Numerical Analysis
PART1 <求解方程>
1,二分法
def bisect(f,a,b,TOL=0.000004):
u_a = a
u_b = b
while(u_b-u_a)/2.0 > TOL:
c = (u_a+u_b)/2.0
if f(c) == :
break
if f(u_a)*f(c) < :
u_b = c
else:
u_a = c u_c = (u_a + u_b) / 2.0
return u_c f = lambda x: x*x*x + x -
ret = bisect(f,-1.0,1.0)
print(ret) print(f(ret))
2,不动点迭代法求解方程(FPI)
例如求cosx - x = 0 方程 事实上可以化成x = cosx
x^3 + x - 1 = 0 也可以化成 x=1 - x^3
等式左边是x 右边设为f(x)
即是:x = f(x)
过程如下:
x1 = f(x0)
x2 = f(x1)
x3 = f(x2)
........
例如求cosx = x 即(cosx - x = 0)的解: 他的不动点是0.7390851332
def fpi(f,x0,k):
xvalues = []
xvalues.append(x0)
for i in range(k):
xvalues.append(f(xvalues[i]))
print(xvalues)
return xvalues[-1] # return last import math
f = lambda x:math.cos(x)
v = fpi(f,0,10)
print(v)
上述代码迭代十次 可以看到生成的数值为:
[0, 1.0, 0.5403023058681398, 0.8575532158463933, 0.6542897904977792, 0.7934803587425655, 0.7013687736227566,
0.7639596829006542, 0.7221024250267077, 0.7504177617637605, 0.7314040424225098, 0.7442373549005569,
0.7356047404363473, 0.7414250866101093, 0.7375068905132428, 0.7401473355678757, 0.7383692041223232,
0.739567202212256, 0.7387603198742114, 0.7393038923969057, 0.7389377567153446]
20次基本达到了与精确解
PART2 <求解方程组>
3,雅克比(jacobi)和高斯-赛德尔(Gauss-Seidel) 解方程组
结论:高斯-赛德尔的收敛速度比雅克比快的多。Gauss-Seidel20次迭代达到精确解,jacobi 20次还没得到
还有个高斯-赛德尔SOR 实现起来比较简单。
D代表对角阵,除了对角元素其他都为0
L,除了对角元素往下的元素,其他都为0
U,除了对角元素往上的元素,其他都为0
注意这里的LU和 LU分解是有本质的区别。

高斯赛的尔 用的我蓝色标识的字:

import numpy as np class GMatrix:
@staticmethod
def Invert(matrix):
nm = np.linalg.inv(matrix.mmatrix)
gm = GMatrix()
gm.assignNumPyMatrix(nm)
return gm def __init__(self, nx=0, ny=0):
self.rows = nx
self.columns = ny
self.mmatrix = np.matrix(np.zeros((nx, ny))) def assignNumPyMatrix(self, matrix):
self.mmatrix = matrix def changeShape(self, nx, ny):
self.mmatrix = np.matrix(np.zeros((nx, ny))) def debug(self):
print("{\n", ">>SHAPE:", (self.mmatrix.shape))
print(self.mmatrix)
print('}\n') def numPyMatrix(self):
return self.mmatrix def set(self, i, j, var):
self.mmatrix[i - 1, j - 1] = var def get(self, i, j):
return self.mmatrix[i - 1, j - 1] def L(self):
n = self.rows
m = GMatrix(n, n) for j in range(1, n, 1):
for i in range(j + 1, n + 1):
# print(i, j)
m.set(i, j, self.get(i, j))
return m def U(self):
n = self.rows
m = GMatrix(n, n)
for i in range(1, n + 1, 1):
for j in range(i + 1, n + 1):
m.set(i, j, self.get(i, j))
return m def D(self):
"""
this matrix diagonal values
1,make a empty matrix
2,copy diagonal value to this empty matrix
"""
n = self.rows
m = GMatrix(n, n)
for i in range(self.rows):
index = i + 1
m.set(index, index, self.get(index, index))
return m def DInvert(self):
"""
invert diagonal matrix !
:return:
"""
n = self.rows
m = GMatrix(n, n)
for i in range(n):
index = i + 1
m.set(index, index, 1 / self.get(index, index))
return m def __mul__(self, other):
nm = self.mmatrix * other.mmatrix # USE NumPy matrix * matrix
m = GMatrix()
m.assignNumPyMatrix(nm)
return m def __add__(self, other):
nm = self.mmatrix + other.mmatrix # USE NumPy matrix + matrix
m = GMatrix()
m.assignNumPyMatrix(nm)
return m def __sub__(self, other):
nm = self.mmatrix - other.mmatrix # USE NumPy matrix - matrix
m = GMatrix()
m.assignNumPyMatrix(nm)
return m def Jacobi_Solver(x0, L, U, invertD, b,iter =20):
"""
x0 = INIT_VECTOR_VALUE
xk+1 = Inv(D)*[ b-(L+U)xk ] ,k = 0,1,2,......
:return:
"""
nextX = x0
for x in range(iter):
nextX = invertD * (b - (L + U) * nextX)
return nextX def Gauss_Seidel_Solver(x0, L, U, D, b,iter =10):
"""
xk+1 = inv(L+D) * (b- U*xk) """
nextX = x0
for x in range(iter):
nextX = GMatrix.Invert(L+D) * (b - U * nextX)
return nextX def unit_test_matrix():
m = GMatrix(2, 2)
m.set(1, 1, 3)
m.set(1, 2, 1)
m.set(2, 1, 1)
m.set(2, 2, 2) # and also can this
# m.numPyMatrix()[0, 0] = 3
# m.numPyMatrix()[0, 1] = 1
# m.numPyMatrix()[1, 0] = 1
# m.numPyMatrix()[1, 1] = 2
m.debug()
m.D().debug()
m.L().debug()
m.U().debug()
m.DInvert().debug() def unit_test_jacobi():
"""
| 3 1 | |u| |5|
| | | | = | |
| 1 2 | |v| |5| --------
AX = b
--------
:return:
""" # CONSTRUCT THE A MATRIX
A = GMatrix(2, 2)
A.set(1, 1, 3) # A11 = 3
A.set(1, 2, 1) # A12 = 1
A.set(2, 1, 1) # A21 = 1
A.set(2, 2, 2) # A22 = 2
#A.debug() # CONSTRUCT THE b vector
b = GMatrix(2, 1)
b.set(1, 1, 5)
b.set(2, 1, 5) # INIT zero vector to iter
x0 = GMatrix(2,1) # [0,0]T vector initialize invert_D = A.DInvert() L = A.L()
U = A.U() print("get the jacobi result ")
Jacobi_Solver(x0,L,U,invert_D,b).debug() def unit_test_Gauss_Seidel():
"""
| 3 1 | |u| |5|
| | | | = | |
| 1 2 | |v| |5| --------
AX = b
--------
:return:
""" # CONSTRUCT THE A MATRIX
A = GMatrix(2, 2)
A.set(1, 1, 3) # A11 = 3
A.set(1, 2, 1) # A12 = 1
A.set(2, 1, 1) # A21 = 1
A.set(2, 2, 2) # A22 = 2 # CONSTRUCT THE b vector
b = GMatrix(2, 1)
b.set(1, 1, 5)
b.set(2, 1, 5) # INIT zero vector to iter
x0 = GMatrix(2, 1) # [0,0]T vector initialize D = A.D()
L = A.L()
U = A.U() print("get the Gauss_Seidel result ")
Gauss_Seidel_Solver(x0, L, U, D, b).debug() unit_test_jacobi()
unit_test_Gauss_Seidel()
4,楚列斯基分解choleskyDecomposition
这类情况只适合于正定矩阵。
楚列斯基分解的目的就是将正定矩阵分解成A = transpose(R) * R .
求解方程组直接使用回代法即可求出向量解,

这类方法不是迭代法,最重要的是分解矩阵.
所以是要求出来这个上三角矩阵R,比如分解如下矩阵:
[[ 4. -2. 2.]
[ -2. 2. -4.]
[ 2. -4. 11.]]
import numpy as np
import math class GMatrix:
def __init__(self, shape):
self.nn = shape
self.Mat = np.zeros((shape, shape)) def setRawData(self, *args):
if len(args) != self.nn * self.nn:
raise ValueError deserialize = []
for i in range(self.nn):
rhtmp = []
for j in range(self.nn):
rhtmp.append(args[i * self.nn + j])
deserialize.append(rhtmp)
self.tupleToMatrix(deserialize) def tupleToMatrix(self, tupleObj):
"""
:param tupleObj: ([1,2],[3,4])
will set matrix above tuple obj
"""
for i in range(self.nn):
# get row data of args
row_data = tupleObj[i]
for j in range(self.nn):
self.Mat[i, j] = row_data[j] def setRowsData(self, *args):
if len(args) != self.nn:
raise ValueError
self.tupleToMatrix(args) def __str__(self):
return str(self.Mat) def divideConstant(self, var):
self.Mat[:, :] = self.Mat[:, :] / var def __add__(self, other):
self.Mat[:, :] = self.Mat[:, :] + other.mat[:, :] def __sub__(self, other):
self.Mat[:, :] = self.Mat[:, :] - other.mat[:, :] def nextLayer(self):
array = self.Mat[1:, 1:]
m = GMatrix(a.Mat.shape[0])
m.Mat = array
return m def getupu(self):
self.Mat = np.triu(self.Mat)
return self def choleskyDecomposition(op=GMatrix(2)):
""" DEFINE MATRIX:
R11 R12 ... R1n
R21 R22 ... R2n
. . .
. . .
Rn1 Rn2 ... Rnn """
if len(op.Mat.flatten()) == 1:
op.Mat[op.nn - 1:, op.nn - 1:] = np.sqrt(op.Mat[op.nn - 1:, op.nn - 1:])
return # First make the matrix A11 to sqrt(A11)
op.Mat[0, 0] = math.sqrt(op.Mat[0, 0]) # R11
op.Mat[0, 1:] = op.Mat[0, 1:] / op.Mat[0,0] # (R12 R13 .... R1n) = (R12 R13 ...R1n) / R11 # cal u.transpose(u)
u = np.matrix(op.Mat[0,1:]) # it's a row vector
ut = np.transpose(u) # it's a column vector uut = ut*u
# extract_layer - uut
op.Mat[1:,1:] = op.Mat[1:,1:] - uut
choleskyDecomposition(op.nextLayer()) a = GMatrix(3) a.setRawData(4, -2, 2, -2, 2, -4, 2, -4, 11)
print(a)
choleskyDecomposition(a)
print(a.getupu())
分解结果R:
[[ 2. -1. 1.]
[ 0. 1. -3.]
[ 0. 0. 1.]]
Mathematica 检查结果:

5,共轭梯度法:
6,预条件共轭梯度法:
BVP:
差分法比较简单略.
排列法求解BVP问题:
如下例,n=2书中已经给答案,n=4的矩阵未给出,顺便自己解下矩阵n=4的情况。
算出c1,c2,c3,c4:



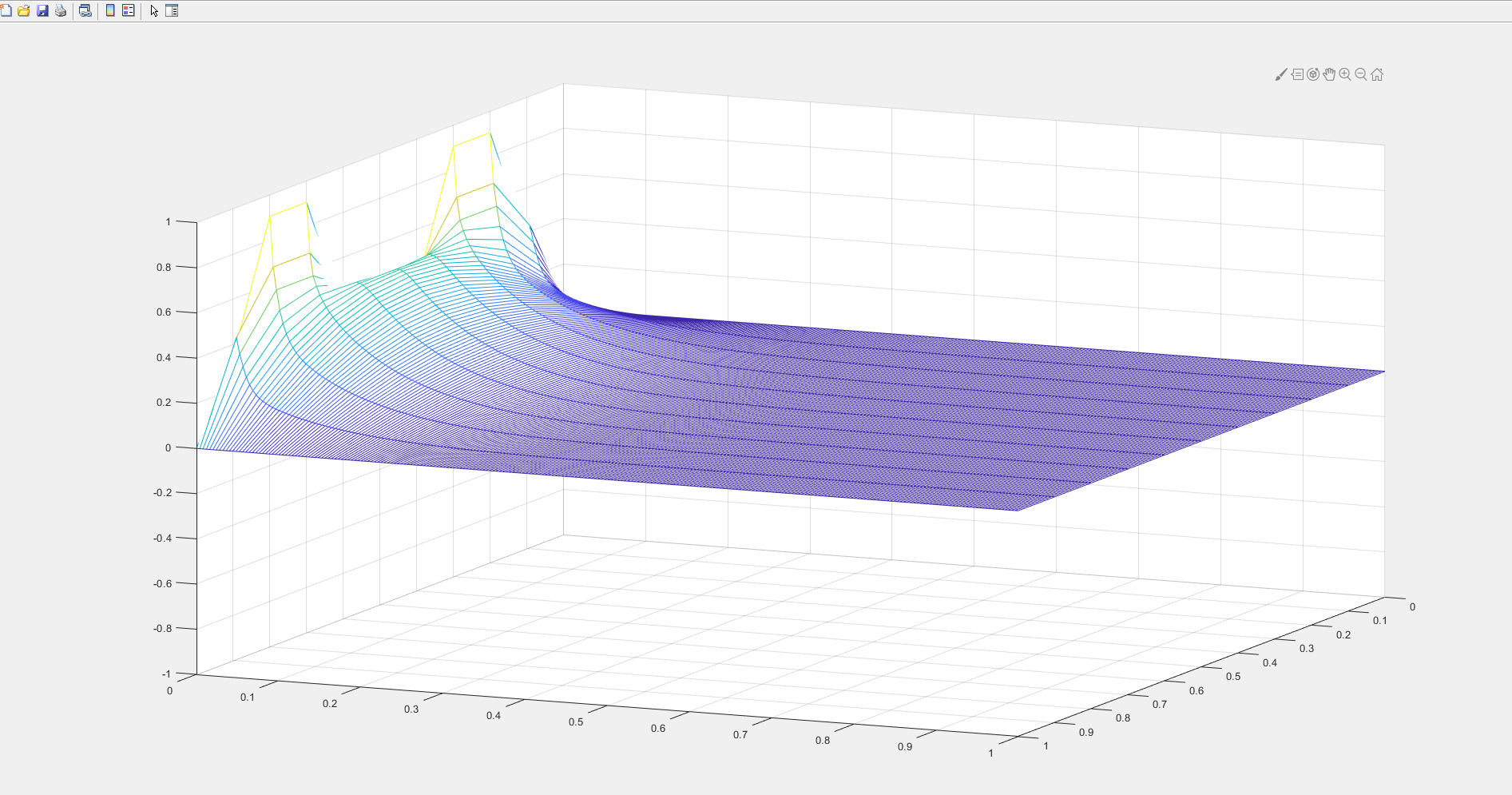
PDE 解热方程:
这次将时间方向放入坐标轴,可以用三维图像直接看到 在时间步上,热方程是如何传递的.
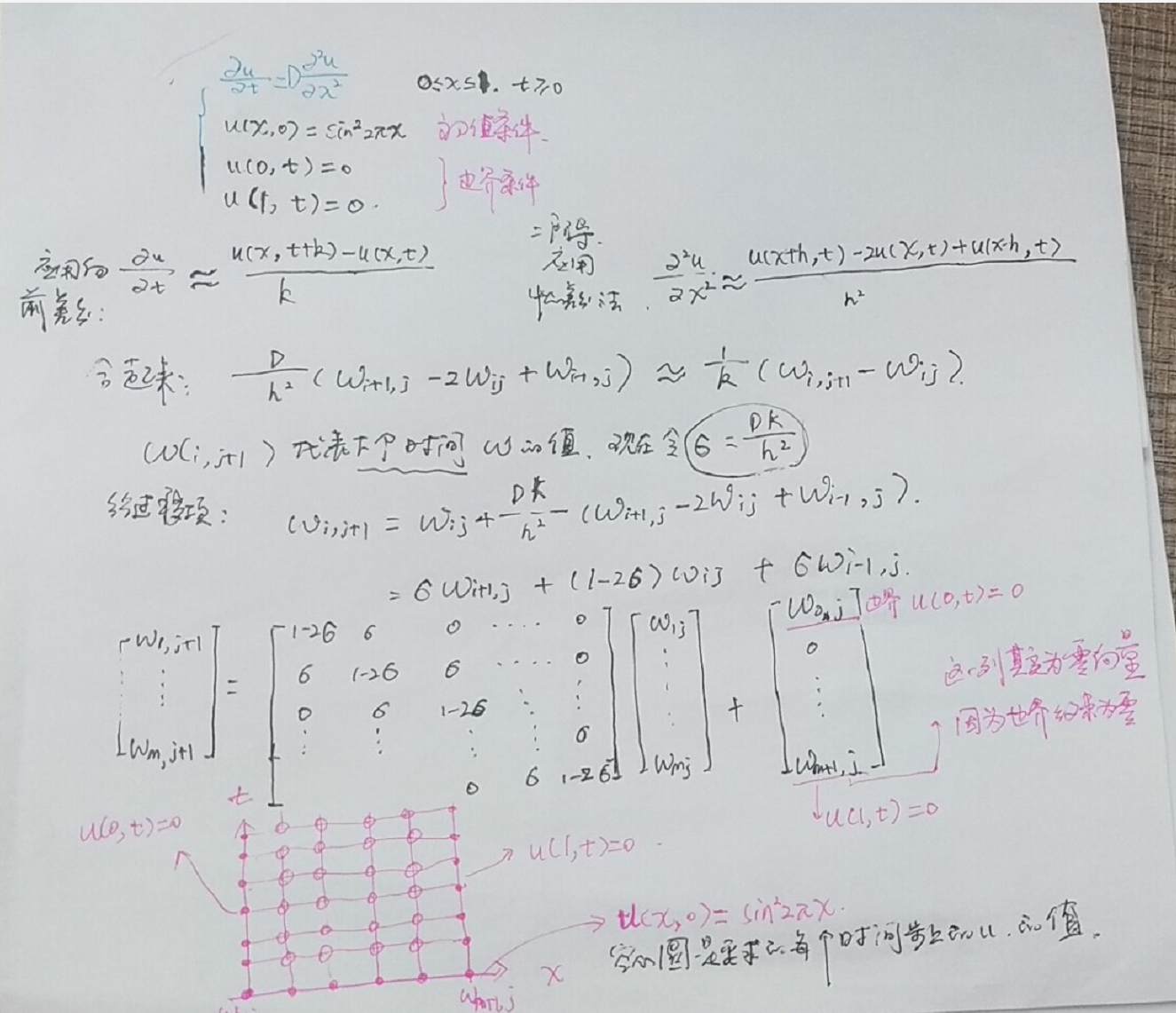
clc;
clear w a b c d M N f l r m sigma ;
xl = 0;
xr = 1;
yb = 0;
yt = 1; M = 10;
N = 250; f = @(x) sin(2*pi*x).^2;
l = @(t) 0*t;
r = @(t) 0*t; D =1;
h = (xr-xl) / M
k = (yt-yb) / N
m = M -1;
n=N;
sigma = D*k/(h*h); lside = l(yb+(0:n)*k);
rside = r(yb+(0:n)*k); % 定义矩阵a
a = diag(1-2*sigma*ones(m,1));
a = a + diag(sigma*ones(m-1,1),1); %自身加上 往右offset 1列 sigma倍数
a = a + diag(sigma*ones(m-1,1),-1); %自身加上 往左偏移 1列sigma倍数
a % 设置w第一列 ,初值条件,注意 要转置,因为 设置 w的第一列向量
w(:,1) = f(xl + (1:m) * h)' disp('START FOR LOOP')
% 给w 在时间250 迭代成列向量,则w是251列向量
for j = 1:n
rhs = w(:,1)';
w(:,j+1) = a*w(:,j) ;
end
disp('END FOR LOOP') w = [lside;w;rside];
x = (0:m+1)*h; t= (0:n)*k;
mesh(x,t,w')
view(60,30);
axis([xl xr yb yt -1 1]);
Numerical Analysis的更多相关文章
- 为什么要学习Numerical Analysis
前几日我发了一个帖子,预告自己要研究一下 Numerical Analysis 非常多人问我为啥,我统一回答为AI-----人工智能 我在和教授聊天的时候,忽然到了语言发展上 我说:老S啊(和我关系 ...
- <<Numerical Analysis>>笔记
2ed, by Timothy Sauer DEFINITION 1.3A solution is correct within p decimal places if the error is l ...
- <Numerical Analysis>(by Timothy Sauer) Notes
2ed, by Timothy Sauer DEFINITION 1.3A solution is correct within p decimal places if the error is l ...
- Residual (numerical analysis)
In many cases, the smallness of the residual means that the approximation is close to the solution, ...
- List of numerical libraries,Top Numerical Libraries For C#
Top Numerical Libraries For C# AlgLib (http://alglib.net) ALGLIB is a numerical analysis and data pr ...
- dir命令只显示文件名
dir /b 就是ls -f的效果 1057 -- FILE MAPPING_web_archive.7z 2007 多校模拟 - Google Search_web_archive.7z 2083 ...
- OpenCASCADE Gauss Integration
OpenCASCADE Gauss Integration eryar@163.com Abstract. Numerical integration is the approximate compu ...
- 【原创】开源Math.NET基础数学类库使用(06)直接求解线性方程组
本博客所有文章分类的总目录:[总目录]本博客博文总目录-实时更新 开源Math.NET基础数学类库使用总目录:[目录]开源Math.NET基础数学类库使用总目录 前言 ...
- RapidJSON 代码剖析(四):优化 Grisu
我曾经在知乎的一个答案里谈及到 V8 引擎里实现了 Grisu 算法,我先引用该文的内容简单介绍 Grisu.然后,再谈及 RapidJSON 对它做了的几个底层优化. (配图中的<Grisù& ...
随机推荐
- 13 在 Django REST framework 善用 SerializerMethodField方法
01-使用SerializerMethodField 来优化不必要的查询 class RepairQueueSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer): # rq_ ...
- SpringMVC model 多余字段 忽略
spring-mybaits的model中如何通过注解忽略非数据库字段?——CSDN问答频道https://ask.csdn.net/questions/643534 ObjectMapper忽略多余 ...
- mysql提取.sql备份文件中的单个表以及表数据
背景:随着业务模块的不断在增多,数据库mysql容量也是越来越大,做测试时,整个备份还原比较耗费时间,由于有时候仅仅需要单个表或者少数几个表,要想从整个备份文件中提取指定的表以及数据,需要以下方法. ...
- Windows下的命令神器Cmder
1. 下载地址: https://cmder.net/ 建议安装完整版本 2.设置与基本使用 1)将cmder添加到环境变量中PATH 2)添加到右键 Cmder.exe /REGISTER ALL ...
- svg-sprite使用
chainWebpack(config) { config.module .rule('svg') .exclude.add(path.resolve(__dirname,'src/assets/ic ...
- Kafka简介及使用PHP处理Kafka消息
Kafka简介及使用PHP处理Kafka消息 Kafka 是一种高吞吐的分布式消息系统,能够替代传统的消息队列用于解耦合数据处理,缓存未处理消息等,同时具有更高的吞吐率,支持分区.多副本.冗余,因此被 ...
- 【pytorch】关于Embedding和GRU、LSTM的使用详解
1. Embedding的使用 pytorch中实现了Embedding,下面是关于Embedding的使用. torch.nn包下的Embedding,作为训练的一层,随模型训练得到适合的词向量. ...
- hdu P3374 String Problem
今天又在lyk大佬的博客学会了——最小表示法(异常激动发篇题解纪念一下说在前面:给luogu提个建议最小表示法的题太少了,都被hdu抢去了!!! 我们先看一下题目 看完后可以用一个字概括——蒙,两个字 ...
- web自动化框架如何设计
web自动化框架如何设计po模式总结: 1. 页面对象模型:当页面特别多的时候,代码更好的维护 2. Po是pageObject设计模式,用来管理和维护一组web元素的对象库 3. 每一个page c ...
- 【linux】线上服务器要关注哪些参数
服务器(nginx/apache): 1.吞吐率. 2.并发连接数. 3.qps. 4.并发连接数详细数据统计,包括读取请求.持久连接.发送响应内容.关闭连接.等待连接. 5.连接线程池利用率. 关系 ...
