SpringBoot之旅第六篇-启动原理及自定义starter
一、引言
SpringBoot的一大优势就是Starter,由于SpringBoot有很多开箱即用的Starter依赖,使得我们开发变得简单,我们不需要过多的关注框架的配置。
在日常开发中,我们也会自定义一些Starter,特别是现在微服务框架,我们一个项目分成了多个单体项目,而这些单体项目中会引用公司的一些组件,这个时候我们定义Starter,可以使这些单体项目快速搭起,我们只需要关注业务开发。
在此之前我们再深入的了解下SpringBoot启动原理。而后再将如何自定义starter。
二、 启动原理
要想了解启动原理,我们可以Debug模式跟着代码一步步探究,我们从入口方法开始:
- public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources,
- String[] args) {
- return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
- }
这里是创建一个SpringApplication对象,并调用了run方法
2.1 创建SpringApplication对象
- public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
- this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
- Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
- //保存主配置类
- this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
- //确定web应用类型
- this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
- //从类路径下找到META-INF/spring.factories配置的所有ApplicationContextInitializer;然后保存起来
- setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
- ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
- //从类路径下找到ETA-INF/spring.factories配置的所有ApplicationListener
- setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
- //从多个配置类中找到有main方法的主配置类
- this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
- }
从这个方法中可以看出,这个
第一步:保存主配置类。
第二步:确定web应用类型。
第三步:setInitializers方法,这个方法走我们看带入的参数是getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class),我们再往下查看getSpringFactoriesInstances
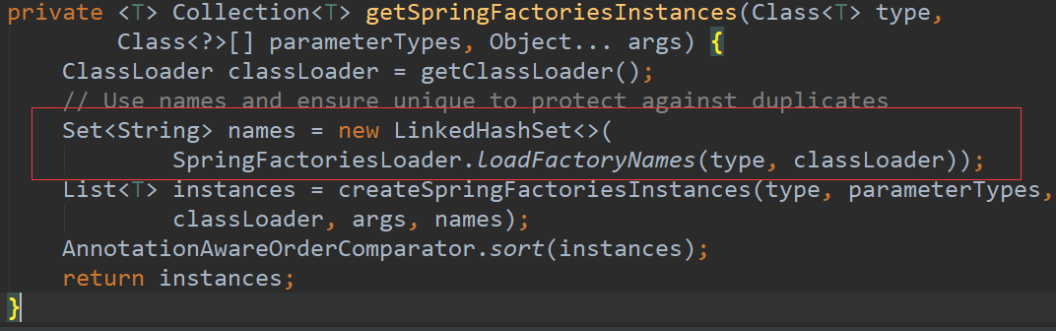
再进入这个方法:
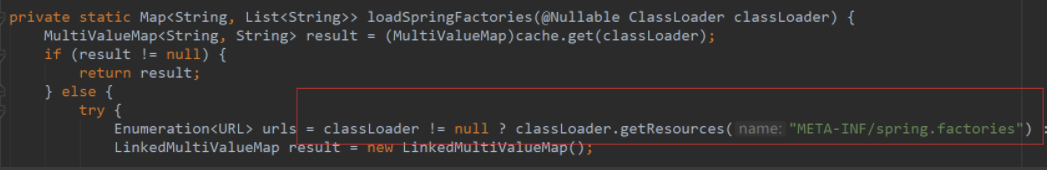
这里就是从类路径下找到META-INF/spring.factories配置的所有ApplicationContextInitializer,然后再保存起来,放开断点,我们可以看到这个时候获取到的

第四步:从类路径下找到ETA-INF/spring.factories配置的所有ApplicationListener,原理也基本类似,进入断点
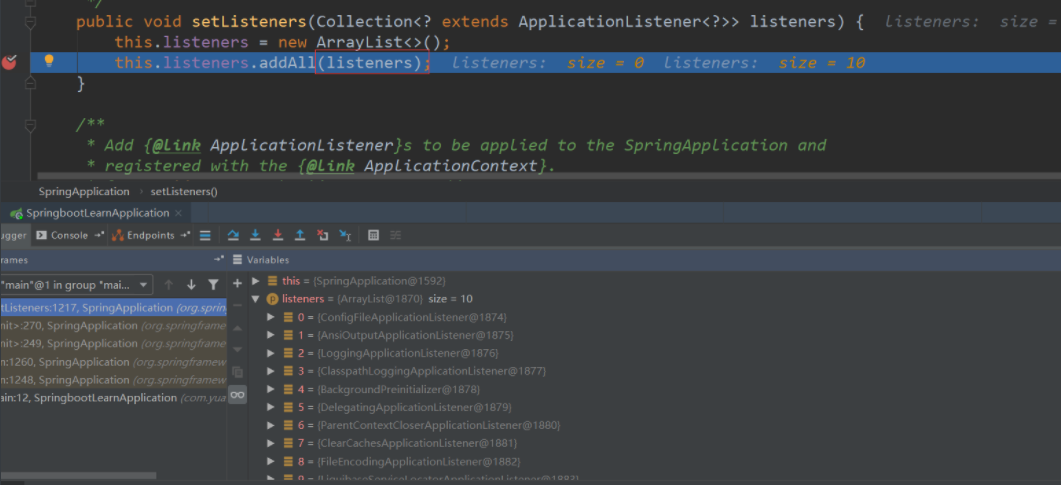
第五步:从多个配置类中找到有main方法的主配置类。这个执行完之后,SpringApplication就创建完成
2.2 run方法
先贴出代码
- public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
- StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
- stopWatch.start();
- ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
- Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
- configureHeadlessProperty();
- //从类路径下META-INF/spring.factories获取SpringApplicationRunListeners
- SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
- //回调所有的获取SpringApplicationRunListener.starting()方法
- listeners.starting();
- try {
- //封装命令行参数
- ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
- args);
- //准备环境
- ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
- applicationArguments);//创建环境完成后回调SpringApplicationRunListener.environmentPrepared();表示环境准备完成
- configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
- //打印Banner图
- Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
- //创建ApplicationContext,决定创建web的ioc还是普通的ioc
- context = createApplicationContext();
- //异常分析报告
- exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(
- SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
- new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
- //准备上下文环境,将environment保存到ioc中
- //applyInitializers():回调之前保存的所有的ApplicationContextInitializer的initialize方法
- //listeners.contextPrepared(context)
- //prepareContext运行完成以后回调所有的SpringApplicationRunListener的contextLoaded()
- prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
- printedBanner);
- //刷新容器,ioc容器初始化(如果是web应用还会创建嵌入式的Tomcat)
- //扫描,创建,加载所有组件的地方,(配置类,组件,自动配置)
- refreshContext(context);
- afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
- stopWatch.stop();
- if (this.logStartupInfo) {
- new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
- .logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
- }
- //所有的SpringApplicationRunListener回调started方法
- listeners.started(context);
- //从ioc容器中获取所有的ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner进行回调,
- //ApplicationRunner先回调,CommandLineRunner再回调
- callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
- }
- catch (Throwable ex) {
- handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
- throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
- }
- try {
- //所有的SpringApplicationRunListener回调running方法
- listeners.running(context);
- }
- catch (Throwable ex) {
- handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
- throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
- }
- //整个SpringBoot应用启动完成以后返回启动的ioc容器
- return context;
- }
前面的代码不用分析,主要是准备对象,我们从 SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args)开始分析,
第一步:是从类路径下META-INF/spring.factories获取SpringApplicationRunListeners,
这个方法跟前面分析的两个获取配置方法类似。
第二步:回调所有的获取SpringApplicationRunListener.starting()方法。
第三步: 封装命令行参数。
第四步:准备环境,调用prepareEnvironment方法。
第五步:打印Banner图(就是启动时的标识图)。
第六步:创建ApplicationContext,决定创建web的ioc还是普通的ioc。
第七步:异常分析报告。
第八步:准备上下文环境,将environment保存到ioc中,这个方法需要仔细分析下,我们再进入这个方法
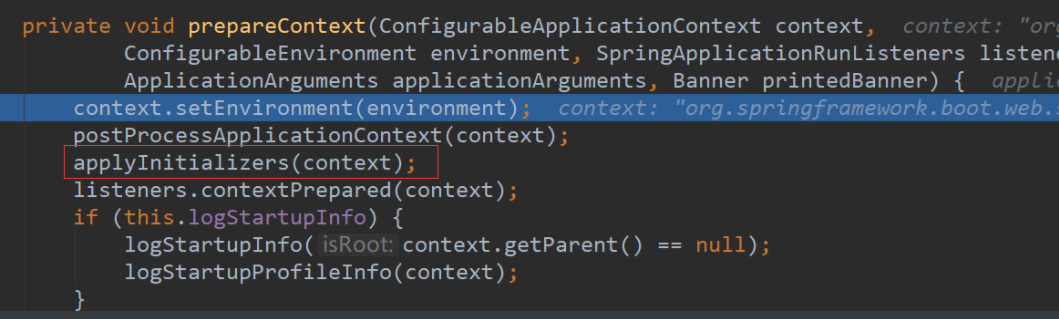
这里面有一个applyInitializers方法,这里是回调之前保存的所有的ApplicationContextInitializer的initialize方法
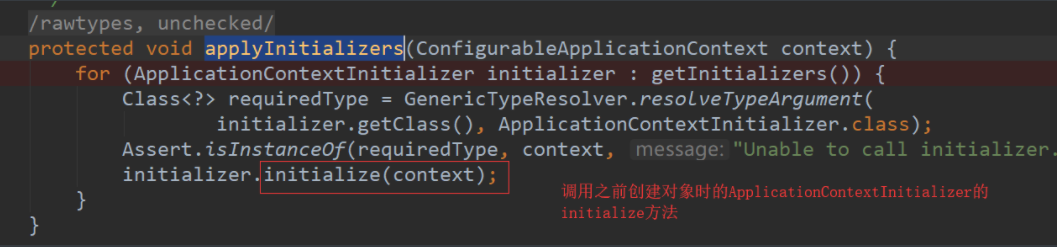
还有一个listeners.contextPrepared(context),这里是回调所有的SpringApplicationRunListener的contextPrepared(),
最后listeners.contextLoaded(context) 是prepareContext运行完成以后回调所有的SpringApplicationRunListener的contextLoaded()。
第九步:刷新容器,ioc容器初始化(如果是web应用还会创建嵌入式的Tomcat),这个就是扫描,创建,加载所有组件的地方,(配置类,组件,自动配置)。
第十步:所有的SpringApplicationRunListener回调started方法。
第十一步:从ioc容器中获取所有的ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner进行回调,ApplicationRunner先回调,CommandLineRunner再回调。
第十二步:所有的SpringApplicationRunListener回调running方法。
第十三步:整个SpringBoot应用启动完成以后返回启动的ioc容器。
这就是run的全部过程,想要更详细的了解还需自己去看源码。
三、自定义starter
自定义starter(场景启动器),我们要做的事情是两个:确定依赖和编写自动配置。我们重点要做的就是编写自动配置,我们之前写过一些自动配置,主要是注解配置的使用,主要的注解有:
@Configuration :指定这个类是一个配置类
@ConditionalOnXXX :在指定条件成立的情况下自动配置类生效
@AutoConfigureAfter:指定自动配置类的顺序
@Bean:给容器中添加组件
@ConfigurationPropertie:结合相关xxxProperties类来绑定相关的配置
@EnableConfigurationProperties:让xxxProperties生效加入到容器中
按照这些注解写好自动配置类后,我们还需要进行自动配置的加载,加载方式是将需要启动就加载的自动配置类,配置在META-INF/spring.factories,启动器的大致原理是如此,而启动器的实际设计是有一定模式的,就是启动器模块是一个空 JAR 文件,仅提供辅助性依赖管理,而自动配置模块应该再重新设计一个,然后启动器再去引用这个自动配置模块。Springboot就是如此设计的:
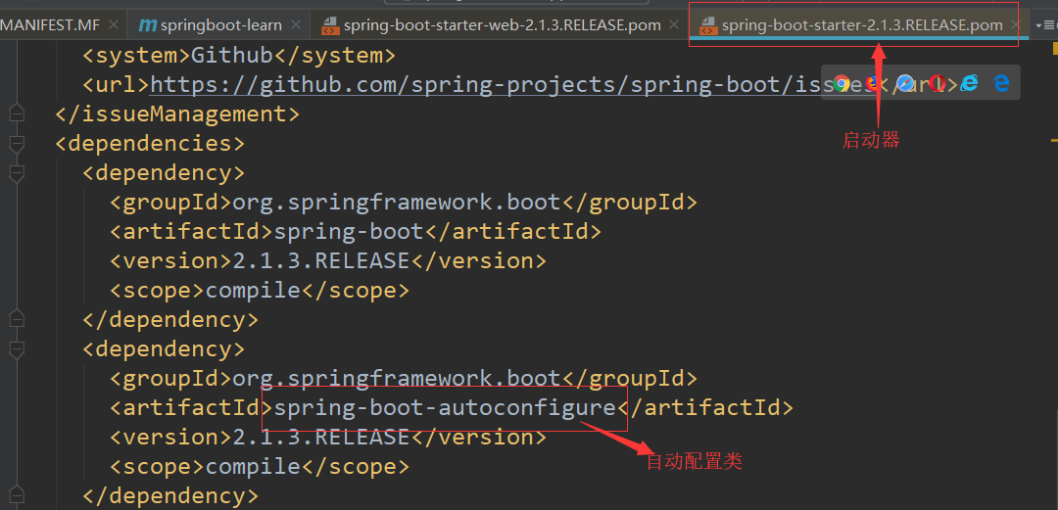
另外还有一个命名规则:
官方命名空间
– 前缀:“spring-boot-starter-”
– 模式:spring-boot-starter-模块名
– 举例:spring-boot-starter-web、spring-boot-starter-actuator、spring-boot-starter-jdbc
自定义命名空间
– 后缀:“-spring-boot-starter”
– 模式:模块-spring-boot-starter
– 举例:mybatis-spring-boot-starter
3.1 创建自定义starter
第一步:因为我们需要创建两个模块,所以先新建一个空的项目,然后以模块形式创建两个模块。
第二步:再创建两个模块,一个starter和一个自动配置模块
具体的创建过程就不赘述了,就是最简单的项目,去掉不需要的文件,创建完成结构如下:
第三步:我们先将自动配置模块导入starter中,让启动模块依赖自动配置模块
启动模块的POM文件加入依赖
- <dependencies>
- <!--引入自动配置模块-->
- <dependency>
- <groupId>com.yuanqinnan-starter</groupId>
- <artifactId>yuanqinnan-springboot-starter-autoconfigurer</artifactId>
- <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
- </dependency>
- </dependencies>
自动配置模块的完整POM文件:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
- <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
- <parent>
- <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
- <version>2.1.4.RELEASE</version>
- <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
- </parent>
- <groupId>com.yuanqinnan-starter</groupId>
- <artifactId>yuanqinnan-springboot-starter-autoconfigurer</artifactId>
- <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
- <packaging>jar</packaging>
- <properties>
- <java.version>1.8</java.version>
- </properties>
- <dependencies>
- <!--引入spring-boot-starter;所有starter的基本配置-->
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
- </dependency>
- </dependencies>
- </project>
至此,两个项目基本创建完成,现在我们实现简单的配置。
第五步:对自动配置类进行自动配置代码编写
先编写一个配置类,用于配置:
- @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "yuanqinnan.hello")
- public class HelloProperties {
- //前缀
- private String prefix;
- //后缀
- private String suffix;
- public String getPrefix() {
- return prefix;
- }
- public void setPrefix(String prefix) {
- this.prefix = prefix;
- }
- public String getSuffix() {
- return suffix;
- }
- public void setSuffix(String suffix) {
- this.suffix = suffix;
- }
- }
再编写一个服务
- public class HelloService {
- HelloProperties helloProperties;
- public HelloProperties getHelloProperties() {
- return helloProperties;
- }
- public void setHelloProperties(HelloProperties helloProperties) {
- this.helloProperties = helloProperties;
- }
- public String sayHello(String name) {
- return helloProperties.getPrefix() + "-" + name + helloProperties.getSuffix();
- }
- }
然后再将这个服务注入组件:
- @Configuration
- @ConditionalOnWebApplication //web应用才生效
- @EnableConfigurationProperties(HelloProperties.class)
- public class HelloServiceAutoConfiguration {
- @Autowired
- HelloProperties helloProperties;
- @Bean
- public HelloService helloService(){
- HelloService service = new HelloService();
- service.setHelloProperties(helloProperties);
- return service;
- }
- }
这个时候我们的自动配置以及写完,还差最后一步,因为SpringBoot读取自动配置是在META-INF的spring.factories文件中,所以我们还要将我们的自动配置类写入其中
- org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
- com.yuanqinnan.starter.HelloServiceAutoConfiguration
最后的结构如下:
至此,代码以及编写完成,这个时候我们将其装入仓库中,让其他项目引用
3.2 使用自定义starter
创建一个web项目,然后在项目中引入依赖
- <!--引入自定义starter-->
- <dependency>
- <groupId>com.yuanqinnan.starter</groupId>
- <artifactId>yuanqinnan-springboot-starter</artifactId>
- <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
- </dependency>
在application.properties 配置中加上配置:
- yuanqinnan.hello.prefix=早安
- yuanqinnan.hello.suffix=晚安
加入测试:
- @Autowired
- HelloService helloService;
-
- @Test
- public void contextLoads() {
- System.out.println(helloService.sayHello("世界"));
- }
这样自定义Starter和引用自定义都已完成,Springboot的核心知识已经总结完成,后面再进行Springboot的一些高级场景整合,如缓存、消息、检索、分布式等。
SpringBoot之旅第六篇-启动原理及自定义starter的更多相关文章
- 【SpringBoot1.x】SpringBoot1.x 启动配置原理 和 自定义starter
SpringBoot1.x 启动配置原理 和 自定义starter 启动配置原理 本节源码 启动过程主要为: new SpringApplication(sources) 创建 SpringAppli ...
- SpringBoot之旅第四篇-web开发
一.引言 有了自动配置,springboot使web开发变得简单,这个在springboot之旅中的第一篇中就有体现,实际的开发中当然不会这么简单,很多时候我们都需要自己去定制一些东西.web开发的东 ...
- java框架之SpringBoot(10)-启动流程及自定义starter
启动流程 直接从 SpringBoot 程序入口的 run 方法看起: public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Object source, ...
- SpringBoot源码学习系列之启动原理简介
本博客通过debug方式简单跟一下Springboot application启动的源码,Springboot的启动源码是比较复杂的,本博客只是简单梳理一下源码,浅析其原理 为了方便跟源码,先找个Ap ...
- SpringBoot之旅第五篇-数据访问
一.引言 大部分系统都离不开数据访问,数据库包括SQL和NOSQL,SQL是指关系型数据库,常见的有SQL Server,Oracle,MySQL(开源),NOSQL是泛指非关系型数据库,常见的有Mo ...
- SpringBoot非官方教程 | 第六篇:springboot整合mybatis
转载请标明出处: 原文首发于:https://www.fangzhipeng.com/springboot/2017/07/11/springboot-mybatis/ 本文出自方志朋的博客 本文主要 ...
- SpringBoot之旅第三篇-日志
一.前言 日志对于一个系统的重要性不言而喻,日志能帮我们快速定位线上问题,市场上存在非常多的日志框架,比较常见的有 JUL,JCL,Log4j,Log4j2,Logback.SLF4j.jboss-l ...
- Spring之旅第六篇-事务管理
一.什么是事务 什么是事务(Transaction)?事务是数据库中的概念,是指访问并可能更新数据库中各种数据项的一个程序执行单元(unit). 有个非常经典的转账问题:A向B转款1000元,A转出成 ...
- SpringBoot之旅第七篇-Docker
一.引言 记得上大三时,要给微机房电脑安装系统,除了原生的操作系统外,还要另外安装一些必要的开发软件,如果每台电脑都重新去安装的话工作量就很大了,这个时候就使用了windows镜像系统,我们将要安装的 ...
随机推荐
- Github Page 绑定域名
http://kyle.xlau.org/posts/github-cname.html CNAME 创建一个CNAME文件,内容是你的域名,如: xlau.org 然后把此文件添加到Github仓库 ...
- Qt中的ui指针和this指针
初学qt,对其ui指针和this指针产生疑问,画了个把小时终于搞懂了. 首先看ui指针的定义: 在mainwindow.h中 private: Ui::MainWindow *ui; Ui又是什么? ...
- Linq小整理
Linq(Language Integrated Query)中文翻译为语言集成查询 (1)源起 .net的设计者在类库中定义了一系列的扩展方法 来方便用户操作集合对象 这些扩展方法构成了LINQ的查 ...
- 成功实现在VS2017下编译含<pthread.h>的代码:
VS2017配置使用#<pthread.h> https://blog.csdn.net/cry1994/article/details/79115394(原来SystemWow64里面存 ...
- mysql 30大优化策略
mysql 30大优化策略 1.应尽量避免在 where 子句中使用!=或<>操作符,否则将引擎放弃使用索引而进行全表扫描. 2.对查询进行优化,应尽量避免全表扫描,首先应考虑在 wher ...
- 解决jequry使用keydown无法跳转的问题
问题描述 代码 <script> $("document").ready(function() { $("#button").click(funct ...
- 更新版PowerBI发布了-- Power BI Report Server Update – March 2018
新版的PowerBI server 和 Desktop 终于发布了. 详细增加功能见以下链接: 下载最新版PowerBI Report Server: https://powerbi.microso ...
- Unity3D学习(二):使用JSON进行对象数据的存储读取
前言 前段时间完成了自己的小游戏Konster的制作,今天重新又看了下代码.原先对关卡解锁数据的存储时用了Unity自带的PlayerPref(字典式存储数据). 读取关卡数据的代码: void Aw ...
- Struts标签库详解【3】
struts2标签库详解 要在jsp中使用Struts2的标志,先要指明标志的引入.通过jsp的代码的顶部加入以下的代码: <%@taglib prefix="s" uri= ...
- 小苹果WP(实验吧-隐写术)
本文由荒原之梦原创,原文链接:http://zhaokaifeng.com/?p=706 前言:本文是实验吧训练题库里隐写术部分的一道题:"小苹果"的Write Up. 题目链接: ...
