201771010135 杨蓉庆《面对对象程序设计(java)》第十五周学习总结
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握Java应用程序的打包操作;
(2) 了解应用程序存储配置信息的两种方法;
(3) 掌握基于JNLP协议的java Web Start应用程序的发布方法;
(5) 掌握Java GUI 编程技术。
一、理论知识
JAR 文件
1、JAR文件是压缩的,它使用 ZIP 压缩格式。
2、Java程序的打包:程序编译完成后,程序员 将.class文件压缩打包为.jar文件后,GUI界面 程序就可以直接双击图标运行。
3、⚫jar命令格式: jar {ctxui} [vfm0Me] [jar-file] [manifest-file] [entry-point] [-C dir] files…
⚫-c 创建一个新的或者空的存档文件并加入文件。
-m 将一个清单文件(manifest)添加到JAR文件中。
-u 更新已存在的JAR文件(c和u不能同时出现)
-x 解压存档中的命名的(或所有的〕文件
⚫(1) 创建JAR文件:jar cf jar-file(文件名) input-file(s)
(2) 查看JAR文件:jar tf jar-file (查看t) t---want to view the Table of contents of the JAR file.
(*代表通配符,任意长度的字符。 ?仅代表一个位置是任意的)
(3) 提取JAR文件:jar xf jar-file [archived-file(s)] x---want to extract files from the JAR archive
(4) 更新JAR文件:jar uf jar-file input-file(s) u---want to update an existing JAR file.
(5) 索引JAR文件:jar i jar-file i---index an existing JAR file.
4、清单文件:每个JAR文件中包含一个用于描述归档特征的清单文 件(manifest)。清单文件被命名为MANIFEST.MF,它位于JAR文件的一个特殊的META-INF子目录中。
(2)清单文件的节与节之间用空行分开,最后一行必须以 换行符结束。否则,清单文件将无法被正确地读取。
例:– 创建一个包含清单的JAR文件,应该运行: jar cfm MyArchive.jar manifest.mf com/*.class
(3)运行JAR文件:用户可以通过下面的命令来启动应用程序: java –jar MyProgram.jar
窗口操作系统,可通过双击JAR文件图标来启动应用程序。
5、资源:Java中,应用程序使用的类通常需要一些相关的数据文件,这些文件称为资源(Resource)。
(–图像和声音文件。 –带有消息字符串和按钮标签的文本文件。 二进制数据文件,如:描述地图布局的文件。)
(1)利用资源机制对于非类文件也可以进行同样操作 ,具体步骤如下:
– 获得资源的Class对象。
– 如果资源是一个图像或声音文件,那么就需要调用 getresource(filename)获得资源的URL位置,然后利 用getImage或getAudioClip方法进行读取。 – 如果资源是文本或二进制文件,那么就可以使用 getResouceAsStream方法读取文件中的数据。
(2)资源文件可以与类文件放在同一个目录中,也可以将资源文件放在其它子目录中。具体有以下两 种方式:
–相对资源名:如data/text/about.txt 它会被解释为相对于加载这个资源的类所在 的包。
–绝对资源名:如/corejava/title.txt
(3)编译、创建JAR文件和执行这个程序的命令如下: – javac ResourceTest.java
– jar cvfm ResourceTest.jar ResourceTest.mf *.class *.gif *.txt
– java –jar ResourceTest.jar
⚫
◼ 应用程序首选项存储
◼ Java Web Start
⚫ Java Web Start是一个用Java编写的应用程序,它是Sun 公司推出的一项在Internet上发布应用程序的技术;
⚫ 通过Java Web Start可以使一个应用程序很容易地通过 web部署在各个平台上,包括Windows,Linux,Solaris等。
⚫ Java Web Start的工作过程是基于Java Network Launch Protocol(JNLP) 协议的 。 一个后缀为 JNLP的文件包含了应用程序的说明以及如何启动 这个应用程序的所有信息,Java Web Start技术 部署应用程序的关键就在于JNLP文件的编写以及 发布。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第13章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材585页程序13-1,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 将所生成的JAR文件移到另外一个不同的目录中,再运行该归档文件,以便确认程序是从JAR文件中,而不是从当前目录中读取的资源。
l 掌握创建JAR文件的方法;
package resource; import java.awt.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* @version 1.41 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ResourceTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new ResourceTestFrame();
frame.setTitle("ResourceTest");//设置标题
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//关闭界面的操作
frame.setVisible(true);//使结果为可见的
});
}
} /**
* A frame that loads image and text resources.
*/
class ResourceTestFrame extends JFrame
{ //定义像素长和宽
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 300; public ResourceTestFrame()//定义ResourceTestFrame类
{//利用about.gif图像文件制作图标
setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
URL aboutURL = getClass().getResource("about.gif");
Image img = new ImageIcon(aboutURL).getImage();
//在找到ResourceTest类的地方查找about.gif图像文件
setIconImage(img); JTextArea textArea = new JTextArea();
//读取about.txt文件
InputStream stream = getClass().getResourceAsStream("about.txt");
try (Scanner in = new Scanner(stream, "UTF-8"))
{
while (in.hasNext())
textArea.append(in.nextLine() + "\n");
}//捕获异常
add(textArea);
}
}
resource
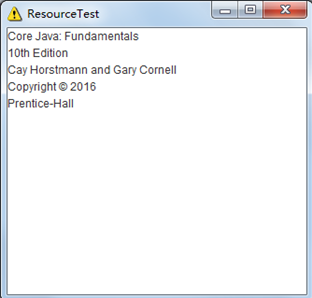
测试程序2
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材588页-589程序13-2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 了解Properties类中常用的方法;
package properties; import java.awt.EventQueue;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Properties; import javax.swing.*; /**
* A program to test properties. The program remembers the frame position, size,
* and title.
* @version 1.01 2015-06-16
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PropertiesTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {//lamda表达式
PropertiesFrame frame = new PropertiesFrame();
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
} /**
* A frame that restores position and size from a properties file and updates
* the properties upon exit.
*/
class PropertiesFrame extends JFrame
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; private File propertiesFile;//属性映射文件
private Properties settings; public PropertiesFrame()
{
// get position, size, title from properties
//获得位置、大小、标题 String userDir = System.getProperty("user.home");
//找到用户的主目录,调用System.getProperty方法
File propertiesDir = new File(userDir,".corejava");
if (!propertiesDir.exists()) propertiesDir.mkdir();
propertiesFile = new File(propertiesDir, "program.properties"); Properties defaultSettings = new Properties();
//defaultSettings构造器提供属性映射参数
defaultSettings.setProperty("left", "0");
defaultSettings.setProperty("top", "0");
defaultSettings.setProperty("width", "" + DEFAULT_WIDTH);
defaultSettings.setProperty("height", "" + DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
defaultSettings.setProperty("title", "");
settings = new Properties(defaultSettings); if (propertiesFile.exists())
try (InputStream in = new FileInputStream(propertiesFile))
{
settings.load(in);//使文件加载属性
}
catch (IOException ex)//抛出异常
{
ex.printStackTrace();
} int left = Integer.parseInt(settings.getProperty("left"));
int top = Integer.parseInt(settings.getProperty("top"));
int width = Integer.parseInt(settings.getProperty("width"));
int height = Integer.parseInt(settings.getProperty("height"));
setBounds(left, top, width, height); // if no title given, ask user String title = settings.getProperty("title");
if (title.equals(""))
title = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("Please supply a frame title:");
if (title == null) title = "";
setTitle(title); addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter()//添加窗口指定监听器
{
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent event)
{
settings.setProperty("left", "" + getX());
settings.setProperty("top", "" + getY());
settings.setProperty("width", "" + getWidth());
settings.setProperty("height", "" + getHeight());
settings.setProperty("title", getTitle());//
try (OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(propertiesFile))
{
settings.store(out, "Program Properties");
}
catch (IOException ex)
{
ex.printStackTrace();
}
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
properties
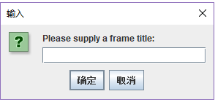

测试程序3
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材593页-594程序13-3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 了解Preferences类中常用的方法;
package preferences; import java.awt.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.prefs.*; import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.filechooser.*; /**
* A program to test preference settings. The program remembers the frame
* position, size, and title.
* @version 1.03 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PreferencesTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
PreferencesFrame frame = new PreferencesFrame();
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
} /**
* A frame that restores position and size from user preferences and updates the
* preferences upon exit.
*/
class PreferencesFrame extends JFrame
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200;
private Preferences root = Preferences.userRoot();//访问树中的一个结点
private Preferences node = root.node("/com/horstmann/corejava");//提供一个节点路径名 public PreferencesFrame()
{
// get position, size, title from preferences int left = node.getInt("left", 0);
int top = node.getInt("top", 0);
int width = node.getInt("width", DEFAULT_WIDTH);
int height = node.getInt("height", DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
setBounds(left, top, width, height);//设置节点信息 // if no title given, ask user String title = node.get("title", "");
if (title.equals(""))//对象比较
title = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("Please supply a frame title:");
if (title == null) title = "";
setTitle(title); // set up file chooser that shows XML files final JFileChooser chooser = new JFileChooser();
chooser.setCurrentDirectory(new File("."));
chooser.setFileFilter(new FileNameExtensionFilter("XML files", "xml")); // set up menus JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar();//创建新的菜单栏
setJMenuBar(menuBar);
JMenu menu = new JMenu("File");
menuBar.add(menu); JMenuItem exportItem = new JMenuItem("Export preferences");//添加菜单项目
menu.add(exportItem);
exportItem
.addActionListener(event -> {
if (chooser.showSaveDialog(PreferencesFrame.this) == JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION)
//this引用
{
try
{
savePreferences();//保存首选项
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(chooser
.getSelectedFile());
node.exportSubtree(out);
out.close();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();//捕获异常
}
}
}); JMenuItem importItem = new JMenuItem("Import preferences");
menu.add(importItem);//add方法
importItem
.addActionListener(event -> {
if (chooser.showOpenDialog(PreferencesFrame.this) == JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION)
{
try
{
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(chooser
.getSelectedFile());
Preferences.importPreferences(in);
in.close();//获得属性的设置
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
preferences
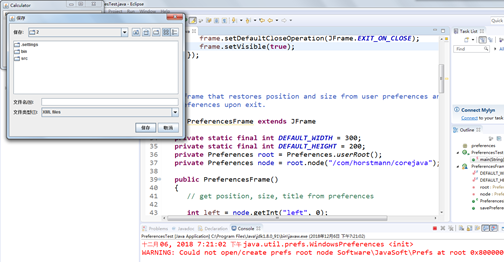
测试程序4
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材619页-622程序13-6,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握基于JNLP协议的java Web Start应用程序的发布方法。
Calculator
package webstart; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL; import javax.jnlp.BasicService;
import javax.jnlp.FileContents;
import javax.jnlp.FileOpenService;
import javax.jnlp.FileSaveService;
import javax.jnlp.PersistenceService;
import javax.jnlp.ServiceManager;
import javax.jnlp.UnavailableServiceException;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JMenu;
import javax.swing.JMenuBar;
import javax.swing.JMenuItem;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane; /**
* A frame with a calculator panel and a menu to load and save the calculator history.
*/
public class CalculatorFrame extends JFrame
{
private CalculatorPanel panel; public CalculatorFrame()
{
setTitle();
panel = new CalculatorPanel();
add(panel); JMenu fileMenu = new JMenu("File");
JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar();
menuBar.add(fileMenu);
setJMenuBar(menuBar); JMenuItem openItem = fileMenu.add("Open");
openItem.addActionListener(event -> open());
JMenuItem saveItem = fileMenu.add("Save");
saveItem.addActionListener(event -> save()); pack();
} /**
* Gets the title from the persistent store or asks the user for the title if there is no prior
* entry.
*/
public void setTitle()
{
try
{
String title = null; BasicService basic = (BasicService) ServiceManager.lookup("javax.jnlp.BasicService");
URL codeBase = basic.getCodeBase(); PersistenceService service = (PersistenceService) ServiceManager
.lookup("javax.jnlp.PersistenceService");
URL key = new URL(codeBase, "title"); try
{
FileContents contents = service.get(key);
InputStream in = contents.getInputStream();
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
title = reader.readLine();
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e)
{
title = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("Please supply a frame title:");
if (title == null) return; service.create(key, 100);
FileContents contents = service.get(key);
OutputStream out = contents.getOutputStream(true);
PrintStream printOut = new PrintStream(out);
printOut.print(title);
}
setTitle(title);
}
catch (UnavailableServiceException | IOException e)
{
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, e);
}
} /**
* Opens a history file and updates the display.
*/
public void open()
{
try
{
FileOpenService service = (FileOpenService) ServiceManager
.lookup("javax.jnlp.FileOpenService");
FileContents contents = service.openFileDialog(".", new String[] { "txt" }); JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, contents.getName());
if (contents != null)
{
InputStream in = contents.getInputStream();
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null)
{
panel.append(line);
panel.append("\n");
}
}
}
catch (UnavailableServiceException e)
{
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, e);
}
catch (IOException e)
{
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, e);
}
} /**
* Saves the calculator history to a file.
*/
public void save()
{
try
{
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
PrintStream printOut = new PrintStream(out);
printOut.print(panel.getText());
InputStream data = new ByteArrayInputStream(out.toByteArray());
FileSaveService service = (FileSaveService) ServiceManager
.lookup("javax.jnlp.FileSaveService");
service.saveFileDialog(".", new String[] { "txt" }, data, "calc.txt");
}
catch (UnavailableServiceException e)
{
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, e);
}
catch (IOException e)
{
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, e);
}
}
}
CalculatorFrame
package webstart; import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.text.*; /**
A panel with calculator buttons and a result display.
*/
public class CalculatorPanel extends JPanel
{
private JTextArea display;
private JPanel panel;
private double result;
private String lastCommand;
private boolean start; /**
Lays out the panel.
*/
public CalculatorPanel()
{
setLayout(new BorderLayout()); result = 0;
lastCommand = "=";
start = true; // add the display display = new JTextArea(10, 20); add(new JScrollPane(display), BorderLayout.NORTH); ActionListener insert = new InsertAction();
ActionListener command = new CommandAction(); // add the buttons in a 4 x 4 grid panel = new JPanel();
panel.setLayout(new GridLayout(4, 4)); addButton("7", insert);
addButton("8", insert);
addButton("9", insert);
addButton("/", command); addButton("4", insert);
addButton("5", insert);
addButton("6", insert);
addButton("*", command); addButton("1", insert);
addButton("2", insert);
addButton("3", insert);
addButton("-", command); addButton("0", insert);
addButton(".", insert);
addButton("=", command);
addButton("+", command); add(panel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
} /**
Gets the history text.
@return the calculator history
*/
public String getText()
{
return display.getText();
} /**
Appends a string to the history text.
@param s the string to append
*/
public void append(String s)
{
display.append(s);
} /**
Adds a button to the center panel.
@param label the button label
@param listener the button listener
*/
private void addButton(String label, ActionListener listener)
{
JButton button = new JButton(label);
button.addActionListener(listener);
panel.add(button);
} /**
This action inserts the button action string to the
end of the display text.
*/
private class InsertAction implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
String input = event.getActionCommand();
start = false;
display.append(input);
}
} /**
This action executes the command that the button
action string denotes.
*/
private class CommandAction implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
String command = event.getActionCommand(); if (start)
{
if (command.equals("-"))
{
display.append(command);
start = false;
}
else
lastCommand = command;
}
else
{
try
{
int lines = display.getLineCount();
int lineStart = display.getLineStartOffset(lines - 1);
int lineEnd = display.getLineEndOffset(lines - 1);
String value = display.getText(lineStart, lineEnd - lineStart);
display.append(" ");
display.append(command);
calculate(Double.parseDouble(value));
if (command.equals("="))
display.append("\n" + result);
lastCommand = command;
display.append("\n");
start = true;
}
catch (BadLocationException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
} /**
Carries out the pending calculation.
@param x the value to be accumulated with the prior result.
*/
public void calculate(double x)
{
if (lastCommand.equals("+")) result += x;
else if (lastCommand.equals("-")) result -= x;
else if (lastCommand.equals("*")) result *= x;
else if (lastCommand.equals("/")) result /= x;
else if (lastCommand.equals("=")) result = x;
}
}
CalculatorPanel

实验2:GUI综合编程练习
练习1:采用GUI界面设计以下程序,并进行部署与发布:
l 编制一个程序,将身份证号.txt 中的信息读入到内存中;
l 按姓名字典序输出人员信息;
l 查询最大年龄的人员信息;
l 查询最小年龄人员信息;
l 输入你的年龄,查询身份证号.txt中年龄与你最近人的姓名、身份证号、年龄、性别和出生地;
l 查询人员中是否有你的同乡。
l 输入身份证信息,查询所提供身份证号的人员信息,要求输入一个身份证数字时,查询界面就显示满足查询条件的查询结果,且随着输入的数字的增多,查询匹配的范围逐渐缩小。
package 身份证; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.*; public class Main extends JFrame {
private static ArrayList<Student> studentlist;
private static ArrayList<Student> list;
private JPanel panel;
private JPanel buttonPanel;
private static final int DEFAULT_WITH = 900;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 500; public Main() {
studentlist = new ArrayList<>();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
File file = new File("D:\\java\\身份证号.txt");
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis));
String temp = null;
while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) { Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp); linescanner.useDelimiter(" ");
String name = linescanner.next();
String number = linescanner.next();
String sex = linescanner.next();
String age = linescanner.next();
String province = linescanner.nextLine();
Student student = new Student();
student.setName(name);
student.setnumber(number);
student.setsex(sex);
int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
student.setage(a);
student.setprovince(province);
studentlist.add(student); }
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("学生信息文件找不到");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("学生信息文件读取错误");
e.printStackTrace();
}
panel = new JPanel();
panel.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
JTextArea jt = new JTextArea();
panel.add(jt);
add(panel, BorderLayout.NORTH);
buttonPanel = new JPanel();
buttonPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 8));
JButton jButton = new JButton("字典排序");
JButton jButton1 = new JButton("年龄最大和年龄最小");
JLabel lab = new JLabel("查找你的同乡");
JTextField jt1 = new JTextField();
JLabel lab1 = new JLabel("查找与你年龄相近的人:");
JTextField jt2 = new JTextField();
JLabel lab2 = new JLabel("输入你的身份证号码:");
JTextField jt3 = new JTextField();
JButton jButton2 = new JButton("退出");
jButton.setBounds(900, 200,100, 90);
jButton1.setBounds(50, 120, 90, 60);
jt1.setBounds(900, 120, 100, 80);
jt2.setBounds(800, 200, 100, 80);
jt3.setBounds(450, 120, 80, 90);
jButton2.setBounds(800,200, 60, 50);
jButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
Collections.sort(studentlist);
jt.setText(studentlist.toString());
}
});
jButton1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
int max = 0, min = 100;
int j, k1 = 0, k2 = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < studentlist.size(); i++) {
j = studentlist.get(i).getage();
if (j > max) {
max = j;
k1 = i;
}
if (j < min) {
min = j;
k2 = i;
} }
jt.setText("年龄最大:" + studentlist.get(k1) + "年龄最小:" + studentlist.get(k2));
}
});
jButton2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
dispose();
System.exit(0);
}
});
jt1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String find = jt1.getText();
String text="";
String place = find.substring(0, 3);
for (int i = 0; i < studentlist.size(); i++) {
if (studentlist.get(i).getprovince().substring(1, 4).equals(place)) {
text+="\n"+studentlist.get(i);
jt.setText("老乡:" + text);
}
}
}
});
jt2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String yourage = jt2.getText();
int a = Integer.parseInt(yourage);
int near = agenear(a);
int value = a - studentlist.get(near).getage();
jt.setText("年龄相近:" + studentlist.get(near));
}
});
jt3.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.sort(studentlist);
String key = jt3.getText();
for (int i = 1; i < studentlist.size(); i++) {
if (studentlist.get(i).getnumber().contains(key)) {
list.add(studentlist.get(i));
jt.setText("你或许是:\n" + list); }
}
}
});
buttonPanel.add(jButton);
buttonPanel.add(jButton1);
buttonPanel.add(lab);
buttonPanel.add(jt1);
buttonPanel.add(lab1);
buttonPanel.add(jt2);
buttonPanel.add(lab2);
buttonPanel.add(jt3);
buttonPanel.add(jButton2);
add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
setSize(DEFAULT_WITH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
} public static int agenear(int age) {
int min = 53, value = 0, k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < studentlist.size(); i++) {
value = studentlist.get(i).getage() - age;
if (value < 0)
value = -value;
if (value < min) {
min = value;
k = i;
}
}
return k;
} }
Main
package 身份证;
public class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
private String name;
private String number ;
private String sex ;
private int age;
private String province;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getnumber() {
return number;
}
public void setnumber(String number) {
this.number = number;
}
public String getsex() {
return sex ;
}
public void setsex(String sex ) {
this.sex =sex ;
}
public int getage() {
return age;
}
public void setage(int age) {
// int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
this.age= age;
}
public String getprovince() {
return province;
}
public void setprovince(String province) {
this.province=province ;
}
public int compareTo(Student o) {
return this.name.compareTo(o.getName());
}
public String toString() {
return name+"\t"+sex+"\t"+age+"\t"+number+"\t"+province+"\n";
}
}
Student
package 身份证; import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*; public class ButtonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new Main();
frame.setTitle("身份证");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
ButtonTest

练习2:采用GUI界面设计以下程序,并进行部署与发布
l 编写一个计算器类,可以完成加、减、乘、除的操作
l 利用计算机类,设计一个小学生100以内数的四则运算练习程序,由计算机随机产生10道加减乘除练习题,学生输入答案,由程序检查答案是否正确,每道题正确计10分,错误不计分,10道题测试结束后给出测试总分;
将程序中测试练习题及学生答题结果输出到文件,文件名为test.txt。
package S; import java.io.*;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Scanner; public class jisuan {
public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); PrintWriter output = null;
try {
output = new PrintWriter("text.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
int a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
int b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
int m = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 4);
switch (m) {
case 1:
while (b == 0) {
b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
}
while (a % b != 0) {
a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
}
System.out.println(a + "/" + b + "=");
int c1 = in.nextInt();
output.println(a + "/" + b + "=" + c1);
if (c1 == a / b) {
System.out.println("恭喜答案正确");
sum += 10;
} else {
System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误");
} break; case 2:
System.out.println( a + "*" + b + "=");
int c2 = in.nextInt();
output.println(a + "*" + b + "=" + c2);
if (c2 == a * b) {
System.out.println("恭喜答案正确");
sum += 10;
} else {
System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误");
}
break;
case 3:
System.out.println( a + "+" + b + "=");
int c3 = in.nextInt();
output.println(a + "+" + b + "=" + c3);
if (c3 == a + b) {
System.out.println("恭喜答案正确");
sum += 10;
} else {
System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误");
} break;
case 4:
while (a < b) {
a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
}
System.out.println( a + "-" + b + "=");
int c4 = in.nextInt();
output.println(a + "-" + b + "=" + c4);
if (c4 == a - b) {
System.out.println("恭喜答案正确");
sum += 10;
} else {
System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误");
}
break; } }
System.out.println("成绩" + sum);
output.println("成绩" + sum);
output.close();
}
}
jisuan
package S;
public class math<T> {
private T a;
private T b; public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
} public int reduce(int a, int b) {
return a - b;
} public int multiplication(int a, int b) {
return a * b;
} public int division(int a, int b) {
if (b != 0 && a % b == 0)
return a / b;
else
return 0;
}
}
math


三、实验总结
本章我们学习的知识好像也不是特别难,但实际操作就完全不一样了,由于个人能力有限,在编写程序时候有借鉴别人的代码,虽然想在此基础上进行变化,但最终结果不尽人意,所以只能做到这个样子,而且测试程序也做不太出来,老是发现有错,所以这次实验感觉很不合格,得反省更改……
201771010135 杨蓉庆《面对对象程序设计(java)》第十五周学习总结的更多相关文章
- 201771010135杨蓉庆《面向对象程序设计(java)》第四周学习总结
学习目标 1.掌握类与对象的基础概念,理解类与对象的关系: 2.掌握对象与对象变量的关系: 3.掌握预定义类的基本使用方法,熟悉Math类.String类.math类.Scanner类.LocalDa ...
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第八周学习总结
第八周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 一.接口.lambda和内部类: Comparator与comparable接口: 1.comparable接口的方法是compareTo,只有一个参数:comp ...
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第七周学习总结
第七周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 1.继承是面向对象程序设计(Object Oriented Programming-OOP)中软件重用的关键技术.继承机制使用已经定义的类作为基础建立新的类定义,新 ...
- 201771010128 王玉兰《面象对象程序设计 (Java) 》第六周学习总结
---恢复内容开始--- 第一部分:基础知识总结: 1.继承 A:用已有类来构建新类的一种机制,当定义了一个新类继承一个类时,这个新类就继承了这个类的方法和域以适应新的情况: B:特点:具有层次结构. ...
- 201771010135杨蓉庆 《面向对象程序设计(java)》第三周学习总结
一:第1-3章学习内容: 第一章:复习基本数据类型 整型 byte(1个字节 表示范围:-2^7 ~ (2^7)-1) short(2个字节 表示范围:-2^15~(2^15)-1) int(4个字节 ...
- 201771010135杨蓉庆《面向对象程序设计(java)》第六周学习总结
实验六 继承定义与使用 1.实验目的与要求 (1) 理解继承的定义: (2) 掌握子类的定义要求 (3) 掌握多态性的概念及用法: (4) 掌握抽象类的定义及用途: (5) 掌握类中4个成员访问权限修 ...
- 201771010135杨蓉庆《面向对象程序设计(java)》第二周学习总结
第一部分:理论知识学习部分 3.1 标识符:由字母.下划线.美元符号和数字组成, 且第一个符号不能为数字,可用作:类名.变量名.方法名.数组名.文件名等.有Hello.$1234.程序名.www_12 ...
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十五周学习
第十五周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 JAR文件: 应用程序首选项存储: Java Web Start JAR文件: 1.Java程序的打包:程序编译完成后,程序员将.class文件压缩打包为.jar ...
- 201521123061 《Java程序设计》第十二周学习总结
201521123061 <Java程序设计>第十二周学习总结 1. 本周学习总结 1.1 以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结多流与文件相关内容. 2. 书面作业 将Student对 ...
- 201521123072《java程序设计》第十二周学习总结
201521123072<java程序设计>第十二周学习总结 1. 本周学习总结 1.1 以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结多流与文件相关内容. 2. 书面作业 将Student对象 ...
随机推荐
- vue项目出现Module not found: Error: Can't resolve 'stylus-loader'错误解决方案
因为没有安装stylus和stylus-loader npm install stylus stylus-loader --save-dev 安装成功后,使用npm install重新建立依赖 打开项 ...
- C++-hihoCode1546-[快速幂]
枚举子集,要求子集的min+max<=k,求子集个数,答案对1000000007取模 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; ,M ...
- 浅析ReDoS
ReDoS(Regular expression Denial of Service) 正则表达式拒绝服务攻击.开发人员使用了正则表达式来对用户输入的数据进行有效性校验, 当编写校验的正则表达式存在缺 ...
- [SDOI2014] 重建 - 矩阵树定理,概率期望
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define eps 1e-6 using namespace std; const int N = 55; namespace mat ...
- Openstack 简单梳理,(自用 慎点)
这个图里面的彩色方块,就是OpenStack最核心的组件. 推荐几个大咖,大家可以百度找他们的博客来看:陈沙克.何明桂.孔令贤,Cloudman.
- Spring Boot Actuator未授权访问
当我们发现某一个网页的logo是一篇叶子或者报错信息如下图所示的话,就可以尝试Spring Boot Actuator未授权访问. /dump - 显示线程转储(包括堆栈跟踪) /autoconfig ...
- python后续学习
关于使用python输出中文字符的问题: Python中默认的编码格式是 ASCII 格式,在没修改编码格式时无法正确打印汉字,所以在读取中文时会报错. 解决方法为只要在文件开头加入 # -*- co ...
- 1059 Prime Factors (25分)
1059 Prime Factors (25分) 1. 题目 2. 思路 先求解出int范围内的所有素数,把输入x分别对素数表中素数取余,判断是否为0,如果为0继续除该素数知道余数不是0,遍历到sqr ...
- 2020 CCPC比赛
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/4010/A 这道题枚举区间长度的贡献值: 当区间长度为1时,就是所有元音数的个数: 当区间长度为2时,区间[2,n-1]的数贡 ...
- 题解【UVA10054】The Necklace
题目描述 输入格式 输出格式 题意简述 有一种由彩色珠子连接而成的项链.每个珠子的两半由不同颜色组成.如图所示,相邻两个珠子在接触的地方颜色相同.现在有一些零碎的珠子,需要确认它们是否可以复原成完整的 ...
