJS源码学习01】了解整个requireJS的结构
前言
现在工作中基本离不开requireJS这种模块管理工具了,之前一直在用,但是对其原理不甚熟悉,整两天我们来试着学习其源码,而后在探寻其背后的AMD思想吧
于是今天的目标是熟悉requireJS整体框架结构,顺便看看之前的简单demo
程序入口
源码阅读仍然有一定门槛,通看的做法不适合我等素质的选手,所以还是得由入口开始,requireJS的入口便是引入时候指定的data-main
<script src="require.js" type="text/javascript" data-main="main.js"></script>
在js引入后,会自动执行指向data-main的js函数,这个就是我们所谓的入口,跟着这条线,我们就进入了requirejs的大门
首先,引入js文件本身不会干什么事情,那么requirejs内部做了什么呢?
① 除了一些初始化操作以为第一件干的事情,值执行这段代码:
//Create default context.
req({});
这段代码会构造默认的参数,其调用的又是整个程序的入口
req = requirejs = function (deps, callback, errback, optional) {}
这里具体干了什么我们先不予关注,继续往后面走,因为貌似,这里与data-main暂时不相干,因为这段会先于data-main逻辑运行
然后,进入data-main相关的逻辑了:
//Look for a data-main script attribute, which could also adjust the baseUrl.
if (isBrowser && !cfg.skipDataMain) {
//Figure out baseUrl. Get it from the script tag with require.js in it.
eachReverse(scripts(), function (script) {
//Set the 'head' where we can append children by
//using the script's parent.
if (!head) {
head = script.parentNode;
} //Look for a data-main attribute to set main script for the page
//to load. If it is there, the path to data main becomes the
//baseUrl, if it is not already set.
dataMain = script.getAttribute('data-main');
if (dataMain) {
//Preserve dataMain in case it is a path (i.e. contains '?')
mainScript = dataMain; //Set final baseUrl if there is not already an explicit one.
if (!cfg.baseUrl) {
//Pull off the directory of data-main for use as the
//baseUrl.
src = mainScript.split('/');
mainScript = src.pop();
subPath = src.length ? src.join('/') + '/' : './'; cfg.baseUrl = subPath;
} //Strip off any trailing .js since mainScript is now
//like a module name.
mainScript = mainScript.replace(jsSuffixRegExp, ''); //If mainScript is still a path, fall back to dataMain
if (req.jsExtRegExp.test(mainScript)) {
mainScript = dataMain;
} //Put the data-main script in the files to load.
cfg.deps = cfg.deps ? cfg.deps.concat(mainScript) : [mainScript]; return true;
}
});
}
因为requireJS不止用于浏览器,所以这里有一个判断,我们暂时不予关注,看看他干了些什么
① 他会去除页面所有的script标签,然后倒叙遍历之
scripts() => [<script src="require.js" type="text/javascript" data-main="main.js"></script>]
这个地方遇到两个方法
eachReverse
与each一致,只不过由逆序遍历
function eachReverse(ary, func) {
if (ary) {
var i;
for (i = ary.length - 1; i > -1; i -= 1) {
if (ary[i] && func(ary[i], i, ary)) {
break;
}
}
}
}
scripts
便是document.getElementsByTagName('script');返回所有的script标签
然后开始的head便是html中的head标签,暂时不予理睬
if (isBrowser) {
head = s.head = document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0];
//If BASE tag is in play, using appendChild is a problem for IE6.
//When that browser dies, this can be removed. Details in this jQuery bug:
//http://dev.jquery.com/ticket/2709
baseElement = document.getElementsByTagName('base')[0];
if (baseElement) {
head = s.head = baseElement.parentNode;
}
}
dataMain = script.getAttribute('data-main');
然后这一句便可以获取当前指定运行的文件名,比如这里
dataMain => main.js
如果不存在就不会有什么操作了
PS:我原来记得默认指向main.js,看来是我记错了......
然后下来做了一些处理,会根据指定的main.js初步确定bashUrl,其实就是与main.js统一目录
最后做了关键的一个步骤:
cfg.deps = cfg.deps ? cfg.deps.concat(mainScript) : [mainScript];
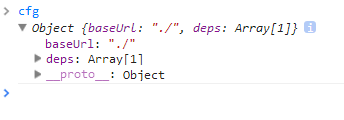
将main放入带加载的配置中,而本身不干任何事情,继续接下来的逻辑......然后此逻辑暂时结束,根据这些参数进入下一步骤
req/requirejs
根据上一步骤的处理,会形成上面截图的参数,而后再一次执行入口函数req,这个时候就会发生不一样的事情了
/**
* Main entry point.
*
* If the only argument to require is a string, then the module that
* is represented by that string is fetched for the appropriate context.
*
* If the first argument is an array, then it will be treated as an array
* of dependency string names to fetch. An optional function callback can
* be specified to execute when all of those dependencies are available.
*
* Make a local req variable to help Caja compliance (it assumes things
* on a require that are not standardized), and to give a short
* name for minification/local scope use.
*/
req = requirejs = function (deps, callback, errback, optional) { //Find the right context, use default
var context, config,
contextName = defContextName; // Determine if have config object in the call.
if (!isArray(deps) && typeof deps !== 'string') {
// deps is a config object
config = deps;
if (isArray(callback)) {
// Adjust args if there are dependencies
deps = callback;
callback = errback;
errback = optional;
} else {
deps = [];
}
} if (config && config.context) {
contextName = config.context;
} context = getOwn(contexts, contextName);
if (!context) {
context = contexts[contextName] = req.s.newContext(contextName);
} if (config) {
context.configure(config);
} return context.require(deps, callback, errback);
};
这个时候我们的第一个参数deps就不再是undefined了,而是一个对象,这里便将其配置放到了config变量中保持deps为一数组,然后干了些其他事情
这里有个变量context,需要特别注意,后面我们来看看他有些什么,这里有一个新的函数
function getOwn(obj, prop) {
return hasProp(obj, prop) && obj[prop];
}
function hasProp(obj, prop) {
return hasOwn.call(obj, prop);
}
hasOwn = op.hasOwnProperty
这里会获取非原型属性将其扩展,首次执行时候会碰到一个非常重要的函数newContext 因为他是一个核心,我们这里暂时选择忽略,不然整个全部就陷进去了
经过newContext处理后的context就变成这个样子了:

if (config) {
context.configure(config);
}
这里就会将我们第一步的参数赋值进对象,具体干了什么,我们依旧不予理睬,main.js干了两件事情:
① 暂时性设置了baseUrl
② 告诉requireJS你马上要加载我了
于是最后终于调用require开始处理逻辑
return context.require(deps, callback, errback);
require
因为context.require = context.makeRequire();而该函数本身又返回localRequire函数,所以事实上这里是执行的localRequire函数,内部维护着一个闭包
因为nextContext只会运行一次,所以很多require实际用到的变量都是nextContext闭包所维护,比如我们这里便可以使用config变量
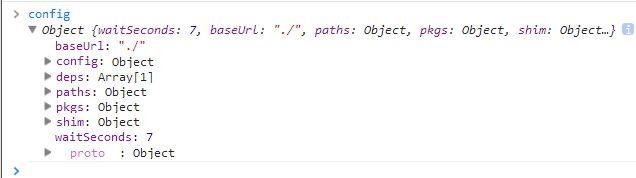
这里依旧有一些特殊处理,比如deps是字符串的情况,但是我们暂时不予关注.......
PS:搞了这么久很多不予关注了,欠了很多帐啊!
他这里应该是有一个BUG,所以这里用到了一个settimeout延时
PS:因为settimeout的使用,整个这块的程序全部会抛到主干逻辑之后了
然后接下来的步骤比较关键了,我们先抛开一切来理一理这个newContext
newContext
newContext占了源码的主要篇幅,他也只会在初始化时候执行一次,而后便不再执行了:
if (!context) {
context = contexts[contextName] = req.s.newContext(contextName);
}
现在,我们就目前而知来简单理一理,requireJS的结构
① 变量声明,工具类
在newContext之前,完全是做一些变量的定义,或者做一些简单的操作,里面比较关键的是contexts/cfg对象,会被后面无数次的用到
② 实例化上下文/newContext
紧接着就是newContext这洋洋洒洒一千多行代码了,其中主要干了什么暂时不知道,据我观察应该是做环境相关的准备
③ 对外接口
上面操作结束后便提供了几个主要对外接口
requirejs
require.config
虽然这里是两个函数,其实都是requirejs这一关入口
而后,require自己撸了一把,实例化了默认的参数,这里便调用了newContext,所以以后都不会调用,其中的函数多处于其闭包环境
接下来根据引入script标签的data-main做了一次文章,初始化了简单的参数,并将main.js作为了依赖项,这里会根据main.js重写cfg对象
最后requirejs执行一次reg(cfg),便真的开始了所有操作,这个时候我们就进入newContext,看看他主要干了什么
PS:所有require并未提供任何借口出来,所以在全局想查看其contexts或者cfg是不行的,而且每次操作都可能导致其改变
要了解newContext函数,还是需要进入其入口
if (!context) {
context = contexts[contextName] = req.s.newContext(contextName);
}
从script标签引入require库时候,会因为这段代码执行一次newContext函数,从此后,该函数不会被执行,其实现的原因不是我等现在能明白的,先看懂实现再说吧
//Create default context.
req({});
所以上面说了那么多,看了这么久,其实最关键的还是首次加载,首次加载就决定了运行上下文了
整体结构
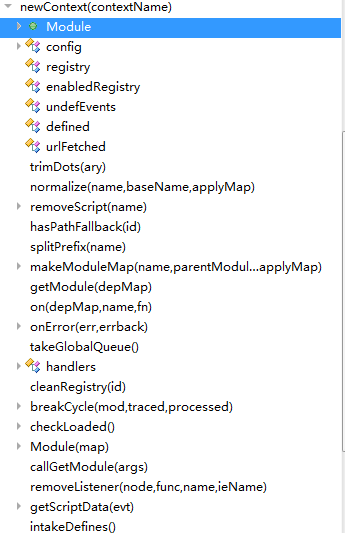
newContext的基本结构大概是这样:
① 函数作用域内变量定义(中间初始化了一发handlers变量)
② 一堆工具函数定义
③ Module模块(这块给人的感觉不明觉厉...应该是核心吧)
④ 实例化context对象,将该对象返回,然后基本结束
进入newContext后,第一步是基本变量定义,这种对外的框架一般都不会到处命名变量,而是将所有变量全部提到函数最前面
一来是js解析时候声明本身会提前,而来可能是到处命名变量会让我们找不到吧......
开始定义了很多变量,我们一来都不知道是干神马的,但是config变量却引起了我们的注意,这里先放出来,继续往下就是一连串的函数了,值得说明的是,这些变量会被重复利用哦
一眼看下来,该函数本身并没有做什么实际的事情,这个时候我们就需要找其入口,这里的入口是
//首次调用
req({})
=>
//触发newContext,做首次初始化并返回给context对象
context = contexts[contextName] = req.s.newContext(contextName)
=>
//注意这里require函数其实处于了mackRequire函数的闭包环境
context.require = context.makeRequire();
=>
//首次调用newContext返回对象初始化变量
context.configure(config);
所以,在首次初始化后,并未做特别的处理,直到configure的调用,于是让我们进入该函数
/**
* Set a configuration for the context.
* @param {Object} cfg config object to integrate.
*/
configure: function (cfg) {
//Make sure the baseUrl ends in a slash.
if (cfg.baseUrl) {
if (cfg.baseUrl.charAt(cfg.baseUrl.length - 1) !== '/') {
cfg.baseUrl += '/';
}
} //Save off the paths and packages since they require special processing,
//they are additive.
var pkgs = config.pkgs,
shim = config.shim,
objs = {
paths: true,
config: true,
map: true
}; eachProp(cfg, function (value, prop) {
if (objs[prop]) {
if (prop === 'map') {
if (!config.map) {
config.map = {};
}
mixin(config[prop], value, true, true);
} else {
mixin(config[prop], value, true);
}
} else {
config[prop] = value;
}
}); //Merge shim
if (cfg.shim) {
eachProp(cfg.shim, function (value, id) {
//Normalize the structure
if (isArray(value)) {
value = {
deps: value
};
}
if ((value.exports || value.init) && !value.exportsFn) {
value.exportsFn = context.makeShimExports(value);
}
shim[id] = value;
});
config.shim = shim;
} //Adjust packages if necessary.
if (cfg.packages) {
each(cfg.packages, function (pkgObj) {
var location; pkgObj = typeof pkgObj === 'string' ? { name: pkgObj} : pkgObj;
location = pkgObj.location; //Create a brand new object on pkgs, since currentPackages can
//be passed in again, and config.pkgs is the internal transformed
//state for all package configs.
pkgs[pkgObj.name] = {
name: pkgObj.name,
location: location || pkgObj.name,
//Remove leading dot in main, so main paths are normalized,
//and remove any trailing .js, since different package
//envs have different conventions: some use a module name,
//some use a file name.
main: (pkgObj.main || 'main')
.replace(currDirRegExp, '')
.replace(jsSuffixRegExp, '')
};
}); //Done with modifications, assing packages back to context config
config.pkgs = pkgs;
} //If there are any "waiting to execute" modules in the registry,
//update the maps for them, since their info, like URLs to load,
//may have changed.
eachProp(registry, function (mod, id) {
//If module already has init called, since it is too
//late to modify them, and ignore unnormalized ones
//since they are transient.
if (!mod.inited && !mod.map.unnormalized) {
mod.map = makeModuleMap(id);
}
}); //If a deps array or a config callback is specified, then call
//require with those args. This is useful when require is defined as a
//config object before require.js is loaded.
if (cfg.deps || cfg.callback) {
context.require(cfg.deps || [], cfg.callback);
}
},
首次传入的是空对象,所以开始一段代码暂时没有意义,这里使用的config变量正是newContext维护的闭包,也就是上面让注意的
config = {
//Defaults. Do not set a default for map
//config to speed up normalize(), which
//will run faster if there is no default.
waitSeconds: 7,
baseUrl: './',
paths: {},
pkgs: {},
shim: {},
config: {}
},
下面用到了一个新的函数:
eachProp
这个函数会遍历对象所有非原型属性,并且使用第二个参数(函数)执行之,如果返回true便停止,首次执行时候cfg为空对象,便没有往下走,否则config变量会被操作,具体我们暂时不管
/**
* Cycles over properties in an object and calls a function for each
* property value. If the function returns a truthy value, then the
* iteration is stopped.
*/
function eachProp(obj, func) {
var prop;
for (prop in obj) {
if (hasProp(obj, prop)) {
if (func(obj[prop], prop)) {
break;
}
}
}
}
这个所谓的入口执行后实际的意义基本等于什么都没有干......
但是,这里可以得出一个弱弱的结论就是
configure是用于设置参数滴
所以所谓的入口其实没有干事情,这个时候第二个入口便出现了
context.require
return context.require(deps, callback, errback);
参数设置结束后便会执行context的require方法,这个是真正的入口,他实际调用顺序为:
context.require = context.makeRequire();
=>
localRequire
所以真正调用localRequire时候,已经执行了一番makeRequire函数了,现在处于了其上下文,正因为localRequire被处理过,其多了几个函数属性
除此之外,暂时没有看出其它变化,所以这里在某些特定场景是等价的
function localRequire(deps, callback, errback) {
var id, map, requireMod;
if (options.enableBuildCallback && callback && isFunction(callback)) {
callback.__requireJsBuild = true;
}
if (typeof deps === 'string') {
if (isFunction(callback)) {
//Invalid call
return onError(makeError('requireargs', 'Invalid require call'), errback);
}
//If require|exports|module are requested, get the
//value for them from the special handlers. Caveat:
//this only works while module is being defined.
if (relMap && hasProp(handlers, deps)) {
return handlers[deps](registry[relMap.id]);
}
//Synchronous access to one module. If require.get is
//available (as in the Node adapter), prefer that.
if (req.get) {
return req.get(context, deps, relMap, localRequire);
}
//Normalize module name, if it contains . or ..
map = makeModuleMap(deps, relMap, false, true);
id = map.id;
if (!hasProp(defined, id)) {
return onError(makeError('notloaded', 'Module name "' +
id +
'" has not been loaded yet for context: ' +
contextName +
(relMap ? '' : '. Use require([])')));
}
return defined[id];
}
//Grab defines waiting in the global queue.
intakeDefines();
//Mark all the dependencies as needing to be loaded.
context.nextTick(function () {
//Some defines could have been added since the
//require call, collect them.
intakeDefines();
requireMod = getModule(makeModuleMap(null, relMap));
//Store if map config should be applied to this require
//call for dependencies.
requireMod.skipMap = options.skipMap;
requireMod.init(deps, callback, errback, {
enabled: true
});
checkLoaded();
});
return localRequire;
}
过程中会执行一次intakeDefines,他的意义是定义全局队列,其意义暂时不明,然后进入了前面说的那个settimeout
在主干逻辑结束后,这里会进入时钟队列的回调,其中的代码就比较关键了,只不过首次不能体现
context.nextTick(function () {
//Some defines could have been added since the
//require call, collect them.
intakeDefines();
requireMod = getModule(makeModuleMap(null, relMap));
//Store if map config should be applied to this require
//call for dependencies.
requireMod.skipMap = options.skipMap;
requireMod.init(deps, callback, errback, {
enabled: true
});
checkLoaded();
});
这段代码事实上是比较奇特的,他会完全脱离整个require代码,比如整个
return context.require(deps, callback, errback);
执行了后上面才会慢慢执行
PS:require这段比较重要,留待明天分析,今天先看整体逻辑
下面的主要逻辑又到了这里
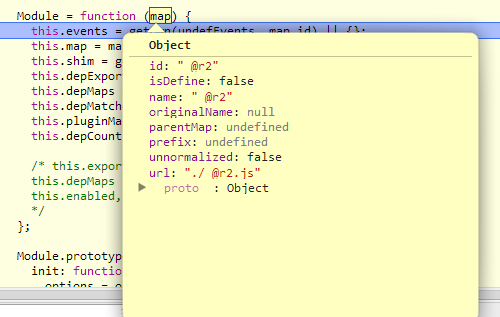
requireMod = getModule(makeModuleMap(null, relMap));
我们这里主要先看getModule先,首先makeModuleMap比较关键,他会根据规则创建一些模块唯一标识的东西,暂时是什么当然是先不管啦......
PS:其规则应该与加载的require数量有关,最后会形成这个东西
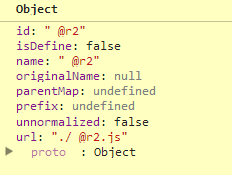
/**
* Creates a module mapping that includes plugin prefix, module
* name, and path. If parentModuleMap is provided it will
* also normalize the name via require.normalize()
*
* @param {String} name the module name
* @param {String} [parentModuleMap] parent module map
* for the module name, used to resolve relative names.
* @param {Boolean} isNormalized: is the ID already normalized.
* This is true if this call is done for a define() module ID.
* @param {Boolean} applyMap: apply the map config to the ID.
* Should only be true if this map is for a dependency.
*
* @returns {Object}
*/
function makeModuleMap(name, parentModuleMap, isNormalized, applyMap) {
var url, pluginModule, suffix, nameParts,
prefix = null,
parentName = parentModuleMap ? parentModuleMap.name : null,
originalName = name,
isDefine = true,
normalizedName = ''; //If no name, then it means it is a require call, generate an
//internal name.
if (!name) {
isDefine = false;
name = '_@r' + (requireCounter += 1);
} nameParts = splitPrefix(name);
prefix = nameParts[0];
name = nameParts[1]; if (prefix) {
prefix = normalize(prefix, parentName, applyMap);
pluginModule = getOwn(defined, prefix);
} //Account for relative paths if there is a base name.
if (name) {
if (prefix) {
if (pluginModule && pluginModule.normalize) {
//Plugin is loaded, use its normalize method.
normalizedName = pluginModule.normalize(name, function (name) {
return normalize(name, parentName, applyMap);
});
} else {
normalizedName = normalize(name, parentName, applyMap);
}
} else {
//A regular module.
normalizedName = normalize(name, parentName, applyMap); //Normalized name may be a plugin ID due to map config
//application in normalize. The map config values must
//already be normalized, so do not need to redo that part.
nameParts = splitPrefix(normalizedName);
prefix = nameParts[0];
normalizedName = nameParts[1];
isNormalized = true; url = context.nameToUrl(normalizedName);
}
} //If the id is a plugin id that cannot be determined if it needs
//normalization, stamp it with a unique ID so two matching relative
//ids that may conflict can be separate.
suffix = prefix && !pluginModule && !isNormalized ?
'_unnormalized' + (unnormalizedCounter += 1) :
''; return {
prefix: prefix,
name: normalizedName,
parentMap: parentModuleMap,
unnormalized: !!suffix,
url: url,
originalName: originalName,
isDefine: isDefine,
id: (prefix ?
prefix + '!' + normalizedName :
normalizedName) + suffix
};
}
然后是我们关键的getModule函数
function getModule(depMap) {
var id = depMap.id,
mod = getOwn(registry, id);
if (!mod) {
mod = registry[id] = new context.Module(depMap);
}
return mod;
}
可以看到,一旦我们加载了一个模块便不会重新加载了,这是一个很重要的发现哦
registry 该全局变量用于存储加载模块的键值对
第一步当然是加载啦,但是首次应该会跳过,因为当然事实上没有需要加载的模块,一起跟下去吧
Module
然后进入我们关键的Module类模块了
Module = function (map) {
this.events = getOwn(undefEvents, map.id) || {};
this.map = map;
this.shim = getOwn(config.shim, map.id);
this.depExports = [];
this.depMaps = [];
this.depMatched = [];
this.pluginMaps = {};
this.depCount = 0;
/* this.exports this.factory
this.depMaps = [],
this.enabled, this.fetched
*/
};
Module.prototype = {
init: function (depMaps, factory, errback, options) {
options = options || {};
//Do not do more inits if already done. Can happen if there
//are multiple define calls for the same module. That is not
//a normal, common case, but it is also not unexpected.
if (this.inited) {
return;
}
this.factory = factory;
if (errback) {
//Register for errors on this module.
this.on('error', errback);
} else if (this.events.error) {
//If no errback already, but there are error listeners
//on this module, set up an errback to pass to the deps.
errback = bind(this, function (err) {
this.emit('error', err);
});
}
//Do a copy of the dependency array, so that
//source inputs are not modified. For example
//"shim" deps are passed in here directly, and
//doing a direct modification of the depMaps array
//would affect that config.
this.depMaps = depMaps && depMaps.slice(0);
this.errback = errback;
//Indicate this module has be initialized
this.inited = true;
this.ignore = options.ignore;
//Could have option to init this module in enabled mode,
//or could have been previously marked as enabled. However,
//the dependencies are not known until init is called. So
//if enabled previously, now trigger dependencies as enabled.
if (options.enabled || this.enabled) {
//Enable this module and dependencies.
//Will call this.check()
this.enable();
} else {
this.check();
}
},
defineDep: function (i, depExports) {
//Because of cycles, defined callback for a given
//export can be called more than once.
if (!this.depMatched[i]) {
this.depMatched[i] = true;
this.depCount -= 1;
this.depExports[i] = depExports;
}
},
fetch: function () {
if (this.fetched) {
return;
}
this.fetched = true;
context.startTime = (new Date()).getTime();
var map = this.map;
//If the manager is for a plugin managed resource,
//ask the plugin to load it now.
if (this.shim) {
context.makeRequire(this.map, {
enableBuildCallback: true
})(this.shim.deps || [], bind(this, function () {
return map.prefix ? this.callPlugin() : this.load();
}));
} else {
//Regular dependency.
return map.prefix ? this.callPlugin() : this.load();
}
},
load: function () {
var url = this.map.url;
//Regular dependency.
if (!urlFetched[url]) {
urlFetched[url] = true;
context.load(this.map.id, url);
}
},
/**
* Checks if the module is ready to define itself, and if so,
* define it.
*/
check: function () {
if (!this.enabled || this.enabling) {
return;
}
var err, cjsModule,
id = this.map.id,
depExports = this.depExports,
exports = this.exports,
factory = this.factory;
if (!this.inited) {
this.fetch();
} else if (this.error) {
this.emit('error', this.error);
} else if (!this.defining) {
//The factory could trigger another require call
//that would result in checking this module to
//define itself again. If already in the process
//of doing that, skip this work.
this.defining = true;
if (this.depCount < 1 && !this.defined) {
if (isFunction(factory)) {
//If there is an error listener, favor passing
//to that instead of throwing an error. However,
//only do it for define()'d modules. require
//errbacks should not be called for failures in
//their callbacks (#699). However if a global
//onError is set, use that.
if ((this.events.error && this.map.isDefine) ||
req.onError !== defaultOnError) {
try {
exports = context.execCb(id, factory, depExports, exports);
} catch (e) {
err = e;
}
} else {
exports = context.execCb(id, factory, depExports, exports);
}
if (this.map.isDefine) {
//If setting exports via 'module' is in play,
//favor that over return value and exports. After that,
//favor a non-undefined return value over exports use.
cjsModule = this.module;
if (cjsModule &&
cjsModule.exports !== undefined &&
//Make sure it is not already the exports value
cjsModule.exports !== this.exports) {
exports = cjsModule.exports;
} else if (exports === undefined && this.usingExports) {
//exports already set the defined value.
exports = this.exports;
}
}
if (err) {
err.requireMap = this.map;
err.requireModules = this.map.isDefine ? [this.map.id] : null;
err.requireType = this.map.isDefine ? 'define' : 'require';
return onError((this.error = err));
}
} else {
//Just a literal value
exports = factory;
}
this.exports = exports;
if (this.map.isDefine && !this.ignore) {
defined[id] = exports;
if (req.onResourceLoad) {
req.onResourceLoad(context, this.map, this.depMaps);
}
}
//Clean up
cleanRegistry(id);
this.defined = true;
}
//Finished the define stage. Allow calling check again
//to allow define notifications below in the case of a
//cycle.
this.defining = false;
if (this.defined && !this.defineEmitted) {
this.defineEmitted = true;
this.emit('defined', this.exports);
this.defineEmitComplete = true;
}
}
},
callPlugin: function () {
var map = this.map,
id = map.id,
//Map already normalized the prefix.
pluginMap = makeModuleMap(map.prefix);
//Mark this as a dependency for this plugin, so it
//can be traced for cycles.
this.depMaps.push(pluginMap);
on(pluginMap, 'defined', bind(this, function (plugin) {
var load, normalizedMap, normalizedMod,
name = this.map.name,
parentName = this.map.parentMap ? this.map.parentMap.name : null,
localRequire = context.makeRequire(map.parentMap, {
enableBuildCallback: true
});
//If current map is not normalized, wait for that
//normalized name to load instead of continuing.
if (this.map.unnormalized) {
//Normalize the ID if the plugin allows it.
if (plugin.normalize) {
name = plugin.normalize(name, function (name) {
return normalize(name, parentName, true);
}) || '';
}
//prefix and name should already be normalized, no need
//for applying map config again either.
normalizedMap = makeModuleMap(map.prefix + '!' + name,
this.map.parentMap);
on(normalizedMap,
'defined', bind(this, function (value) {
this.init([], function () { return value; }, null, {
enabled: true,
ignore: true
});
}));
normalizedMod = getOwn(registry, normalizedMap.id);
if (normalizedMod) {
//Mark this as a dependency for this plugin, so it
//can be traced for cycles.
this.depMaps.push(normalizedMap);
if (this.events.error) {
normalizedMod.on('error', bind(this, function (err) {
this.emit('error', err);
}));
}
normalizedMod.enable();
}
return;
}
load = bind(this, function (value) {
this.init([], function () { return value; }, null, {
enabled: true
});
});
load.error = bind(this, function (err) {
this.inited = true;
this.error = err;
err.requireModules = [id];
//Remove temp unnormalized modules for this module,
//since they will never be resolved otherwise now.
eachProp(registry, function (mod) {
if (mod.map.id.indexOf(id + '_unnormalized') === 0) {
cleanRegistry(mod.map.id);
}
});
onError(err);
});
//Allow plugins to load other code without having to know the
//context or how to 'complete' the load.
load.fromText = bind(this, function (text, textAlt) {
/*jslint evil: true */
var moduleName = map.name,
moduleMap = makeModuleMap(moduleName),
hasInteractive = useInteractive;
//As of 2.1.0, support just passing the text, to reinforce
//fromText only being called once per resource. Still
//support old style of passing moduleName but discard
//that moduleName in favor of the internal ref.
if (textAlt) {
text = textAlt;
}
//Turn off interactive script matching for IE for any define
//calls in the text, then turn it back on at the end.
if (hasInteractive) {
useInteractive = false;
}
//Prime the system by creating a module instance for
//it.
getModule(moduleMap);
//Transfer any config to this other module.
if (hasProp(config.config, id)) {
config.config[moduleName] = config.config[id];
}
try {
req.exec(text);
} catch (e) {
return onError(makeError('fromtexteval',
'fromText eval for ' + id +
' failed: ' + e,
e,
[id]));
}
if (hasInteractive) {
useInteractive = true;
}
//Mark this as a dependency for the plugin
//resource
this.depMaps.push(moduleMap);
//Support anonymous modules.
context.completeLoad(moduleName);
//Bind the value of that module to the value for this
//resource ID.
localRequire([moduleName], load);
});
//Use parentName here since the plugin's name is not reliable,
//could be some weird string with no path that actually wants to
//reference the parentName's path.
plugin.load(map.name, localRequire, load, config);
}));
context.enable(pluginMap, this);
this.pluginMaps[pluginMap.id] = pluginMap;
},
enable: function () {
enabledRegistry[this.map.id] = this;
this.enabled = true;
//Set flag mentioning that the module is enabling,
//so that immediate calls to the defined callbacks
//for dependencies do not trigger inadvertent load
//with the depCount still being zero.
this.enabling = true;
//Enable each dependency
each(this.depMaps, bind(this, function (depMap, i) {
var id, mod, handler;
if (typeof depMap === 'string') {
//Dependency needs to be converted to a depMap
//and wired up to this module.
depMap = makeModuleMap(depMap,
(this.map.isDefine ? this.map : this.map.parentMap),
false,
!this.skipMap);
this.depMaps[i] = depMap;
handler = getOwn(handlers, depMap.id);
if (handler) {
this.depExports[i] = handler(this);
return;
}
this.depCount += 1;
on(depMap, 'defined', bind(this, function (depExports) {
this.defineDep(i, depExports);
this.check();
}));
if (this.errback) {
on(depMap, 'error', bind(this, this.errback));
}
}
id = depMap.id;
mod = registry[id];
//Skip special modules like 'require', 'exports', 'module'
//Also, don't call enable if it is already enabled,
//important in circular dependency cases.
if (!hasProp(handlers, id) && mod && !mod.enabled) {
context.enable(depMap, this);
}
}));
//Enable each plugin that is used in
//a dependency
eachProp(this.pluginMaps, bind(this, function (pluginMap) {
var mod = getOwn(registry, pluginMap.id);
if (mod && !mod.enabled) {
context.enable(pluginMap, this);
}
}));
this.enabling = false;
this.check();
},
on: function (name, cb) {
var cbs = this.events[name];
if (!cbs) {
cbs = this.events[name] = [];
}
cbs.push(cb);
},
emit: function (name, evt) {
each(this.events[name], function (cb) {
cb(evt);
});
if (name === 'error') {
//Now that the error handler was triggered, remove
//the listeners, since this broken Module instance
//can stay around for a while in the registry.
delete this.events[name];
}
}
};
总的来说,这个模块还是很长的,首先是其构造函数
这里仍有很多东西读不懂,所以就全部过吧,反正今天的主要目的是熟悉整体框架
这里实例化结束后便形成了一个模块暂存于requireMod变量中,函数执行结束后变量会销毁,该模块会存与全局registery对象中
这里会执行其init方法干具体业务的事情
requireMod.init(deps, callback, errback, {
enabled: true
});
这里又会执行
this.enable();
enable: function () {
enabledRegistry[this.map.id] = this;
this.enabled = true;
//Set flag mentioning that the module is enabling,
//so that immediate calls to the defined callbacks
//for dependencies do not trigger inadvertent load
//with the depCount still being zero.
this.enabling = true;
//Enable each dependency
each(this.depMaps, bind(this, function (depMap, i) {
var id, mod, handler;
if (typeof depMap === 'string') {
//Dependency needs to be converted to a depMap
//and wired up to this module.
depMap = makeModuleMap(depMap,
(this.map.isDefine ? this.map : this.map.parentMap),
false,
!this.skipMap);
this.depMaps[i] = depMap;
handler = getOwn(handlers, depMap.id);
if (handler) {
this.depExports[i] = handler(this);
return;
}
this.depCount += 1;
on(depMap, 'defined', bind(this, function (depExports) {
this.defineDep(i, depExports);
this.check();
}));
if (this.errback) {
on(depMap, 'error', bind(this, this.errback));
}
}
id = depMap.id;
mod = registry[id];
//Skip special modules like 'require', 'exports', 'module'
//Also, don't call enable if it is already enabled,
//important in circular dependency cases.
if (!hasProp(handlers, id) && mod && !mod.enabled) {
context.enable(depMap, this);
}
}));
//Enable each plugin that is used in
//a dependency
eachProp(this.pluginMaps, bind(this, function (pluginMap) {
var mod = getOwn(registry, pluginMap.id);
if (mod && !mod.enabled) {
context.enable(pluginMap, this);
}
}));
this.enabling = false;
this.check();
},
然后又会调用 this.check();这个家伙操作结束后接下来checkLoaded就会创建script标签了......
/**
* Checks if the module is ready to define itself, and if so,
* define it.
*/
check: function () {
if (!this.enabled || this.enabling) {
return;
} var err, cjsModule,
id = this.map.id,
depExports = this.depExports,
exports = this.exports,
factory = this.factory; if (!this.inited) {
this.fetch();
} else if (this.error) {
this.emit('error', this.error);
} else if (!this.defining) {
//The factory could trigger another require call
//that would result in checking this module to
//define itself again. If already in the process
//of doing that, skip this work.
this.defining = true; if (this.depCount < 1 && !this.defined) {
if (isFunction(factory)) {
//If there is an error listener, favor passing
//to that instead of throwing an error. However,
//only do it for define()'d modules. require
//errbacks should not be called for failures in
//their callbacks (#699). However if a global
//onError is set, use that.
if ((this.events.error && this.map.isDefine) ||
req.onError !== defaultOnError) {
try {
exports = context.execCb(id, factory, depExports, exports);
} catch (e) {
err = e;
}
} else {
exports = context.execCb(id, factory, depExports, exports);
} if (this.map.isDefine) {
//If setting exports via 'module' is in play,
//favor that over return value and exports. After that,
//favor a non-undefined return value over exports use.
cjsModule = this.module;
if (cjsModule &&
cjsModule.exports !== undefined &&
//Make sure it is not already the exports value
cjsModule.exports !== this.exports) {
exports = cjsModule.exports;
} else if (exports === undefined && this.usingExports) {
//exports already set the defined value.
exports = this.exports;
}
} if (err) {
err.requireMap = this.map;
err.requireModules = this.map.isDefine ? [this.map.id] : null;
err.requireType = this.map.isDefine ? 'define' : 'require';
return onError((this.error = err));
} } else {
//Just a literal value
exports = factory;
} this.exports = exports; if (this.map.isDefine && !this.ignore) {
defined[id] = exports; if (req.onResourceLoad) {
req.onResourceLoad(context, this.map, this.depMaps);
}
} //Clean up
cleanRegistry(id); this.defined = true;
} //Finished the define stage. Allow calling check again
//to allow define notifications below in the case of a
//cycle.
this.defining = false; if (this.defined && !this.defineEmitted) {
this.defineEmitted = true;
this.emit('defined', this.exports);
this.defineEmitComplete = true;
} }
},
然后今天累了,明天继续吧......
结语
今天的目标是熟悉requireJS的整体结构,如果没有错觉或者解读失误,我们应该大概了解了requireJS的整体结构,于是让我们明天继续吧
PS:尼玛这个框架还真是有点难,小钗感觉有点小吃力啊,估计要读到下周才能真正理解一点的了........
【requireJS源码学习01】了解整个requireJS的结构的更多相关文章
- 【requireJS源码学习03】细究requireJS的加载流程
前言 这个星期折腾了一周,中间没有什么时间学习,周末又干了些其它事情,这个时候正好有时间,我们一起来继续学习requireJS吧 还是那句话,小钗觉得requireJS本身还是有点难度的,估计完全吸收 ...
- 【iScroll源码学习01】准备阶段 - 叶小钗
[iScroll源码学习01]准备阶段 - 叶小钗 时间 2013-12-29 18:41:00 博客园-原创精华区 原文 http://www.cnblogs.com/yexiaochai/p/3 ...
- 【requireJS源码学习02】data-main加载的实现
前言 经过昨天的学习,我们大概了解到了requireJS的主要结构,这里先大概的回顾一下 首先从总体结构来说,require这里分为三块: ① newContext之前变量声明或者一些工具函数 ② n ...
- 【iScroll源码学习01】准备阶段
前言 我们昨天初步了解了为什么会出现iScroll:[SPA]移动站点APP化研究之上中下页面的iScroll化(上),然后简单的写了一个demo来模拟iScroll,其中了解到了以下知识点: ① v ...
- VUE 源码学习01 源码入口
VUE[version:2.4.1] Vue项目做了不少,最近在学习设计模式与Vue源码,记录一下自己的脚印!共勉!注:此处源码学习方式为先了解其大模块,从宏观再去到微观学习,以免一开始就研究细节然后 ...
- jQuery 源码学习 - 01 - 简洁的 $('...')
首先贴上学习参考资料:[深入浅出jQuery]源码浅析--整体架构,备用地址:chokcoco/jQuery-. jQuery 库,js 开发的一个里程碑,它的出现,让网页开发者们告别荒蛮的上古时代, ...
- Spring源码学习01:IntelliJ IDEA2019.3编译Spring5.3.x源码
目录 Spring源码学习01:IntelliJ IDEA2019.3编译Spring5.3.x源码 前言 工欲善其事必先利其器.学习和深读Spring源码一个重要的前提:编译源码到我们的本地环境.这 ...
- [Go语言]从Docker源码学习Go——if语句和map结构
if语句 继续看docker.go文件的main函数 if reexec.Init() { return } go语言的if不需要像其它语言那样必须加括号,而且,可以在判断以前,增加赋值语句 语法 I ...
- 【iScroll源码学习04】分离IScroll核心
前言 最近几天我们前前后后基本将iScroll源码学的七七八八了,文章中未涉及的各位就要自己去看了 1. [iScroll源码学习03]iScroll事件机制与滚动条的实现 2. [iScroll源码 ...
随机推荐
- Linux学习笔记(13)-进程通信|命名管道
匿名管道只能在具有亲属关系的进程间通信,那么如果想要在不具有亲戚关系,想在陌生人之间通信,那又该怎么办呢? 别慌,Linux身为世界上*强大的操作系统,当然提供了这种机制,那便是命名管道-- 所谓命名 ...
- SQLServer生成三位姓名及11位国内电话号码(生成测试数据用)
SELECT SUBSTRING(N'王李张刘陈杨黄赵吴周徐孙马朱胡郭何高林郑谢罗梁宋唐许韩冯邓曹彭曾肖田董袁潘于蒋蔡余杜叶程苏魏吕丁任沈姚卢姜崔钟谭陆汪范金石廖贾夏韦付方白邹孟熊秦邱江尹薛闫段雷侯龙 ...
- storm学习好文链接
大圆的那些事:http://www.cnblogs.com/panfeng412/tag/Storm/ xcc的博客:http://blog.csdn.net/damacheng/article/ca ...
- 从倒影说起,谈谈 CSS 继承 inherit(转)
从倒影说起,谈谈 CSS 继承 inherit 给定一张有如下背景图的 div: 制作如下的倒影效果: 方法很多,但是我们当然要寻找最快最便捷的方法,至少得是无论图片怎么变化,div 大小怎么变化,我 ...
- Day 1:学习Windows Phone 使用 SQLite
private void move(string fn) { StreamResourceInfo sr = Application.GetResourceStream(new Uri(fn, Uri ...
- 【转载】64 位 Windows 内核虚拟地址空间布局(基于 X64 CPU)
原文链接:http://shayi1983.blog.51cto.com/4681835/1734822 本文为原创翻译,原文出处为 http://www.codemachine.com/articl ...
- VS2015 调试时 编辑并继续不可用
最近在项目中遇到一次调试时 编辑并继续不可用.结合网上说的工具->设置->调试->常规下的一些操作,到后来还是不可用,最后把项目的解决方案平台改成Mixed Platform ,之后 ...
- WPF上传文件到服务器
利用WebClient 上传文件到服务器 创建一个空网站,创建一个UploadFile.aspx项, 服务器报500错误:检查文件保存路径是否存在,检查文件大小限制 protected void Pa ...
- Erlang error handling
Erlang error handling Contents Preface try-catch Process link Erlang-way error handling OTP supervis ...
- [WPF] 我的WPF自学日记2,自定义入口
在winform中入口文件就是Program.cs,而在WPF中看不到,因为它是自动生成的,可以说隐藏了,我们可以自定义一个入口文件,然后修改项目属性中的启动对象为我们自定义的入口文件. 首先新建入口 ...
