从动态代理到Spring AOP(中)
一.前言
上一章节主要介绍了JDK动态代理和CGLIB动态代理:https://www.cnblogs.com/GrimMjx/p/11194283.html
这一章主要结合我们之前学习的动态代理的基础来学习Sring AOP,本章学习需要Spring IOC的基础。首先会有一个Spring AOP的例子,后面逐渐深入会把一些关键的源码贴出来供大家学习。
二.一个栗子
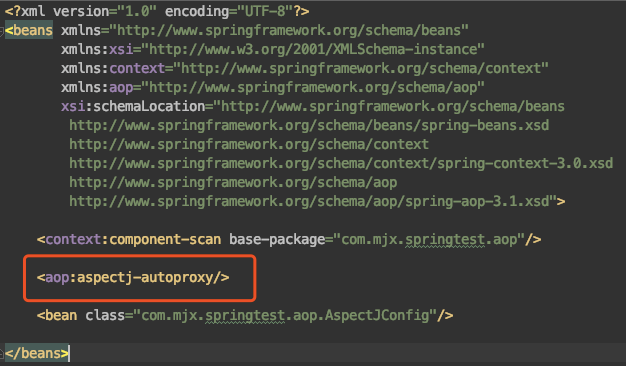
2.1 创建Spring配置文件
本例子使用xml的方式来配置Spring,如果你用Springboot可以用@EnableAspectJAutoProxy来开启AOP功能。xml配置Spring是否使用注解AOP的方式是<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>,配置文件中有这句话Spring就会支持注解的AOP。
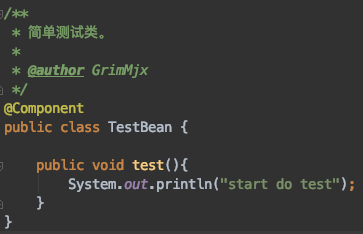
2.2 创建要被代理的bean
这个bean的某个方法可能封装着核心逻辑,如果我们想对这个方法的前后加入日志或者其他逻辑进行增强,直接修改这个bean不符合面向对象的设计,还好Spring AOP帮我们做到这一点。那我们先创建一个简单的bean:
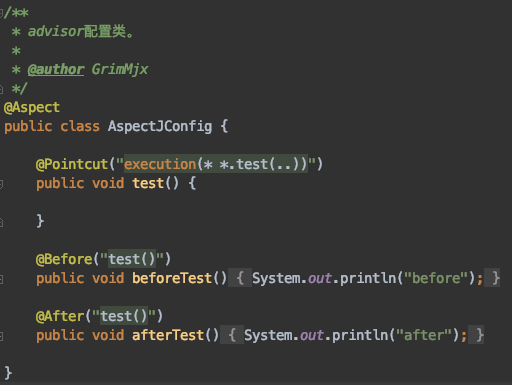
2.3 创建Advisor
Spring2.0可以采用@AspectJ注解对POJO进行标记,从而定义一个包含切点信息和增强横切逻辑的切面然后织入匹配的目标Bean中
在AspectJConfig中,我们简单的对test方法前后记录日志。记住光用@AspectJ注解是不够的。要么再添加@Component注解要么在xml添加这个bean,官方解释如下:
You may register aspect classes as regular beans in your Spring XML configuration, or autodetect them through classpath scanning - just like any other Spring-managed bean. However, note that the @Aspect annotation is not sufficient for autodetection in the classpath: For that purpose, you need to add a separate @Component annotation (or alternatively a custom stereotype annotation that qualifies, as per the rules of Spring’s component scanner).
再来看一下代码:
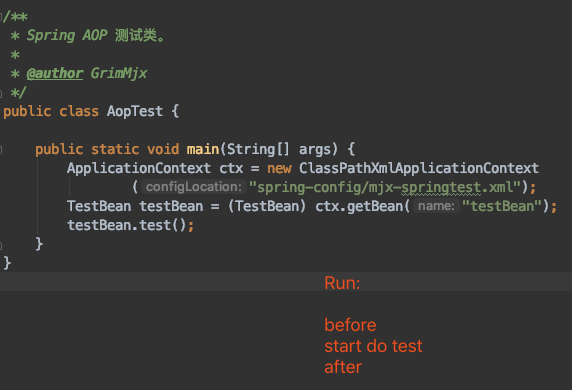
2.4 测试
我们可以写一个简单的测试类,通过容器拿到TestBean这个bean,然后调用test方法,看一下结果:
三.源码赏析
最好带着问题去看源码,要不然自己也是跟着走一遍,源码是无尽,开发思想是有尽的。比如今天看了ConcurrentHashMap的size方法对cas的优化,再看看LongAdder是咋玩的,学到了分散思想。
-谁来创建AOP的?
-谁来解析@Aspect注解的类?
-JDK动态代理怎么创建的?
-CGlib动态代理怎么创建的?
-有什么好的设计方式吗?
-等等
3.1 谁来创建?
是AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator。(名字就很通俗易懂)
Spring扫到<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>后,AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser会注册这位创建者。对于Spring AOP的实现,AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator是负责代理的创建者,也是我们赏析的开始。先来看下这个创建者的类图:
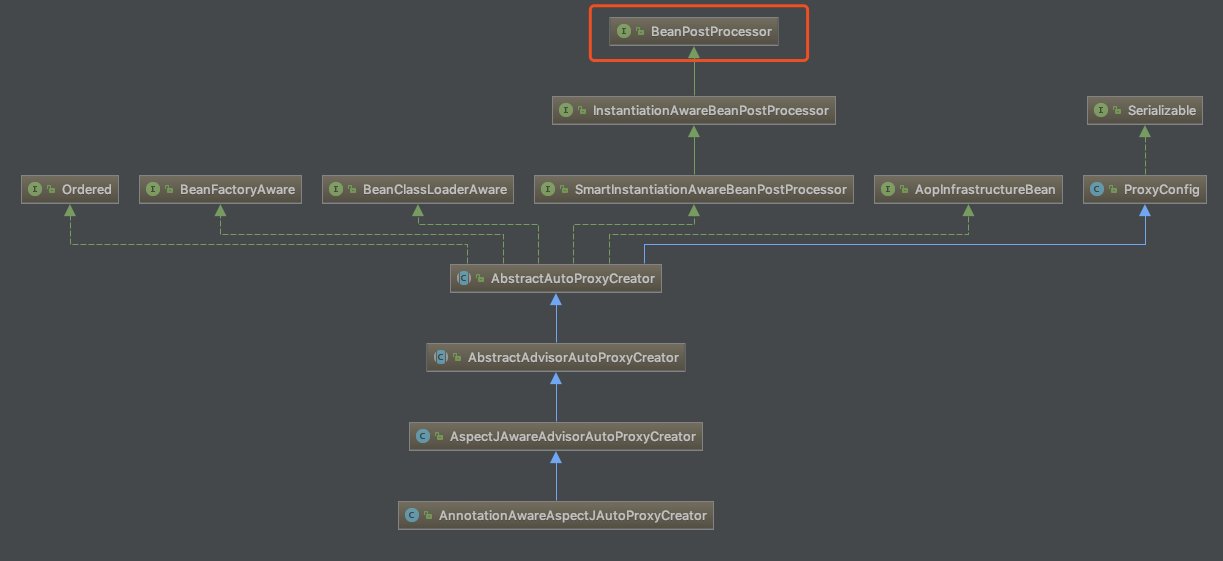
当Spring加载每个Bean的时候会在实例化前调用postProcessorAfterInitialization方法,对于AOP的逻辑也由此开始:

3.2 获取所有增强器
还记得之前的栗子吗?有个类是有@AspectJ注解的AspectJConfig类,这个类里面有@PointCut注解,这个注解的意思是对哪些方法进行增强,这里@Pointcut("execution(* *.test(..))")表示要对所有test方法进行增强。通过不同的切点表达函数可以实现对某些你想要类或者方法进行增强。
那么,什么叫增强器?Spring AOP在JoinPoint“周围”维护一系列的拦截器。有哪些Advice呢?
- @Before - 在JoinPoint方法之前执行
- @AfterReturning - 在JoinPoint方法正常执行后执行
- @AfterThrowing - 在JoinPoint方法抛出异常退出并执行
- @After - 无论JoinPoint方法正常返回还是异常返回都会执行
- @Around - 在JoinPoint方法前后执行
例子中,有2个增强器。那我们看下源码是如何拿到所有的增强器的,看这个方法:org.springframework.aop.aspectj.annotation.BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilder#buildAspectJAdvisors
/**
* Look for AspectJ-annotated aspect beans in the current bean factory,
* and return to a list of Spring AOP Advisors representing them.
* <p>Creates a Spring Advisor for each AspectJ advice method.
* @return the list of {@link org.springframework.aop.Advisor} beans
* @see #isEligibleBean
*/
public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors() {
List<String> aspectNames = null;
synchronized (this) {
aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
List<Advisor> advisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>();
aspectNames = new LinkedList<String>();
// 获取容器内所有的beanName
String[] beanNames =
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false);
// for循环,找出增强方法
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 过滤不合法的bean,子类实现
if (!isEligibleBean(beanName)) {
continue;
}
// We must be careful not to instantiate beans eagerly as in this
// case they would be cached by the Spring container but would not
// have been weaved
// 获取到bean类型
Class beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName);
if (beanType == null) {
continue;
}
// 如果存在@AspectJ注解
if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) {
// 加入list
aspectNames.add(beanName);
AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);
if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName); // 解析获取增强方法
List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
// 放入缓存
this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors);
}
else {
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
}
advisors.addAll(classAdvisors);
}
else {
// Per target or per this.
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bean with name '" + beanName +
"' is a singleton, but aspect instantiation model is not singleton");
}
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new PrototypeAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
}
this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames;
return advisors;
}
}
if (aspectNames.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.EMPTY_LIST;
}
List<Advisor> advisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>();
for (String aspectName : aspectNames) {
// 从缓冲拿出增强器
List<Advisor> cachedAdvisors = this.advisorsCache.get(aspectName);
if (cachedAdvisors != null) {
advisors.addAll(cachedAdvisors);
}
else {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = this.aspectFactoryCache.get(aspectName);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
return advisors;
}
到此我们找到了所有声明@AspectJ注解的类,接下来是不是该找用@Before,@After等等那些注解的方法了?
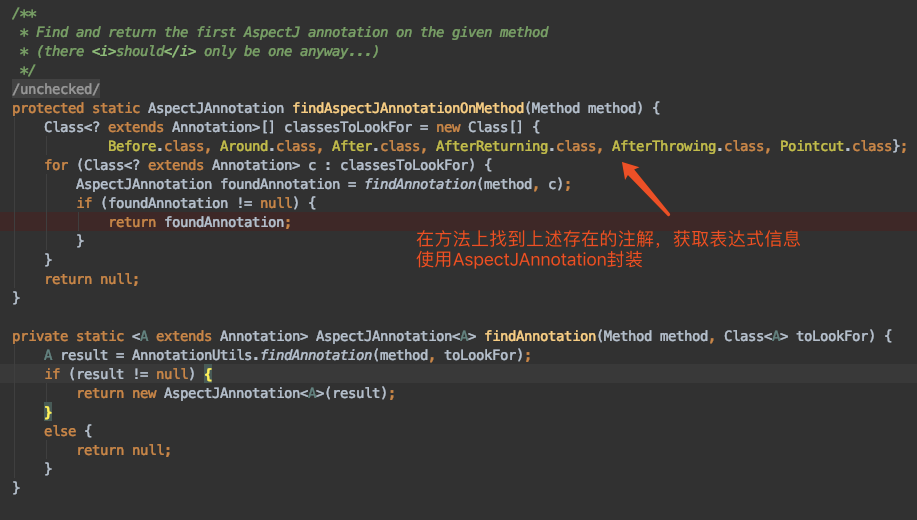
等等,我们要的是Advisor,所有增强由Advisor的实现类InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl封装,不同的注解会封装成不同的增强器。
public Advice getAdvice(Method candidateAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut ajexp,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aif, int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) {
/** 检查开始 */
Class<?> candidateAspectClass = aif.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
validate(candidateAspectClass);
// 之前讲过,获取到方法上的注解信息
AspectJAnnotation<?> aspectJAnnotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (aspectJAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
// If we get here, we know we have an AspectJ method.
// Check that it's an AspectJ-annotated class
if (!isAspect(candidateAspectClass)) {
throw new AopConfigException("Advice must be declared inside an aspect type: " +
"Offending method '" + candidateAdviceMethod + "' in class [" +
candidateAspectClass.getName() + "]");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Found AspectJ method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
/** 检查结束 */ // 根据不同的注解生成不同的增强器
AbstractAspectJAdvice springAdvice;
switch (aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType()) {
case AtBefore:
springAdvice = new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, ajexp, aif);
break;
case AtAfter:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, ajexp, aif);
break;
case AtAfterReturning:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterReturningAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, ajexp, aif);
AfterReturning afterReturningAnnotation = (AfterReturning) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterReturningAnnotation.returning())) {
springAdvice.setReturningName(afterReturningAnnotation.returning());
}
break;
case AtAfterThrowing:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, ajexp, aif);
AfterThrowing afterThrowingAnnotation = (AfterThrowing) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing())) {
springAdvice.setThrowingName(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing());
}
break;
case AtAround:
springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, ajexp, aif);
break;
case AtPointcut:
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Processing pointcut '" + candidateAdviceMethod.getName() + "'");
}
return null;
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"Unsupported advice type on method " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
// Now to configure the advice...
springAdvice.setAspectName(aspectName);
springAdvice.setDeclarationOrder(declarationOrderInAspect);
String[] argNames = this.parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (argNames != null) {
springAdvice.setArgumentNamesFromStringArray(argNames);
}
springAdvice.calculateArgumentBindings();
return springAdvice;
}
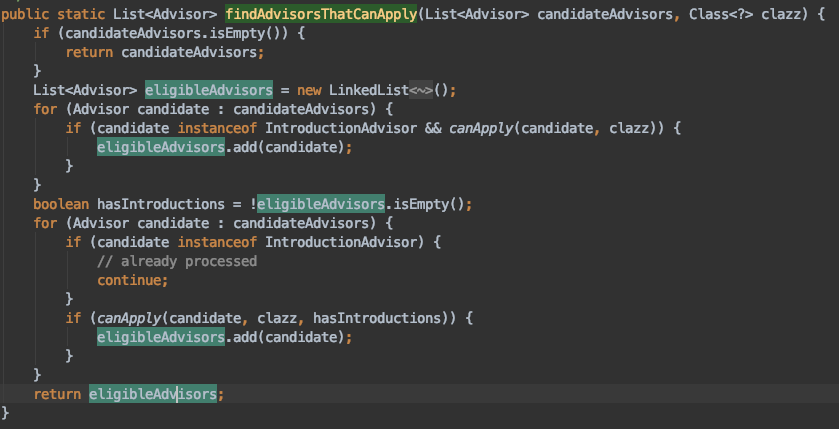
3.3 获取匹配的增强器
前面讲了获取所有的增强器,不一定都适用于现在的bean,我们要选出合适的增强器,也就是满足配置的增强器,具体方法在:org.springframework.aop.support.AopUtils#findAdvisorsThatCanApply:
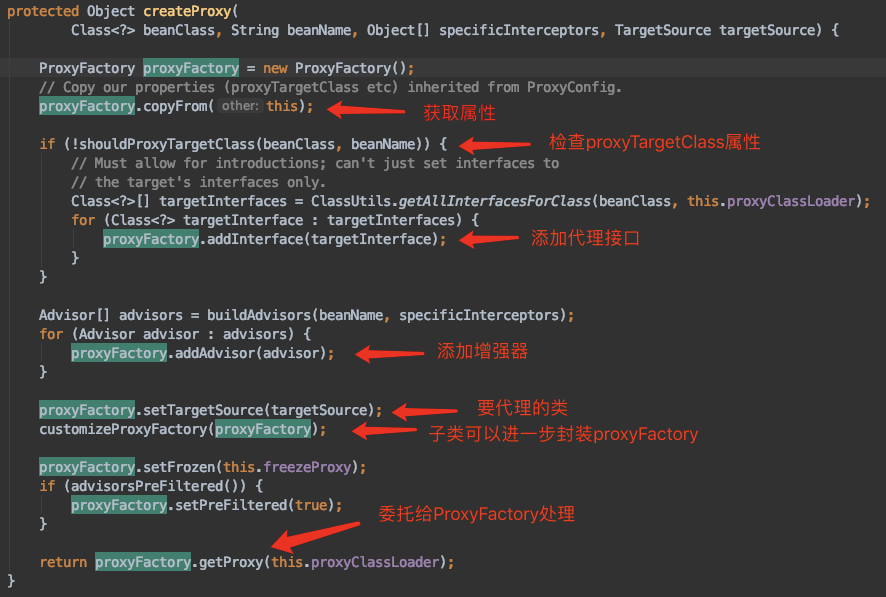
3.4 创建代理
首先看这个方法:org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#createProxy
那么接下来就是代理的创建与获取了:
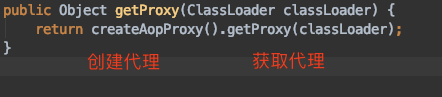
我们先看下如何创建代理的,注释如图:
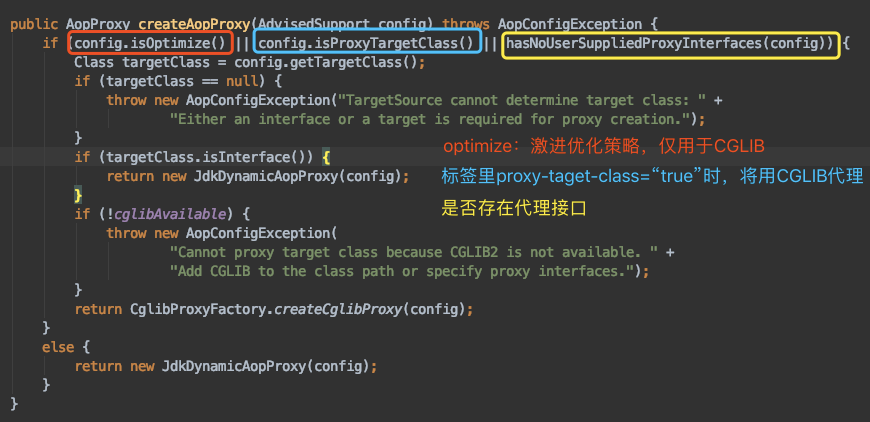
所以我们可以得出以下结论:
- 如果目标类实现了接口,默认使用JDK动态代理实现AOP,但是也可以强制使用CGLIB实现AOP
- 如果目标类没有实现接口,那么必须采用CGLIB库
3.5 调用过程
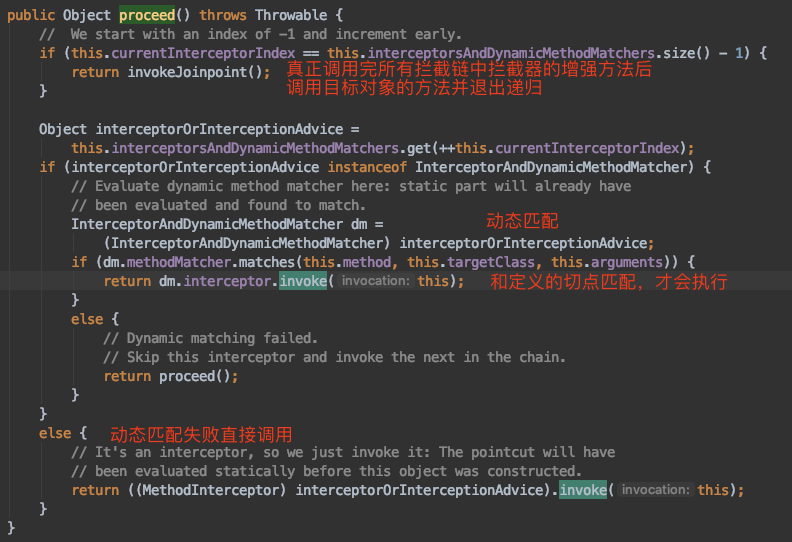
最后就是方法调用的关键方法了,可以说最核心的方法就是这个了,org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation#proceed:
Spring aop的精华都在于此,核心就是递归思想,调用完了拦截链(所有增强器)中的所有拦截器方法后,再调用目标对象的方法
到底invoke方法是啥呢?见下图,我们可以看到是一个接口的方法,不同增强器有不同的实现,我们这里就看Before和After的:

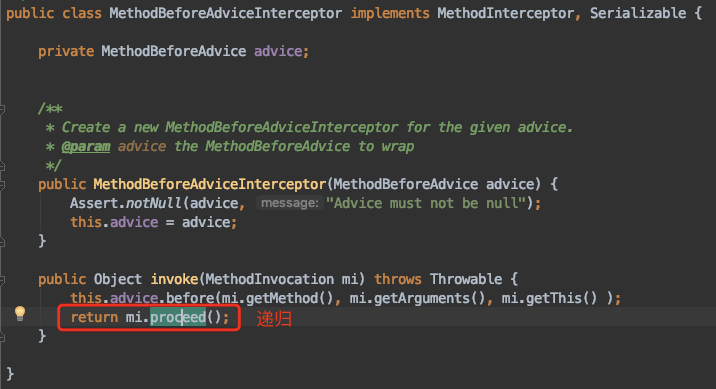
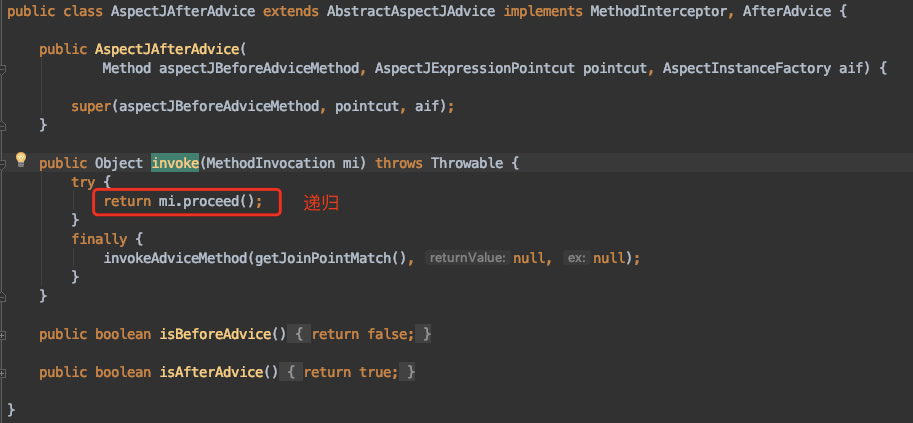
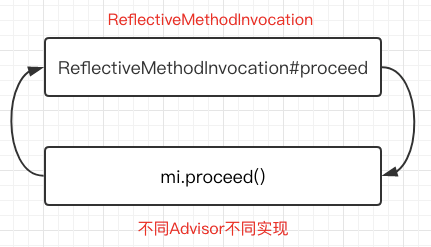
最后画一张图吧,这样比较好理解一点:
四.总结
过程就是先拿出所有适用的Adivsors,然后构造拦截链(chain),最后进行串行调用(递归)。
最后还是希望多写几个demo来实践一下,打打断点。还是那句话,源码是看不完的,最重要的是思想。这是我第一家公司技术总监老羊说的。我觉得还是挺收益的。本文还有很多不足之处,如果有写的不对的地方还请指点一下,感谢。
从动态代理到Spring AOP(中)的更多相关文章
- java:struts框架2(方法的动态和静态调用,获取Servlet API三种方式(推荐IOC(控制反转)),拦截器,静态代理和动态代理(Spring AOP))
1.方法的静态和动态调用: struts.xml: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCT ...
- java中代理,静态代理,动态代理以及spring aop代理方式,实现原理统一汇总
若代理类在程序运行前就已经存在,那么这种代理方式被成为 静态代理 ,这种情况下的代理类通常都是我们在Java代码中定义的. 通常情况下, 静态代理中的代理类和委托类会实现同一接口或是派生自相同的父类. ...
- 从动态代理到Spring AOP(上)
一.前言 虽然平时日常开发很少用到动态代理,但是动态代理在底层框架等有着非常重要的意义.比如Spring AOP使用cglib和JDK动态代理,Hibernate底层使用了javassit和cglib ...
- 反射实现 AOP 动态代理模式(Spring AOP 的实现原理)
枚举 在某些情况下,一个类的对象是有限而且固定的,比如季节类,它只有4个对象.这种实例有限而且固定的类,在Java里被称为枚举类. 枚举就是要让某个类型的变量的取值只能为若干个固定值中的一个,否则,编 ...
- 反射实现 AOP 动态代理模式(Spring AOP 的实现 原理)
好长时间没有用过Spring了. 突然拿起书.我都发现自己对AOP都不熟悉了. 其实AOP的意思就是面向切面编程. OO注重的是我们解决问题的方法(封装成Method),而AOP注重的是许多解决解决问 ...
- 通过JDK动态代理实现 Spring AOP
1.新建一个目标类 接口:public interface IUserService //切面编程 public void addUser(); public void updateUser( ); ...
- Spring AOP中的动态代理
0 前言 1 动态代理 1.1 JDK动态代理 1.2 CGLIB动态代理 1.2.1 CGLIB的代理用法 1.2.2 CGLIB的过滤功能 2 Spring AOP中的动态代理机制 2.1 ...
- 转:Spring AOP中的动态代理
原文链接:Spring AOP中的动态代理 0 前言 1 动态代理 1.1 JDK动态代理 1.2 CGLIB动态代理 1.2.1 CGLIB的代理用法 1.2.2 CGLIB的过滤功能 2 S ...
- Spring AOP中的JDK和CGLib动态代理哪个效率更高?
一.背景 今天有小伙伴面试的时候被问到:Spring AOP中JDK 和 CGLib动态代理哪个效率更高? 二.基本概念 首先,我们知道Spring AOP的底层实现有两种方式:一种是JDK动态代理, ...
随机推荐
- 【时间工具】整理下java时间换算专题
首先总结了一下日期转换基础,最常用的两个工具类Date与calender,转换方法如下: package com.zzt.spider; import java.text.SimpleDateForm ...
- idea上MyBatis第一个例子
接着上面创建的maven项目来. 1.java目录下创建cn.happy.entity包 2.idea下创建数据库连接 配置连接参数 3.把数据库表变成实体类 导入成功,改一下包名就可以用了 4.新建 ...
- Oracle Awr报告_生成
AWR的概念 Oracle数据库是一个使用量很多的数据库,关于Oracle数据库的性能.Oracle10g以后,Oracle提供了一个性能检测的工具:AWR(Automatic Workload Re ...
- POJ 1651:Multiplication Puzzle(区间DP)
http://poj.org/problem?id=1651 题意:给出n个数字,每取中间一个数,就会使得权值加上中间这个数和两边的乘积,求取剩两个数最少的权值是多少. 思路:区间dp. 一开始想了挺 ...
- VueRouter认识
1. 什么是路由? 路由(vue-router)是负责将进入的浏览器请求映射到特定的 组件 代码中.即决定了由谁(组件)去响应客户端请求.简单说路由就是url地址和对应的资源的映射,通过一个路径的ur ...
- django基础知识之上传图片:
上传图片 当Django在处理文件上传的时候,文件数据被保存在request.FILES FILES中的每个键为<input type="file" name="& ...
- C# 中的Request对象的应用
QueryString属性:例:页面1:<a href="页面2.aspx?uanme=王华&uage=18">提交</a> ...
- .Net Core 创建和使用中间件
1. 定义中间内容 1.1 必须有一个RequestDelegate 委托用了进入一个中间件 1.2 通过构造函数设置这个RequestDelegate委托 1.3 必须有一个方法Task Invok ...
- 算法导论--最小生成树(Kruskal和Prim算法)
转载出处:勿在浮沙筑高台http://blog.csdn.net/luoshixian099/article/details/51908175 关于图的几个概念定义: 连通图:在无向图中,若任意两个顶 ...
- Python入门基础(9)__面向对象编程_1
定义一个只包含方法的类 class 类名: def 方法1(self,参数列表): pass def 方法2(self,参数列表): pass 当一个类定义之后,要使用这个类来创键对象.语法如下: 对 ...
