【JDK】JDK源码分析-LinkedList
概述
相较于 ArrayList,LinkedList 在平时使用少一些。
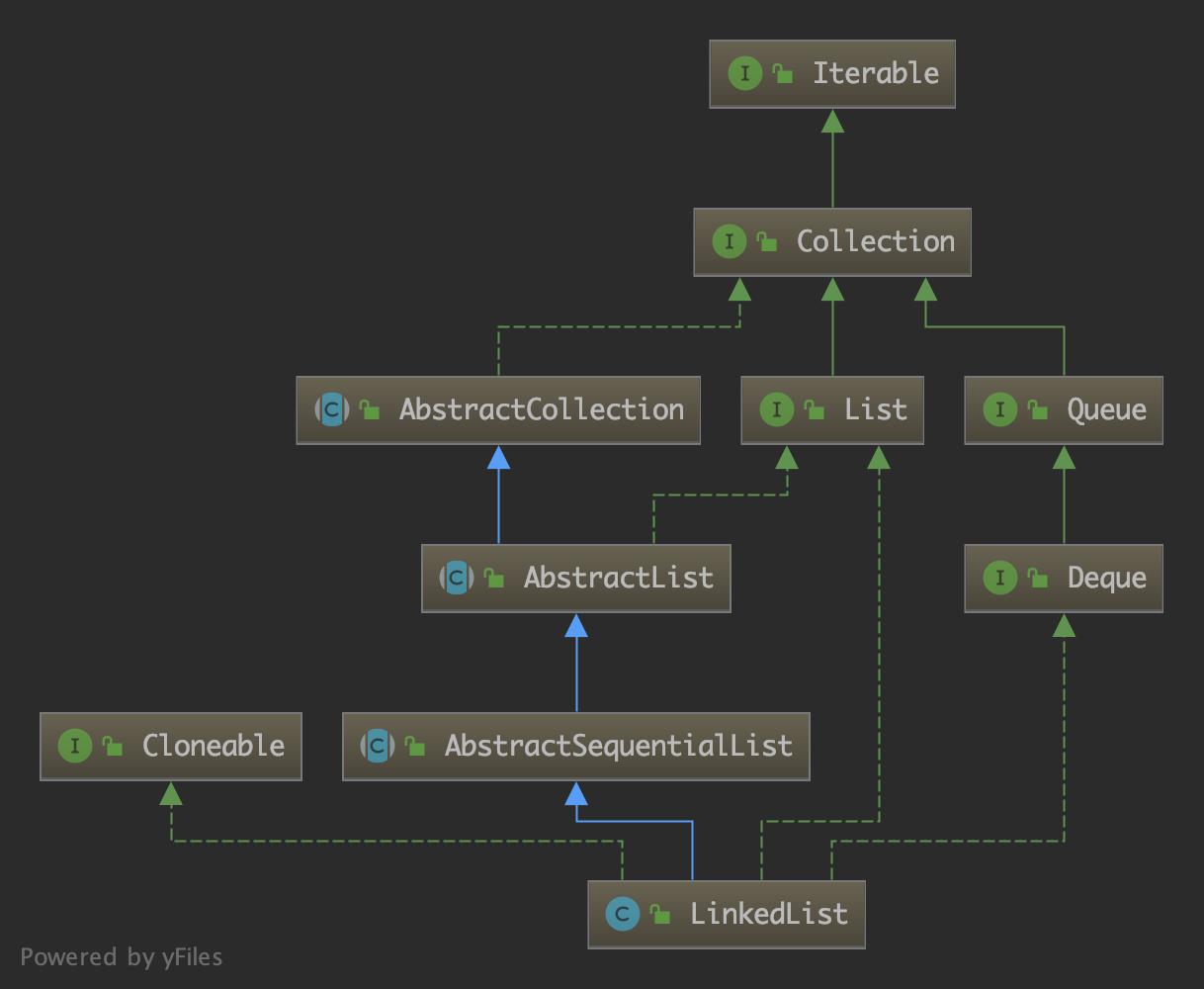
LinkedList 内部是一个双向链表,并且实现了 List 接口和 Deque 接口,因此它也具有 List 的操作以及双端队列和栈的性质。双向链表的结构如下:

前文分析了 Queue 和 Deque 接口,正是因为 LinkedList 实现了 Deque 接口。LinkedList 的继承结构如下:
结点类 Node
查看 LinkedList 的源码可发现它内部有个嵌套类 Node,代码如下:
private static class Node<E> {
E item; // 存储的数据
Node<E> next; // 后继结点
Node<E> prev; // 前驱结点
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
LinkedList 是双向链表的实现,而该 Node 类则是链表的结点。
此外,LinkedList 还有几个成员变量如下:
// list 的长度
transient int size = 0; // 链表头结点
transient Node<E> first; // 链表尾结点
transient Node<E> last;
构造器
LinkedList 有两个构造器,如下:
public LinkedList() {
}
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
PS: 由于链表的容量可以一直增加,因此没有指定容量的构造器。
其中第一个为无参构造器;第二个为使用指定的集合构造,并调用 addAll(),继续跟进该方法,代码如下:
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
// 将集合元素转为数组
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
// 获取当前链表的前驱和后继结点
Node<E> pred, succ;
if (index == size) { // 尾结点的前驱和后继结点
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else { // 若非尾结点,获取指定位置的结点
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
// 循环将数组中的元素插入到链表
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
// 若插入到末尾,则数组中的最后一个元素就是尾结点
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
// 若插入到指定位置,将数组中最后一个元素与下一个位置关联起来
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
其中 node(index) 方法为获取指定位置的结点,代码如下:
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
// 若下标在前一半,则从前往后遍历;否则从后往前遍历
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
该方法通过遍历链表获取指定的元素。
值得注意的是,该方法并非直接从头到尾遍历整个链表,而是先判断下标的位置,若在前一半则从前往后遍历;否则就从后往前遍历。这样能减少遍历结点的个数。
PS: 前文「数据结构与算法笔记(一)」对链表进行过分析,由于其内存空间非连续,因此不支持随机访问(下标访问)。所以,查询某个结点是通过遍历整个链表来实现的。
与此同时,get(index) 方法内部也是这样实现的:
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
常用方法
之前分析 Queue 和 Deque 的时候提到:Queue 中的方法在 Deque 中都有对应的。下面简单分析 LinkedList 中一些常用的方法。
新增结点方法:add(), addLast(), offerLast()
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
可以看到他们都是调用了同一个方法 linkLast(e) 实现的,如下:
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
// 若链表为空,则新结点为头结点
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
// 若链表不为空,将新结点插入到链表尾部
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
该操作就是将指定的结点添加到链表末尾。
删除结点方法:poll(), pollFirst(), removeFirst()
public E poll() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
public E pollFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
可以看到这三个方法都是调用 unlinkFirst() 方法实现的,其代码如下:
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node<E> next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
该方法的操作就是从链表头部移除一个结点。
向单链表插入和删除结点的操作示意图如下(双链表比这里多了前驱结点):

栈的入栈(push)和出栈(pop)操作:
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
可以看到这两个方法直接调用了双端队列的实现方法。即,该栈是一个「链式栈」。
线程安全性
线程安全的概念不再赘述。分析以下场景:
若有线程 T1 对 LinkedList 进行遍历,同时线程 T2 对其进行结构性修改。
对 LinkedList 的遍历是通过 listIterator(index) 方法实现的,如下:
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> {
private Node<E> lastReturned;
private Node<E> next;
private int nextIndex;
// 初始化时二者是相等的
private int expectedModCount = modCount;
ListItr(int index) {
// assert isPositionIndex(index);
next = (index == size) ? null : node(index);
nextIndex = index;
}
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasNext())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next;
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
return lastReturned.item;
}
public void remove() {
checkForComodification();
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
Node<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next;
unlink(lastReturned);
if (next == lastReturned)
next = lastNext;
else
nextIndex--;
lastReturned = null;
expectedModCount++;
}
// ...
// 是否有其他线程对当前对象进行结构修改
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
该类的 next(), add(e) 等方法在执行时会检测 modCount 与创建时是否一致(checkForComodification() 方法),从而判断是否有其他线程对该对象进行了结构修改,若有则抛出 ConcurrentModificationException 异常。
因此,LinkedList 是线程不安全的。
小结
1. LinkedList 内部是「双向链表」,同时实现了 List 接口和 Deque 接口,因此也具备 List、双端队列和栈的性质;
2. 线程不安全。
Stay hungry, stay foolish.

PS: 本文首发于微信公众号。
【JDK】JDK源码分析-LinkedList的更多相关文章
- JDK Collection 源码分析(2)—— List
JDK List源码分析 List接口定义了有序集合(序列).在Collection的基础上,增加了可以通过下标索引访问,以及线性查找等功能. 整体类结构 1.AbstractList 该类作为L ...
- JDK AtomicInteger 源码分析
@(JDK)[AtomicInteger] JDK AtomicInteger 源码分析 Unsafe 实例化 Unsafe在创建实例的时候,不能仅仅通过new Unsafe()或者Unsafe.ge ...
- 设计模式(十八)——观察者模式(JDK Observable源码分析)
1 天气预报项目需求,具体要求如下: 1) 气象站可以将每天测量到的温度,湿度,气压等等以公告的形式发布出去(比如发布到自己的网站或第三方). 2) 需要设计开放型 API,便于其他第三方也能接入气象 ...
- JDK源码分析 – LinkedList
LinkedList类的申明 public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements L ...
- JDK Collection 源码分析(3)—— Queue
@(JDK)[Queue] JDK Queue Queue:队列接口,对于数据的存取,提供了两种方式,一种失败会抛出异常,另一种则返回null或者false. 抛出异常的接口:add,remove ...
- JDK Collection 源码分析(1)—— Collection
JDK Collection JDK Collection作为一个最顶层的接口(root interface),JDK并不提供该接口的直接实现,而是通过更加具体的子接口(sub interface ...
- 源码分析--LinkedList(JDK1.8)
LinkedList与ArrayList一样都是List接口的实现类,底层用双向链表实现. LinkedList本身用一个内部类实现链表元素. private static class Node< ...
- ArrayList 和 LinkedList 源码分析
List 表示的就是线性表,是具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列.它主要有两种存储结构,顺序存储和链式存储,分别对应着 ArrayList 和 LinkedList 的实现,接下来以 jdk7 代码为例 ...
- java集合系列之LinkedList源码分析
java集合系列之LinkedList源码分析 LinkedList数据结构简介 LinkedList底层是通过双端双向链表实现的,其基本数据结构如下,每一个节点类为Node对象,每个Node节点包含 ...
随机推荐
- 支持向量机 (二): 软间隔 svm 与 核函数
软间隔最大化(线性不可分类svm) 上一篇求解出来的间隔被称为 "硬间隔(hard margin)",其可以将所有样本点划分正确且都在间隔边界之外,即所有样本点都满足 \(y_{i ...
- 浅入深出Vue:数据渲染
今天来正式开始 vue的学习,首当其冲的当然是数据的渲染.毕竟数据就是拿来看的,看看如果使用 vue来展示数据. 为什么渲染 俗话说 "人靠衣装马靠鞍", 那咱们的代码就是得靠 U ...
- 【入门】WebRTC知识点概览 | 内有技术干货免费下载
什么是WebRTC WebRTC 即Web Real-Time Communication(网页实时通信)的缩写,是一个支持网页浏览器之间进行实时数据传输(包括音频.视频.数据流)的技术.经过多年的发 ...
- 【面试】MySQL 中NULL和空值的区别?
做一个积极的人 编码.改bug.提升自己 我有一个乐园,面向编程,春暖花开! 01 小木的故事 作为后台开发,在日常工作中如果要接触Mysql数据库,那么不可避免会遇到Mysql中的NULL和空值.那 ...
- JavaWeb入门_模仿天猫整站Tmall_JavaEE实践项目
Tmall_JavaEE 技术栈 Servlet + Jsp + Tomcat , 是Java Web入门非常好的练手项目 效果展示: 模仿天猫前台 模仿天猫后台 项目简介 关联项目 github - ...
- (数据科学学习手札64)在jupyter notebook中利用kepler.gl进行空间数据可视化
一.简介 kepler.gl是由Uber开发的进行空间数据可视化的开源工具,是Uber内部进行空间数据可视化的默认工具,通过其面向Python开放的接口包keplergl,我们可以在jupyter n ...
- JavaScript的数据类型及其检测
一.什么是数据类型 1.基本类型 值是不可改变的 var name = 'java'; name.toUpperCase(); // 输出 'JAVA' console.log(name); // 输 ...
- Web自动化测试 二 ----- HTML
HTML 一.结构 html> 与 </html> 之间的文本描述网页 <body> 与 </body> 之间的文本是可见的页面内容 <h1> 与 ...
- 【名额有限】云开发AI拓展能力等你来体验!
这次来了个超厉害的新能力! 人脸智能打马赛克.人脸智能裁剪--各种操作,都能一步到位! 迫不及待想体验,戳链接:https://wj.qq.com/s2/3986990/e0ef/ 还没有搞懂,继续往 ...
- HDU 1584:蜘蛛牌(DFS)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1584 题意:要让小的牌放到大的牌上面最少移动的距离. 思路:看成让大的牌放在小的牌上面了...用一个标记数组vi ...
