Vuex 源码解析
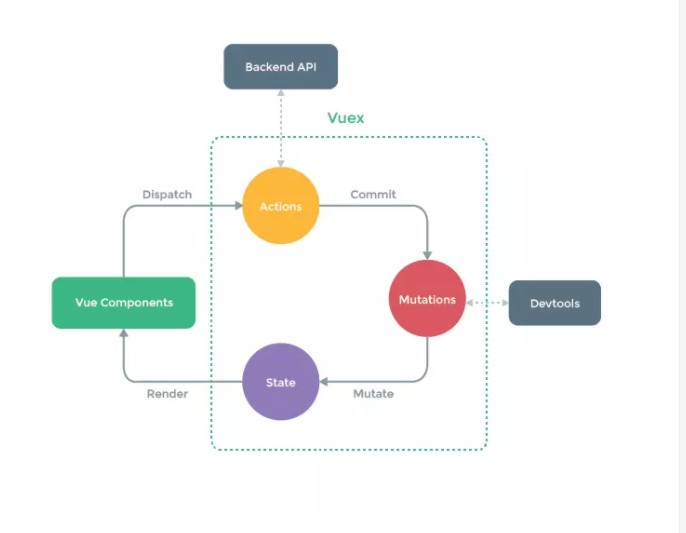
先来看一下这张Vuex的数据流程图,熟悉Vuex使用的同学应该已经有所了解。
Vue.js提供了Vue.use方法用来给Vue.js安装插件,内部通过调用插件的install方法(当插件是一个对象的时候)来进行插件的安装。
我们来看一下Vuex的install实现。
- /*暴露给外部的插件install方法,供Vue.use调用安装插件*/
- export function install (_Vue) {
- if (Vue) {
- /*避免重复安装(Vue.use内部也会检测一次是否重复安装同一个插件)*/
- if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
- console.error(
- '[vuex] already installed. Vue.use(Vuex) should be called only once.'
- )
- }
- return
- }
- /*保存Vue,同时用于检测是否重复安装*/
- Vue = _Vue
- /*将vuexInit混淆进Vue的beforeCreate(Vue2.0)或_init方法(Vue1.0)*/
- applyMixin(Vue)
- }
- /*Vuex的init钩子,会存入每一个Vue实例等钩子列表*/
- function vuexInit () {
- const options = this.$options
- // store injection
- if (options.store) {
- /*存在store其实代表的就是Root节点,直接执行store(function时)或者使用store(非function)*/
- this.$store = typeof options.store === 'function'
- ? options.store()
- : options.store
- } else if (options.parent && options.parent.$store) {
- /*子组件直接从父组件中获取$store,这样就保证了所有组件都公用了全局的同一份store*/
- this.$store = options.parent.$store
- }
- }
vuexInit会尝试从options中获取store,如果当前组件是根组件(Root节点),则options中会存在store,直接获取赋值给$store即可。如果当前组件非根组件,则通过options中的parent获取父组件的$store引用。这样一来,所有的组件都获取到了同一份内存地址的Store实例,于是我们可以在每一个组件中通过this.$store愉快地访问全局的Store实例了。
那么,什么是Store实例?
Store
我们传入到根组件到store,就是Store实例,用Vuex提供到Store方法构造。
- export default new Vuex.Store({
- strict: true,
- modules: {
- moduleA,
- moduleB
- }
- });
我们来看一下Store的实现。首先是构造函数。
- constructor (options = {}) {
- // Auto install if it is not done yet and `window` has `Vue`.
- // To allow users to avoid auto-installation in some cases,
- // this code should be placed here. See #731
- /*
- 在浏览器环境下,如果插件还未安装(!Vue即判断是否未安装),则它会自动安装。
- 它允许用户在某些情况下避免自动安装。
- */
- if (!Vue && typeof window !== 'undefined' && window.Vue) {
- install(window.Vue)
- }
- if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
- assert(Vue, `must call Vue.use(Vuex) before creating a store instance.`)
- assert(typeof Promise !== 'undefined', `vuex requires a Promise polyfill in this browser.`)
- assert(this instanceof Store, `Store must be called with the new operator.`)
- }
- const {
- /*一个数组,包含应用在 store 上的插件方法。这些插件直接接收 store 作为唯一参数,可以监听 mutation(用于外部地数据持久化、记录或调试)或者提交 mutation (用于内部数据,例如 websocket 或 某些观察者)*/
- plugins = [],
- /*使 Vuex store 进入严格模式,在严格模式下,任何 mutation 处理函数以外修改 Vuex state 都会抛出错误。*/
- strict = false
- } = options
- /*从option中取出state,如果state是function则执行,最终得到一个对象*/
- let {
- state = {}
- } = options
- if (typeof state === 'function') {
- state = state()
- }
- // store internal state
- /* 用来判断严格模式下是否是用mutation修改state的 */
- this._committing = false
- /* 存放action */
- this._actions = Object.create(null)
- /* 存放mutation */
- this._mutations = Object.create(null)
- /* 存放getter */
- this._wrappedGetters = Object.create(null)
- /* module收集器 */
- this._modules = new ModuleCollection(options)
- /* 根据namespace存放module */
- this._modulesNamespaceMap = Object.create(null)
- /* 存放订阅者 */
- this._subscribers = []
- /* 用以实现Watch的Vue实例 */
- this._watcherVM = new Vue()
- // bind commit and dispatch to self
- /*将dispatch与commit调用的this绑定为store对象本身,否则在组件内部this.dispatch时的this会指向组件的vm*/
- const store = this
- const { dispatch, commit } = this
- /* 为dispatch与commit绑定this(Store实例本身) */
- this.dispatch = function boundDispatch (type, payload) {
- return dispatch.call(store, type, payload)
- }
- this.commit = function boundCommit (type, payload, options) {
- return commit.call(store, type, payload, options)
- }
- // strict mode
- /*严格模式(使 Vuex store 进入严格模式,在严格模式下,任何 mutation 处理函数以外修改 Vuex state 都会抛出错误)*/
- this.strict = strict
- // init root module.
- // this also recursively registers all sub-modules
- // and collects all module getters inside this._wrappedGetters
- /*初始化根module,这也同时递归注册了所有子modle,收集所有module的getter到_wrappedGetters中去,this._modules.root代表根module才独有保存的Module对象*/
- installModule(this, state, [], this._modules.root)
- // initialize the store vm, which is responsible for the reactivity
- // (also registers _wrappedGetters as computed properties)
- /* 通过vm重设store,新建Vue对象使用Vue内部的响应式实现注册state以及computed */
- resetStoreVM(this, state)
- // apply plugins
- /* 调用插件 */
- plugins.forEach(plugin => plugin(this))
- /* devtool插件 */
- if (Vue.config.devtools) {
- devtoolPlugin(this)
- }
- }
Store的构造类除了初始化一些内部变量以外,主要执行了installModule(初始化module)以及resetStoreVM(通过VM使store“响应式”)。
installModule
installModule的作用主要是用为module加上namespace名字空间(如果有)后,注册mutation、action以及getter,同时递归安装所有子module。
- /*初始化module*/
- function installModule (store, rootState, path, module, hot) {
- /* 是否是根module */
- const isRoot = !path.length
- /* 获取module的namespace */
- const namespace = store._modules.getNamespace(path)
- // register in namespace map
- /* 如果有namespace则在_modulesNamespaceMap中注册 */
- if (module.namespaced) {
- store._modulesNamespaceMap[namespace] = module
- }
- // set state
- if (!isRoot && !hot) {
- /* 获取父级的state */
- const parentState = getNestedState(rootState, path.slice(0, -1))
- /* module的name */
- const moduleName = path[path.length - 1]
- store.`_withCommit`(() => {
- /* 将子module设置称响应式的 */
- Vue.set(parentState, moduleName, module.state)
- })
- }
- const local = module.context = makeLocalContext(store, namespace, path)
- /* 遍历注册mutation */
- module.forEachMutation((mutation, key) => {
- const namespacedType = namespace + key
- registerMutation(store, namespacedType, mutation, local)
- })
- /* 遍历注册action */
- module.forEachAction((action, key) => {
- const namespacedType = namespace + key
- registerAction(store, namespacedType, action, local)
- })
- /* 遍历注册getter */
- module.forEachGetter((getter, key) => {
- const namespacedType = namespace + key
- registerGetter(store, namespacedType, getter, local)
- })
- /* 递归安装mudule */
- module.forEachChild((child, key) => {
- installModule(store, rootState, path.concat(key), child, hot)
- })
- }
resetStoreVM
在说resetStoreVM之前,先来看一个小demo。
- let globalData = {
- d: 'hello world'
- };
- new Vue({
- data () {
- return {
- $$state: {
- globalData
- }
- }
- }
- });
- /* modify */
- setTimeout(() => {
- globalData.d = 'hi~';
- }, 1000);
- Vue.prototype.globalData = globalData;
- /* 任意模板中 */
- <div>{{globalData.d}}</div>
上述代码在全局有一个globalData,它被传入一个Vue对象的data中,之后在任意Vue模板中对该变量进行展示,因为此时globalData已经在Vue的prototype上了所以直接通过this.prototype访问,也就是在模板中的{{prototype.d}}。此时,setTimeout在1s之后将globalData.d进行修改,我们发现模板中的globalData.d发生了变化。其实上述部分就是Vuex依赖Vue核心实现数据的“响应式化”。
不熟悉Vue.js响应式原理的同学可以通过笔者另一篇文章响应式原理了解Vue.js是如何进行数据双向绑定的。
接着来看代码。
- /* 通过vm重设store,新建Vue对象使用Vue内部的响应式实现注册state以及computed */
- function resetStoreVM (store, state, hot) {
- /* 存放之前的vm对象 */
- const oldVm = store._vm
- // bind store public getters
- store.getters = {}
- const wrappedGetters = store._wrappedGetters
- const computed = {}
- /* 通过Object.defineProperty为每一个getter方法设置get方法,比如获取this.$store.getters.test的时候获取的是store._vm.test,也就是Vue对象的computed属性 */
- forEachValue(wrappedGetters, (fn, key) => {
- // use computed to leverage its lazy-caching mechanism
- computed[key] = () => fn(store)
- Object.defineProperty(store.getters, key, {
- get: () => store._vm[key],
- enumerable: true // for local getters
- })
- })
- // use a Vue instance to store the state tree
- // suppress warnings just in case the user has added
- // some funky global mixins
- const silent = Vue.config.silent
- /* Vue.config.silent暂时设置为true的目的是在new一个Vue实例的过程中不会报出一切警告 */
- Vue.config.silent = true
- /* 这里new了一个Vue对象,运用Vue内部的响应式实现注册state以及computed*/
- store._vm = new Vue({
- data: {
- $$state: state
- },
- computed
- })
- Vue.config.silent = silent
- // enable strict mode for new vm
- /* 使能严格模式,保证修改store只能通过mutation */
- if (store.strict) {
- enableStrictMode(store)
- }
- if (oldVm) {
- /* 解除旧vm的state的引用,以及销毁旧的Vue对象 */
- if (hot) {
- // dispatch changes in all subscribed watchers
- // to force getter re-evaluation for hot reloading.
- store._withCommit(() => {
- oldVm._data.$$state = null
- })
- }
- Vue.nextTick(() => oldVm.$destroy())
- }
- }
- forEachValue(wrappedGetters, (fn, key) => {
- // use computed to leverage its lazy-caching mechanism
- computed[key] = () => fn(store)
- Object.defineProperty(store.getters, key, {
- get: () => store._vm[key],
- enumerable: true // for local getters
- })
- })
之后Vuex采用了new一个Vue对象来实现数据的“响应式化”,运用Vue.js内部提供的数据双向绑定功能来实现store的数据与视图的同步更新。
- store._vm = new Vue({
- data: {
- $$state: state
- },
- computed
- })
这时候我们访问store._vm.test也就访问了Vue实例中的属性。
这两步执行完以后,我们就可以通过this.$store.getter.test访问vm中的test属性了。
严格模式
Vuex的Store构造类的option有一个strict的参数,可以控制Vuex执行严格模式,严格模式下,所有修改state的操作必须通过mutation实现,否则会抛出错误。
- /* 使能严格模式 */
- function enableStrictMode (store) {
- store._vm.$watch(function () { return this._data.$$state }, () => {
- if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
- /* 检测store中的_committing的值,如果是true代表不是通过mutation的方法修改的 */
- assert(store._committing, `Do not mutate vuex store state outside mutation handlers.`)
- }
- }, { deep: true, sync: true })
- }
首先,在严格模式下,Vuex会利用vm的$watch方法来观察$$state,也就是Store的state,在它被修改的时候进入回调。我们发现,回调中只有一句话,用assert断言来检测store._committing,当store._committing为false的时候会触发断言,抛出异常。
我们发现,Store的commit方法中,执行mutation的语句是这样的。
- this._withCommit(() => {
- entry.forEach(function commitIterator (handler) {
- handler(payload)
- })
- })
再来看看_withCommit的实现。
- _withCommit (fn) {
- /* 调用withCommit修改state的值时会将store的committing值置为true,内部会有断言检查该值,在严格模式下只允许使用mutation来修改store中的值,而不允许直接修改store的数值 */
- const committing = this._committing
- this._committing = true
- fn()
- this._committing = committing
- }
我们发现,通过commit(mutation)修改state数据的时候,会再调用mutation方法之前将committing置为true,接下来再通过mutation函数修改state中的数据,这时候触发$watch中的回调断言committing是不会抛出异常的(此时committing为true)。而当我们直接修改state的数据时,触发$watch的回调执行断言,这时committing为false,则会抛出异常。这就是Vuex的严格模式的实现。
接下来我们来看看Store提供的一些API。
commit(mutation)
- /* 调用mutation的commit方法 */
- commit (_type, _payload, _options) {
- // check object-style commit
- /* 校验参数 */
- const {
- type,
- payload,
- options
- } = unifyObjectStyle(_type, _payload, _options)
- const mutation = { type, payload }
- /* 取出type对应的mutation的方法 */
- const entry = this._mutations[type]
- if (!entry) {
- if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
- console.error(`[vuex] unknown mutation type: ${type}`)
- }
- return
- }
- /* 执行mutation中的所有方法 */
- this._withCommit(() => {
- entry.forEach(function commitIterator (handler) {
- handler(payload)
- })
- })
- /* 通知所有订阅者 */
- this._subscribers.forEach(sub => sub(mutation, this.state))
- if (
- process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
- options && options.silent
- ) {
- console.warn(
- `[vuex] mutation type: ${type}. Silent option has been removed. ` +
- 'Use the filter functionality in the vue-devtools'
- )
- }
- }
commit方法会根据type找到并调用_mutations中的所有type对应的mutation方法,所以当没有namespace的时候,commit方法会触发所有module中的mutation方法。再执行完所有的mutation之后会执行_subscribers中的所有订阅者。我们来看一下_subscribers是什么。
Store给外部提供了一个subscribe方法,用以注册一个订阅函数,会push到Store实例的_subscribers中,同时返回一个从_subscribers中注销该订阅者的方法。
- /* 注册一个订阅函数,返回取消订阅的函数 */
- subscribe (fn) {
- const subs = this._subscribers
- if (subs.indexOf(fn) < 0) {
- subs.push(fn)
- }
- return () => {
- const i = subs.indexOf(fn)
- if (i > -1) {
- subs.splice(i, 1)
- }
- }
- }
在commit结束以后则会调用这些_subscribers中的订阅者,这个订阅者模式提供给外部一个监视state变化的可能。state通过mutation改变时,可以有效补获这些变化。
dispatch(action)
来看一下dispatch的实现。
- /* 调用action的dispatch方法 */
- dispatch (_type, _payload) {
- // check object-style dispatch
- const {
- type,
- payload
- } = unifyObjectStyle(_type, _payload)
- /* actions中取出type对应的ation */
- const entry = this._actions[type]
- if (!entry) {
- if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
- console.error(`[vuex] unknown action type: ${type}`)
- }
- return
- }
- /* 是数组则包装Promise形成一个新的Promise,只有一个则直接返回第0个 */
- return entry.length > 1
- ? Promise.all(entry.map(handler => handler(payload)))
- : entry[0](payload)
- }
以及registerAction时候做的事情。
- /* 遍历注册action */
- function registerAction (store, type, handler, local) {
- /* 取出type对应的action */
- const entry = store._actions[type] || (store._actions[type] = [])
- entry.push(function wrappedActionHandler (payload, cb) {
- let res = handler.call(store, {
- dispatch: local.dispatch,
- commit: local.commit,
- getters: local.getters,
- state: local.state,
- rootGetters: store.getters,
- rootState: store.state
- }, payload, cb)
- /* 判断是否是Promise */
- if (!isPromise(res)) {
- /* 不是Promise对象的时候转化称Promise对象 */
- res = Promise.resolve(res)
- }
- if (store._devtoolHook) {
- /* 存在devtool插件的时候触发vuex的error给devtool */
- return res.catch(err => {
- store._devtoolHook.emit('vuex:error', err)
- throw err
- })
- } else {
- return res
- }
- })
- }
watch
熟悉Vue的朋友应该很熟悉watch这个方法。这里采用了比较巧妙的设计,_watcherVM是一个Vue的实例,所以watch就可以直接采用了Vue内部的watch特性提供了一种观察数据getter变动的方法。
registerModule
- /* 注册一个动态module,当业务进行异步加载的时候,可以通过该接口进行注册动态module */
- registerModule (path, rawModule) {
- /* 转化称Array */
- if (typeof path === 'string') path = [path]
- if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
- assert(Array.isArray(path), `module path must be a string or an Array.`)
- assert(path.length > 0, 'cannot register the root module by using registerModule.')
- }
- /*注册*/
- this._modules.register(path, rawModule)
- /*初始化module*/
- installModule(this, this.state, path, this._modules.get(path))
- // reset store to update getters...
- /* 通过vm重设store,新建Vue对象使用Vue内部的响应式实现注册state以及computed */
- resetStoreVM(this, this.state)
- }
registerModule用以注册一个动态模块,也就是在store创建以后再注册模块的时候用该接口。内部实现实际上也只有installModule与resetStoreVM两个步骤,前面已经讲过,这里不再累述。
unregisterModule
- /* 注销一个动态module */
- unregisterModule (path) {
- /* 转化称Array */
- if (typeof path === 'string') path = [path]
- if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
- assert(Array.isArray(path), `module path must be a string or an Array.`)
- }
- /*注销*/
- this._modules.unregister(path)
- this._withCommit(() => {
- /* 获取父级的state */
- const parentState = getNestedState(this.state, path.slice(0, -1))
- /* 从父级中删除 */
- Vue.delete(parentState, path[path.length - 1])
- })
- /* 重制store */
- resetStore(this)
- }
同样,与registerModule对应的方法unregisterModule,动态注销模块。实现方法是先从state中删除模块,然后用resetStore来重制store。
resetStore
- /* 重制store */
- function resetStore (store, hot) {
- store._actions = Object.create(null)
- store._mutations = Object.create(null)
- store._wrappedGetters = Object.create(null)
- store._modulesNamespaceMap = Object.create(null)
- const state = store.state
- // init all modules
- installModule(store, state, [], store._modules.root, true)
- // reset vm
- resetStoreVM(store, state, hot)
- }
这里的resetStore其实也就是将store中的_actions等进行初始化以后,重新执行installModule与resetStoreVM来初始化module以及用Vue特性使其“响应式化”,这跟构造函数中的是一致的。
插件
Vue提供了一个非常好用的插件Vue.js devtools
- /* 从window对象的__VUE_DEVTOOLS_GLOBAL_HOOK__中获取devtool插件 */
- const devtoolHook =
- typeof window !== 'undefined' &&
- window.__VUE_DEVTOOLS_GLOBAL_HOOK__
- export default function devtoolPlugin (store) {
- if (!devtoolHook) return
- /* devtoll插件实例存储在store的_devtoolHook上 */
- store._devtoolHook = devtoolHook
- /* 出发vuex的初始化事件,并将store的引用地址传给deltool插件,使插件获取store的实例 */
- devtoolHook.emit('vuex:init', store)
- /* 监听travel-to-state事件 */
- devtoolHook.on('vuex:travel-to-state', targetState => {
- /* 重制state */
- store.replaceState(targetState)
- })
- /* 订阅store的变化 */
- store.subscribe((mutation, state) => {
- devtoolHook.emit('vuex:mutation', mutation, state)
- })
- }
Vuex 源码解析的更多相关文章
- Vuex源码解析
写在前面 因为对Vue.js很感兴趣,而且平时工作的技术栈也是Vue.js,这几个月花了些时间研究学习了一下Vue.js源码,并做了总结与输出. 文章的原地址:https://github.com/a ...
- vuex 源码解析(四) mutation 详解
mutation是更改Vuex的store中的状态的唯一方法,mutation类似于事件注册,每个mutation都可以带两个参数,如下: state ;当前命名空间对应的state payload ...
- vuex 源码解析(三) getter属性详解
有时候我们需要从store中的state中派生出一些状态,例如: <div id="app"> <p>{{reverseMessage}}</p> ...
- VueX源码分析(5)
VueX源码分析(5) 最终也是最重要的store.js,该文件主要涉及的内容如下: Store类 genericSubscribe函数 resetStore函数 resetStoreVM函数 ins ...
- VueX源码分析(3)
VueX源码分析(3) 还剩余 /module /plugins store.js /plugins/devtool.js const devtoolHook = typeof window !== ...
- VueX源码分析(4)
VueX源码分析(4) /module store.js /module/module.js import { forEachValue } from '../util' // Base data s ...
- VueX源码分析(2)
VueX源码分析(2) 剩余内容 /module /plugins helpers.js store.js helpers要从底部开始分析比较好.也即先从辅助函数开始再分析那4个map函数mapSta ...
- VueX源码分析(1)
VueX源码分析(1) 文件架构如下 /module /plugins helpers.js index.esm.js index.js store.js util.js util.js 先从最简单的 ...
- 【原】Android热更新开源项目Tinker源码解析系列之三:so热更新
本系列将从以下三个方面对Tinker进行源码解析: Android热更新开源项目Tinker源码解析系列之一:Dex热更新 Android热更新开源项目Tinker源码解析系列之二:资源文件热更新 A ...
随机推荐
- iView的表单table
// html<div class="exam-list"> <Table :columns="columns7" :data="d ...
- 1006 -- Biorhythms
Biorhythms Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 138926 Accepted: 44590 Des ...
- 从一个url地址到最终页面渲染完成,发生了什么?
从一个url地址到最终页面渲染完成,发生了什么? 1.DNS 解析 : 将域名地址解析为IP地址 浏览器DNS缓存 系统DNS缓存 路由器DNS缓存 网络运营商DNS缓存 递归搜索: www.baid ...
- 使用python+ffmpeg批量转换格式
需求: 给定一个文件夹路径,遍历该文件夹内的所有文件以及子文件夹内的文件,当所有后缀名为wav格式的文件转换为ogg格式的文件. import os # 获取目录下的所有文件列表 import fn ...
- Codeforces 319C DP 斜率优化
题意:在一颗森林有n颗数,编号从1到n,第i棵树高度是a[i].有一个伐木工想要砍伐这片森林,它的电锯每次可以将树的高度减少1,然后就必须要充电,充电的代价是他已经砍倒的树种编号最大的那颗树的代价(b ...
- 【CSS】选择器优先级
CSS的选择器优先级的权重 在 Selectors Level 3 规范中,一个选择器的优先级(权重)由依次串联的a.b.c三个标记来计算 a: ID选择器 如#header b: class选择器如 ...
- Fabric.js的使用
最近项目有一个绘制的功能,搜了一圈发现fabric.js口碑不错,但是文档稀缺,于是东看看西搜搜的把项目的需求都给实现了,想分享一下. 篇幅有点长,但看完后可以轻松驾驭fabric.我的项目是基于VU ...
- Java中几种排序算法
1.冒泡排序算法 通过多次比较(相邻两个数)和交换来实现排序 public class bubble { public static void bubbleSort(int[] a) { int te ...
- Windows version PE System Key
{ }
- Robot Framework:环境安装
Windows Python2.7 前置条件:安装python2.7,下载地址:https://www.p ...
