linux添加新磁盘和创建分区
Linux磁盘概念及其管理工具fdisk:http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2016-08/134664.htm
一、
进入linux虚拟机 右键 open in terminal
su 输入密码切换为root用户
fdisk -l 查看磁盘情况
我的目前只有sda一个磁盘
添加sdb磁盘:关机,菜单栏中找到虚拟机—设置,点击硬盘—添加,按步骤走就可以了,启动虚拟机,就有sdb了
二、
虽然硬盘分区表中最多能存储四个分区,但我们实际使用时一般只分为两个分区,一个是主分区(Primary Partion)一个是扩展分区(extended partition)两种,主分区可以马上被使用但不能再分区,扩展分区必须再进行分区后才能使用,也就是说它必须还要进行二次分区。那么由扩充分区再分下去的是什么呢?它就是逻辑分区(Logical Partion),况且逻辑分区没有数量上限制。 对习惯于使用Dos或Windows的朋友来说,有几个分区就有几个驱动器,并且每个分区都会获得一个字母标识符,然后就可以选用这个字母来指定在这个分区上的文件和目录,它们的文件结构都是独立的,非常好理解。
但是初上手Red Hat Linux吗,可就有点恼人了。因为对Linux用户来说无论有几个分区,分给哪一目录使用,它归根结底就只有一个根目录,一个独立且唯一的文件结构。Red Hat Linux中每个分区都是用来组成整个文件系统的一部分,因为它采用了一种叫“挂载点”的处理方法,它的整个文件系统中包含了一整套的文件和目录,且将一个分区和一个目录联系起来。这时要载入的一个分区将使它的存储空间在一个目录下获得。
1、 fdisk -l 查看磁盘情况
2、 下面对/dev/sdb 进行分区:
[root@localhost Desktop]# fdisk /dev/sdb
Device contains neither a valid DOS partition table, nor Sun, SGI or OSF disklabel
Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x1949791c.
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
After that, of course, the previous content won't be recoverable.
Warning: invalid flag 0x0000 of partition table 4 will be corrected by w(rite)
WARNING: DOS-compatible mode is deprecated. It's strongly recommended to
switch off the mode (command 'c') and change display units to
sectors (command 'u').
Command (m for help): m //输入m查看帮助文档
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition //添加一个新的分区
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)
#fdisk选中/dev/sdb 输入m所有基本选项都出现,输入n新建分区
Command (m for help): n
Command action
e extended //扩展分区
3、有扩展分区和主分区,逻辑分区在扩展分区中建立。注意到括号中的1-4,最多只能建四个主分区(包括扩展分区)。先建一个主分区:
#继续上面的操作
Command (m for help): n
Command action
e extended //扩展分区
p primary partition (1-4) //主分区
p #输入p创建主分区
Partition number (1-4): 1 #分区号为1
First cylinder (1-2610, default 1): #直接回车默认从第一个柱面开始划分
Using default value 1
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (1-2610, default 2610): +2G
#加空间大小,这里有很多种选择:+后面单位可以接M,G,K(记得要大写)表示划分你所加的空间,也可以是柱面数。不管怎样都不能超过该磁盘剩余的空间否则无效。
Command (m for help): p #分好后查看分区信息,刚所做的所有一目了然。
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x1949791c
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 262 2104483+ 83 Linux
4、同上所述建立扩展分区:
Command (m for help): n
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
e
Partition number (1-4): 4
First cylinder (263-2610, default 263):
Using default value 263
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (263-2610, default 2610): +4G
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x1949791c
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 262 2104483+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb4 263 785 4200997+ 5 Extended
5、扩展分区建好就可以在扩展分区建立逻辑分区了
Command (m for help): n
Command action
l logical (5 or over)
p primary partition (1-4)
l #创建逻辑分区
First cylinder (263-785, default 263):
Using default value 263
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (263-785, default 785): +2G
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x1949791c
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 262 2104483+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb4 263 785 4200997+ 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 263 524 2104483+ 83 Linux6、上面显示已经建好一个主分区,一个逻辑分区,但是这些现在还没有生效,需要保存退出。
Command (m for help): w #保存退出
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.7、退出后查看:
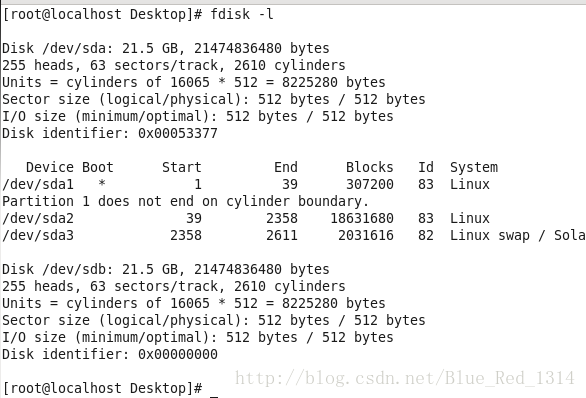
[root@localhost Desktop]# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/sda: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00053377
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 1 39 307200 83 Linux
Partition 1 does not end on cylinder boundary.
/dev/sda2 39 2358 18631680 83 Linux
/dev/sda3 2358 2611 2031616 82 Linux swap / Solaris
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x1949791c
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 262 2104483+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb4 263 785 4200997+ 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 263 524 2104483+ 83 Linux
8、这时需要给它设置文件系统并进行格式化。
mkfs -t ext3 /dev/sdb5
给它设置ext3的文件系统,并格式化。
[root@localhost Desktop]# mkfs -t ext3 /dev/sdb5
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
131648 inodes, 526120 blocks
26306 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=541065216
17 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
7744 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (16384 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 26 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
9、在新建个目录,mkdir /data15 ;
用来挂载这个分区。mount /dev/sdb5 /data15 ;
[root@localhost Desktop]# mkdir /data15;
[root@localhost Desktop]# mount /dev/sdb5 /data15;
10、查看是否挂载成功:df -TH /data15/
[root@localhost Desktop]# df -TH /data15/
Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sdb5 ext3 2.2G 71M 2.0G 4% /data15
11、这样就可以正常使用了。可是重启之后又要手动挂载怎么办?
很简单,我们只要配置一下就OK了。
vim /etc/fstab
编辑文件 将/dev/sdb5 /data15 ext3 defaults 0 0加入即可
#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Mon Oct 24 02:05:13 2016
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
UUID=147a6e0f-8fa6-4bb5-a27a-91aaa7cf178f / ext4 defaults 1 1
UUID=410da4b5-ac87-43e3-ab4a-b33df31e38cf /boot ext4 defaults 1 2
UUID=d0c4ed83-d5d3-4245-af14-1434f4b3438f swap swap defaults 0 0
tmpfs /dev/shm tmpfs defaults 0 0
devpts /dev/pts devpts gid=5,mode=620 0 0
sysfs /sys sysfs defaults 0 0
proc /proc proc defaults 0 0
/dev/sdb5 /data15 ext3 defaults 0 0
~
~
~
~
"/etc/fstab" 16L, 841C 【o】 英文小写字母o,在目前光标所在行的下一行处插入新的一行并开始插入
【O】 英文大写字母O,在目前光标所在行的上一行处插入新的一行并开始插入
:wq保存退出
11、查看
[root@localhost Desktop]# ls /data*
/data15:
lost+found
重复以上操作,对sdb1进行挂载
[root@localhost Desktop]# mkfs -t ext3 /dev/sdb1
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
131648 inodes, 526120 blocks
26306 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=541065216
17 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
7744 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (16384 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 22 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
[root@localhost Desktop]# mount /dev/sdb1 /data5
[root@localhost Desktop]# df -TH /data5/
Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sdb1 ext3 2.2G 71M 2.0G 4% /data5
[root@localhost Desktop]# vim /etc/fstab
[root@localhost Desktop]# ls /data*
/data15:
lost+found
/data5:
lost+found
[root@localhost Desktop]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda2 18G 4.0G 13G 24% /
tmpfs 491M 372K 491M 1% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 291M 34M 242M 13% /boot
/dev/sdb5 2.0G 68M 1.9G 4% /data15
/dev/sdb1 2.0G 68M 1.9G 4% /data5
同上,又创建了一个逻辑分区
[root@localhost Desktop]# fdisk /dev/sdb
WARNING: DOS-compatible mode is deprecated. It's strongly recommended to
switch off the mode (command 'c') and change display units to
sectors (command 'u').
Command (m for help): m
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)
Command (m for help): n
Command action
l logical (5 or over)
p primary partition (1-4)
l
First cylinder (525-785, default 525):
Using default value 525
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (525-785, default 785): 4G
Value out of range.
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (525-785, default 785): 3G
Value out of range.
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (525-785, default 785): 1G
Value out of range.
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (525-785, default 785):
Using default value 785
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x1949791c
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 262 2104483+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb4 263 785 4200997+ 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 263 524 2104483+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb6 525 785 2096451 83 Linux
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
WARNING: Re-reading the partition table failed with error 16: Device or resource busy.
The kernel still uses the old table. The new table will be used at
the next reboot or after you run partprobe(8) or kpartx(8)
Syncing disks.
- 上一篇 将json格式的参数改
linux添加新磁盘和创建分区的更多相关文章
- Virtualbox中Linux添加新磁盘并创建分区
原文:https://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2017-01/139616.htm ----------------------------------------------- ...
- Linux添加新硬盘,设置分区和开机自动挂载之图文教程!
虚拟机添加硬盘的步骤就不多废话了,主要列出添加硬盘后要进行设置的几个详细步骤: 1.查看磁盘信息:fdisk -ls 添加前如下图所示: 添加后如下图: 也可以用:ls /dev/sd*查看,如下图: ...
- Linux 添加新磁盘 && 创建分区 && 挂载
参考: 挂载目录 分区:https://blog.csdn.net/arenn/article/details/78866251 挂载:https://www.jb51.net/article/108 ...
- Linux 添加新磁盘,在线扩充空间
CentOS 7开发环境中的home 目录空间满了,需要增加空间 到虚拟机上执行"ls /sys/class/scsi_host",然后重新扫描SCSI总线来添加设备.如右图.然后 ...
- linux添加新磁盘
先fdisk -l 看一下有哪些没有挂载的盘符. 然后将创建的文件夹与待挂载的盘符绑定,即:mount /dev/vdc /data
- Linux系统格式化新磁盘并挂载分区
Linux系统格式化新磁盘并挂载分区 在虚拟机的设置界面中,我们可以选择添加硬盘 添加好硬盘后,我们输入命令fdisk -l 看到有一个未经分区的硬盘 Fdisk命令编辑这个硬盘 输入n创建分区,p选 ...
- Linux添加新硬盘自动挂载硬盘
Linux添加新硬盘自动挂载硬盘的具体步骤 1.插入新硬盘,启动Linux服务器,使用fdisk -l 查看硬盘 #fdisk -l Disk /dev/sdb: 1000.2 GB, 1000204 ...
- VMWare EXSi 添加新磁盘时 报错 HostStorageSystem.ComputeDiskPartitionInfo 的处理
给 VMWare EXSi 添加新磁盘时报错 : Call "HostStorageSystem.ComputeDiskPartitionInfo" for object &quo ...
- 给Linux添加新用户,新建用户,新建帐号
给Linux添加新用户,新建用户,新建帐号 添加用户组 sudo groupadd groupname 添加用户 sudo useradd username -m -s /sbin/nologin - ...
随机推荐
- linux查看tomcat安装路径
#查看tomcat安装路径 sudo find / -name *tomcat*
- helm-chart4,流程控制和变量
控制结构(模板说法中称为"动作")提供了控制模板生成流程的能力.Helm的模板语言提供了以下控制结构: if/ else用于创建条件块 with 指定范围 range,它提供了一个 ...
- 转:2016年崛起的js项目
近几年 JS 社区创新和演化的速度是有目共睹的,几个月前比较时髦的技术很可能现在已经过时了. 2016 已经过去,你有没有担心错过了什么重要的内容?在这篇调查报告中我们会为你解读社区的主流趋势. 我们 ...
- GMA Round 1 数列求单项
传送门 数列求单项 在数列{$a_n$}中,$a_1=-\frac{1}{4}$,$\frac{1}{a_{n+1}}+\frac{1}{a_n}=\begin{cases}-3(n为偶数)\\3(n ...
- Servlet(9)—HttpServlet和改进Servlet实例
HttpServlet:针对Http协议定义的一个Servlet基类,唯一的功能就是强制类型转换ServletRequest转换成HttpServletRequest,ServletResponse转 ...
- JDBC(8)—Blob
Blob LOB,即:Large Objects(大对象),是用来存储大量的二进制和文本数据的一种数据类型(一个lob字段可以存储多达四个G的数据).LOB分为两种类型:内部LOB和外部LOB --内 ...
- React组件通信技巧
效果图 communication.gif 点击查看Github完整源码 1.父向子通信 直接标签中插入参数即可 //number只是个例子 let _number = this.state.numb ...
- 基于SOUI开发一个简单的小工具
基于DriectUI有很多库,比如 Duilib (免费) soui (免费) DuiVision (免费) 炫彩 (界面库免费,UI设计器付费,不提供源码) skinui (免费使用,但不开放源码, ...
- Could not parse multipart servlet request; nested exception is org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileUploadBase$IOFileUploadException: Processing of multipart/form-data request failed.
org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartException: Could not parse multipart servlet request; nes ...
- Linux输入子系统框架分析(1)
在Linux下的输入设备键盘.触摸屏.鼠标等都能够用输入子系统来实现驱动.输入子系统分为三层,核心层和设备驱动层.事件层.核心层和事件层由Linux输入子系统本身实现,设备驱动层由我们实现.我们在设备 ...