Spark day03
- 补充算子
transformations
- mapPartitionWithIndex
类似于mapPartitions,除此之外还会携带分区的索引值。
- repartition
增加或减少分区。会产生shuffle。(多个分区分到一个分区不会产生shuffle)
- coalesce
coalesce常用来减少分区,第二个参数是减少分区的过程中是否产生shuffle。
true为产生shuffle,false不产生shuffle。默认是false。
如果coalesce设置的分区数比原来的RDD的分区数还多的话,第二个参数设置为false不会起作用,如果设置成true,效果和repartition一样。即repartition(numPartitions) = coalesce(numPartitions,true)
- groupByKey
作用在K,V格式的RDD上。根据Key进行分组。作用在(K,V),返回(K,Iterable <V>)。
- zip
将两个RDD中的元素(KV格式/非KV格式)变成一个KV格式的RDD,两个RDD的每个分区元素个数必须相同。
- zipWithIndex
该函数将RDD中的元素和这个元素在RDD中的索引号(从0开始)组合成(K,V)对。
Action
- countByKey
作用到K,V格式的RDD上,根据Key计数相同Key的数据集元素。
- countByValue
根据数据集每个元素相同的内容来计数。返回相同内容的元素对应的条数。
- reduce
根据聚合逻辑聚合数据集中的每个元素。
- PV&UV
- Spark-Submit提交参数
Options:
- --master
MASTER_URL, 可以是spark://host:port, mesos://host:port, yarn, yarn-cluster,yarn-client, local
- --deploy-mode
DEPLOY_MODE, Driver程序运行的地方,client或者cluster,默认是client。
- --class
CLASS_NAME, 主类名称,含包名
- --jars
逗号分隔的本地JARS, Driver和executor依赖的第三方jar包
- --files
用逗号隔开的文件列表,会放置在每个executor工作目录中
- --conf
spark的配置属性
- --driver-memory
Driver程序使用内存大小(例如:1000M,5G),默认1024M
- --executor-memory
每个executor内存大小(如:1000M,2G),默认1G
Spark standalone with cluster deploy mode only:
- --driver-cores
Driver程序的使用core个数(默认为1),仅限于Spark standalone模式
Spark standalone or Mesos with cluster deploy mode only:
- --supervise
失败后是否重启Driver,仅限于Spark alone或者Mesos模式
Spark standalone and Mesos only:
- --total-executor-cores
executor使用的总核数,仅限于SparkStandalone、Spark on Mesos模式
Spark standalone and YARN only:
- --executor-cores
每个executor使用的core数,Spark on Yarn默认为1,standalone默认为worker上所有可用的core。
YARN-only:
- --driver-cores
driver使用的core,仅在cluster模式下,默认为1。
- --queue
QUEUE_NAME 指定资源队列的名称,默认:default
- --num-executors
一共启动的executor数量,默认是2个。
- 资源调度源码分析
- 资源请求简单图
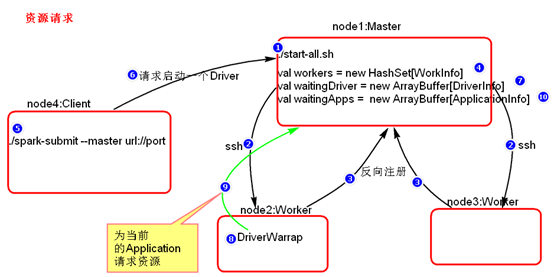
- 资源调度Master路径:
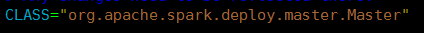
|
路径:spark-1.6.0/core/src/main/scala/org.apache.spark/deploy/Master/Master.scala |
- 提交应用程序,submit的路径:

|
路径:spark-1.6.0/core/src/main/scala/org.apache.spark/ deploy/SparkSubmit.scala |
- 总结:
- Executor在集群中分散启动,有利于task计算的数据本地化。
- 默认情况下(提交任务的时候没有设置--executor-cores选项),每一个Worker为当前的Application启动一个Executor,这个Executor会使用这个Worker的所有的cores和1G内存。
- 如果想在Worker上启动多个Executor,提交Application的时候要加--executor-cores这个选项。
- 默认情况下没有设置--total-executor-cores,一个Application会使用Spark集群中所有的cores。
- 结论演示
使用Spark-submit提交任务演示。也可以使用spark-shell
- 默认情况每个worker为当前的Application启动一个Executor,这个Executor使用集群中所有的cores和1G内存。
|
./spark-submit --master spark://node1:7077 --class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi ../lib/spark-examples-1.6.0-hadoop2.6.0.jar 10000 |
- 在workr上启动多个Executor,设置--executor-cores参数指定每个executor使用的core数量。
|
./spark-submit --master spark://node1:7077 --executor-cores 1 --class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi ../lib/spark-examples-1.6.0-hadoop2.6.0.jar 10000 |
- 内存不足的情况下启动core的情况。Spark启动是不仅看core配置参数,也要看配置的core的内存是否够用。
|
./spark-submit --master spark://node1:7077 --executor-cores 1 --executor-memory 3g --class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi ../lib/spark-examples-1.6.0-hadoop2.6.0.jar 10000 |
- --total-executor-cores集群中共使用多少cores
注意:一个进程不能让集群多个节点共同启动。
|
./spark-submit --master spark://node1:7077 --executor-cores 1 --executor-memory 2g --total-executor-cores 3 --class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi ../lib/spark-examples-1.6.0-hadoop2.6.0.jar 10000 |
- 任务调度源码分析
- Action算子开始分析
任务调度可以从一个Action类算子开始。因为Action类算子会触发一个job的执行。
- 划分stage,以taskSet形式提交任务
DAGScheduler 类中getMessingParentStages()方法是切割job划分stage。可以结合以下这张图来分析:
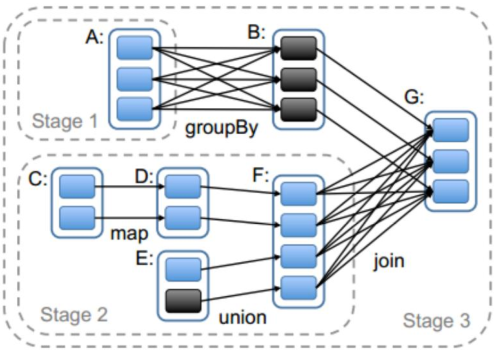
- 二次排序
|
SparkConf sparkConf = new SparkConf() .setMaster("local") .setAppName("SecondarySortTest"); final JavaSparkContext sc = new JavaSparkContext(sparkConf);
JavaRDD<String> secondRDD = sc.textFile("secondSort.txt");
JavaPairRDD<SecondSortKey, String> pairSecondRDD = secondRDD.mapToPair(new PairFunction<String, SecondSortKey, String>() {
/** * */ private
@Override public Tuple2<SecondSortKey, String> call(String line) throws Exception { String[] splited = line.split(" "); int int SecondSortKey secondSortKey = new SecondSortKey(first,second); return } });
pairSecondRDD.sortByKey(false).foreach(new VoidFunction<Tuple2<SecondSortKey,String>>() {
/** * */ private
@Override public System.out.println(tuple._2); } }); |
|
public /** * */ private private private public return } public this.first = first; } public return } public this.second = second; } public SecondSortKey(int super(); this.first = first; this.second = second; } @Override public if(getFirst() - o1.getFirst() ==0 ){ return getSecond() - o1.getSecond(); }else{ return getFirst() - o1.getFirst(); } } } |
- 分组取topN和topN
|
SparkConf conf = new SparkConf() .setMaster("local") .setAppName("TopOps"); JavaSparkContext sc = new JavaSparkContext(conf); JavaRDD<String> linesRDD = sc.textFile("scores.txt");
JavaPairRDD<String, Integer> pairRDD = linesRDD.mapToPair(new PairFunction<String, String, Integer>() {
/** * */ private
@Override public Tuple2<String, Integer> call(String str) throws Exception { String[] splited = str.split("\t"); String clazzName = splited[0]; Integer score = Integer.valueOf(splited[1]); return } });
pairRDD.groupByKey().foreach(new VoidFunction<Tuple2<String,Iterable<Integer>>>() {
/** * */ private
@Override public String clazzName = tuple._1; Iterator<Integer> iterator = tuple._2.iterator();
Integer[] top3 = new Integer[3];
while (iterator.hasNext()) { Integer score = iterator.next();
for (int if(top3[i] == null){ top3[i] = score; break; }else for (int top3[j] = top3[j-1]; } top3[i] = score; break; } } } System.out.println("class Name:"+clazzName); for(Integer sscore : top3){ System.out.println(sscore); } } }); |
- SparkShell的使用
- 概念:
SparkShell是Spark自带的一个快速原型开发工具,也可以说是Spark的scala REPL(Read-Eval-Print-Loop),即交互式shell。支持使用scala语言来进行Spark的交互式编程。
- 使用:
启动Standalone集群,./start-all.sh
在客户端上启动spark-shell:
|
./spark-shell --master spark://node1:7077 |
启动hdfs,创建目录spark/test,上传文件wc.txt
|
启动hdfs集群: start-all.sh 创建目录: hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /spark/test 上传wc.txt hdfs dfs -put /root/test/wc.txt /spark/test/ wc附件:
|
运行wordcount
|
sc.textFile("hdfs://node1:9000/spark/test/wc.txt") .flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_,1)).reduceByKey(_+_).foreach(println) |
Spark day03的更多相关文章
- spark基于win上面的操作
自己前面的小练习一直都是在linux上面写的,可是最近由于要把他迁移到win上面,我在自己的csdn博客有对如何在win上面搭建spark环境做出说明,好了,我们还是先看看 今天的内容吧 1.假如你有 ...
- Spark踩坑记——Spark Streaming+Kafka
[TOC] 前言 在WeTest舆情项目中,需要对每天千万级的游戏评论信息进行词频统计,在生产者一端,我们将数据按照每天的拉取时间存入了Kafka当中,而在消费者一端,我们利用了spark strea ...
- Spark RDD 核心总结
摘要: 1.RDD的五大属性 1.1 partitions(分区) 1.2 partitioner(分区方法) 1.3 dependencies(依赖关系) 1.4 compute(获取分区迭代列表) ...
- spark处理大规模语料库统计词汇
最近迷上了spark,写一个专门处理语料库生成词库的项目拿来练练手, github地址:https://github.com/LiuRoy/spark_splitter.代码实现参考wordmaker ...
- Hive on Spark安装配置详解(都是坑啊)
个人主页:http://www.linbingdong.com 简书地址:http://www.jianshu.com/p/a7f75b868568 简介 本文主要记录如何安装配置Hive on Sp ...
- Spark踩坑记——数据库(Hbase+Mysql)
[TOC] 前言 在使用Spark Streaming的过程中对于计算产生结果的进行持久化时,我们往往需要操作数据库,去统计或者改变一些值.最近一个实时消费者处理任务,在使用spark streami ...
- Spark踩坑记——初试
[TOC] Spark简介 整体认识 Apache Spark是一个围绕速度.易用性和复杂分析构建的大数据处理框架.最初在2009年由加州大学伯克利分校的AMPLab开发,并于2010年成为Apach ...
- Spark读写Hbase的二种方式对比
作者:Syn良子 出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/cssdongl 转载请注明出处 一.传统方式 这种方式就是常用的TableInputFormat和TableOutputForm ...
- (资源整理)带你入门Spark
一.Spark简介: 以下是百度百科对Spark的介绍: Spark 是一种与 Hadoop 相似的开源集群计算环境,但是两者之间还存在一些不同之处,这些有用的不同之处使 Spark 在某些工作负载方 ...
随机推荐
- Delphi 设计模式:《HeadFirst设计模式》Delphi7代码---模板方法模式之CoffeineBeverageWithHook[转]
模板方法模式定义了一个算法骨架,允许子类对算法的某个或某些步骤进行重写(override). 1 2{<HeadFirst设计模式>之模板方法模式 } 3{ 编译工具: Del ...
- 数据库连接池 - (druid、c3p0、dbcp)
概述: 在这里所谓的数据库连接是指通过网络协议与数据库服务之间建立的TCP连接.通常,与数据库服务进行通信的网络协议无需由应用程序本身实现. 原因有三: 实现复杂度大,需要充分理解和掌握相应的通信协议 ...
- MySQL数据库 字段操作 多表关系(更新中...)
外键 (foreign key) ## 外键 ```mysql # 作者(author):id,name,sex,age,mobile, detail_id # 作者详情(author_detail) ...
- VS中warning MSB8004和error MSB4018解决方案
问题如下: warning MSB8004: Output Directory does not end with a trailing slash. This build instance wil ...
- --1.plsql中学习job
--1.plsql中学习job --学习job --建表 create table test_job(para_date date); commit; insert into test_job val ...
- 对于ssm过程中的乱码问题的处理
首先是数据库乱码问题: 1.可以先检测一下是否是数据库的问题: 可以先输入查询语句SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'character_set_%';,查看所有的编码是否是UTF-8. (一般 ...
- ios那些事之如何在ios5上运行gdb
为啥要在ios上运行gdb? 这个问题见仁见智喽.对于搞开发的同学们来所, 有了gdb更方便跟踪分析别人的程序,取长补短:)这里不是教大家crack:) 运行环境: Mac OS 10.7.4 Xco ...
- liunx定时删除文件(产生的日志.........)
linux是一个很能自动产生文件的系统,日志.邮件.备份等.虽然现在硬盘廉价,我们可以有很多硬盘空间供这些文件浪费,让系统定时清理一些不需要的文件很有一种爽快的事情.不用你去每天惦记着是否需要清理日志 ...
- 大量的Close_wait 发现的 too many open file 错
突然频繁出现大量的 Close_wait,查看程序日志,发现 connection 在 accept 时报错,Too many open file. 估计程序里有这个漏洞,当 accept 时报错,没 ...
- 2019.9.20 csp-s模拟测试48 反思总结
头疼,不说废话了,祝大家rp++. T1: 暴力枚举,n3. 枚举两个串开始匹配的位置,每一次尽量修改. #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> ...

