Map的深浅拷贝的探究
1. 复制map示例
首先看一个例子,当我使用不同方法将一个源map拷贝到另一个map后,改变源map,复制后的map理应不受影响
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry; public class MapTest { public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, BigDecimal> detailsmap = new HashMap<String, BigDecimal>();
Map<String, BigDecimal> detailsmapByEquals = new HashMap<String, BigDecimal>();
Map<String, BigDecimal> detailsmapByPutAll = new HashMap<String, BigDecimal>();
Map<String, BigDecimal> detailsmapByIterator = new HashMap<String, BigDecimal>(); detailsmap.put("key1", new BigDecimal("123.22"));
detailsmap.put("key2", new BigDecimal("156.2"));
// 通过“=”的方式复制map对象
detailsmapByEquals = detailsmap;
// 通过putAll的方式复制map对象
detailsmapByPutAll.putAll(detailsmap);
// 通过iterator的方式复制map对象
mapCopy(detailsmapByIterator, detailsmap); System.out.println("detailsmap 的内容为:" + detailsmap);
detailsmap.remove("key2");
System.out.println("移除key2的 detailsmap 的内容为:" + detailsmap); System.out.println("通过 “=” 复制的map当前值为:" + detailsmapByEquals);
System.out.println("通过 “putAll方法” 复制的map当前值为:" + detailsmapByPutAll);
System.out.println("通过 “iterator方法” 复制的map当前值为:" + detailsmapByIterator); } public static void mapCopy(Map detailsmapByIterator, Map detailsmap) {
// 将detailsmap内容拷贝到detailsmapByIterator
if (detailsmapByIterator == null) {
detailsmapByIterator = new HashMap();
} if(detailsmap == null){
return;
} Iterator it = detailsmap.entrySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Map.Entry entry = (Entry) it.next();
Object key = entry.getKey();
detailsmapByIterator.put(key, detailsmap.get(key) != null?detailsmap.get(key):"");
}
} }
查看输出:

可以看到通过“=”复制的map内容随源map的改变而改变,而通过putAll方法和Iterator复制的map则不受源map改变的影响。
2. Map的两种拷贝类型
Map的拷贝分为两种情况:
- 浅拷贝:只拷贝对象的引用,两个引用仍然指向同一个对象,在内存中占用同一块内存。被拷贝对象的所有变量都含有与原来的对象相同的值,而所有的对其他对象的引用仍然指向原来的对象。即浅拷贝仅仅拷贝对象的引用,而不拷贝它所引用的对象。
- 深拷贝:被拷贝对象的所有变量都含有与原来的对象相同的值,除去那些引用其他对象的变量。那些引用其他对象的变量将指向被拷贝过的新对象,而不再是原有的那些被引用的对象。即深拷贝把要拷贝的对象所引用的对象都拷贝了一遍。
如示例中的三种拷贝方法:针对map中的数据为统一的、简单的基本数据类型,当拷贝的数据通过“=”复制map的方法为浅拷贝,putAll方法为深拷贝,iterator遍历添加的方式为深拷贝。
3. putAll方法并非深拷贝
两种深拷贝方法,iterator遍历添加的方式,由于是重新创建了一个对象,且遍历添加源Map的元素,因此在内存中另开辟了一块内存,毋庸置疑是深拷贝;而对于putAll方法参考其源码:
/**
* Copies all of the mappings from the specified map to this map.
* These mappings will replace any mappings that this map had for
* any of the keys currently in the specified map.
*
* @param m mappings to be stored in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
*/
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
int numKeysToBeAdded = m.size();
if (numKeysToBeAdded == 0)
return; /*
* Expand the map if the map if the number of mappings to be added
* is greater than or equal to threshold. This is conservative; the
* obvious condition is (m.size() + size) >= threshold, but this
* condition could result in a map with twice the appropriate capacity,
* if the keys to be added overlap with the keys already in this map.
* By using the conservative calculation, we subject ourself
* to at most one extra resize.
*/
if (numKeysToBeAdded > threshold) {
int targetCapacity = (int)(numKeysToBeAdded / loadFactor + 1);
if (targetCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
targetCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
int newCapacity = table.length;
while (newCapacity < targetCapacity)
newCapacity <<= 1;
if (newCapacity > table.length)
resize(newCapacity);
} for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet())
put(e.getKey(), e.getValue());
}
通过源码可以看到putAll() 方法的实现仅仅是将源Map的第一层put进Map中,这种方式对于value为基本类型的map复制是实现深拷贝的效果的,但是当value为对象时,是不会奏效的。这里简单使用源Map内嵌Map的方式测试putAll方法,看其是否实现了深层次的复制:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map; public class MapDeepCopy { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
Map<String, Object> mapCopy = new HashMap<String, Object>();
// Map中要嵌套Map
Map mapInner = new HashMap();
mapInner.put("num", "100");
map.put("key1", mapInner);
map.put("key2", "600"); // 复制
mapCopy.putAll(map);
System.out.println("使用“putAll”方法复制map到mapCopy中,此时mapCopy值为:————"+mapCopy); // 更改复制之后的map中内嵌map的内容
((Map) mapCopy.get("key1")).put("num", "200");
System.out.println("更改复制之后的mapCopy内容,更改之后mapCopy值为:————"+mapCopy);
System.out.println("此时源map map的值为:————"+map);// 源Map也被改变
}
}
输出如下,说明map和mapCopy中的mapInner元素使用的还是同一块内存:

4. Map深拷贝的实现
有一种方法,是使用序列化的方式来实现对象的深拷贝,但是前提是,对象必须是实现了Serializable接口才可以,Map本身没有实现 Serializable 这个接口,所以这种方式不能序列化Map,也就是不能深拷贝Map。但是HashMap是可以的,因为它实现了 Serializable。下面的方式,基于HashMap来讲,非Map的拷贝。
/**
* @Title: 对象深度克隆---使用序列化进行深拷贝
* @Description: 使用序列化的方式来实现对象的深拷贝,但是前提是,对象必须是实现了 Serializable接口才可以,Map本身没有实现
Serializable 这个接口,所以这种方式不能序列化Map,也就是不能深拷贝Map。但是HashMap是可以的,因为它
实现了Serializable。
* @param obj
* @return T
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T extends Serializable> T clone(T obj) {
T clonedObj = null;
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(baos);
oos.writeObject(obj);
oos.close();
ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(
baos.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bais);
clonedObj = (T) ois.readObject();
ois.close(); } catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} return clonedObj;
}
调用
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List; public class MapTest { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(100);
list.add(200); HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
// 放基本类型数据
map.put("basic", 100);
// 放对象
map.put("list", list); HashMap<String, Object> mapNew = new HashMap<String, Object>();
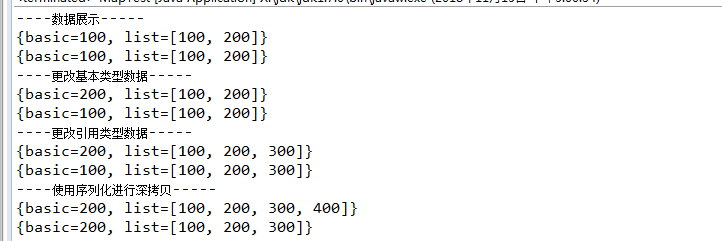
mapNew.putAll(map); System.out.println("----数据展示-----");
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(mapNew); System.out.println("----更改基本类型数据-----");
map.put("basic", 200);
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(mapNew); System.out.println("----更改引用类型数据-----");
list.add(300);
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(mapNew); System.out.println("----使用序列化进行深拷贝-----");
mapNew = clone(map);
list.add(400);
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(mapNew);
}
}
输出如下:
附:
【4. Map深拷贝的实现】转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/cxxjohnson/p/6258742.html
Map的深浅拷贝的探究的更多相关文章
- Python-Day3知识点——深浅拷贝、函数基本定义、内置函数
一.深浅拷贝 import copy #浅拷贝 n1={'k1':'wu','k2':123,'k3':['carl',852]} n2=n1 n3=copy.copy(n1) print(id(n1 ...
- python基础知识5——赋值与深浅拷贝——整数和字符串,列表元组字典
深浅copy 一.数字和字符串 对于 数字 和 字符串 而言,赋值.浅拷贝和深拷贝无意义,因为其永远指向同一个内存地址. 1 import copy 2 # ######### 数字.字符串 #### ...
- iOS 深浅拷贝
-(void)copyDemo { // 在非集合类对象中:对immutable对象进行copy操作,是指针复制,mutableCopy操作时内容复制:对mutable对象进行copy和mutable ...
- [Python笔记]第三篇:深浅拷贝、函数
本篇主要内容:深浅拷贝,自定义函数,三目运算,lambda表达式, 深浅拷贝 一.数字和字符串 对于 数字 和 字符串 而言,赋值.浅拷贝和深拷贝无意义,因为其永远指向同一个内存地址. import ...
- python-Day3-set 集合-counter计数器-默认字典(defaultdict) -可命名元组(namedtuple)-有序字典(orderedDict)-双向队列(deque)--Queue单项队列--深浅拷贝---函数参数
上节内容回顾:C语言为什么比起他语言块,因为C 会把代码变异成机器码Pyhton 的 .pyc文件是什么python 把.py文件编译成的.pyc文件是Python的字节码, 字符串本质是 字符数组, ...
- Python学习笔记——基础篇2【第三周】——计数器、有序字典、元组、单(双)向队列、深浅拷贝、函数、装饰器
目录 1.Python计数器Counter 2.Python有序字典OrderredDict 3.Python默认字典default 4.python可命名元组namedtuple 5.Python双 ...
- python--关于赋值与深浅拷贝的认识
作为一个自学python的小白,平时用到深浅拷贝的机会很少,因此对其也是一知半解.但是,作为一个立志成为后端工程狮的男人,眼里揉不了沙子,于是专门花时间补了补课,在此记录一下学习心得. 在讲深浅 ...
- 深浅拷贝,原生和JQuery方法实现
7-17: 1:e.target.parentNode.remove();成功,查询一下JS原生的remove方法 2:复习JS DOM的原生操作方法,比如innerHTML(),insertBefo ...
- Python--day06(深浅拷贝、元组、字典、集合)
1. 深浅拷贝 1.1 值拷贝 s1直接将ls中存放的地址拿过来s1内部的值发生任何变化,s2都会随之变化 s1 = ['1','2','3','a']s2 = s1print(id(s1),id ...
随机推荐
- 一次问题追查----短字符串签名算法引发的bug
近期开发代码, 出现了一些诡异现象.追查原因是公司使用的签名函数出现的问题. 问题: 代码使用的签名库函数, 对于<=4字节的字符串, 签名就是本身. #include<stdio.h&g ...
- JS实现千分位
方法一:正则实现 function format (num) { ,}(?=(\d{})+$)/g; return (num + '').replace(reg, '$&,'); } 解释: ...
- Google Guava新手教程
以下资料整理自网络 一.Google Guava入门介绍 引言 Guavaproject包括了若干被Google的 Java项目广泛依赖 的核心库,比如:集合 [collections] . ...
- Android -- ConditionVariable
线程操作经常用到wait和notify,用起来稍显繁琐,而Android给我们封装好了一个ConditionVariable类,用于线程同步.提供了三个方法block().open().close() ...
- ueditor插入自定义内容和样式
UEditor是由百度web前端研发部开发所见即所得富文本web编辑器,具有轻量,可定制,注重用户体验等特点 通过UEditor提供的API接口可以很方便的读写操作内容并设置编辑器里的样式 页 ...
- 不可不知的Python模块: collections
原文:http://www.zlovezl.cn/articles/collections-in-python/ Python作为一个“内置电池”的编程语言,标准库里面拥有非常多好用的模块.比如今天想 ...
- 转载:Unicode和Utf-8有何区别 转载自知乎 原文作者不详
作者:于洋链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/23374078/answer/69732605来源:知乎著作权归作者所有.商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出 ...
- Sublime Text 3 配置 PHPCS 插件
Download php code sniffer addon via Package Control in ST3. Download The php-cs-fixer File From This ...
- ext js/Ext.Net_演示 htmleditor 上传&插入图片
本文内容 解决方案结构 HtmlEditor_Upload.js 脚本 HtmlEditorUploadImg.ashx 上传图片到服务器 演示 htmleditor 控件添加插入图片功能 解决方 ...
- Swift 2.x 升为 swift 3后语法不兼容问题适配
[解决方法]设置 Build Settings —-> Use Legacy Swift Language Version —-> 改为YES
