拒绝造轮子!如何移植并使用Linux内核的通用链表(附完整代码实现)
在实际的工作中,我们可能会经常使用链表结构来存储数据,特别是嵌入式开发,经常会使用linux内核最经典的双向链表 list_head。本篇文章详细介绍了Linux内核的通用链表是如何实现的,对于经常使用的函数都给出了详细的说明和测试用例,并且移植了Linux内核的链表结构,在任意平台都可以方便的调用内核已经写好的函数。建议收藏,以备不时之需!
@
链表简介
链表是一种常用的组织有序数据的数据结构,它通过指针将一系列数据节点连接成一条数据链,是线性表的一种重要实现方式。相对于数组,链表具有更好的动态性,建立链表时无需预先知道数据总量,可以随机分配空间,可以高效地在链表中的任意位置实时插入或删除数据。
通常链表数据结构至少应包含两个域:数据域和指针域,数据域用于存储数据,指针域用于建立与下一个节点的联系。按照指针域的组织以及各个节点之间的联系形式,链表又可以分为单链表、双链表、循环链表等多种类型,下面分别给出这几类常见链表类型的示意图:
单链表
单链表是最简单的一类链表,它的特点是仅有一个指针域指向后继节点(next),因此,对单链表的遍历只能从头至尾(通常是NULL空指针)顺序进行。

双链表
通过设计前驱和后继两个指针域,双链表可以从两个方向遍历,这是它区别于单链表的地方。如果打乱前驱、后继的依赖关系,就可以构成"二叉树";如果再让首节点的前驱指向链表尾节点、尾节点的后继指向首节点,就构成了循环链表;如果设计更多的指针域,就可以构成各种复杂的树状数据结构。

循环链表
循环链表的特点是尾节点的后继指向首节点。前面已经给出了双链表的示意图,它的特点是从任意一个节点出发,沿两个方向的任何一个,都能找到链表中的任意一个数据。如果去掉前驱指针,就是单循环链表。

关于链表的更详细的内容可以看这两篇博客
史上最全单链表的增删改查反转等操作汇总以及5种排序算法
详解双向链表的基本操作.
Linux内核中的链表
上面介绍了普通链表的实现方式,可以看到数据域都是包裹在节点指针中的,通过节点指针访问下一组数据。但是 Linux内核的链表实现可以说比较特殊,只有前驱和后继指针,而没有数据域。链表的头文件是在include/list.h(Linux2.6内核)下。在实际工作中,也可以将内核中的链表拷贝出来供我们使用,就需不要造轮子了。
链表的定义
内核链表只有前驱和后继指针,并不包含数据域,这个链表具备通用性,使用非常方便。因此可以很容易的将内核链表结构体包含在任意数据的结构体中,非常容易扩展。我们只需要将链表结构体包括在数据结构体中就可以。下面看具体的代码。
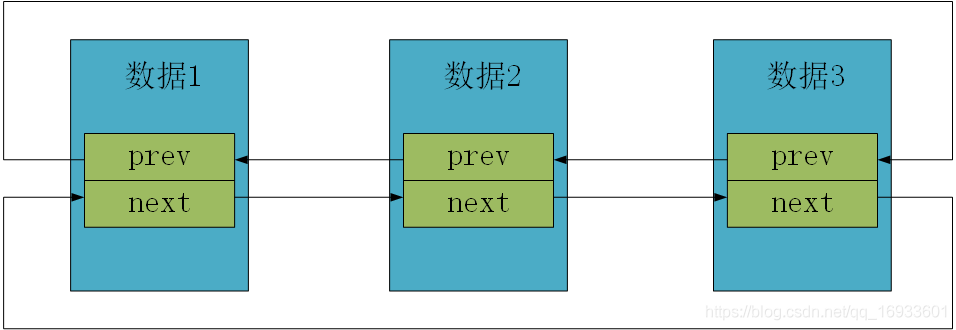
内核链表的结构
//链表结构
struct list_head
{
struct list_head *prev;
struct list_head *next;
};
当需要用内核的链表结构时,只需要在数据结构体中定义一个struct list_head{}类型的结构体成员对象就可以。这样,我们就可以很方便地使用内核提供给我们的一组标准接口来对链表进行各种操作。我们定义一个学生结构体,里面包含学号和数学成绩。结构体如下:
struct student
{
struct list_head list;//暂且将链表放在结构体的第一位
int ID;
int math;
};
链表的初始化
内核实现
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }
#define LIST_HEAD(name) \
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list)
{
list->next = list;
list->prev = list;
}
说明
INIT_LIST_HEAD 和LIST_HEAD都可以初始化链表,二者的区别如下:
LIST_HEAD(stu_list) 初始化链表时会顺便创建链表对象。
//LIST_HEAD(stu_list)展开如下
struct list_head stu_list= { &(stu_list), &(stu_list) };
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&stu1.stu_list) 初始化链表时需要我们已经有了一个链表对象stu1_list。
`我们可以看到链表的初始化其实非常简单,就是让链表的前驱和后继都指向了自己。
举例
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&stu1.stu_list);
链表增加节点
内核实现
/*
* Insert a new entry between two known consecutive entries.
*
* This is only for internal list manipulation where we know
* the prev/next entries already!
*/
#ifndef CONFIG_DEBUG_LIST
static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{
next->prev = new;
new->next = next;
new->prev = prev;
prev->next = new;
}
#else
extern void __list_add(struct list_head *new,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next);
#endif
/**
* list_add - add a new entry
* @new: new entry to be added
* @head: list head to add it after
*
* Insert a new entry after the specified head.
* This is good for implementing stacks.
*/
#ifndef CONFIG_DEBUG_LIST
static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head, head->next);
}
#else
extern void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head);
#endif
/**
* list_add_tail - add a new entry
* @new: new entry to be added
* @head: list head to add it before
*
* Insert a new entry before the specified head.
* This is useful for implementing queues.
*/
static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head->prev, head);
}
说明
list_add为头插法,即在链表头部(head节点)前插入节点。最后打印的时候,先插入的先打印,后插入的后打印。例如原链表为1->2->3,使用list_add插入4后变为,4->1->2->3。因为链表时循环的,而且通常没有首尾节点的概念,所以可以把任何一个节点当成head。
同理,list_add_tail为尾插法,即在链表尾部(head节点)插入节点。最后打印的时候,先插入的后打印,后插入的先打印。例如原链表为1->2->3,使用list_add_tail插入4后变为,1->2->3->4。
举例
#include "mylist.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct student
{
struct list_head stu_list;
int ID;
int math;
};
int main()
{
struct student *p;
struct student *q;
struct student stu1;
struct student stu2;
struct list_head *pos;
//链表的初始化
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&stu1.stu_list);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&stu2.stu_list);
//头插法创建stu stu1链表
for (int i = 0;i < 6;i++) {
p = (struct student *)malloc(sizeof(struct student));
p->ID=i;
p->math = i+80;
//头插法
list_add(&p->stu_list,&stu1.stu_list);
//尾插法
//list_add_tail(&p->list,&stu.list);
}
printf("list_add: \r\n");
list_for_each(pos, &stu1.stu_list) {
printf("ID = %d,math = %d\n",((struct student*)pos)->ID,((struct student*)pos)->math);
}
//尾插法创建stu stu1链表
for (int i = 0;i < 6;i++) {
p = (struct student *)malloc(sizeof(struct student));
p->ID=i;
p->math = i+80;
//头插法
//list_add(&p->stu_list,&stu1.stu_list);
//尾插法
list_add_tail(&p->stu_list,&stu2.stu_list);
}
printf("list_add_tail: \r\n");
list_for_each(pos, &stu2.stu_list) {
printf("ID = %d,math = %d\n",((struct student*)pos)->ID,((struct student*)pos)->math);
}
return 0;
}

链表删除节点
内核实现
//原来内核设置的删除链表后的指向位置
// # define POISON_POINTER_DELTA 0
// #define LIST_POISON1 ((void *) 0x00100100 + POISON_POINTER_DELTA)
// #define LIST_POISON2 ((void *) 0x00200200 + POISON_POINTER_DELTA)
//这里我们设置为NULL 内核中定义NULL 为0
#define NULL ((void *)0)
#define LIST_POISON1 NULL
#define LIST_POISON2 NULL
/*
* Delete a list entry by making the prev/next entries
* point to each other.
*
* This is only for internal list manipulation where we know
* the prev/next entries already!
*/
static inline void __list_del(struct list_head * prev, struct list_head * next)
{
next->prev = prev;
prev->next = next;
}
/**
* list_del - deletes entry from list.
* @entry: the element to delete from the list.
* Note: list_empty() on entry does not return true after this, the entry is
* in an undefined state.
*/
#ifndef CONFIG_DEBUG_LIST
static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
entry->next = LIST_POISON1;
entry->prev = LIST_POISON2;
}
#else
extern void list_del(struct list_head *entry);
#endif
说明
链表删除之后,entry的前驱和后继会分别指向LIST_POISON1和LIST_POISON2,这个是内核设置的一个区域,但是在本例中将其置为了NULL。
举例
#include "mylist.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct student
{
struct list_head stu_list;
int ID;
int math;
};
int main()
{
struct student *p;
struct student *q;
struct student stu1;
struct student stu2;
struct list_head *pos1;
//注意这里的pos2,后面会解释为什么定义为
struct student *pos2;
//stu = (struct student*)malloc(sizeof(struct student));
//链表的初始化
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&stu1.stu_list);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&stu2.stu_list);
LIST_HEAD(stu);
//头插法创建stu stu1链表
for (int i = 0;i < 6;i++) {
p = (struct student *)malloc(sizeof(struct student));
p->ID=i;
p->math = i+80;
//头插法
list_add(&p->stu_list,&stu1.stu_list);
//尾插法
//list_add_tail(&p->list,&stu.list);
}
printf("list_add: \r\n");
list_for_each(pos1, &stu1.stu_list) {
printf("ID = %d,math = %d\n",((struct student*)pos1)->ID,((struct student*)pos1)->math);
}
//删除
list_for_each_entry(pos2,&stu1.stu_list,stu_list) {
if (pos2->ID == 4) {
list_del(&pos2->stu_list);
break;
}
}
printf("list_del\r\n");
list_for_each_entry(pos2,&stu1.stu_list,stu_list) {
printf("ID = %d,math = %d\n",pos2->ID,pos2->math);
}
return 0;
}
链表替换节点
内核实现
/**
* list_replace - replace old entry by new one
* @old : the element to be replaced
* @new : the new element to insert
*
* If @old was empty, it will be overwritten.
*/
static inline void list_replace(struct list_head *old,
struct list_head *new)
{
new->next = old->next;
new->next->prev = new;
new->prev = old->prev;
new->prev->next = new;
}
static inline void list_replace_init(struct list_head *old,
struct list_head *new)
{
list_replace(old, new);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(old);//重新初始化
}
说明
list_replace使用新的节点替换旧的节点。
list_replace_init与list_replace不同之处在于,list_replace_init会将旧的节点重新初始化,让前驱和后继指向自己。
举例
#include "mylist.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct student
{
struct list_head stu_list;
int ID;
int math;
};
int main()
{
struct student *p;
struct student *q;
struct student stu1;
struct student stu2;
struct list_head *pos1;
struct student *pos2;
struct student new_obj={.ID=100,.math=100};
//stu = (struct student*)malloc(sizeof(struct student));
//链表的初始化
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&stu1.stu_list);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&stu2.stu_list);
LIST_HEAD(stu);
//头插法创建stu stu1链表
for (int i = 0;i < 6;i++) {
p = (struct student *)malloc(sizeof(struct student));
p->ID=i;
p->math = i+80;
//头插法
list_add(&p->stu_list,&stu1.stu_list);
//尾插法
//list_add_tail(&p->list,&stu.list);
}
printf("list_add: \r\n");
list_for_each(pos1, &stu1.stu_list) {
printf("ID = %d,math = %d\n",((struct student*)pos1)->ID,((struct student*)pos1)->math);
}
//替换
list_for_each_entry(pos2,&stu1.stu_list,stu_list) {
if (pos2->ID == 4) {
list_replace(&pos2->stu_list,&new_obj.stu_list);
break;
}
}
printf("list_replace\r\n");
list_for_each_entry(pos2,&stu1.stu_list,stu_list) {
printf("ID = %d,math = %d\n",pos2->ID,pos2->math);
}
return 0;
}
链表删除并插入节点
内核实现
/**
* list_move - delete from one list and add as another's head
* @list: the entry to move
* @head: the head that will precede our entry
*/
static inline void list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_del(list->prev, list->next);
list_add(list, head);
}
/**
* list_move_tail - delete from one list and add as another's tail
* @list: the entry to move
* @head: the head that will follow our entry
*/
static inline void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
__list_del(list->prev, list->next);
list_add_tail(list, head);
}
说明
list_move函数实现的功能是删除list指向的节点,同时将其以头插法插入到head中。list_move_tail和list_move功能类似,只不过是将list节点插入到了head的尾部。
举例
#include "mylist.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct student
{
struct list_head stu_list;
int ID;
int math;
};
int main()
{
struct student *p;
struct student *q;
struct student stu1;
struct student stu2;
struct list_head *pos1;
struct student *pos2;
struct student new_obj={.ID=100,.math=100};
//stu = (struct student*)malloc(sizeof(struct student));
//链表的初始化
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&stu1.stu_list);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&stu2.stu_list);
LIST_HEAD(stu);
//头插法创建stu stu1链表
for (int i = 0;i < 6;i++) {
p = (struct student *)malloc(sizeof(struct student));
p->ID=i;
p->math = i+80;
//头插法
list_add(&p->stu_list,&stu1.stu_list);
//尾插法
//list_add_tail(&p->list,&stu.list);
}
printf("list_add: \r\n");
list_for_each(pos1, &stu1.stu_list) {
printf("ID = %d,math = %d\n",((struct student*)pos1)->ID,((struct student*)pos1)->math);
}
//移位替换
list_for_each_entry(pos2,&stu1.stu_list,stu_list) {
if (pos2->ID == 0) {
list_move(&pos2->stu_list,&stu1.stu_list);
break;
}
}
printf("list_move\r\n");
list_for_each_entry(pos2,&stu1.stu_list,stu_list) {
printf("ID = %d,math = %d\n",pos2->ID,pos2->math);
}
return 0;
}
链表的合并
内核实现
static inline void __list_splice(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
struct list_head *first = list->next;
struct list_head *last = list->prev;
struct list_head *at = head->next;
first->prev = head;
head->next = first;
last->next = at;
at->prev = last;
}
/**
* list_splice - join two lists
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*/
static inline void list_splice(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list))
__list_splice(list, head);
}
/**
* list_splice_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list.
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*
* The list at @list is reinitialised
*/
static inline void list_splice_init(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list)) {
__list_splice(list, head);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);//置空
}
}
说明
list_splice完成的功能是合并两个链表。假设当前有两个链表,表头分别是stu_list1和stu_list2(都是struct list_head变量),当调用list_splice(&stu_list1,&stu_list2)时,只要stu_list1非空,stu_list1链表的内容将被挂接在stu_list2链表上,位于stu_list2和stu_list2.next(原stu_list2表的第一个节点)之间。新stu_list2链表将以原stu_list1表的第一个节点为首节点,而尾节点不变。
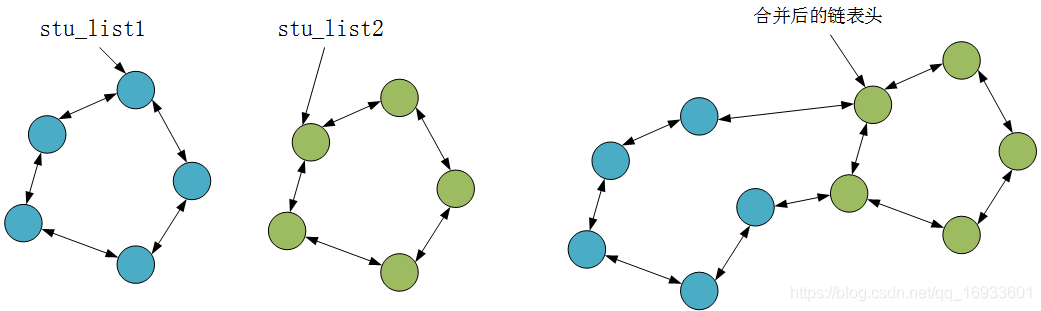
list_splice_init和list_splice类似,只不过在合并完之后,调用INIT_LIST_HEAD(list)将list设置为空链。
用例
#include "mylist.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct student
{
struct list_head stu_list;
int ID;
int math;
};
int main()
{
struct student *p;
struct student *q;
struct student stu1;
struct student stu2;
struct list_head *pos1;
struct student *pos2;
struct student new_obj={.ID=100,.math=100};
//stu = (struct student*)malloc(sizeof(struct student));
//链表的初始化
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&stu1.stu_list);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&stu2.stu_list);
LIST_HEAD(stu);
//头插法创建stu1 list链表
for (int i = 0;i < 6;i++) {
p = (struct student *)malloc(sizeof(struct student));
p->ID=i;
p->math = i+80;
//头插法
list_add(&p->stu_list,&stu1.stu_list);
//尾插法
//list_add_tail(&p->list,&stu.list);
}
printf("stu1: \r\n");
list_for_each(pos1, &stu1.stu_list) {
printf("ID = %d,math = %d\n",((struct student*)pos1)->ID,((struct student*)pos1)->math);
}
//头插法创建stu2 list 链表
for (int i = 0;i < 3;i++) {
q = (struct student *)malloc(sizeof(struct student));
q->ID=i;
q->math = i+80;
//头插法
list_add(&q->stu_list,&stu2.stu_list);
//尾插法
//list_add_tail(&p->list,&stu.list);
}
printf("stu2: \r\n");
list_for_each(pos1, &stu2.stu_list) {
printf("ID = %d,math = %d\n",((struct student*)pos1)->ID,((struct student*)pos1)->math);
}
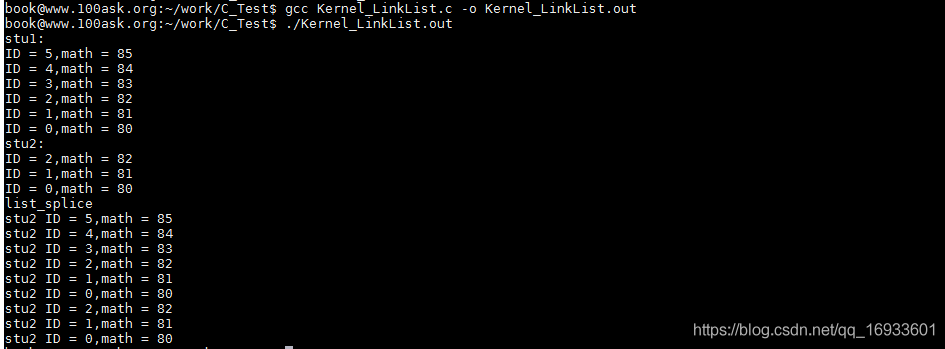
//合并
list_splice(&stu1.stu_list,&stu2.stu_list);
printf("list_splice\r\n");
list_for_each(pos1, &stu2.stu_list) {
printf("stu2 ID = %d,math = %d\n",((struct student*)pos1)->ID,((struct student*)pos1)->math);
}
return 0;
}
链表的遍历
内核实现
//计算member在type中的位置
#define offsetof(type, member) (size_t)(&((type*)0)->member)
//根据member的地址获取type的起始地址
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \
const typeof(((type *)0)->member)*__mptr = (ptr); \
(type *)((char *)__mptr - offsetof(type, member)); })
/**
* list_entry - get the struct for this entry
* @ptr: the &struct list_head pointer.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*/
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \
container_of(ptr, type, member)
/**
* list_first_entry - get the first element from a list
* @ptr: the list head to take the element from.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*
* Note, that list is expected to be not empty.
*/
#define list_first_entry(ptr, type, member) \
list_entry((ptr)->next, type, member)
/**
* list_for_each - iterate over a list
* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
#define list_for_each(pos, head) \
for (pos = (head)->next; prefetch(pos->next), pos != (head); \
pos = pos->next)
/**
* __list_for_each - iterate over a list
* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
*
* This variant differs from list_for_each() in that it's the
* simplest possible list iteration code, no prefetching is done.
* Use this for code that knows the list to be very short (empty
* or 1 entry) most of the time.
*/
#define __list_for_each(pos, head) \
for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)
/**
* list_for_each_prev - iterate over a list backwards
* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
#define list_for_each_prev(pos, head) \
for (pos = (head)->prev; prefetch(pos->prev), pos != (head); \
pos = pos->prev)
/**
* list_for_each_safe - iterate over a list safe against removal of list entry
* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another &struct list_head to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
#define list_for_each_safe(pos, n, head) \
for (pos = (head)->next, n = pos->next; pos != (head); \
pos = n, n = pos->next)
/**
* list_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member); \
prefetch(pos->member.next), &pos->member != (head); \
pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_reverse - iterate backwards over list of given type.
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_reverse(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list_entry((head)->prev, typeof(*pos), member); \
prefetch(pos->member.prev), &pos->member != (head); \
pos = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member))
/**
* list_prepare_entry - prepare a pos entry for use in list_for_each_entry_continue()
* @pos: the type * to use as a start point
* @head: the head of the list
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*
* Prepares a pos entry for use as a start point in list_for_each_entry_continue().
*/
#define list_prepare_entry(pos, head, member) \
((pos) ? : list_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_continue - continue iteration over list of given type
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*
* Continue to iterate over list of given type, continuing after
* the current position.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_continue(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \
prefetch(pos->member.next), &pos->member != (head); \
pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_from - iterate over list of given type from the current point
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*
* Iterate over list of given type, continuing from current position.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_from(pos, head, member) \
for (; prefetch(pos->member.next), &pos->member != (head); \
pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_safe - iterate over list of given type safe against removal of list entry
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe(pos, n, head, member) \
for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member), \
n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_safe_continue
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*
* Iterate over list of given type, continuing after current point,
* safe against removal of list entry.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe_continue(pos, n, head, member) \
for (pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member), \
n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_safe_from
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*
* Iterate over list of given type from current point, safe against
* removal of list entry.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe_from(pos, n, head, member) \
for (n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*
* Iterate backwards over list of given type, safe against removal
* of list entry.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse(pos, n, head, member) \
for (pos = list_entry((head)->prev, typeof(*pos), member), \
n = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.prev, typeof(*n), member))
说明
list_entry(ptr, type, member)可以得到节点结构体的地址,得到地址后就可以对结构体中的元素进行操作了。依靠list_entry(ptr, type, member)函数,内核链表的增删查改都不需要知道list_head结构体所嵌入式的对象,就可以完成各种操作。(为什么这里使用container_of来定义list_entry(ptr, type, member)结构体呢,下面会详细解释)
list_first_entry(ptr, type, member)得到的是结构体中第一个元素的地址
list_for_each(pos, head)是用来正向遍历链表的,pos相当于一个临时的节点,用来不断指向下一个节点。
list_for_each_prev(pos, head)和list_for_each_entry_reverse(pos, head, member)是用来倒着遍历链表的
list_for_each_safe(pos, n, head)和list_for_each_entry_safe(pos, n, head, member),这两个函数是为了避免在遍历链表的过程中因pos节点被释放而造成的断链这个时候就要求我们另外提供一个与pos同类型的指针n,在for循环中暂存pos下一个节点的地址。(内核的设计者考虑的真是全面!)
list_prepare_entry(pos, head, member)用于准备一个结构体的首地址,用在list_for_each_entry_contine()中
list_for_each_entry_continue(pos, head, member)从当前pos的下一个节点开始继续遍历剩余的链表,不包括pos.如果我们将pos、head、member传入list_for_each_entry,此宏将会从链表的头节点开始遍历。
list_for_each_entry_continue_reverse(pos, head, member)从当前的pos的前一个节点开始继续反向遍历剩余的链表,不包括pos。
list_for_each_entry_from(pos, head, member)从pos开始遍历剩余的链表。
list_for_each_entry_safe_continue(pos, n, head, member)从pos节点的下一个节点开始遍历剩余的链表,并防止因删除链表节点而导致的遍历出错。
list_for_each_entry_safe_from(pos, n, head, member) 从pos节点开始继续遍历剩余的链表,并防止因删除链表节点而导致的遍历出错。其与list_for_each_entry_safe_continue(pos, n, head, member)的不同在于在第一次遍历时,pos没有指向它的下一个节点,而是从pos开始遍历。
list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse(pos, n, head, member)从pos的前一个节点开始反向遍历一个链表,并防止因删除链表节点而导致的遍历出错。
list_safe_reset_next(pos, n, member) 返回当前pos节点的下一个节点的type结构体首地址。
举例
#include "mylist.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct student
{
struct list_head stu_list;
int ID;
int math;
};
int main()
{
struct student *p;
struct student *q;
struct student stu1;
struct student stu2;
struct list_head *pos1;
struct student *pos2;
struct student new_obj={.ID=100,.math=100};
//stu = (struct student*)malloc(sizeof(struct student));
//链表的初始化
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&stu1.stu_list);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&stu2.stu_list);
LIST_HEAD(stu);
//头插法创建stu stu1链表
for (int i = 0;i < 6;i++) {
p = (struct student *)malloc(sizeof(struct student));
p->ID=i;
p->math = i+80;
//头插法
list_add(&p->stu_list,&stu1.stu_list);
//尾插法
//list_add_tail(&p->list,&stu.list);
}
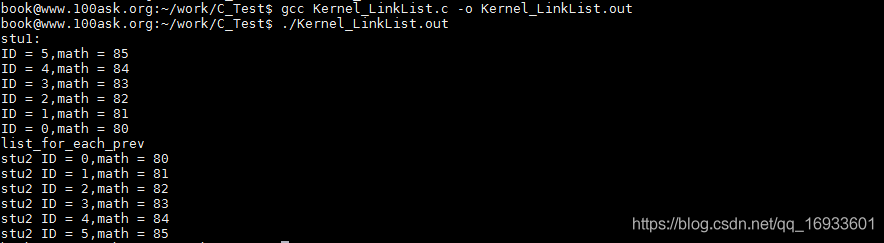
printf("stu1: \r\n");
list_for_each(pos1, &stu1.stu_list) {
printf("ID = %d,math = %d\n",((struct student*)pos1)->ID,((struct student*)pos1)->math);
}
printf("list_for_each_prev\r\n");
list_for_each_prev(pos1, &stu1.stu_list){
printf("stu2 ID = %d,math = %d\n",((struct student*)pos1)->ID,((struct student*)pos1)->math);
}
return 0;
}
例子就不都写出来了,感兴趣的可以自己试试。
疑惑解答
之前我们定义结构体的时候是把 struct list_head放在首位的,当使用list_for_each遍历的时候,pos获取的位置就是结构体的位置,也就是链表的位置。如下所示
struct student
{
struct list_head list;//暂且将链表放在结构体的第一位
int ID;
int math;
};
list_for_each(pos, &stu1.stu_list) {
printf("ID = %d,math = %d\n",((struct student*)pos)->ID,((struct student*)pos)->math);
}
但是当我们把struct list_head list;放在最后时,pos获取的显然就已经不是链表的位置了,那么当我们再次调用list_for_each时就会出错。
struct student
{
int ID;
int math;
struct list_head list;//暂且将链表放在结构体的第一位
};
list_for_each_entry这个函数表示在遍历的时候获取entry,该宏中的pos类型为容器结构类型的指针,这与前面list_for_each中的使用的类型不再相同(这也就是为什么我们上面会分别定义pos1和pos2的原因了),不过这也是情理之中的事,毕竟现在的pos,我要使用该指针去访问数据域的成员age了;head是你使用INIT_LIST_HEAD初始化的那个对象,即头指针,注意,不是头结点;member就是容器结构中的链表元素对象。使用该宏替代前面的方法。这个时候就要用到container_of这个宏了。(再一次感叹内核设计者的伟大)。
关于container_of宏将在下一篇文章详细介绍,这里先知道如何使用就可以。
list.h移植源码
这里需要注意一点,如果是在GNU中使用GCC进行程序开发,可以不做更改,直接使用上面的函数即可;但如果你想把其移植到Windows环境中进行使用,可以直接将prefetch语句删除即可,因为prefetch函数它通过对数据手工预取的方法,减少了读取延迟,从而提高了性能,也就是prefetch是GCC用来提高效率的函数,如果要移植到非GNU环境,可以换成相应环境的预取函数或者直接删除也可,它并不影响链表的功能。
/*
* @Description: 移植Linux2.6内核list.h
* @Version: V1.0
* @Autor: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_16933601
* @Date: 2020-09-12 22:54:51
* @LastEditors: Carlos
* @LastEditTime: 2020-09-16 00:35:17
*/
#ifndef _MYLIST_H
#define _MYLIST_H
//原来链表删除后指向的位置,这里我们修改成 0
// # define POISON_POINTER_DELTA 0
// #define LIST_POISON1 ((void *) 0x00100100 + POISON_POINTER_DELTA)
// #define LIST_POISON2 ((void *) 0x00200200 + POISON_POINTER_DELTA)
#define NULL ((void *)0)
#define LIST_POISON1 NULL
#define LIST_POISON2 NULL
//计算member在type中的位置
#define offsetof(type, member) (size_t)(&((type*)0)->member)
//根据member的地址获取type的起始地址
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \
const typeof(((type *)0)->member)*__mptr = (ptr); \
(type *)((char *)__mptr - offsetof(type, member)); })
//链表结构
struct list_head
{
struct list_head *prev;
struct list_head *next;
};
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }
#define LIST_HEAD(name) \
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list)
{
list->next = list;
list->prev = list;
}
static inline void init_list_head(struct list_head *list)
{
list->prev = list;
list->next = list;
}
#ifndef CONFIG_DEBUG_LIST
static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{
next->prev = new;
new->next = next;
new->prev = prev;
prev->next = new;
}
#else
extern void __list_add(struct list_head *new,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next);
#endif
//从头部添加
/**
* list_add - add a new entry
* @new: new entry to be added
* @head: list head to add it after
*
* Insert a new entry after the specified head.
* This is good for implementing stacks.
*/
#ifndef CONFIG_DEBUG_LIST
static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head, head->next);
}
#else
extern void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head);
#endif
//从尾部添加
static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head->prev, head);
}
static inline void __list_del(struct list_head *prev, struct list_head *next)
{
prev->next = next;
next->prev = prev;
}
static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
entry->next = LIST_POISON1;
entry->prev = LIST_POISON2;
}
static inline void __list_splice(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
struct list_head *first = list->next;
struct list_head *last = list->prev;
struct list_head *at = head->next;
first->prev = head;
head->next = first;
last->next = at;
at->prev = last;
}
/**
* list_empty - tests whether a list is empty
* @head: the list to test.
*/
static inline int list_empty(const struct list_head *head)
{
return head->next == head;
}
/**
* list_splice - join two lists
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*/
static inline void list_splice(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list))
__list_splice(list, head);
}
/**
* list_replace - replace old entry by new one
* @old : the element to be replaced
* @new : the new element to insert
*
* If @old was empty, it will be overwritten.
*/
static inline void list_replace(struct list_head *old,
struct list_head *new)
{
new->next = old->next;
new->next->prev = new;
new->prev = old->prev;
new->prev->next = new;
}
static inline void list_replace_init(struct list_head *old,
struct list_head *new)
{
list_replace(old, new);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(old);
}
/**
* list_move - delete from one list and add as another's head
* @list: the entry to move
* @head: the head that will precede our entry
*/
static inline void list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_del(list->prev, list->next);
list_add(list, head);
}
/**
* list_move_tail - delete from one list and add as another's tail
* @list: the entry to move
* @head: the head that will follow our entry
*/
static inline void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
__list_del(list->prev, list->next);
list_add_tail(list, head);
}
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \
container_of(ptr, type, member)
#define list_first_entry(ptr, type, member) \
list_entry((ptr)->next, type, member)
#define list_for_each(pos, head) \
for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)
/**
* list_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))
/**
* list_for_each_prev - iterate over a list backwards
* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
#define list_for_each_prev(pos, head) \
for (pos = (head)->prev; pos != (head); \
pos = pos->prev)
养成习惯,先赞后看!如果觉得写的不错,欢迎关注,点赞,收藏,转发,谢谢!
以上代码均为测试后的代码。如有错误和不妥的地方,欢迎指出。
欢迎欢迎关注我的公众号:嵌入式与Linux那些事,领取秋招笔试面试大礼包(华为小米等大厂面经,嵌入式知识点总结,笔试题目,简历模版等)和2000G学习资料。公众号主要分享Linux驱动开发,数据结构与算法,计算机基础,C/C++等相关知识,有任何问题均可以加我微信,欢迎骚扰!。
拒绝造轮子!如何移植并使用Linux内核的通用链表(附完整代码实现)的更多相关文章
- 嵌入式Linux内核tasklet机制(附实测代码)
Linux 中断编程分为中断顶半部,中断底半部 中断顶半部: 做紧急,耗时短的事情,同时还启动中断底半部. 中断底半部: 做耗时的事件,这个事件在执行过程可以被中断. 中断底半部实现方法: taskl ...
- linux内核数据结构之链表
linux内核数据结构之链表 1.前言 最近写代码需用到链表结构,正好公共库有关于链表的.第一眼看时,觉得有点新鲜,和我之前见到的链表结构不一样,只有前驱和后继指针,而没有数据域.后来看代码注释发现该 ...
- linux内核数据结构之链表【转】
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/Anker/p/3475643.html 1.前言 最近写代码需用到链表结构,正好公共库有关于链表的.第一眼看时,觉得有点新鲜,和我之前见到的链表结 ...
- linux内核中的链表
1.内核中的链表 linux内核链表与众不同,他不是把将数据结构塞入链表,而是将链表节点塞入数据,在2.1内核中引入了官方链表,从此内核中所有的链表使用都采用此链表,千万不要在重复造车轮子了!链表实现 ...
- linux内核的双链表list_head、散列表hlist_head
一.双链表list_head 1.基本概念 linux内核提供的标准链表可用于将任何类型的数据结构彼此链接起来. 不是数据内嵌到链表中,而是把链表内嵌到数据对象中. 即:加入链表的数据结构必须包含一个 ...
- 【漏洞预警】Intel爆CPU设计问题,导致win和Linux内核重设计(附测试poc)
目前研究人员正抓紧检查 Linux 内核的安全问题,与此同时,微软也预计将在本月补丁日公开介绍 Windows 操作系统的相关变更. 而 Linux 和 Windows 系统的这些更新势必会对 Int ...
- linux 内核源代码情景分析——linux 内核源代码中的C语言代码
linux 内核的主体是以GNU的C语言编写的,GNU为此提供了编译工具gcc.GNU对C语言本身作了不少扩充. 1) gcc 从 C++ 语言中吸收了"inline"和" ...
- 《linux 内核全然剖析》 fork.c 代码分析笔记
fork.c 代码分析笔记 verifiy_area long last_pid=0; //全局变量,用来记录眼下最大的pid数值 void verify_area(void * addr,int s ...
- linux 内核源代码情景分析——linux 内核源码中的汇编语言代码
1. 用汇编语言编写部分核心代码的原因: ① 操作系统内核中的底层程序直接与硬件打交道,需要用到一些专用的指令,而这些指令在C语言中并无对应的语言成分: ② CPU中的一些特殊指令也没有对应的C语言成 ...
随机推荐
- beef抓包简析
搭建完了beef就想简答的抓下包分析下 这是第一个包,追踪它 返回demo页面,并发现其中的脚本 window.location.protocol表示协议http, window.location.h ...
- 金九银十已到!掌握这300道java高频面试题,助你面试BAT无忧!
前言 不知不觉已经到了九月了,回首看年初的时候简直像做梦一样.不得不说时间真的是无情一般的流逝,题外话就不多说了!回归正题,现在已经到了今年最后一波大好的跳槽涨薪的时机了,错过了这一次可能你就得等到明 ...
- java后端开发三年!你还不了解Spring 依赖注入,凭什么给你涨薪
前言 前两天和一个同学吃饭的时候同学跟我说了一件事,说他公司有个做了两年的人向他提出要涨薪资,他就顺口问了一个问题关于spring依赖注入的,那个要求涨薪的同学居然被问懵了...事后回家想了想这一块确 ...
- 破解版的OCR文字识别软件,真的好用吗?
很多小伙伴在下载OCR文字识别软件时,会习惯性去找破解版的软件.那么到底什么是破解版的软件呢?其实破解的软件,都是通过非法的手段,破除正版软件的安全权限制作而成的.因此,使用这些破解软件会存在很多安全 ...
- Eclipse的环境配置
1.想要配置Eclipse的环境,就要先下载Eclipse,并安装它,不会下载安装的小伙伴可以点击下面给的链接,里面有我写的详细的教程,这里就不重复了 Eclipse下载与安装:https://blo ...
- LeetCode 767. 重构字符串
给定一个字符串S,检查是否能重新排布其中的字母,使得两相邻的字符不同. 若可行,输出任意可行的结果.若不可行,返回空字符串. 示例 1: 输入: S = "aab"输出: &quo ...
- Asp.NetCore之AutoMapper基础篇
应用场景 现在由于前后端技术的分离,后端程序员在使用ORM框架开发后台API接口的时候,往往会将数据库的"数据模型"直接提供给前端.而大多数时候,可能这些数据并不能够满足前端展示的 ...
- 使用 Zuul 聚合多个微服务的 Swagger 文档
在 Spring Boot 中集成 Swagger 可参考之前的文章:Spring Boot 2 集成 Swagger, 在各个微服务中的配置与之相同:本文仅介绍在 Zuul 中的配置 在 Zuul ...
- Spring Cloud 学习 (八) Spring Boot Admin
Spring Boot Admin 用于管理和监控一个或者多个 Spring Boot 程序 新建 spring-boot-admin-server pom <parent> <ar ...
- 基于CefSharp开发(五)浏览器菜单样式
一.菜单分析 上图为Edge浏览器现有的菜单内容,菜单中即有子菜单也有组合菜单. 本章节将开发浏览器菜单样式,菜单部分功能将后期进行处理. 二.创建菜单用户控件 新建用户控件命名为WebMenuUc, ...
