iOS - Quartz 2D 二维绘图
1、Quartz 2D 简介
Quartz 2D 属于 Core Graphics(所以大多数相关方法的都是以 CG 开头),是 iOS/Mac OSX 提供的在内核之上的强大的 2D 绘图引擎,并且这个绘图引擎是设备无关的。也就是说,不用关心设备的大小,设备的分辨率,只要利用 Quartz 2D,这些设备相关的会自动处理。
1、Quartz 2D 在 iOS 开发中的价值
- 绘制一些系统 UIKit 框架中不好展示的内容,例如饼图
- 自定义一些控件
- 不添加 UI 控件的情况下,使 UI 内容更丰富
- 绘制图形:线条\三角形\矩形\圆\弧等
- 绘制文字
- 绘制\生成图片(图像)
- 读取\生成 PDF
- 截图\裁剪图片
- 自定义 UI 控件
- iOS 中,大部分控件都是 Quartz 2D 绘制出来的
2、Quartz 2D 提供的强大功能
- 透明层(transparency layers)
- 阴影
- 基于 path 的绘图(path-based drawing)
- 离屏渲染(offscreen rendering)
- 复杂的颜色处理(advanced color management)
- 抗锯齿渲染(anti-aliased rendering)
- PDF 创建,展示,解析
- 配合 Core Animation, OpenGL ES, UIKit 完成复杂的功能
3、画板/图形上下文
既然提到绘图,那自然有一个容器来包含绘制的结果,然后把这个结果渲染到屏幕上去,而 Quartz 2D 的容器就是 CGContextRef 数据模型,这种数据模型是 C 的结构体,存储了渲染到屏幕上需要的一切信息。
图形上下文就相当于画布,不同类型的画布就是决定着画得内容将展示在哪里。Quartz 2D 提供了以下几种类型的 Graphics Context
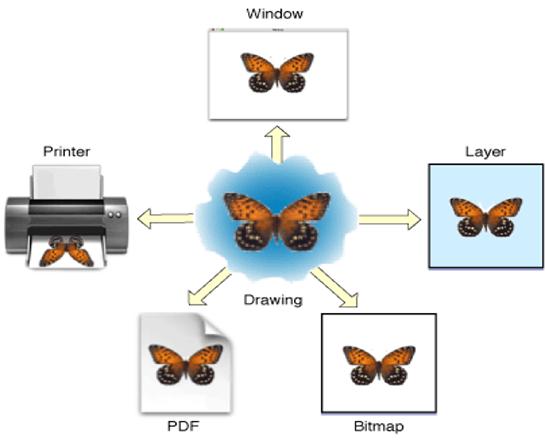
- Bitmap Graphics Context:位图上下文,在这个上下文上绘制或者渲染的内容,可以获取成图片(需要主动创建一个位图上下文来使用,使用完毕,一定要销毁)。
- PDF Graphics Context
- Window Graphics Context
- Layer Graphics Context:图层上下文,针对 UI 控件的上下文。
- Printer Graphics Context
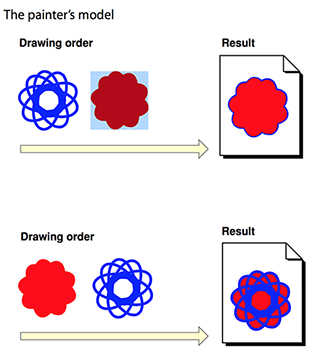
4、绘制模型
Quartz 2D 采用 painter’s model,意味着每一次绘制都是一层,然后按照顺序一层层的叠加到画板上。
5、数据类型
Quartz 2D 中的数据类型都是透明的,也就是说用户只需要使用即可,不需要实际访问其中的变量。Quartz 2D 的 API 是纯 C 语言的,来自于 Core Graphics 框架,数据类型和函数基本都以 CG 作为前缀。
- CGPathRef :路径类型,用来绘制路径(注意带有 ref 后缀的一般都是绘制的画板)
- CGImageRef:绘制 bitmap
- CGLayerRef:绘制 layer,layer 可复用,可离屏渲染
- CGPatternRef :重复绘制
- CGFunctionRef:定义回调函数,CGShadingRef 和 CGGradientRef 的辅助类型
- CGShadingRef 和 CGGradientRef:绘制渐变(例如颜色渐变)
- CGColorRef 和 CGColorSpaceRef:定义如何处理颜色
- CGFontRef:绘制文字
- 其他类型
6、绘制状态
在使用 Quartz 2D 进行绘图的时候,经常需要设置颜色、字体,设置 context 的坐标原点变换,context 旋转。这些影响的都是当前绘制状态。Context 中利用堆栈的方式来保存绘制状态。调用 CGContextSaveGState 来保存当前绘制状态的 copy 到堆栈中,利用 CGContextRestoreGState 弹出堆栈最顶层的绘制状态,设置为当前的绘制状态。注意,不是所有的参数都会保存,以下表格中的参数会保存。

7、Quartz 2D 的内存管理
使用含有 “Create” 或 “Copy” 的函数创建的对象,使用完后必须释放,否则将导致内存泄露。使用不含有 “Create” 或 “Copy” 的函数获取的对象,则不需要释放。
如果 retain 了一个对象,不再使用时,需要将其 release 掉,可以使用 Quartz 2D 的函数来指定 retain 和 release 一个对象。例如,如果创建了一个 CGColorSpace 对象,则使用函数CGColorSpaceRetain 和 CGColorSpaceRelease 来 retain 和 release 对象。
也可以使用 Core Foundation 的 CFRetain 和 CFRelease。注意不能传递 NULL 值给这些函数。
8、drawRect 方法
因为在 drawRect: 方法中才能取得跟 view 相关联的图形上下文,才让我们可以在 drawRect: 方法中绘制。注意:在其他地方拿不到 view 相关的上下文,所以不能实现绘制。
在 drawRect: 方法中取得上下文后,就可以绘制东西到 view 上。View 内部有个 layer(图层)属性,drawRect: 方法中取得的是一个 Layer Graphics Context,因此,绘制的东西其实是绘制到 view 的 layer 上去了。View 之所以能显示东西,完全是因为它内部的 layer。
drawRect: 方法的调用
- 当 view 第一次显示到屏幕上(被加到 UIWindow 上显示出来)时,系统会创建好一个跟当前 view 相关的 Layer 上下文。
- 系统会通过此上下文,在 drawRect: 方法中绘制好当前 view 的内容。
- 主动让 view 重绘内容的时候,调用 setNeedsDisplay 或者 setNeedsDisplayInRect: 方法。我们主动调用 drawRect: 方法是无效的。
- 调用 view 的 setNeedsDisplay 或者 setNeedsDisplayInRect: 方法后,屏幕并不是立即刷新,而是会在下一次刷新屏幕的时候把绘制的内容显示出来。
9、绘图的核心步骤
获得上下文。
绘制/拼接绘图路径。
将路径添加到上下文。
渲染上下文。
所有的绘图,都是这个步骤,即使使用贝塞尔路径,也只是对这个步骤进行了封装。对于绘图而言,拿到上下文很关键。
10、自定义 view
如何利用 Quartz 2D 绘制东西到 view 上
- 首先,得有图形上下文,因为它能保存绘图信息,并且决定着绘制到什么地方去。
- 其次,那个图形上下文必须跟view相关联,才能将内容绘制到 view 上面。
自定义 view 的步骤
- 新建一个类,继承自 UIView。
- 实现
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect方法,然后在这个方法中。 - 取得跟当前 view 相关联的图形上下文。
- 绘制相应的图形内容。
- 利用图形上下文将绘制的所有内容渲染显示到 view 上面。
2、Quartz 2D 基本设置
2.1 Quartz 2D 坐标系
和 UIKit 的坐标系不一样,Quartz 2D 的坐标系是在左下角的。Quartz 2D 利用坐标系的旋转位移等操作来绘制复杂的动画。
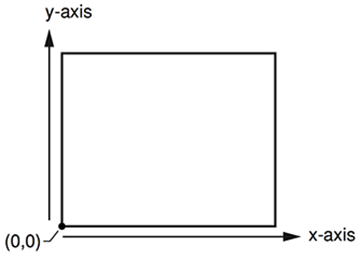
但是有两个地方的坐标系是正常的 UIKit 坐标系
- UIView 的 context
- 通过这个方法 UIGraphicsBeginImageContextWithOptions 返回的 context。
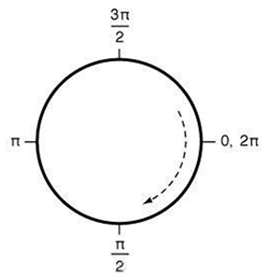
Quartz 2D 中的圆形坐标
2.2 Stroke 描边
影响描边的因素
- 线的宽度 - CGContextSetLineWidth
- 交叉线的处理方式 - CGContextSetLineJoin
- 线顶端的处理方式 - CGContextSetLineCap
- 进一步限制交叉线的处理方式 - CGContextSetMiterLimit
- 是否要虚线 - Line dash pattern
- 颜色控件 - CGContextSetStrokeColorSpace
- 画笔颜色 - CGContextSetStrokeColor/CGContextSetStrokeColorWithColor
- 描边模式 - CGContextSetStrokePattern
CGContextSetMiterLimit
如果当前交叉线绘图模式是 kCGLineJoinMiter(CGContextSetLineJoin),Quartz 2D 根据设置的 miter 值来判断线的 join 是 bevel 或者 miter。具体的模式是:将 miter 的长度除以线的宽度,如果小于设置的 mitetLimit 值,则 join style 为 bevel。
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGContextMoveToPoint(ctx, 10, 10);
CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, 50, 50);
CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, 10, 90); CGContextSetLineWidth(ctx, 10.0); CGContextSetLineJoin(ctx, kCGLineJoinMiter);
CGContextSetMiterLimit(ctx, 10.0); CGContextStrokePath(ctx);
}
效果,将 Miter 设置为 1,则效果如下
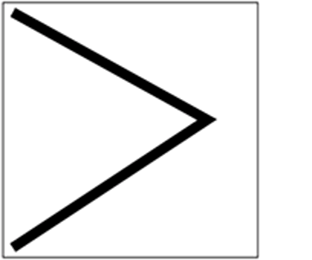
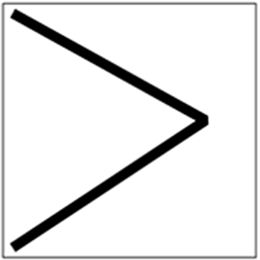
2.3 Fill 填充
Quartz 2D 填充的时候会认为 subpath 是封闭的,然后根据规则来填充。有两种规则
- nonzero winding number rule:沿着当前点,画一条直线到区域外,检查交叉点,如果交叉点从左到右,则加一,从右到左,则减去一。如果结果不为 0,则绘制。可参见这个 link。
- even-odd rule:沿着当前点,花一条线到区域外,然后检查相交的路径,偶数则绘制,奇数则不绘制。
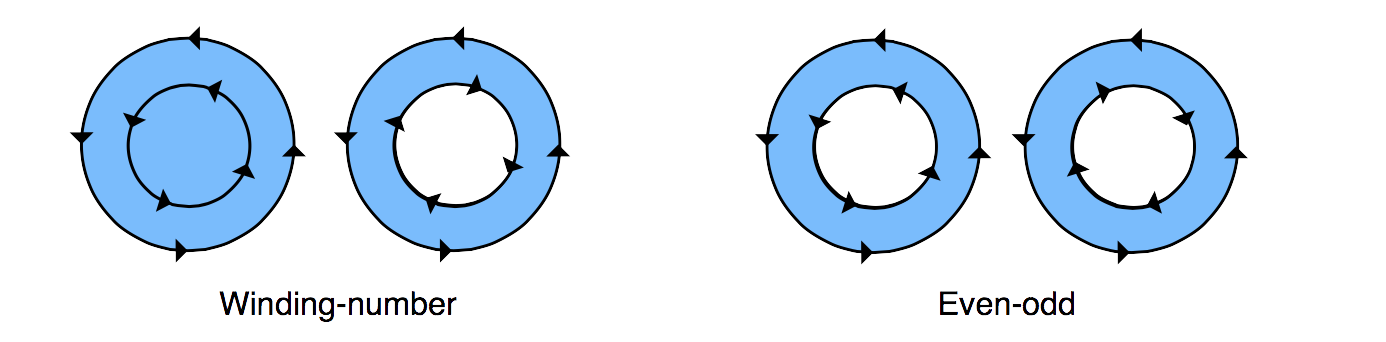
相关函数
- CGContextEOFillPath:用 even-odd rule 来填充
- CGContextFillPath :用 nonzero winding number rule 方式填充
- CGContextFillRect/CGContextFillRects:填充指定矩形区域内 path
- CGContextFillEllipseInRect:填充椭圆
- CGContextDrawPath :绘制当前 path(根据参数 stroke/fill)
2.4 Clip 切割/遮盖
顾名思义,根据 path 只绘制指定的区域,在区域外的都不会绘制。
相关函数
- CGContextClip :按照 nonzero winding number rule 规则切割
- CGContextEOClip:按照 even-odd 规则切割
- CGContextClipToRect :切割到指定矩形
- CGContextClipToRects:切割到指定矩形组
- CGContextClipToMask :切割到 mask
举个例子,截取圆形区域。
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); CGContextAddArc(ctx, 125, 125, 100, 0, M_PI * 2, true);
CGContextSetFillColorWithColor(ctx, [UIColor lightGrayColor].CGColor); // 按指定的路径切割,要放在区域填充之前(下一句之前)
CGContextClip(ctx); CGContextFillRect(ctx, rect); // 上面两句相当于这一句
// CGContextFillPath(ctx);
}
效果,切割前后


2.5 Subpath 子路径
很简单,在 stroke/fill 或者 CGContextBeginPath/CGContextClosePath 以后就新开启一个子路径。注意 CGContextClosePath,会连接第一个点和最后一个点。
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); CGContextBeginPath(ctx);
CGContextAddArc(ctx, 125, 125, 100, 0, M_PI * 2, true);
CGContextSetFillColorWithColor(ctx, [UIColor lightGrayColor].CGColor);
CGContextClosePath(ctx); CGContextFillPath(ctx);
}
2.6 Blend 混合模式
Quartz 2D 中,默认的颜色混合模式采用如下公式
result = (alpha * foreground) + (1 - alpha) * background
可以使用 CGContextSetBlendMode 来设置不同的颜色混合模式,注意设置 blend 是与 context 绘制状态相关的,一切与状态相关的设置都要想到状态堆栈。
官方文档里的例子,blend 模式较多,具体参见官方文档。
background 和 foreGround


Normal Blend Mode 效果

Multiply Blend Mode 效果,交叉部分会显得比较暗,用上一层和底层相乘,至少和一层一样暗。

Screen Blend Mode 效果,交叉部分比较亮,上层的 reverse 和下层的 reverse 相乘,至少和一个一样亮。

2.7 CTM 状态矩阵
Quartz 2D 默认采用设备无关的 user space 来进行绘图,当 context(画板)建立之后,默认的坐标系原点以及方向也就确认了,可以通过 CTM(current transformation matrix)来修改坐标系的原点。从数组图像处理的角度来说,就是对当前 context state 乘以一个状态矩阵。其中的矩阵运算开发者可以不了解。
最初的状态
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGContextAddRect(context, CGRectMake(50, 50, 100, 50));
CGContextSetFillColorWithColor(context,[UIColor blueColor].CGColor);
CGContextFillPath(context);
}
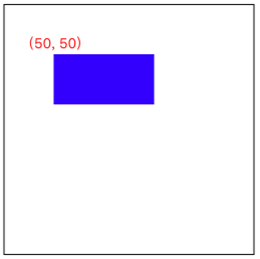
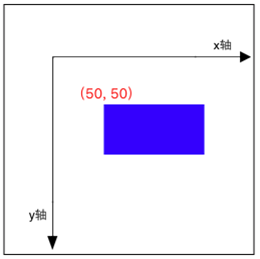
Translate 平移
在绘制之前,进行坐标系移动,代码中,我们是还是在(50,50)点绘制,但是要注意,当前坐标系的原点已经移了。
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // Translate
CGContextTranslateCTM(context, 50, 50); CGContextAddRect(context, CGRectMake(50, 50, 100, 50));
CGContextSetFillColorWithColor(context, [UIColor blueColor].CGColor);
CGContextFillPath(context);
}
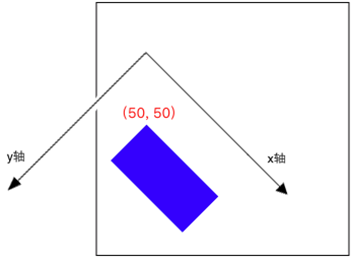
Rotate 旋转
在 Transform 的基础上我们再 Rotate 45 度,注意 CGContextRotateCTM 传入的参数是弧度。
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // Translate
CGContextTranslateCTM(context, 50, 50); // Rotate
CGContextRotateCTM(context, M_PI_4); CGContextAddRect(context, CGRectMake(50, 50, 100, 50));
CGContextSetFillColorWithColor(context, [UIColor blueColor].CGColor);
CGContextFillPath(context);
}
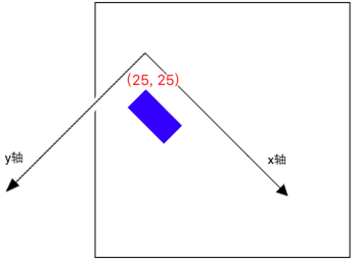
Scale 缩放
对于 Scale 相对来说,好理解一点,无非就是成比例放大缩小。
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // Translate
CGContextTranslateCTM(context, 50, 50); // Rotate
CGContextRotateCTM(context, M_PI_4); // Scale
CGContextScaleCTM(context, 0.5, 0.5); CGContextAddRect(context, CGRectMake(50, 50, 100, 50));
CGContextSetFillColorWithColor(context, [UIColor blueColor].CGColor);
CGContextFillPath(context);
}
Affine Transforms
可以通过以下方法先创建放射矩阵,然后然后再把放射矩阵映射到 CTM。
- CGAffineTransform
- CGAffineTransformTranslate
- CGAffineTransformMakeRotation
- CGAffineTransformRotate
- CGAffineTransformMakeScale
- CGAffineTransformScale
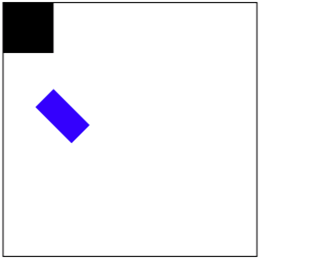
2.8 GState 状态保存恢复
在复杂的绘图中,我们可能只是想对一个 subpath 设置,如进行旋转、移动和缩放等,这时候状态堆栈就起到作用了。
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // 保存状态,入栈
CGContextSaveGState(context); CGContextTranslateCTM(context, 50, 50);
CGContextRotateCTM(context, M_PI_4);
CGContextScaleCTM(context, 0.5, 0.5); CGContextAddRect(context, CGRectMake(50, 50, 100, 50));
CGContextSetFillColorWithColor(context, [UIColor blueColor].CGColor);
CGContextFillPath(context); // 恢复,推出栈顶部状态
CGContextRestoreGState(context); // 这里坐标系已经回到了最开始的状态
CGContextAddRect(context, CGRectMake(0, 0, 50, 50));
CGContextFillPath(context);
}
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // 描述第一条路径
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPath];
[path moveToPoint:CGPointMake(10, 125)];
[path addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(240, 125)]; // 获取上下文,保存上下文状态
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGContextSaveGState(ctx); // 设置属性绘制路径
path.lineWidth = 10;
[[UIColor redColor] set];
[path stroke]; // 描述第二条路径
path = [UIBezierPath bezierPath];
[path moveToPoint:CGPointMake(125, 10)];
[path addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(125, 240)]; // 还原上下文状态
CGContextRestoreGState(ctx); // 绘制路径
[path stroke];
}
效果
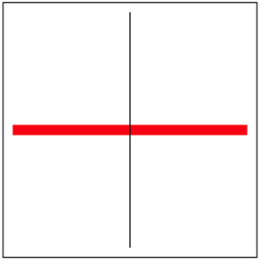
2.9 Shadow 阴影
shadow(阴影)的目的是为了使 UI 更具有立体感。注意 Shadow 也是绘制状态相关的,意味着如果仅仅要绘制一个 subpath 的 shadow,要注意 save 和 restore 状态。

shadow 主要有三个影响因素,其中不同的 blur 效果如图。
- x off-set 决定阴影沿着 x 的偏移量
- y off-set 决定阴影沿着 y 的偏移量
- blur value 决定了阴影的边缘区域是不是模糊的

相关函数
CGContextSetShadow
CGContextSetShadowWithColor:唯一区别是设置了阴影颜色
参数
- context:绘制画板
- offset :阴影偏移量,参考 context 的坐标系
- blur :非负数,决定阴影的模糊程度
设置阴影
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGContextAddArc(context, 50, 50, 100, 0, M_PI_2, 0);
CGContextSetLineCap(context, kCGLineCapRound);
CGContextSetLineWidth(context, 10.0); // 设置阴影
CGContextSetShadow(context, CGSizeMake(15.0, 15.0), 1.0);
// CGContextSetShadowWithColor(context, CGSizeMake(15.0, 15.0), 8.0, [UIColor redColor].CGColor); CGContextStrokePath(context);
}
效果


2.10 Gradient 渐变
渐变无非就是从一种颜色逐渐变换到另一种颜色,Quartz 2D 提供了两种渐变模型。通过这两种渐变的嵌套使用,Quartz 2D 能够绘制出非常漂亮的图形。
axial gradient:线性渐变,使用的时候设置好两个顶点的颜色,也可以设置中间过渡色。


radial gradient:圆形渐变,这种模式的渐变允许一个圆到另一个圆的渐变,一个点到一个圆的渐变。

可以对渐变结束或者开始的额外区域使用指定颜色填充。
渐变的两种绘制模型
CGGradient:使用这种数据类型只需要制定两个顶点的颜色,以及绘制模式,其余的 Quartz 2D 会给绘制,但是渐变的数学模型不灵活。
CGShading :使用这种数据类型需要自己定义 CFFunction 来计算每一个点的渐变颜色,较为复杂,但是能够更灵活的绘制。
1、CGGradient 绘制
创建一个 CGGradient 对象,指定颜色域(一般就是 RGB),指定颜色变化的数组,指定对应颜色位置的数组,指定每个数组数据的个数。
用 CGContextDrawLinearGradient 或者 CGContextDrawRadialGradient 绘制。
释放 CGGradient 对象。
CGGradientCreateWithColorComponents 函数
CGGradientRef __nullable CGGradientCreateWithColorComponents(CGColorSpaceRef cg_nullable space,
const CGFloat * cg_nullable components,
const CGFloat * __nullable locations,
size_t count)
参数:
space :颜色域
components:颜色变化的数组
locations :对应颜色位置的数组
count :每个数组数据的个数
线性渐变
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // 设置渐变
CGColorSpaceRef deviceRGB = CGColorSpaceCreateDeviceRGB(); CGFloat components[8] = {1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, // 红色
0.0, 1.0, 0.0, // 绿色
1.0}; CGFloat locations[2] = {0.0, 1.0};
size_t num_of_locations = 2;
CGGradientRef gradient = CGGradientCreateWithColorComponents(deviceRGB,
components,
locations,
num_of_locations); // 渐变开始结束点位置
CGPoint startPoint = CGPointMake(0, 0);
CGPoint endPoint = CGPointMake(250, 250); // 创建线性渐变
CGContextDrawLinearGradient(context,
gradient,
startPoint,
endPoint,
0); CGColorSpaceRelease(deviceRGB);
CGGradientRelease(gradient);
}
效果
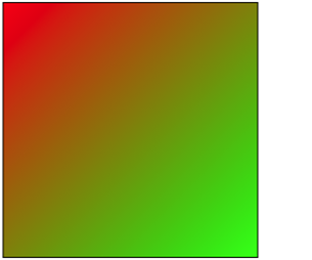
圆形渐变
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // 设置渐变
CGColorSpaceRef deviceRGB = CGColorSpaceCreateDeviceRGB(); CGFloat components[8] = {1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, // 红色
0.0, 1.0, 0.0, // 绿色
1.0}; CGFloat locations[2] = {0.0, 1.0};
size_t num_of_locations = 2;
CGGradientRef gradient = CGGradientCreateWithColorComponents(deviceRGB,
components,
locations,
num_of_locations); // 渐变开始结束圆心位置
CGPoint startCenter = CGPointMake(80, 80);
CGPoint endCenter = CGPointMake(120, 120); // 渐变开始结束半径
CGFloat startRadius = 0.0;
CGFloat endRadius = 100.0; // 创建圆形渐变
CGContextDrawRadialGradient(context,
gradient,
startCenter,
startRadius,
endCenter,
endRadius,
0); CGColorSpaceRelease(deviceRGB);
CGGradientRelease(gradient);
}
效果
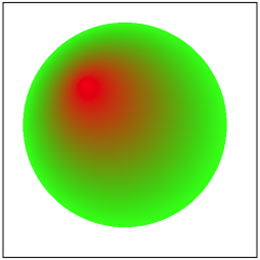
2.11 Bitmap 位图
Bitmap 叫做位图,每一个像素点由 1-32bit 组成。每个像素点包括多个颜色组件和一个 Alpha 组件(例如:RGBA)。
iOS 中指出如下格式的图片 JPEG, GIF, PNG, TIF, ICO, GMP, XBM 和 CUR。其他格式的图片要给 Quartz 2D 传入图片的数据分布信息。
数据类型 CGImageRef,在 Quartz 2D 中,Bitmap 的数据由 CGImageRef 封装。由以下几个函数可以创建 CGImageRef 对象
CGImageCreate:最灵活,但也是最复杂的一种方式,要传入 11 个参数。
CGImageSourceCreate:ImageAtIndex:通过已经存在的 Image 对象来创建
CGImageSourceCreate:ThumbnailAtIndex:和上一个函数类似,不过这个是创建缩略图
CGBitmapContextCreateImage:通过 Copy Bitmap Graphics 来创建
CGImageCreateWith:ImageInRect:通过在某一个矩形内数据来创建
函数 CGImageCreate
CGImageRef _Nullable CGImageCreate(size_t width,
size_t height,
size_t bitsPerComponent,
size_t bitsPerPixel,
size_t bytesPerRow,
CGColorSpaceRef _Nullable space,
CGBitmapInfo bitmapInfo,
CGDataProviderRef _Nullable provider,
const CGFloat * _Nullable decode,
bool shouldInterpolate,
CGColorRenderingIntent intent);
参数:
width/height :图片的像素宽度,高度
bitsPerComponent:每个 component 的占用 bit 个数,和上文提到的一样
bitsPerPixel :每个像素点占用的 bit 个数。例如 32bit RGBA 中,就是 32
bytesPerRow :每一行占用的 byte 个数
colorspace :颜色空间
bitmapInfo :和上文提到的那个函数一样
provider :bitmap 的数据源
decode :解码 array,传入 null,则保持原始数据
interpolation :是否要像素差值来平滑图像
intent :指定了从一个颜色空间 map 到另一个颜色空间的方式
函数 CGBitmapContextCreate
CGContextRef _Nullable CGBitmapContextCreate(void * _Nullable data,
size_t width,
size_t height,
size_t bitsPerComponent,
size_t bytesPerRow,
CGColorSpaceRef _Nullable space,
uint32_t bitmapInfo);
参数:
data :是一个指针,指向存储绘制的 bitmap context 的实际数据的地址,最少大小为 bytesPerRow * height。可以传入 null,让 Quartz 自动分配计算
width, height:bitmap 的宽度,高度,以像素为单位
bytesPerRow :每一行的 byte 数目。如果 data 传入 null,这里传入 0,则会自动计算一个 component 占据多少位。对于 32bit 的 RGBA 空间,则是 8(8*4=32)
space :颜色空间,一般就是 DeviceRGB
bitmapInfo :一个常量,指定了是否具有 alpha 通道,alpha 通道的位置,像素点存储的数据类型是 float 还是 Integer 等信息 其中 bitmapInfo 可以传入的参数如下 enum CGImageAlphaInfo {
kCGImageAlphaNone,
kCGImageAlphaPremultipliedLast,
kCGImageAlphaPremultipliedFirst,
kCGImageAlphaLast,
kCGImageAlphaFirst,
kCGImageAlphaNoneSkipLast,
kCGImageAlphaNoneSkipFirst,
kCGImageAlphaOnly
};
1、重绘图片
原图(2560 * 1600)

重新绘制成 250 * 100,并在图片中间加上我们自定义的绘制
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { CGColorSpaceRef rgb = CGColorSpaceCreateDeviceRGB(); // 图片绘图区域的大小
CGSize targetSize = CGSizeMake(250, 125); // 获取图形上下文
CGContextRef bitmapCtx = CGBitmapContextCreate(NULL,
targetSize.width,
targetSize.height,
8,
targetSize.width * 4,
rgb,
kCGImageAlphaPremultipliedFirst); // 绘制图片
CGRect imageRect;
imageRect.origin = CGPointMake(0, 0); // 设置图片的位置,左下角坐标系
imageRect.size = CGSizeMake(250, 100); // 设置图片的大小
UIImage *imageToDraw = [UIImage imageNamed:@"image.jpg"];
CGContextDrawImage(bitmapCtx, imageRect, imageToDraw.CGImage); // 绘制自定义图形
CGContextAddArc(bitmapCtx, 100, 40, 20, M_PI_4, M_PI_2, true);
CGContextSetLineWidth(bitmapCtx, 4.0);
CGContextSetStrokeColorWithColor(bitmapCtx, [UIColor redColor].CGColor);
CGContextStrokePath(bitmapCtx); // 渲染生成 CGImage
CGImageRef imageRef = CGBitmapContextCreateImage(bitmapCtx); // 转换成 UIImage
UIImage *image = [[UIImage alloc] initWithCGImage:imageRef]; CGImageRelease(imageRef);
CGContextRelease(bitmapCtx);
CGColorSpaceRelease(rgb); UIImageView *imageView = [[UIImageView alloc] initWithImage:image];
[self addSubview:imageView];
}
效果

2、截取图片
截取图片
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { CGColorSpaceRef rgb = CGColorSpaceCreateDeviceRGB(); // 图片绘图区域的大小
CGSize targetSize = CGSizeMake(250, 125); // 获取图形上下文
CGContextRef bitmapCtx = CGBitmapContextCreate(NULL,
targetSize.width,
targetSize.height,
8,
targetSize.width * 4,
rgb,
kCGImageAlphaPremultipliedFirst); UIImage *imageToDraw = [UIImage imageNamed:@"image.jpg"]; // 渲染生成 CGImage
CGRect imageRect = CGRectMake(0, 0, 250, 100); // 左上角坐标系,位置设置不起作用
CGImageRef partImageRef = CGImageCreateWithImageInRect(imageToDraw.CGImage, imageRect); // 转换成 UIImage
UIImage *image = [[UIImage alloc] initWithCGImage:partImageRef]; CGImageRelease(partImageRef);
CGContextRelease(bitmapCtx);
CGColorSpaceRelease(rgb); UIImageView *imageView = [[UIImageView alloc] initWithImage:image];
[self addSubview:imageView];
}
效果

3、Quartz 2D 常用函数
1、常用拼接路径函数
// 新建一个起点
void CGContextMoveToPoint(CGContextRef c, CGFloat x, CGFloat y) // 添加新的线段到某个点
void CGContextAddLineToPoint(CGContextRef c, CGFloat x, CGFloat y) // 封闭路径
void CGContextClosePath(CGContextRef cg_nullable c) // 添加一个矩形
void CGContextAddRect(CGContextRef c, CGRect rect) // 添加一个椭圆
void CGContextAddEllipseInRect(CGContextRef context, CGRect rect) // 添加一个圆弧
void CGContextAddArc(CGContextRef c, CGFloat x, CGFloat y, CGFloat radius, CGFloat startAngle, CGFloat endAngle, int clockwise)
2、常用绘制路径函数
// Mode 参数决定绘制的模式
void CGContextDrawPath(CGContextRef c, CGPathDrawingMode mode) // 绘制空心路径
void CGContextStrokePath(CGContextRef c) // 绘制实心路径
void CGContextFillPath(CGContextRef c)
- 一般以 CGContextDraw、CGContextStroke、CGContextFill 开头的函数,都是用来绘制路径的。
3、图形上下文栈的操作函数
// 将当前的上下文 Copy 一份,保存到栈顶(那个栈叫做 “图形上下文栈”)
void CGContextSaveGState(CGContextRef c) // 将栈顶的上下文出栈,替换掉当前的上下文
void CGContextRestoreGState(CGContextRef c)
4、矩阵操作函数
// 缩放
void CGContextScaleCTM(CGContextRef c, CGFloat sx, CGFloat sy) // 旋转
void CGContextRotateCTM(CGContextRef c, CGFloat angle) // 平移
void CGContextTranslateCTM(CGContextRef c, CGFloat tx, CGFloat ty)
- 利用矩阵操作,能让绘制到上下文中的所有路径一起发生变化。
4、贝塞尔路径
贝塞尔路径(UIBezierPath)是 UIKit 框架中对 Quartz 2D 绘图的封装。实际操作起来,使用贝塞尔路径,更为方便。用法与 CGContextRef 类似,但是 OC 对其进行了封装,更加面向对象。
具体讲解见 Quartz 2D 贝塞尔曲线
二阶贝塞尔曲线示意图
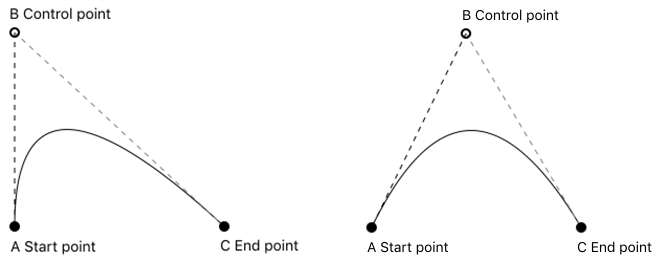
三阶贝塞尔曲线示意图
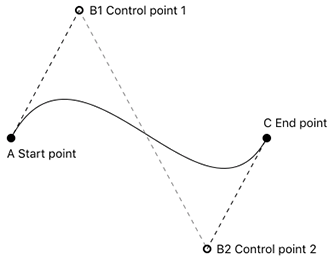
贝塞尔路径常用的方法
// 设置起始点
- (void)moveToPoint:(CGPoint)point; // 添加直线到一点
- (void)addLineToPoint:(CGPoint)point; // 封闭闭路径
- (void)closePath; // 返回一个描述椭圆的路径
+ (UIBezierPath *)bezierPathWithOvalInRect:(CGRect)rect; // 贝塞尔曲线
- (void)addQuadCurveToPoint:(CGPoint)endPoint controlPoint:(CGPoint)controlPoint; // 三次贝塞尔曲线
- (void)addCurveToPoint:(CGPoint)endPoint controlPoint1:(CGPoint)controlPoint1 controlPoint2:(CGPoint)controlPoint2; // 绘制圆弧
- (void)addArcWithCenter:(CGPoint)center radius:(CGFloat)radius startAngle:(CGFloat)startAngle endAngle:(CGFloat)endAngle clockwise:(BOOL)clockwise;
5、基本图形绘制
5.1 绘制直线
1、绘制直线
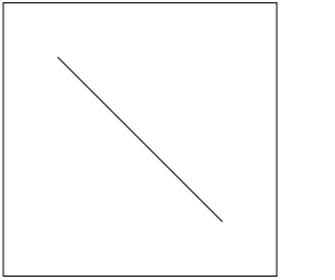
在 Quartz 2D 中,使用方法 CGContextMoveToPoint 移动画笔到一个点来开始新的子路径,使用 CGContextAddLineToPoint 来从当前开始点添加一条线到结束点,CGContextAddLineToPoint 调用后,此时的终点会重新设置为新的开始点。贝塞尔路径是对 Quartz 2D 绘图的 OC 封装。
方式 1,最原始方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // 获取上下文
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // 创建路径
CGMutablePathRef path = CGPathCreateMutable(); // 描述路径, 设置起点,path:给哪个路径设置起点
CGPathMoveToPoint(path, NULL, 50, 50); // 添加一根线到某个点
CGPathAddLineToPoint(path, NULL, 200, 200); // 把路径添加到上下文
CGContextAddPath(ctx, path); // 渲染上下文
CGContextStrokePath(ctx);
}
方式 2,简化方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // 获取上下文
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // 描述路径,设置起点
CGContextMoveToPoint(ctx, 50, 50); // 添加一根线到某个点
CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, 200, 200); // 渲染上下文
CGContextStrokePath(ctx);
}
方式 3,贝塞尔路径方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // 创建路径
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPath]; // 设置起点
[path moveToPoint:CGPointMake(50, 50)]; // 添加一根线到某个点
[path addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(200, 200)]; // 绘制路径
[path stroke];
}
方式 4,原始方式和贝塞尔路径方式同时使用
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // 创建路径
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPath];
[path moveToPoint:CGPointMake(10, 125)];
[path addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(240, 125)]; // 获取上下文
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // 添加路径
CGContextAddPath(ctx, path.CGPath); // 设置属性
CGContextSetStrokeColorWithColor(ctx, [UIColor redColor].CGColor);
CGContextSetLineWidth(ctx, 5); // 绘制路径
CGContextStrokePath(ctx);
}
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // 获取上下文,描述路径
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGContextMoveToPoint(ctx, 50, 50);
CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, 200, 200); // 创建贝塞尔路径
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPath]; // 添加路径
CGContextAddPath(ctx, path.CGPath); // 设置属性
[[UIColor redColor] set];
path.lineWidth = 5; // 绘制路径
[path stroke];
}
效果
2、设置画线状态
线的顶端模式,使用 CGContextSetLineCap 来设置,一共有三种
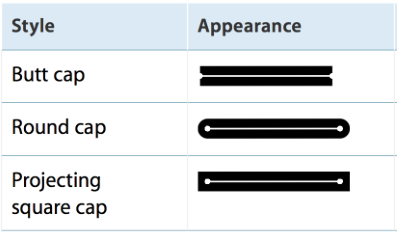
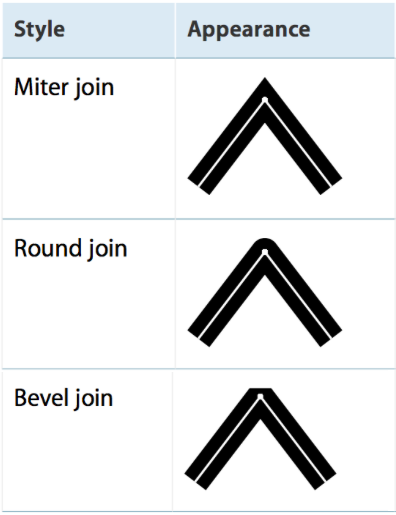
线的相交模式,使用CGContextSetLineJoin 来设置,一共也有三种
方式 1,原始方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // 画线 // 获取上下文
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // 描述路径
CGContextMoveToPoint(ctx, 50, 50);
CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, 200, 200); // 画第二条线,默认下一根线的起点就是上一根线终点
// CGContextMoveToPoint(ctx, 200, 50);
CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, 50, 225); // 设置画线状态,一定要放在渲染之前 // 设置颜色
CGContextSetStrokeColorWithColor(ctx, [UIColor redColor].CGColor); // 设置线宽
CGContextSetLineWidth(ctx, 5); // 设置相交样式
CGContextSetLineJoin(ctx, kCGLineJoinRound); // 设置顶端样式
CGContextSetLineCap(ctx, kCGLineCapSquare); // 渲染
CGContextStrokePath(ctx);
}
方式 2,贝塞尔路径方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // 画线 // 创建路径
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPath]; // 描述路径
[path moveToPoint:CGPointMake(50, 50)];
[path addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(200, 200)]; // 画第二条线,默认下一根线的起点就是上一根线终点
// [path moveToPoint:CGPointMake(200, 50)];
[path addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(50, 225)]; // 设置画线状态,一定要放在渲染之前 // 设置颜色
[[UIColor redColor] set]; // 设置线宽
path.lineWidth = 5; // 设置相交样式
path.lineJoinStyle = kCGLineJoinRound; // 设置顶端样式
path.lineCapStyle = kCGLineCapSquare; // 渲染
[path stroke];
}
效果
5.2 绘制虚线
绘制虚线
方式 1,原始方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // phase :第一个虚线段从哪里开始,例如传入 3,则从第 3 个单位开始
// lengths:一个 C 数组,表示绘制部分和空白部分的分配。例如传入 [2, 2],则绘制 2 个单位,然后空白 2 个单位,以此重复
// count : lengths 的数量 // 获取上下文
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // 绘制直线
CGContextMoveToPoint(ctx, 50, 50);
CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, 200, 200); // 设置虚线
CGFloat lengths[] = {5};
CGContextSetLineDash(ctx, 1, lengths, 1); // 渲染
CGContextStrokePath(ctx);
}
方式 2,贝塞尔路径方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // phase :第一个虚线段从哪里开始,例如传入 3,则从第 3 个单位开始
// pattern:一个 C 数组,表示绘制部分和空白部分的分配。例如传入 [2, 2],则绘制 2 个单位,然后空白 2 个单位,以此重复
// count : lengths 的数量 // 创建路径
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPath]; // 绘制直线
[path moveToPoint:CGPointMake(50, 50)];
[path addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(200, 200)]; // 设置虚线
CGFloat lengths[] = {5};
[path setLineDash:lengths count:1 phase:1]; // 渲染
[path stroke];
}
效果
5.3 绘制曲线
Quartz 2D 使用计算机图形学中的多项式来绘制曲线,支持二次和三次曲线。
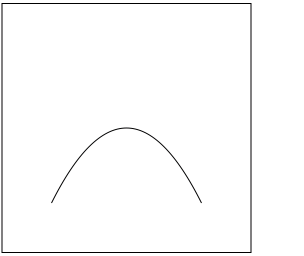
1、绘制二次曲线
方式 1,原始方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // cpx, cpy:控制点
// x, y :曲线终点 // 获取上下文
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // 设置起点
CGContextMoveToPoint(ctx, 50, 200); // 绘制曲线
CGContextAddQuadCurveToPoint(ctx, 125, 50, 200, 200); // 绘制空心路径
CGContextStrokePath(ctx); // 绘制实心路径
// CGContextFillPath(ctx);
}
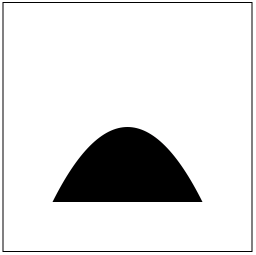
方式 2,贝塞尔路径方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // controlPoint:控制点
// endPoint :曲线终点 // 创建路径
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPath]; // 设置起点
[path moveToPoint:CGPointMake(50, 200)]; // 绘制曲线
[path addQuadCurveToPoint:CGPointMake(200, 200) controlPoint:CGPointMake(125, 50)]; // 绘制空心路径
[path stroke]; // 绘制实心路径
// [path fill];
}
效果
2、绘制三次曲线
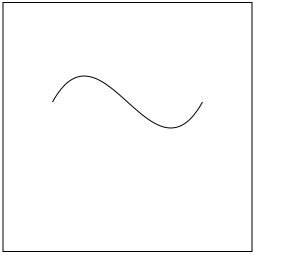
方式 1,原始方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // cp1x, cp1y:控制点 1
// cp2x, cp2y:控制点 2
// x, y :曲线终点 // 获取上下文
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // 设置起点
CGContextMoveToPoint(ctx, 50, 100); // 绘制曲线
CGContextAddCurveToPoint(ctx, 100, 10, 150, 190, 200, 100); // 绘制空心路径
CGContextStrokePath(ctx); // 绘制实心路径
// CGContextFillPath(ctx);
}
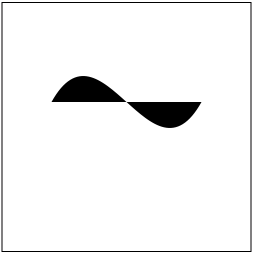
方式 2,贝塞尔路径方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // controlPoint1:控制点 1
// controlPoint2:控制点 2
// endPoint :曲线终点 // 创建路径
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPath]; // 设置起点
[path moveToPoint:CGPointMake(50, 100)]; // 绘制曲线
[path addCurveToPoint:CGPointMake(200, 100)
controlPoint1:CGPointMake(100, 10)
controlPoint2:CGPointMake(150, 190)]; // 绘制空心路径
[path stroke]; // 绘制实心路径
// [path fill];
}
效果
3、绘制图形设置
方式 1,原始方式
// 设置空心路径的颜色
CGContextSetStrokeColorWithColor(ctx, [UIColor redColor].CGColor); // 设置实心路径的填充颜色
CGContextSetFillColorWithColor(ctx, [UIColor redColor].CGColor); // 绘制空心路径
CGContextStrokePath(ctx); // 绘制实心路径
CGContextFillPath(ctx);
方式 2,贝塞尔路径方式
// 设置空心路径的颜色
[[UIColor redColor] setStroke]; // 设置实心路径的填充颜色
[[UIColor redColor] setFill]; // 设置空心路径和实心路径的颜色
[[UIColor redColor] set]; // 绘制空心路径
[path stroke]; // 绘制实心路径
[path fill];
效果
5.4 绘制三角形
绘制三角形
方式 1,原始方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // 获取上下文
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // 描述路径
CGContextMoveToPoint(ctx, 100, 50); CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, 20, 200);
CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, 200, 200); // 封闭路径,自动连接首尾
CGContextClosePath(ctx); // 渲染 // 绘制空心路径
CGContextStrokePath(ctx); // 绘制实心路径
// CGContextFillPath(ctx);
}
方式 2,贝塞尔路径方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // 创建路径
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPath]; // 描述路径
[path moveToPoint:CGPointMake(100, 50)]; [path addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(20, 200)];
[path addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(200, 200)]; // 封闭路径,自动连接首尾
[path closePath]; // 渲染 // 绘制空心路径
[path stroke]; // 绘制实心路径
// [path fill];
}
效果
5.5 绘制矩形
绘制矩形
方式 1,原始方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // 获取上下文
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // 描述路径
CGContextAddRect(ctx, CGRectMake(20, 50, 200, 100)); // 绘制空心路径
CGContextStrokePath(ctx); // 绘制实心路径
// CGContextFillPath(ctx);
}
方式 2,贝塞尔路径方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // 创建路径,绘制图形
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithRect:CGRectMake(20, 50, 200, 100)]; // 绘制空心路径
[path stroke]; // 绘制实心路径
// [path fill];
}
效果


5.6 绘制圆角矩形
绘制圆角矩形
方式 1,原始方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // x1, y1:圆角两个切线的交点
// x2, y2:圆角终点
// radius:圆角半径 // 获取上下文
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); CGFloat x = 20;
CGFloat y = 50;
CGFloat w = 200;
CGFloat h = 100;
CGFloat r = 20; CGContextMoveToPoint(ctx, x, y + r);
CGContextAddArcToPoint(ctx, x, y, x + r, y, r); // 左上角
CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, x + w - r, y);
CGContextAddArcToPoint(ctx, x + w, y, x + w, y + r, r); // 右上角
CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, x + w, y + h - r);
CGContextAddArcToPoint(ctx, x + w, y + h, x + w - r, y + h, r); // 右下角
CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, x + r, y + h);
CGContextAddArcToPoint(ctx, x, y + h, x, y + h - r, r); // 左下角
CGContextClosePath(ctx); // 绘制空心路径
CGContextStrokePath(ctx); // 绘制实心路径
// CGContextFillPath(ctx);
}
方式 2,贝塞尔路径方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // rect :矩形位置尺寸
// cornerRadius:圆角半径 // 创建路径,绘制图形
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithRoundedRect:CGRectMake(20, 50, 200, 100)
cornerRadius:20]; // 绘制空心路径
[path stroke]; // 绘制实心路径
// [path fill];
}
效果
5.7 绘制圆弧
绘制圆弧
Quartz 2D 提供了两个方法来绘制圆弧
CGContextAddArc,普通的圆弧一部分(以某圆心,某半径,某弧度的圆弧)。
CGContextAddArcToPoint,用来绘制圆角。
函数体
void CGContextAddArcToPoint(CGContextRef cg_nullable c,
CGFloat x1,
CGFloat y1,
CGFloat x2,
CGFloat y2,
CGFloat radius)
参数
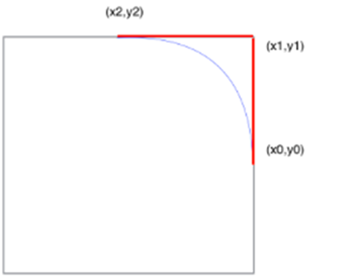
c :图形上下文
x1, y1:和当前点 (x0, y0) 决定了第一条切线(x0, y0)-> (x1, y1)
x2, y2:和 (x1, y1) 决定了第二条切线
radius:相切的半径。
也就是说,绘制一个半径为 radius 的圆弧,和上述两条直线都相切。图中的两条红线就是上文提到的两条线,分别是 (x0,y0) -> (x1,y1) 和 (x1,y1) -> (x2,y2),那么和这两条线都想切的自然就是图中的蓝色圆弧了.

方式 1,原始方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // x, y :圆心
// radius :半径
// startAngle:开始弧度
// endAngle :结束弧度
// clockwise :方向,false 顺时针,true 逆时针 // 获取上下文
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // 描述路径
CGContextAddArc(ctx, 125, 125, 100, 0, M_PI_2, false); // 绘制空心路径
CGContextStrokePath(ctx); // 绘制实心路径
// CGContextFillPath(ctx);
}
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // x1, y1:圆角两个切线的交点
// x2, y2:圆角终点
// radius:圆角半径 // 获取上下文
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // 设置起点
CGContextMoveToPoint(ctx, 225, 125); // 绘制圆弧
CGContextAddArcToPoint(ctx, 225, 225, 125, 225, 100); // 绘制空心路径
CGContextStrokePath(ctx); // 绘制实心路径
// CGContextFillPath(ctx);
}
方式 2,贝塞尔路径方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // Center :圆心
// radius :半径
// startAngle:开始弧度
// endAngle :结束弧度
// clockwise :方向,YES 顺时针,NO 逆时针 // 创建路径,绘制图形
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithArcCenter:CGPointMake(125, 125)
radius:100
startAngle:0
endAngle:M_PI_2
clockwise:YES]; // 绘制空心路径
[path stroke]; // 绘制实心路径
// [path fill];
}
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // Center :圆心
// radius :半径
// startAngle:开始弧度
// endAngle :结束弧度
// clockwise :方向,YES 顺时针,NO 逆时针 // 创建路径,绘制图形
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPath]; // 设置起点
[path moveToPoint:CGPointMake(225, 125)]; // 绘制圆弧
[path addArcWithCenter:CGPointMake(125, 125)
radius:100
startAngle:0
endAngle:M_PI_2
clockwise:YES]; // 绘制空心路径
[path stroke]; // 绘制实心路径
// [path fill];
}
效果
5.8 绘制扇形
绘制扇形
方式 1,原始方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // 获取上下文
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // 描述路径
CGContextAddArc(ctx, 125, 125, 100, 0, M_PI_4, NO); // 绘制到圆心的直线
CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, 125, 125); // 封闭路径
CGContextClosePath(ctx); // 绘制空心路径
CGContextStrokePath(ctx); // 绘制实心路径
// CGContextFillPath(ctx);
}
方式 2,贝塞尔路径方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // 创建路径,绘制图形
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithArcCenter:CGPointMake(125, 125)
radius:100
startAngle:0
endAngle:M_PI_4
clockwise:YES]; // 绘制到圆心的直线
[path addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(125, 125)]; // 封闭路径
[path closePath]; // 绘制空心路径
[path stroke]; // 绘制实心路径
// [path fill];
}
效果
5.9 绘制圆形
绘制圆形
方式 1,原始方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // 获取上下文
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // 描述路径
CGContextAddArc(ctx, 125, 125, 100, 0, M_PI * 2, NO); // 绘制空心路径
CGContextStrokePath(ctx); // 绘制实心路径
// CGContextFillPath(ctx);
}
方式 2,贝塞尔路径方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // 创建路径,绘制图形
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithArcCenter:CGPointMake(125, 125)
radius:100
startAngle:0
endAngle:M_PI * 2
clockwise:YES]; // 绘制空心路径
[path stroke]; // 绘制实心路径
// [path fill];
}
效果
5.10 绘制椭圆形
绘制椭圆形
在矩形中设置不同的宽高方式创建。
方式 1,原始方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // 获取上下文
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // 描述路径
CGContextAddEllipseInRect(ctx, CGRectMake(20, 50, 200, 100)); // 绘制空心路径
CGContextStrokePath(ctx); // 绘制实心路径
// CGContextFillPath(ctx);
}
方式 2,贝塞尔路径方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { // 创建路径,绘制图形
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithOvalInRect:CGRectMake(20, 50, 200, 100)]; // 绘制空心路径
[path stroke]; // 绘制实心路径
// [path fill];
}
效果
6、统计图绘制
6.1 绘制折线图
绘制折线图
方式 1,原始方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { CGFloat x1 = 0;
CGFloat x2 = 0;
CGFloat h1 = 0;
CGFloat h2 = 0;
CGFloat y1 = 0;
CGFloat y2 = 0; CGFloat w = rect.size.width / (self.datas.count - 1); CGFloat largeNum = [self.datas[0] floatValue]; for (int i = 0; i < self.datas.count; i++) {
if ([self.datas[i] floatValue] > largeNum) {
largeNum = [self.datas[i] floatValue];
}
} for (int i = 0; i < self.datas.count - 1; i++) { x1 = w * i;
x2 = w * (i + 1);
h1 = [self.datas[i] floatValue] / (largeNum * 1.2) * rect.size.height;
h2 = [self.datas[i + 1] floatValue] / (largeNum * 1.2) * rect.size.height;
y1 = rect.size.height - h1;
y2 = rect.size.height - h2; CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGContextMoveToPoint(ctx, x1, y1);
CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, x2, y2);
CGContextSetStrokeColorWithColor(ctx, self.color.CGColor);
CGContextStrokePath(ctx);
}
}
方式 2,贝塞尔路径方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { CGFloat x1 = 0;
CGFloat x2 = 0;
CGFloat h1 = 0;
CGFloat h2 = 0;
CGFloat y1 = 0;
CGFloat y2 = 0; CGFloat w = rect.size.width / (self.datas.count - 1); CGFloat largeNum = [self.datas[0] floatValue]; for (int i = 0; i < self.datas.count; i++) {
if ([self.datas[i] floatValue] > largeNum) {
largeNum = [self.datas[i] floatValue];
}
} for (int i = 0; i < self.datas.count - 1; i++) { x1 = w * i;
x2 = w * (i + 1);
h1 = [self.datas[i] floatValue] / (largeNum * 1.2) * rect.size.height;
h2 = [self.datas[i + 1] floatValue] / (largeNum * 1.2) * rect.size.height;
y1 = rect.size.height - h1;
y2 = rect.size.height - h2; UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPath];
[path moveToPoint:CGPointMake(x1, y1)];
[path addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(x2, y2)];
[self.color set];
[path stroke];
}
}
使用
// LineView.h @interface LineView : UIView @property (nonatomic, strong) NSArray<NSNumber *> *datas;
@property (nonatomic, strong) UIColor *color; + (instancetype)lineViewWithFrame:(CGRect)frame
datas:(NSArray<NSNumber *> *)datas
colors:(UIColor *)color; @end // LineView.m + (instancetype)lineViewWithFrame:(CGRect)frame
datas:(NSArray<NSNumber *> *)datas
colors:(UIColor *)color { LineView *line = [[self alloc] init]; line.frame = frame;
line.datas = datas;
line.color = color; return line;
} // ViewController.m CGRect frame = CGRectMake(50, 40, self.view.bounds.size.width - 100, self.view.bounds.size.width - 100);
NSArray *datas = @[@30, @60, @50, @28]; LineView *lineView = [LineView lineViewWithFrame:frame
datas:datas
colors:[UIColor blueColor]]; lineView.layer.borderWidth = 1; [self.view addSubview:lineView];
效果
6.2 绘制柱形图
绘制柱形图
方式 1,原始方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { CGFloat x = 0;
CGFloat y = 0;
CGFloat h = 0; CGFloat m = self.margin; CGFloat w = self.margin ? ((rect.size.width - m) / (self.datas.count) - m) :
(rect.size.width / (2 * self.datas.count + 1)); CGFloat largeNum = [self.datas[0] floatValue]; for (int i = 0; i < self.datas.count; i++) {
if ([self.datas[i] floatValue] > largeNum) {
largeNum = [self.datas[i] floatValue];
}
} for (int i = 0; i < self.datas.count; i++) { x = self.margin ? ((m + w) * i + m) : (2 * w * i + w);
h = [self.datas[i] floatValue] / (largeNum * 1.2) * rect.size.height;
y = rect.size.height - h; CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGContextAddRect(ctx, CGRectMake(x, y, w, h));
CGContextSetFillColorWithColor(ctx, self.colors[i].CGColor);
CGContextFillPath(ctx);
}
}
方式 2,贝塞尔路径方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { CGFloat x = 0;
CGFloat y = 0;
CGFloat h = 0; CGFloat m = self.margin; CGFloat w = self.margin ? ((rect.size.width - m) / (self.datas.count) - m) :
(rect.size.width / (2 * self.datas.count + 1)); CGFloat largeNum = [self.datas[0] floatValue]; for (int i = 0; i < self.datas.count; i++) {
if ([self.datas[i] floatValue] > largeNum) {
largeNum = [self.datas[i] floatValue];
}
} for (int i = 0; i < self.datas.count; i++) { x = self.margin ? ((m + w) * i + m) : (2 * w * i + w);
h = [self.datas[i] floatValue] / (largeNum * 1.2) * rect.size.height;
y = rect.size.height - h; UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithRect:CGRectMake(x, y, w, h)];
[self.colors[i] set];
[path fill];
}
}
使用
// BarView.h @interface BarView : UIView @property (nonatomic, strong) NSArray<NSNumber *> *datas;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSArray<UIColor *> *colors;
@property (nonatomic, assign) CGFloat margin; + (instancetype)barViewWithFrame:(CGRect)frame
datas:(NSArray<NSNumber *> *)datas
colors:(NSArray<UIColor *> *)colors
margin:(CGFloat)margin; @end // BarView.m + (instancetype)barViewWithFrame:(CGRect)frame
datas:(NSArray<NSNumber *> *)datas
colors:(NSArray<UIColor *> *)colors
margin:(CGFloat)margin { BarView *bar = [[self alloc] init]; bar.frame = frame;
bar.datas = datas;
bar.colors = colors;
bar.margin = margin; return bar;
} // ViewController.m CGRect frame = CGRectMake(50, 40, self.view.bounds.size.width - 100, self.view.bounds.size.width - 100);
NSArray *datas = @[@30, @60, @50, @28];
NSArray *colors = @[[UIColor redColor], [UIColor yellowColor], [UIColor blueColor], [UIColor greenColor]]; CGFloat margin = 20; BarView *barView = [BarView barViewWithFrame:frame
datas:datas
colors:colors
margin:margin]; barView.layer.borderWidth = 1; [self.view addSubview:barView];
效果
6.3 绘制饼图
绘制饼图
方式 1,原始方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { CGFloat radius = MIN(rect.size.width, rect.size.height) * 0.5;
CGFloat rx = rect.size.width * 0.5;
CGFloat ry = rect.size.height * 0.5; CGFloat startA = self.startAngle;
CGFloat angle = 0;
CGFloat endA = startA; CGFloat sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < self.datas.count; i++) {
sum += [self.datas[i] floatValue];
} for (int i = 0; i < self.datas.count; i++) { startA = endA;
angle = [self.datas[i] floatValue] / sum * M_PI * 2;
endA = startA + angle; CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGContextAddArc(ctx, rx, ry, radius, startA, endA, NO);
CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, rx, ry);
CGContextClosePath(ctx);
CGContextSetFillColorWithColor(ctx, self.colors[i].CGColor);
CGContextFillPath(ctx);
}
}
方式 2,贝塞尔路径方式
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { CGFloat radius = MIN(rect.size.width, rect.size.height) * 0.5;
CGPoint center = CGPointMake(rect.size.width * 0.5, rect.size.height * 0.5); CGFloat startA = self.startAngle;
CGFloat angle = 0;
CGFloat endA = startA; CGFloat sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < self.datas.count; i++) {
sum += [self.datas[i] floatValue];
} for (int i = 0; i < self.datas.count; i++) { startA = endA;
angle = [self.datas[i] floatValue] / sum * M_PI * 2;
endA = startA + angle; UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithArcCenter:center
radius:radius
startAngle:startA
endAngle:endA
clockwise:YES];
[path addLineToPoint:center];
[path closePath];
[self.colors[i] set];
[path fill];
}
}
使用
// PieView.h @interface PieView : UIView @property (nonatomic, strong) NSArray<NSNumber *> *datas;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSArray<UIColor *> *colors;
@property (nonatomic, assign) CGFloat startAngle; + (instancetype)pieViewWithFrame:(CGRect)frame
datas:(NSArray<NSNumber *> *)datas
colors:(NSArray<UIColor *> *)colors
startAngle:(CGFloat)startAngle; @end // PieView.m + (instancetype)pieViewWithFrame:(CGRect)frame
datas:(NSArray<NSNumber *> *)datas
colors:(NSArray<UIColor *> *)colors
startAngle:(CGFloat)startAngle { PieView *pie = [[self alloc] init]; pie.frame = frame;
pie.datas = datas;
pie.colors = colors;
pie.startAngle = startAngle; return pie;
} // ViewController.m CGRect frame = CGRectMake(50, 40, self.view.bounds.size.width - 100, self.view.bounds.size.width - 100);
NSArray *datas = @[@30, @60, @50, @28];
NSArray *colors = @[[UIColor redColor], [UIColor yellowColor], [UIColor blueColor], [UIColor greenColor]]; CGFloat startAngle = -M_PI_2; PieView *pieView = [PieView pieViewWithFrame:frame
datas:datas
colors:colors
startAngle:startAngle]; pieView.layer.borderWidth = 1; [self.view addSubview:pieView];
效果
7、使用第三方框架绘制图表
使用第三方框架 Charts 绘制 iOS 图表,Charts 是一款用于绘制图表的框架,可以绘制柱状图、折线图、K线图、饼状图等。GitHub 源码 Charts
具体讲解见 Quartz 2D 第三方框架绘制图表
效果
折线图
柱状图
饼图
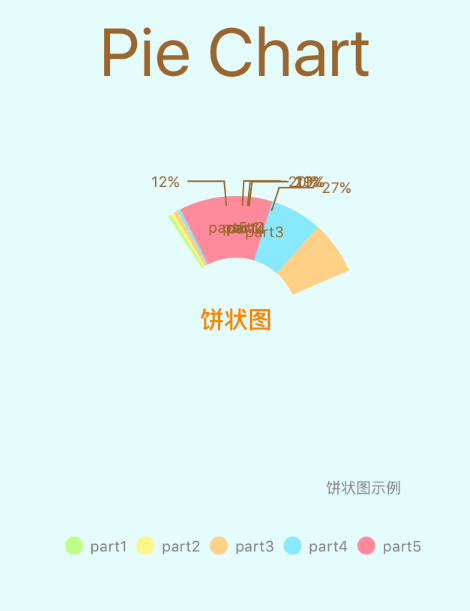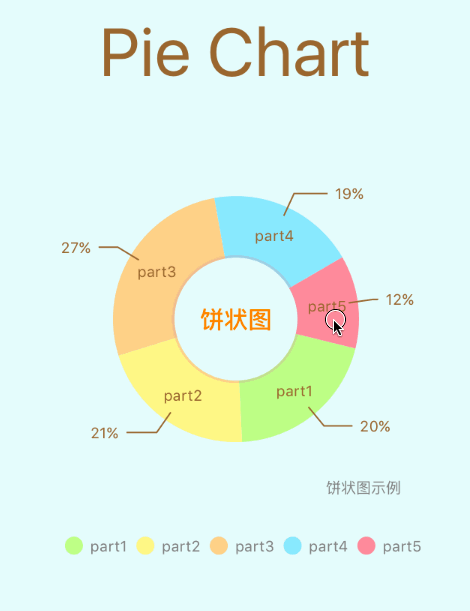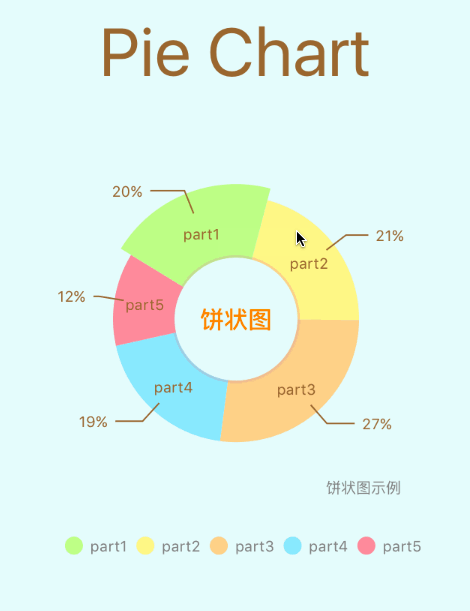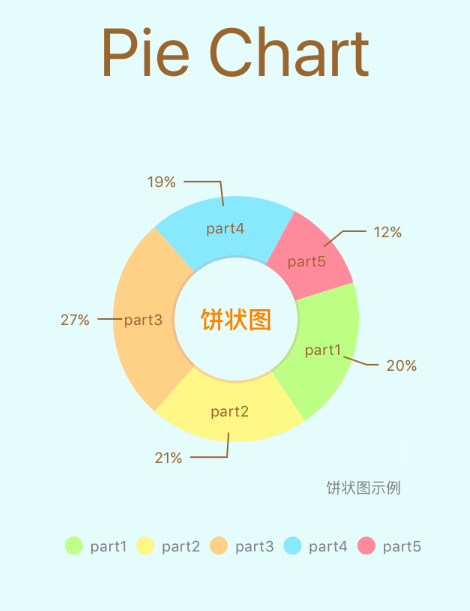
8、文本处理
8.1 在控件视图上绘制/添加文本
如果绘制东西到 view 等视图控件上面,必须写在 drawRect 方法里面,不管有没有手动获取到上下文。
1、绘制/添加文本
在指定位置绘制文本,文本不会自动换行
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { NSString *string = @"QianChia"; // 不设置文本属性
[string drawAtPoint:CGPointZero withAttributes:nil]; // 设置文本属性
[string drawAtPoint:CGPointZero withAttributes:@{NSFontAttributeName:[UIFont systemFontOfSize:50]}];
}
在指定区域绘制文本,文本会自动换行
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { NSString *string = @"QianChia"; // 不设置文本属性
[string drawInRect:rect withAttributes:nil]; // 设置文本属性
[string drawInRect:rect withAttributes:@{NSFontAttributeName:[UIFont systemFontOfSize:50]}];
}
效果


2、设置文本属性
NSMutableDictionary *textDict = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary]; // 设置文本字体
textDict[NSFontAttributeName] = [UIFont systemFontOfSize:50]; // 设置文本颜色
textDict[NSForegroundColorAttributeName] = [UIColor redColor]; // 设置文本的空心线条宽度
textDict[NSStrokeWidthAttributeName] = @5; // 设置文本的空心线条颜色,要使此设置有效必须设置空心线条宽度,此设置有效时前景色设置项无效
textDict[NSStrokeColorAttributeName] = [UIColor blueColor]; // 设置文本阴影,用 drawInRect 方式绘制,不添加空心属性时,文字自动换行后此设置无效
NSShadow *shadow = [[NSShadow alloc] init];
shadow.shadowColor = [UIColor blackColor];
shadow.shadowOffset = CGSizeMake(4, 4);
shadow.shadowBlurRadius = 3;
textDict[NSShadowAttributeName] = shadow;
效果

9、图片处理
9.1 在控件视图上绘制/添加图片
如果绘制东西到 view 等视图控件上面,必须写在 drawRect 方法里面,不管有没有手动获取到上下文。
跟 view 相关联的上下文是 layer 图层上下文,需要在在 view 的 drawRect 方法中获取。跟 image 相关的上下文是 Bitmap 位图上下文,需要我们手动创建。
1、绘制/添加图片
在指定位置绘制图片,图片不会进行缩放
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"demo2"]; [image drawAtPoint:CGPointZero];
}
在指定区域绘制图片,图片会进行缩放
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"demo2"]; [image drawInRect:rect];
}
在指定区域绘制图片,图片会以平铺的样式填充
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"demo3"]; [image drawAsPatternInRect:rect];
}
在图片上绘制图片,不是绘制在 view 视图控件上,不需写在 drawRect 方法里面
UIImage *backImage = [UIImage imageNamed:@"demo5"];
UIImage *headImage = [UIImage imageNamed:@"demo6"]; // size :图片画板(上下文)尺寸(新图片的尺寸)
// opaque:是否透明,NO 不透明,YES 透明
// scale :缩放,如果不缩放,设置为 0 // 开启一个位图上下文
UIGraphicsBeginImageContextWithOptions(backImage.size, NO, 0);
// UIGraphicsBeginImageContext(backImage.size); // 绘制背景图片
CGRect backRect = CGRectMake(0, 0, backImage.size.width, backImage.size.height);
[backImage drawInRect:backRect]; // 绘制头像图片
CGFloat scale = 5;
CGFloat w = backRect.size.width / scale;
CGFloat h = backRect.size.height / scale;
CGFloat x = (backRect.size.width - w) / 2;
CGFloat y = (backRect.size.height - h) / 2;
CGRect headRect = CGRectMake(x, y, w, h);
[headImage drawInRect:headRect]; // 获取绘制好的图片
UIImage *newImage = UIGraphicsGetImageFromCurrentImageContext(); // 关闭位图上下文
UIGraphicsEndImageContext();
效果




2、图片修剪
裁剪图片
先设置裁剪区域,再在指定的区域绘制图片,再裁剪/遮盖掉裁剪区域之外的部分。
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"demo2"]; // 开启图片上下文
UIGraphicsBeginImageContextWithOptions(image.size, NO, 0);
// UIGraphicsBeginImageContext(image.size); // 设置裁剪区域,超出裁剪区域的内容全部裁剪/遮盖掉,必须放在绘制图片之前
UIRectClip(CGRectMake(50, 50, 100, 200)); // 绘制图片
[image drawInRect:CGRectMake(0, 0, image.size.width, image.size.height)]; // 获取绘制好的图片
UIImage *newImage = UIGraphicsGetImageFromCurrentImageContext(); // 关闭图片上下文
UIGraphicsEndImageContext();
效果


擦除图片
先在指定的区域绘制图片,再擦除/遮盖掉擦除区域之内的部分。
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"demo2"]; // 开启图片上下文
UIGraphicsBeginImageContextWithOptions(image.size, NO, 0);
// UIGraphicsBeginImageContext(image.size); // 获取图片上下文
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // 绘制图片
[image drawInRect:CGRectMake(0, 0, image.size.width, image.size.height)]; // 设置擦除区域,擦除/遮盖掉指定区域的图片,必须放在绘制图片之后
CGContextClearRect(ctx, CGRectMake(50, 50, 100, 200)); // 获取绘制好的图片
UIImage *newImage = UIGraphicsGetImageFromCurrentImageContext(); // 关闭图片上下文
UIGraphicsEndImageContext();
效果


切割图片
切割掉切割区域之外的部分。
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"demo2"]; // 设置切割区域
CGRect cutRect = CGRectMake(0, 0, image.size.width / 2, image.size.height); // 切割图片
CGImageRef cgImage = CGImageCreateWithImageInRect(image.CGImage, cutRect); // 转换为 UIImage 格式图片
UIImage *newImage = [[UIImage alloc] initWithCGImage:cgImage]; CGImageRelease(cgImage);
效果


9.2 截取屏幕
具体实现代码见 GitHub 源码 QExtension
1、截取全屏幕图
@implementation UIImage (Draw) + (UIImage *)q_imageWithScreenShot { UIWindow *keyWindow = [UIApplication sharedApplication].keyWindow; // 开启图片上下文
UIGraphicsBeginImageContextWithOptions(keyWindow.bounds.size, NO, [UIScreen mainScreen].scale);
// UIGraphicsBeginImageContext(keyWindow.bounds.size); // 获取图片上下文
CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // 在 context 上渲染
[keyWindow.layer renderInContext:context]; // 从图片上下文获取当前图片
UIImage *screenShot = UIGraphicsGetImageFromCurrentImageContext(); // 关闭图片上下文
UIGraphicsEndImageContext(); return screenShot;
} @end
// 截取全屏幕图
UIImage *image = [UIImage q_imageWithScreenShot]; UIImageWriteToSavedPhotosAlbum(image, nil, nil, nil);
效果
2、截取指定视图控件屏幕图
@implementation UIImage (Draw) + (UIImage *)q_imageWithScreenShotFromView:(UIView *)view { // 开启图片上下文
UIGraphicsBeginImageContextWithOptions(view.bounds.size, NO, [UIScreen mainScreen].scale);
// UIGraphicsBeginImageContext(view.bounds.size); // 获取图片上下文
CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); // 在 context 上渲染
[view.layer renderInContext:context]; // 从图片上下文获取当前图片
UIImage *screenShot = UIGraphicsGetImageFromCurrentImageContext(); // 关闭图片上下文
UIGraphicsEndImageContext(); return screenShot;
} @end
// 截取指定视图控件屏幕图
UIImage *image = [UIImage q_imageWithScreenShotFromView:self.imageView]; UIImageWriteToSavedPhotosAlbum(image, nil, nil, nil);
效果

9.3 调整图片尺寸
具体实现代码见 GitHub 源码 QExtension
调整图片尺寸
@implementation UIImage (Draw) - (UIImage *)q_imageByScalingAndCroppingToSize:(CGSize)size { // 开启图片上下文
UIGraphicsBeginImageContextWithOptions(size, NO, 0);
// UIGraphicsBeginImageContext(size); // 在指定的区域内绘制图片
[self drawInRect:CGRectMake(0, 0, size.width, size.height)]; // 从图片上下文获取当前图片
UIImage *image = UIGraphicsGetImageFromCurrentImageContext(); // 关闭图片上下文
UIGraphicsEndImageContext(); return image;
} @end
// 调整图片的尺寸
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"demo2"];
UIImage *newImage = [image q_imageByScalingAndCroppingToSize:CGSizeMake(150, 150)];
效果


9.4 裁剪圆形图片
具体实现代码见 GitHub 源码 QExtension
裁剪圆形图片
@implementation UIImage (Draw) - (UIImage *)q_imageByCroppingToRound { // 开启图片上下文
UIGraphicsBeginImageContextWithOptions(self.size, NO, 0);
// UIGraphicsBeginImageContext(self.size); // 设置裁剪路径
CGFloat w = self.size.width;
CGFloat h = self.size.height;
CGFloat wh = MIN(self.size.width, self.size.height);
CGRect clipRect = CGRectMake((w - wh) / 2, (h - wh) / 2, wh, wh);
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithOvalInRect:clipRect]; // 裁剪
[path addClip]; // 绘制图片
[self drawAtPoint:CGPointZero]; // 从图片上下文获取当前图片
UIImage *image = UIGraphicsGetImageFromCurrentImageContext(); // 关闭图片上下文
UIGraphicsEndImageContext(); // 切割图片
CGRect cutRect = CGRectMake(w - wh, h - wh, wh * 2, wh * 2);
CGImageRef imageRef = image.CGImage;
CGImageRef cgImage = CGImageCreateWithImageInRect(imageRef, cutRect);
UIImage *newImage = [[UIImage alloc] initWithCGImage:cgImage];
CGImageRelease(cgImage); return newImage;
} @end
// 裁剪圆形图片
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"demo2"];
UIImage *newImage = [image q_imageByCroppingToRound];
效果


9.5 添加图片水印
具体实现代码见 GitHub 源码 QExtension
水印在图片上加的防止他人盗图的半透明 logo、文字、图标。有时候,在手机客户端 app 中也需要用到水印技术。比如,用户拍完照片后,可以在照片上打个水印,标识这个图片是属于哪个用户的。
添加图片水印
@implementation UIImage (Draw) - (UIImage *)q_imageWithWaterMarkString:(nullable NSString *)string
attributes:(nullable NSDictionary<NSString *, id> *)attrs
image:(nullable UIImage *)image
frame:(CGRect)frame { // 开启图片上下文
UIGraphicsBeginImageContextWithOptions(self.size, NO, 0);
// UIGraphicsBeginImageContext(self.size); // 绘制背景图片
CGRect backRect = CGRectMake(0, 0, self.size.width, self.size.height);
[self drawInRect:backRect]; CGRect strRect = frame; // 添加图片水印
if (image) { if ((frame.origin.x == -1) && (frame.origin.y == -1)) { CGFloat w = frame.size.width;
CGFloat h = frame.size.height;
CGFloat x = (backRect.size.width - w) / 2;
CGFloat y = (backRect.size.height - h) / 2; [image drawInRect:CGRectMake(x, y, w, h)];
} else { [image drawInRect:frame]; strRect = CGRectMake(frame.origin.x + frame.size.width + 5, frame.origin.y, 1, 1);
}
} // 添加文字水印
if (string) { if ((frame.origin.x == -1) && (frame.origin.y == -1)) { } else {
[string drawAtPoint:strRect.origin withAttributes:attrs];
}
} // 获取绘制好的图片
UIImage *newImage = UIGraphicsGetImageFromCurrentImageContext(); // 关闭位图上下文
UIGraphicsEndImageContext(); return newImage;
}
@end
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"demo2"]; // 设置水印文本属性
NSMutableDictionary *textAttrs = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
textAttrs[NSFontAttributeName] = [UIFont boldSystemFontOfSize:50];
textAttrs[NSForegroundColorAttributeName] = [[UIColor redColor] colorWithAlphaComponent:0.2];
textAttrs[NSStrokeWidthAttributeName] = @5; // 添加图片水印
self.imageView.image = [image q_imageWithWaterMarkString:@"QianChia"
attributes:textAttrs
image:nil
frame:CGRectMake(30, 300, 50, 50)];
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"demo5"]; // 添加图片水印
self.imageView.image = [image q_imageWithWaterMarkString:nil
attributes:nil
image:[UIImage imageNamed:@"demo8"]
frame:CGRectMake(-1, -1, 88, 88)];
效果




10、Quartz 2D 的使用
10.1 绘制下载进度按钮
具体实现代码见 GitHub 源码 QExtension
具体讲解见 Quartz 2D 下载进度按钮绘制
// 创建进度按钮
QProgressButton *progressButton = [QProgressButton q_progressButtonWithFrame:CGRectMake(100, 100, 100, 50)
title:@"开始下载"
lineWidth:10
lineColor:[UIColor blueColor]
textColor:[UIColor redColor]
backgroundColor:[UIColor yellowColor]
isRound:YES]; // 设置按钮点击事件
[progressButton addTarget:self action:@selector(progressUpdate:) forControlEvents:UIControlEventTouchUpInside]; // 将按钮添加到当前控件显示
[self.view addSubview:progressButton]; // 设置按钮的进度值
self.progressButton.progress = progress; // 设置按钮的进度终止标题,一旦设置了此标题进度条就会停止
self.progressButton.stopTitle = @"下载完成";
效果




10.2 绘制手势截屏
具体实现代码见 GitHub 源码 QExtension
具体讲解见 Quartz 2D 手势截屏绘制
// 创建手势截屏视图
QTouchClipView *touchClipView = [QTouchClipView q_touchClipViewWithView:self.imageView
clipResult:^(UIImage * _Nullable image) { // 获取处理截屏结果
if (image) {
UIImageWriteToSavedPhotosAlbum(image, self, @selector(image:didFinishSavingWithError:contextInfo:), nil);
}
}]; // 添加手势截屏视图
[self.view addSubview:touchClipView];
效果
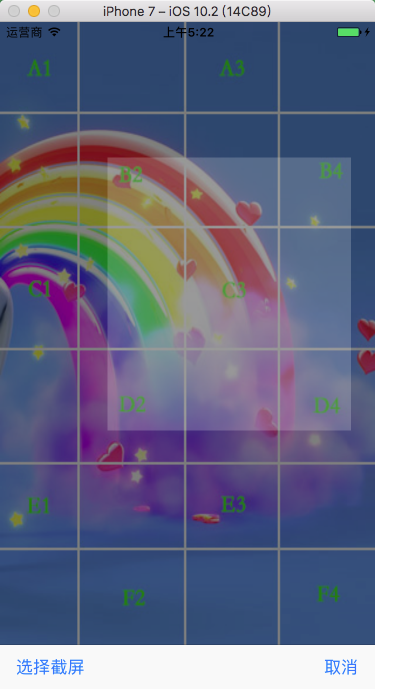
10.3 绘制手势锁
具体实现代码见 GitHub 源码 QExtension
具体讲解见 Quartz 2D 手势锁绘制
// 设置 frame
CGFloat margin = 50;
CGFloat width = self.view.bounds.size.width - margin * 2;
CGRect frame = CGRectMake(margin, 200, width, width); // 创建手势锁视图界面,获取滑动结果
QTouchLockView *touchLockView = [QTouchLockView q_touchLockViewWithFrame:frame
pathResult:^(BOOL isSucceed, NSString * _Nonnull result) { // 处理手势触摸结果
[self dealTouchResult:result isSucceed:isSucceed];
}]; [self.view addSubview:touchLockView];
效果

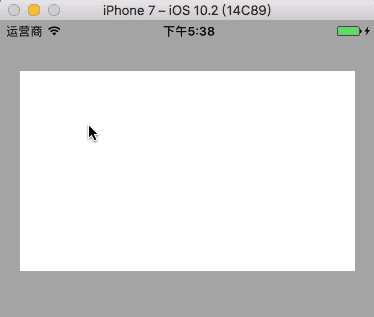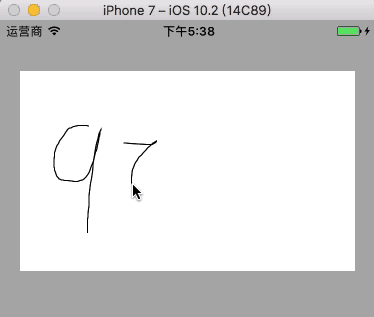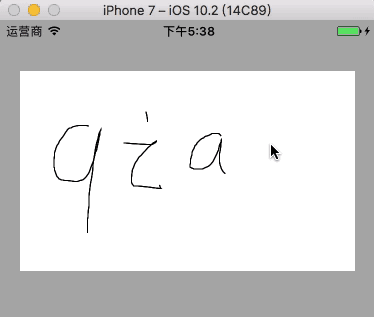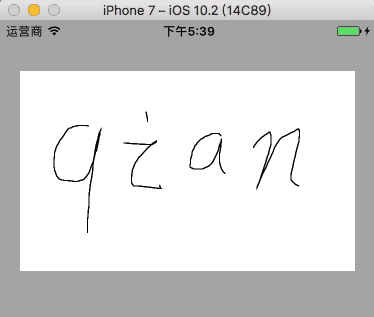
10.4 绘制画板
- 具体讲解见 Quartz 2D 画板绘制
10.4.1 绘制简单画板
绘制简单画板
// 创建画板
CGRect frame = CGRectMake(20, 50, self.view.bounds.size.width - 40, 200);
PaintBoardView *paintBoard = [[PaintBoardView alloc] initWithFrame:frame]; [self.view addSubview:paintBoard];
效果

10.4.2 绘制画板封装
具体实现代码见 GitHub 源码 QExtension
1、创建简单画板
// 创建简单画板
CGRect frame = CGRectMake(20, 50, self.view.bounds.size.width - 40, 200); QPaintBoardView *paintBoardView = [QPaintBoardView q_paintBoardViewWithFrame:frame]; // 可选属性值设置
paintBoardView.paintLineWidth = 5; // default is 1
paintBoardView.paintLineColor = [UIColor redColor]; // default is blackColor
paintBoardView.paintBoardColor = [UIColor cyanColor]; // default is whiteColor [self.view addSubview:paintBoardView];
self.paintBoardView = paintBoardView; // 撤销绘画结果
[self.paintBoardView q_back]; // 清除绘画结果
[self.paintBoardView q_clear]; // 获取绘画结果
UIImage *image = [self.paintBoardView q_getPaintImage];
效果
2、创建画板
// 创建画板
QPaintBoardView *paintBoard = [QPaintBoardView q_paintBoardViewWithFrame:self.view.bounds
lineWidth:0
lineColor:nil
boardColor:nil
paintResult:^(UIImage * _Nullable image) { if (image) {
NSData *data = UIImagePNGRepresentation(image);
[data writeToFile:@"/Users/JHQ0228/Desktop/Images/pic.png" atomically:YES];
}
}]; [self.view addSubview:paintBoard];
效果




10.5 刮奖模拟
刮奖
- (IBAction)scratchBtnClick:(id)button { [button removeFromSuperview];
[self.forImageView removeFromSuperview];
} - (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event { CGPoint startPoint = [touches.anyObject locationInView:self.cerImageView];
CGRect startRect = CGRectMake(startPoint.x - 10, startPoint.y - 10, 20, 20); [self clearRect:startRect imageView:self.cerImageView];
} - (void)touchesMoved:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event { CGPoint touchPoint = [touches.anyObject locationInView:self.cerImageView];
CGRect touchRect = CGRectMake(touchPoint.x - 10, touchPoint.y - 10, 20, 20); [self clearRect:touchRect imageView:self.cerImageView];
} - (void)clearRect:(CGRect)rect imageView:(UIImageView *)imageView { UIGraphicsBeginImageContextWithOptions(imageView.bounds.size, NO, 0);
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
[imageView.layer renderInContext:ctx]; // 设置擦除区域
CGContextClearRect(ctx, rect); UIImage *newImage = UIGraphicsGetImageFromCurrentImageContext();
imageView.image = newImage; UIGraphicsEndImageContext();
}
效果

iOS - Quartz 2D 二维绘图的更多相关文章
- iOS - Quartz 2D 贝塞尔曲线
1.贝塞尔曲线 贝塞尔曲线(Bézier curve),又称贝兹曲线或贝济埃曲线,是应用于二维图形应用程序的数学曲线.一般的矢量图形软件通过它来精确画出曲线,贝兹曲线由线段与节点组成,节点是可拖动的支 ...
- Agg vs. Cairo 二维绘图引擎之比较和选择 .
Agg vs. Cairo 二维绘图引擎之比较和选择 cheungmine 当今时代对于作为二维图形软件开发者, 是幸运的.因为除了Windows GDI/GDI+之外,我们还有很多其他的选择.而且这 ...
- TurboCAD Pro for Mac(二维绘图和三维建模工具)破解版安装
1.软件简介 TurboCAD Pro 是 macOS 系统上一款二维绘图和三维建模工具,具备强大的绘图和设计特性,加上强大的创建复杂的三维模型的工具,三维 OpenGL 的渲染,和超过 11, ...
- 微信连WiFi关注公众号流程更新 解决ios微信扫描二维码不关注就能上网的问题
前几天鼓捣了一下微信连WiFi功能,设置还蛮简单的,但ytkah发现如果是ios版微信扫描微信连WiFi生成的二维码不用关注公众号就可以直接上网了,而安卓版需要关注公众号才能上网,这样就少了很多ios ...
- Matlab 二维绘图函数(plot类)
plot 功能 绘制二维图形的最基本函数. 语法 //x为向量时,以x的元素值为纵坐标,x的序号为横坐标绘制曲线. //x为矩阵时,以其序号为横坐标,按列绘制每列元素值相对于其序号的曲线. polt( ...
- matlab学习笔记8 基本绘图命令-初级二维绘图/交互式绘图
一起来学matlab-matlab学习笔记8 基本绘图命令_5 初级二维绘图/交互式绘图 觉得有用的话,欢迎一起讨论相互学习~Follow Me 参考书籍 <matlab 程序设计与综合应用&g ...
- iOS 读取相册二维码,兼容ios7(使用CIDetector 和 ZXingObjC)
ios从相册读取二维码,在ios8以上,苹果提供了自带的识别图片二维码的功能,这种方式效率最好,也是最推荐的,但是如果你的系统需要向下兼容ios7,就必须用其他方式. 这里我选择的是 ZXingObj ...
- iOS开发——生成二维码——工具类
啥也不说,直接上源码,拷过去就能用.生成二维码的工具类使用方法在ProduceQRCode.h里有示例说明 分别将下面的ProduceQRCode.h和ProduceQRCode.m对应的代码考到自己 ...
- ios 中生成二维码和相册中识别二维码
iOS 使用CIDetector扫描相册二维码.原生扫描 原生扫描 iOS7之后,AVFoundation让我们终于可以使用原生扫描进行扫码了(二维码与条码皆可)AVFoundation可以让我们从设 ...
随机推荐
- 济南清北学堂游记 Day 6.
还剩一天半我就该回去了. 说实话今天挺可惜的,有很多本来可以得到的分数评测时没有拿到.上午的第一题和第二题我都想出了正解,T3敲了一个暴力,虽然暴力写坏了.预计是可以拿210的但是实际上只有很少的分数 ...
- Python学习-使用opencv-python提取手掌和手心及部分掌纹
上次我们成功训练了手掌识别器http://www.cnblogs.com/take-fetter/p/8438747.html,可以成功得到识别的结果如图 接下来需要使用opencv来获取手掌,去除背 ...
- PLECS—直流电机系统2
1.模型图 2,计算及仿真 1)计算 2)仿真 n = 1870.1 r/min (wm = 195.833 rad/s) ...
- 关于CSS的外边距合并问题
首先,需要明确的是只有普通文档流中块框的垂直外边距才会发生外边距合并.行内框.浮动框或绝对定位之间的外边距不会合并. 而在普通文档流中,这又分两种情况,分别是父子元素之间和相邻元素之间. <!D ...
- 【深度学习系列】用PaddlePaddle进行车牌识别(一)
小伙伴们,终于到了实战部分了!今天给大家带来的项目是用PaddlePaddle进行车牌识别.车牌识别其实属于比较常见的图像识别的项目了,目前也属于比较成熟的应用,大多数老牌厂家能做到准确率99%+.传 ...
- web端表格测试用例
表格测试: 表格内容列表排序功能是否正常每一栏的宽度是否足够宽,表格里的文字是否都有折行?是否有因为某一格的内容太多,而将整行的内容拉长?表格是否能左(右)添加(删除)列,表格是否能上(下)添加(删除 ...
- FFMpeg首次使用
FFMpeg在Windows上的使用.去FFMpeg官网上去下载文件. 把下载好的文件放如下图所示的位置. cmd,调出系统的命令行工具.首先进入d盘. 进入到ffmpeg所在的文件夹. 运行 ffm ...
- Angular Universal(统一平台)笔记
angular官网高级文档AngularUniversal部分的翻译总结,这东西在angular4开始正式被官方支持了,目前其实支持的服务器端还没有很多,但好歹包括了node和DotNetCore,算 ...
- 深度学习优化算法Momentum RMSprop Adam
一.Momentum 1. 计算dw.db. 2. 定义v_db.v_dw \[ v_{dw}=\beta v_{dw}+(1-\beta)dw \] \[ v_{db}=\beta v_{db}+( ...
- 本博客由CSDN迁移而来,显示不正常的博文会慢慢修复!
如题,原博客地址http://blog.csdn.net/vicjiao
