最短路径(Floyd算法)
声明:图片及内容基于https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1oa4y1e7Qt?from=articleDetail
多源最短路径的引入

Floyd算法
原理

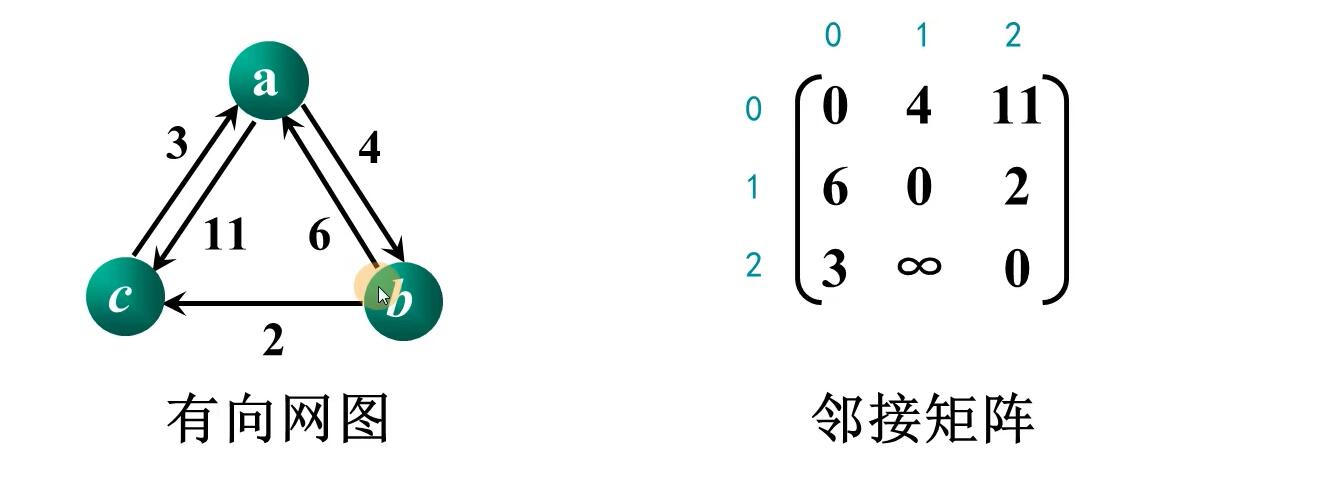

加入a:

加入b:

加入c:

数据结构


核心代码
Floyd()
- void MGraph::Floyd(){
- for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
- for(int j=0;j<vertexNum;j++){
- dist[i][j]=arc[i][j]; //dist数组初始化
- if(dist[i][j]!=INFINIT&&dist[i][j]!=0) //dist为INFINIT则无路径,dist为0则指向自己
- path[i][j]=vertex[i]+vertex[j]; //path数组初始化
- else
- path[i][j]=""; //不符合则path为空串
- }
- }
- for(int k=0;k<vertexNum;k++){ //k个顶点循环k次
- for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){ //k每循环一次,要更新dist和path数组
- for(int j=0;j<vertexNum;j++){
- if(dist[i][k]+dist[k][j]<dist[i][j]){
- dist[i][j]=dist[i][k]+dist[k][j];
- //这里两个path拼接的时候,第一个字符串的最后一个字符和第二个字符串的第一个字符重复
- //用substr去除第一个字符串的最后一个字符
- string tmp=path[i][k].substr(0,path[i][k].length()-1);
- path[i][j]=tmp+path[k][j];
- }
- }
- }
- }
- displayDist();
- displayPath();
- }
完整代码
- #include<iostream>
- #define MAX 50
- #define INFINIT 65535
- #include <string>
- using namespace std;
- class MGraph{
- private:
- int vertexNum,arcNum; //顶点数,边数
- int arc[MAX][MAX]; //邻接矩阵
- string vertex[MAX]; //顶点信息
- int dist[MAX][MAX];
- string path[MAX][MAX];
- public:
- MGraph(string v[],int n,int e);
- void display();
- void Floyd();
- void displayDist();
- void displayPath();
- };
- void MGraph::Floyd(){
- for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
- for(int j=0;j<vertexNum;j++){
- dist[i][j]=arc[i][j]; //dist数组初始化
- if(dist[i][j]!=INFINIT&&dist[i][j]!=0) //dist为INFINIT则无路径,dist为0则指向自己
- path[i][j]=vertex[i]+vertex[j]; //path数组初始化
- else
- path[i][j]=""; //不符合则path为空串
- }
- }
- for(int k=0;k<vertexNum;k++){ //k个顶点循环k次
- for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){ //k每循环一次,要更新dist和path数组
- for(int j=0;j<vertexNum;j++){
- if(dist[i][k]+dist[k][j]<dist[i][j]){
- dist[i][j]=dist[i][k]+dist[k][j];
- //这里两个path拼接的时候,第一个字符串的最后一个字符和第二个字符串的第一个字符重复
- //用substr去除第一个字符串的最后一个字符
- string tmp=path[i][k].substr(0,path[i][k].length()-1);
- path[i][j]=tmp+path[k][j];
- }
- }
- }
- }
- displayDist();
- displayPath();
- }
- void MGraph::displayDist(){ //打印dist数组
- cout<<"dist数组:"<<endl;
- for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
- for(int j=0;j<vertexNum;j++){
- cout<<dist[i][j]<<"\t";
- }
- cout<<endl;
- }
- }
- void MGraph::displayPath(){ //打印path数组
- cout<<"path数组:" <<endl;
- for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
- for(int j=0;j<vertexNum;j++){
- cout<<path[i][j]<<"\t";
- }
- cout<<endl;
- }
- }
- MGraph::MGraph(string v[],int n,int e){ //n是顶点数,e是边数
- vertexNum=n;
- arcNum=e;
- for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
- vertex[i]=v[i];
- }
- for(int i=0;i<arcNum;i++){ //初始化邻接矩阵
- for(int j=0;j<arcNum;j++){
- if(i==j) arc[i][j]=0;
- else arc[i][j]=INFINIT;
- }
- }
- int vi,vj,w;
- for(int i=0;i<arcNum;i++){
- cout<<"请输入有向边的两个顶点和这条边的权值"<<endl;
- cin>>vi>>vj>>w; //输入边依附的两个顶点的编号 和权值
- arc[vi][vj]=w; //有边标志
- }
- }
- void MGraph::display(){
- cout<<"邻接矩阵:"<<endl;
- for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
- for(int j=0;j<vertexNum;j++){
- if(arc[i][j]==INFINIT)
- cout<<"∞"<<"\t";
- else cout<<arc[i][j]<<"\t";
- }
- cout<<endl;
- }
- cout<<endl;
- cout<<"结点信息:"<<endl;
- for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
- cout<<vertex[i]<<" ";
- }
- cout<<endl;
- }
- int main(){
- int n,e;
- string v[MAX];
- cout<<"请输入顶点数和边数"<<endl;
- cin>>n>>e;
- cout<<"请输入顶点信息"<<endl;
- for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
- cin>>v[i];
- }
- MGraph mgraph(v,n,e);
- mgraph.display();
- mgraph.Floyd();
- return 0;
- }
输入:
3 5
a b c
0 1 4
0 2 11
1 0 6
1 2 2
2 0 3
输出:
邻接矩阵:
0 4 11
6 0 2
3 ∞ 0
结点信息:
a b c
dist数组:
0 4 6
5 0 2
3 7 0
path数组:
ab abc
bca bc
ca cab
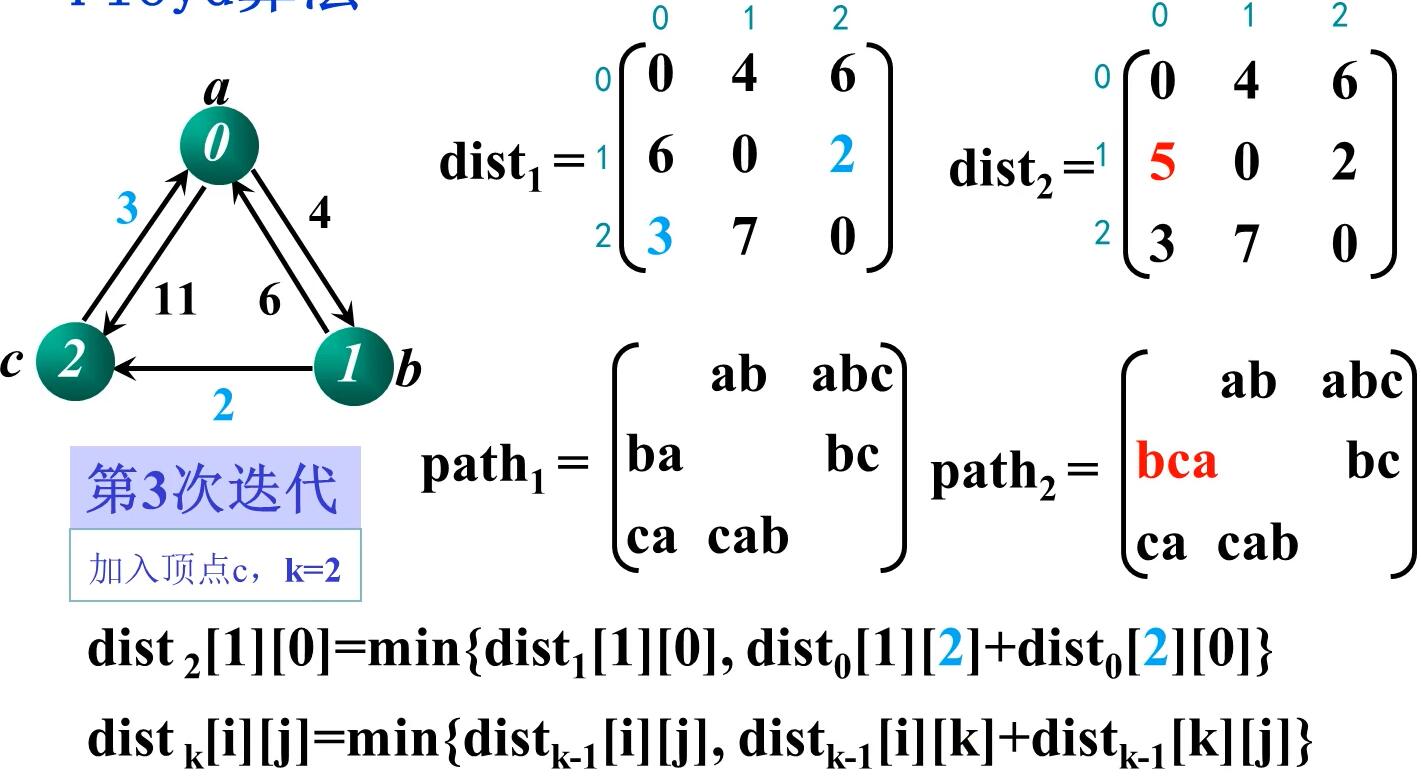
例题:娱乐中心选址

- #include<iostream>
- #define MAX 50
- #define INFINIT 65535
- #include <string>
- using namespace std;
- class MGraph{
- private:
- int vertexNum,arcNum; //顶点数,边数
- int arc[MAX][MAX]; //邻接矩阵
- string vertex[MAX]; //顶点信息
- int dist[MAX][MAX];
- string path[MAX][MAX];
- int rowSum[MAX];
- int rowMax[MAX];
- public:
- MGraph(string v[],int n,int e);
- void display();
- void Floyd();
- void displayDist();
- void displayPath();
- void bestCentralAmusement();
- void displayRowMax();
- void displayRowSum();
- };
- void MGraph::bestCentralAmusement(){
- for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++)
- rowSum[i]=0;
- for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
- for(int j=0;j<vertexNum;j++){
- rowSum[i]+=dist[i][j];
- }
- }
- int tmp;
- for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
- tmp=0;
- for(int j=0;j<vertexNum;j++){
- if(tmp<dist[i][j]) tmp=dist[i][j];
- }
- rowMax[i]=tmp;
- }
- int tmp2=INFINIT;
- int index=-1;
- for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
- if(rowMax[i]<tmp2){
- tmp2=rowMax[i];
- index=i;
- }
- if(tmp2==rowMax[i]){
- if(rowSum[i]<tmp2){
- index=i;
- }else{
- ;
- }
- }
- }
- displayRowMax();
- displayRowSum();
- cout<<"index:"<<index<<endl;
- cout<<"最合适的位置是"<<vertex[index]<<endl;
- }
- void MGraph::displayRowSum(){
- cout<<"rowSum: "<<endl;
- for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++)
- cout<<rowSum[i]<<" ";
- cout<<endl;
- }
- void MGraph::displayRowMax(){
- cout<<"rowMax:"<<endl;
- for(int j=0;j<vertexNum;j++)
- cout<<rowMax[j]<<" ";
- cout<<endl;
- }
- void MGraph::Floyd(){
- for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
- for(int j=0;j<vertexNum;j++){
- dist[i][j]=arc[i][j]; //dist数组初始化
- if(dist[i][j]!=INFINIT&&dist[i][j]!=0) //dist为INFINIT则无路径,dist为0则指向自己
- path[i][j]=vertex[i]+vertex[j]; //path数组初始化
- else
- path[i][j]=""; //不符合则path为空串
- }
- }
- for(int k=0;k<vertexNum;k++){ //k个顶点循环k次
- for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){ //k每循环一次,要更新dist和path数组
- for(int j=0;j<vertexNum;j++){
- if(dist[i][k]+dist[k][j]<dist[i][j]){
- dist[i][j]=dist[i][k]+dist[k][j];
- //这里两个path拼接的时候,第一个字符串的最后一个字符和第二个字符串的第一个字符重复
- //用substr去除第一个字符串的最后一个字符
- string tmp=path[i][k].substr(0,path[i][k].length()-1);
- path[i][j]=tmp+path[k][j];
- }
- }
- }
- }
- displayDist();
- displayPath();
- }
- void MGraph::displayDist(){ //打印dist数组
- cout<<"dist数组:"<<endl;
- for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
- for(int j=0;j<vertexNum;j++){
- cout<<dist[i][j]<<"\t";
- }
- cout<<endl;
- }
- }
- void MGraph::displayPath(){ //打印path数组
- cout<<"path数组:" <<endl;
- for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
- for(int j=0;j<vertexNum;j++){
- cout<<path[i][j]<<"\t";
- }
- cout<<endl;
- }
- }
- MGraph::MGraph(string v[],int n,int e){ //n是顶点数,e是边数
- vertexNum=n;
- arcNum=e;
- for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
- vertex[i]=v[i];
- }
- for(int i=0;i<arcNum;i++){ //初始化邻接矩阵
- for(int j=0;j<arcNum;j++){
- if(i==j) arc[i][j]=0;
- else arc[i][j]=INFINIT;
- }
- }
- int vi,vj,w;
- for(int i=0;i<arcNum;i++){
- cout<<"请输入有向边的两个顶点和这条边的权值"<<endl;
- cin>>vi>>vj>>w; //输入边依附的两个顶点的编号 和权值
- arc[vi][vj]=w; //有边标志
- }
- }
- void MGraph::display(){
- cout<<"邻接矩阵:"<<endl;
- for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
- for(int j=0;j<vertexNum;j++){
- if(arc[i][j]==INFINIT)
- cout<<"∞"<<"\t";
- else cout<<arc[i][j]<<"\t";
- }
- cout<<endl;
- }
- cout<<endl;
- cout<<"结点信息:"<<endl;
- for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
- cout<<vertex[i]<<" ";
- }
- cout<<endl;
- }
- int main(){
- int n,e;
- string v[MAX];
- cout<<"请输入顶点数和边数"<<endl;
- cin>>n>>e;
- cout<<"请输入顶点信息"<<endl;
- for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
- cin>>v[i];
- }
- MGraph mgraph(v,n,e);
- mgraph.display();
- mgraph.Floyd();
- mgraph.bestCentralAmusement();
- return 0;
- }
输入:
5 10
a b c d e
0 1 13
0 3 4
1 0 13
1 2 15
1 4 5
2 3 12
3 0 4
3 2 12
4 2 6
4 3 3
输出:
邻接矩阵:
0 13 ∞ 4 ∞
13 0 15 ∞ 5
∞ ∞ 0 12 ∞
4 ∞ 12 0 ∞
∞ ∞ 6 3 0
结点信息:
a b c d e
dist数组:
0 13 16 4 18
12 0 11 8 5
16 29 0 12 34
4 17 12 0 22
7 20 6 3 0
path数组:
ab adc ad abe
beda bec bed be
cda cdab cd cdabe
da dab dc dabe
eda edab ec ed
rowMax:
18 12 34 22 20
rowSum:
51 36 91 55 36
index:1
最合适的位置是b
最短路径(Floyd算法)的更多相关文章
- 单源最短路径Dijkstra算法,多源最短路径Floyd算法
1.单源最短路径 (1)无权图的单源最短路径 /*无权单源最短路径*/ void UnWeighted(LGraph Graph, Vertex S) { std::queue<Vertex&g ...
- 7-8 哈利·波特的考试(25 分)(图的最短路径Floyd算法)
7-8 哈利·波特的考试(25 分) 哈利·波特要考试了,他需要你的帮助.这门课学的是用魔咒将一种动物变成另一种动物的本事.例如将猫变成老鼠的魔咒是haha,将老鼠变成鱼的魔咒是hehe等等.反方向变 ...
- 最短路径(Floyd)算法
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>/* Floyd算法 */#define VNUM 5#define MV 65536int P[VN ...
- 单源最短路径——Floyd算法
正如我们所知道的,Floyd算法用于求最短路径.Floyd算法可以说是Warshall算法的扩展,三个for循环就可以解决问题,所以它的时间复杂度为O(n^3). Floyd算法的基本思想如下:从任意 ...
- 最短路径Floyd算法【图文详解】
Floyd算法 1.定义概览 Floyd-Warshall算法(Floyd-Warshall algorithm)是解决任意两点间的最短路径的一种算法,可以正确处理有向图或负权的最短路径问题,同时也被 ...
- 【最短路径Floyd算法详解推导过程】看完这篇,你还能不懂Floyd算法?还不会?
简介 Floyd-Warshall算法(Floyd-Warshall algorithm),是一种利用动态规划的思想寻找给定的加权图中多源点之间最短路径的算法,与Dijkstra算法类似.该算法名称以 ...
- 图论之最短路径floyd算法
Floyd算法是图论中经典的多源最短路径算法,即求任意两点之间的最短路径. 它可采用动态规划思想,因为它满足最优子结构性质,即最短路径序列的子序列也是最短路径. 举例说明最优子结构性质,上图中1号到5 ...
- 最短路径—Floyd算法
Floyd算法 所有顶点对之间的最短路径问题是:对于给定的有向网络G=(V,E),要对G中任意两个顶点v,w(v不等于w),找出v到w的最短路径.当然我们可以n次执行DIJKSTRA算法,用FLOYD ...
- 最短路径——Floyd算法(含证明)
通过dij,ford,spfa等算法可以快速的得到单源点的最短路径,如果想要得到图中任意两点之间的最短路径,当然可以选择做n遍的dij或是ford,但还有一个思维量较小的选择,就是floyd算法. 多 ...
- 多源最短路径Floyd算法
多源最短路径是求图中任意两点间的最短路,采用动态规划算法,也称为Floyd算法.将顶点编号为0,1,2...n-1首先定义dis[i][j][k]为顶点 i 到 j 的最短路径,且这条路径只经过最大编 ...
随机推荐
- UIKit and SwiftUI
UIKit and SwiftUI Live Preview Try Again or Resume refs xgqfrms 2012-2020 www.cnblogs.com 发布文章使用:只允许 ...
- flutter package & pub publish
flutter package & pub publish dart-library-package https://pub.dev/packages/dart_library_package ...
- Flutter & release an iOS app
Flutter & release an iOS app https://flutter.dev/docs/deployment/ios .ipa https://en.wikipedia.o ...
- c++ 获取和设置 窗口标题
有些窗口标题中含有中文,可能识别不出来,可以改一下 SetWindowTextW GetWindowTextW 设置: SetWindowTextW( (HWND)0x00370868/*窗口句柄*/ ...
- gitLab的使用 和 git 、 github、gitlab的区别
一.git . github.gitlab的区别 (百度相关内容得到的理解) 二.git最基本作用:版本控制 三.有集成了git的GIT安装包 github和gitlab都使用git该版 ...
- Python算法_递归:汉诺塔
游戏链接:https://zhangxiaoleiv.github.io/app/TowerOfHanoi/Hanoi.html 汉诺塔游戏算法: 1 def hanoi(n,x,y,z): 2 if ...
- Byte Buddy学习笔记
本文转载自Byte Buddy学习笔记 简介 Byte Buddy是一个JVM的运行时代码生成器,你可以利用它创建任何类,且不像JDK动态代理那样强制实现一个接口.Byte Buddy还提供了简单的A ...
- 1094 The Largest Generation ——PAT甲级真题
1094 The Largest Generation A family hierarchy is usually presented by a pedigree tree where all the ...
- 鸿蒙的js开发部模式16:鸿蒙布局Grid网格布局的应用一
鸿蒙入门指南,小白速来!从萌新到高手,怎样快速掌握鸿蒙开发?[课程入口]目录:1.Grid简介2.使用Grid布局实现的效果3.grid-row-gap和grid-colunm-gap属性4.< ...
- Information:java: javacTask: 源发行版 8 需要目标发行版 1.8
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/idiot_qi/article/details/105149846 创建新maven项目跑main,出现这个编译异常 网上找了找,记录一下以备不 ...
