Codeforces Round #329 (Div. 2) D. Happy Tree Party LCA/树链剖分
Bogdan has a birthday today and mom gave him a tree consisting of n vertecies. For every edge of the tree i, some number xi was written on it. In case you forget, a tree is a connected non-directed graph without cycles. After the present was granted, m guests consecutively come to Bogdan's party. When the i-th guest comes, he performs exactly one of the two possible operations:
- Chooses some number yi, and two vertecies ai and bi. After that, he moves along the edges of the tree from vertex ai to vertex biusing the shortest path (of course, such a path is unique in the tree). Every time he moves along some edge j, he replaces his current number yi by
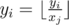 , that is, by the result of integer division yi div xj.
, that is, by the result of integer division yi div xj. - Chooses some edge pi and replaces the value written in it xpi by some positive integer ci < xpi.
As Bogdan cares about his guests, he decided to ease the process. Write a program that performs all the operations requested by guests and outputs the resulting value yi for each i of the first type.
The first line of the input contains integers, n and m (2 ≤ n ≤ 200 000, 1 ≤ m ≤ 200 000) — the number of vertecies in the tree granted to Bogdan by his mom and the number of guests that came to the party respectively.
Next n - 1 lines contain the description of the edges. The i-th of these lines contains three integers ui, vi and xi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n, ui ≠ vi,1 ≤ xi ≤ 1018), denoting an edge that connects vertecies ui and vi, with the number xi initially written on it.
The following m lines describe operations, requested by Bogdan's guests. Each description contains three or four integers and has one of the two possible forms:
- 1 ai bi yi corresponds to a guest, who chooses the operation of the first type.
- 2 pi ci corresponds to a guests, who chooses the operation of the second type.
It is guaranteed that all the queries are correct, namely 1 ≤ ai, bi ≤ n, 1 ≤ pi ≤ n - 1, 1 ≤ yi ≤ 1018 and 1 ≤ ci < xpi, where xpirepresents a number written on edge pi at this particular moment of time that is not necessarily equal to the initial value xpi, as some decreases may have already been applied to it. The edges are numbered from 1 to n - 1 in the order they appear in the input.
For each guest who chooses the operation of the first type, print the result of processing the value yi through the path from ai to bi.
6 6
1 2 1
1 3 7
1 4 4
2 5 5
2 6 2
1 4 6 17
2 3 2
1 4 6 17
1 5 5 20
2 4 1
1 5 1 3
2
4
20
3
2 x y,把第x条边的边权改为y
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std; #pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
#define ls i<<1
#define rs ls | 1
#define mid ((ll+rr)>>1)
#define pii pair<int,int>
#define MP make_pair typedef long long LL;
const long long INF = 1e18;
const double Pi = acos(-1.0);
const int N = 2e5+, M = 5e5+, inf = 2e9, mod = ; LL c[N];
int head[N],t = , fv[N], f[N], deep[N], n, m, pa[N];
struct edge{int to,next,id;}e[N * ];
struct Line {
int x,y;
LL z;
Line(int x = , int y = , int z = ) : x (x), y (y), z (z) {}
}L[N];
void add(int u,int v,int id) {e[t].next = head[u];e[t].to = v;e[t].id = id; head[u] = t++; } int finds(int x) {return x == pa[x]? pa[x]:pa[x] = finds(pa[x]);} void update(int u,int to) {
fv[to] = fv[u];
f[to] = f[u];
}
void dfs(int u,int fa) {
deep[u] = deep[fa] + ;
for(int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].next) {
int to = e[i].to;
if(to == fa) continue;
fv[to] = e[i].id;
f[to] = u;
if(c[e[i].id] == ) {
pa[to] = finds(u);
update(u,to);
}
dfs(to,u);
}
} LL Lca(int u,int v,LL res) {
u = finds(u);
v = finds(v);
while(u != v) {
if(deep[u] < deep[v]) swap(u,v);
// cout<<deep[u]<<" "<<deep[v]<<" "<<fv[u]<<" "<<c[fv[u]]<<endl;
res /= c[fv[u]];
if(res == ) return res;
u = finds(f[u]);
}
return res;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i = ; i <= n; ++i) pa[i] = i;
for(int i = ; i < n; ++i) {
int a,b;
scanf("%d%d%I64d",&a,&b,&c[i]);
add(a,b,i);add(b,a,i);
L[i] = Line(a,b,c[i]);
} c[] = ;
fv[] = ;
f[] = ; dfs(,);
while(m --) {
int op, x;
LL z,y;
scanf("%d%d%I64d",&op,&x,&y);
if(op == ) {
scanf("%I64d",&z);
LL res = Lca(x,y,z);
printf("%I64d\n",res);
}
else {
c[x] = y;
int u = L[x].x;
int v = L[x].y;
if(deep[u] < deep[v]) swap(u,v);
if(c[x] == ) {
pa[u] = finds(v);
update(v,u);
}
}
}
}
树链剖分
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std; #pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000") #define ls i<<1
#define rs ls | 1
#define mid ((ll+rr)>>1)
#define root 1,2,n
#define lson ls , ll , mid
#define rson rs , mid + 1 , rr #define pii pair<int,int>
#define MP make_pair
typedef long long LL;
const long long INF = 1e18+200LL;
const double Pi = acos(-1.0);
const int N = 2e5+, M = 5e5+, inf = 2e9, mod = ; LL sum[N << ],val[N << ];
int head[N], t = , tot, deep[N], top[N], f[N], siz[N], son[N], pos[N << ];
int n,m;
struct edge{int to,next;LL value;}e[N * ];
struct Line{
int x,y;LL z;
Line(int x = , int y = , LL z = ) : x(x), y(y), z(z) {}
}L[N];
void add(int u,int v) {e[t].next=head[u];e[t].to=v;head[u]=t++;}
void dfs1(int u,int fa) {
siz[u] = ;son[u] = ;
deep[u] = deep[fa] + ;
f[u] = fa;
for(int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].next) {
int to = e[i].to;
if(to == fa) continue;
dfs1(to,u);
siz[u] += siz[to];
if(siz[to] > siz[son[u]]) son[u] = to;
}
}
void dfs2(int u,int chan) {
top[u] = son[chan] == u? top[chan] : u;
pos[u] = ++tot;
if(son[u]) dfs2(son[u],u);
for(int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].next) {
int to = e[i].to;
if(to == son[u] || to == chan) continue;
dfs2(to,u);
}
}
void push_up(int i) {
if(log(sum[ls]*1.0) + log(sum[rs] * 1.0) > log(INF * 1.0))
sum[i] = INF;
else sum[i] = sum[ls] * sum[rs];
}
void build(int i,int ll,int rr) {
if(ll == rr) {
sum[i] = val[ll];
return ;
}
build(lson), build(rson);
push_up(i);
}
void update(int i,int ll,int rr,int x,LL c)
{
if(ll == x && rr == x) {
sum[i] = c;
return ;
}
if(x <= mid) update(lson,x,c);
else update(rson,x,c);
push_up(i);
} LL query(int i,int ll,int rr,int x,int y) {
if(ll == x && rr == y) return sum[i];
if(y <= mid) return query(lson,x,y);
else if(x > mid) return query(rson,x,y);
else {
LL fi = query(lson,x,mid);
LL se = query(rson,mid+,y);
if(log(fi*1.0) + log(se * 1.0) > log(INF * 1.0)) {
return INF;
}
else return fi*se;
}
} LL sub_query(int x,int y,LL res) {
while(top[x] != top[y]) {
if(deep[top[x]] < deep[top[y]]) swap(x,y);
// cout<<pos[top[x]]<<" "<<pos[x]<<endl;
res /= query(root,pos[top[x]],pos[x]);
if(res == ) return ;
x = f[top[x]];
}
if(x == y) return res;
if(deep[x] < deep[y]) swap(x,y);
// cout<<query(root,pos[y]+1,pos[x])<<endl;
return res / query(root,pos[y]+,pos[x]);
} int main () {
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i = ; i <= n-; ++i) {
int a,b;
LL c;
scanf("%d%d%I64d",&a,&b,&c);
add(a,b);
add(b,a);
L[i] = Line(a,b,c);
}
dfs1(,);
dfs2(,);
for(int i = ; i < n; ++i) {
if(deep[L[i].x] < deep[L[i].y]) swap(L[i].x,L[i].y);
val[pos[L[i].x]] = L[i].z;
}
build(root);
while(m--) {
int op,x;
LL y,z;
scanf("%d%d%I64d",&op,&x,&y);
if(op == ) {
scanf("%I64d",&z);
printf("%I64d\n",sub_query(x,y,z));
}else {
update(root,pos[L[x].x],y);
}
}
}
Codeforces Round #329 (Div. 2) D. Happy Tree Party LCA/树链剖分的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #329 (Div. 2) D. Happy Tree Party(LCA+并查集)
题目链接 题意:就是给你一颗这样的树,用一个$y$来除以两点之间每条边的权值,比如$3->7$,问最后的y的是多少,修改操作是把权值变成更小的. 这个$(y<=10^{18})$除的权值如 ...
- Codeforces Round #329 (Div. 2) D. Happy Tree Party 树链剖分
D. Happy Tree Party Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/593/p ...
- Codeforces Round #225 (Div. 1) C. Propagating tree dfs序+ 树状数组或线段树
C. Propagating tree Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/383/p ...
- Codeforces Round #225 (Div. 1) C. Propagating tree dfs序+树状数组
C. Propagating tree Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/383/p ...
- Count on a tree SPOJ 10628 主席树+LCA(树链剖分实现)(两种存图方式)
Count on a tree SPOJ 10628 主席树+LCA(树链剖分实现)(两种存图方式) 题外话,这是我第40篇随笔,纪念一下.<( ̄︶ ̄)↗[GO!] 题意 是说有棵树,每个节点上 ...
- Codeforces Round #200 (Div. 1) D Water Tree 树链剖分 or dfs序
Water Tree 给出一棵树,有三种操作: 1 x:把以x为子树的节点全部置为1 2 x:把x以及他的所有祖先全部置为0 3 x:询问节点x的值 分析: 昨晚看完题,马上想到直接树链剖分,在记录时 ...
- Codeforces Round #200 (Div. 1) D. Water Tree 树链剖分+线段树
D. Water Tree time limit per test 4 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input ...
- Codeforces Round #200 (Div. 1)D. Water Tree
简单的树链剖分+线段树 #include<bits\stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define pb push_back #define lson roo ...
- CF 504E Misha and LCP on Tree——后缀数组+树链剖分
题目:http://codeforces.com/contest/504/problem/E 树链剖分,把重链都接起来,且把每条重链的另一种方向的也都接上,在这个 2*n 的序列上跑后缀数组. 对于询 ...
随机推荐
- 隐藏左侧快速导航除DMS导航树之外的其他区域
<style type="text/css"> /*隐藏左侧快速导航除DMS导航树之外的其他区域*/ .ms-quicklaunchouter { display: n ...
- 【leetcode】Minimum Path Sum
Minimum Path Sum Given a m x n grid filled with non-negative numbers, find a path from top left to b ...
- POJ 2570(floyd)
http://poj.org/problem?id=2570 题意:在海底有一些网络节点.每个节点之间都是通过光缆相连接的.不过这些光缆可能是不同公司的. 现在某个公司想从a点发送消息到b点,问哪个公 ...
- linux /usr/bin/ld cannot find 解决
问题: 在linux环境编译应用程式或lib的source code时常常会出现如下的错误讯息: /usr/bin/ld: cannot find -lxxx 这些讯息会随着编译不同类型的source ...
- Linux基础命令总结
1.pwd 查看当前工作目录 2.ls [目录] 列出指定目录下的所有文件,使用 ls -l 或者 ll 列出文件详细列表包括权限.大小等文件默认大小以字节B为单位,目录大小为4096B ls - ...
- Android开发者必备的42个链接
http://mobile.51cto.com/ahot-426035.htm Android开发者必备的42个链接 下面收集了42个帮助大家学习Android的内容链接,部分内容是面向初学者的,帮助 ...
- MongoDB 索引相关知识
背景: MongoDB和MySQL一样,都会产生慢查询,所以都需要对其进行优化:包括创建索引.重构查询等.现在就说明在MongoDB下的索引相关知识点,可以通过这篇文章MongoDB 查询优化分析了解 ...
- Effective C++ -----条款43:学习处理模板化基类内的名称
可在derived class templates内通过“this->“指涉base class templates内的成员名称,或藉由一个明白写出的”base class资格修饰符”完成.
- Linux vmstat字段解析
vmstat命令是最常见的Linux/Unix监控工具,可以展现给定时间间隔的服务器的状态值,包括服务器的CPU使用率,内存使用,虚拟内存交换情况,IO读写情况.这个命令是我查看Linux/Unix最 ...
- 营业额统计(bzoj1588)
Description 营业额统计 Tiger最近被公司升任为营业部经理,他上任后接受公司交给的第一项任务便是统计并分析公司成立以来的营业情况. Tiger拿出了公司的账本,账本上记录了公司成立以来每 ...
