[Logstash-input-redis] 使用详解
redis插件的完整配置
input {
redis {
batch_count => 1 #返回的事件数量,此属性仅在list模式下起作用。
data_type => "list" #logstash redis插件工作方式
key => "logstash-test-list" #监听的键值
host => "127.0.0.1" #redis地址
port => 6379 #redis端口号
password => "123qwe" #如果有安全认证,此项为密码
db => 0 #redis数据库的编号
threads => 1 #启用线程数量
}
}
output {
stdout{}
}
工作流程
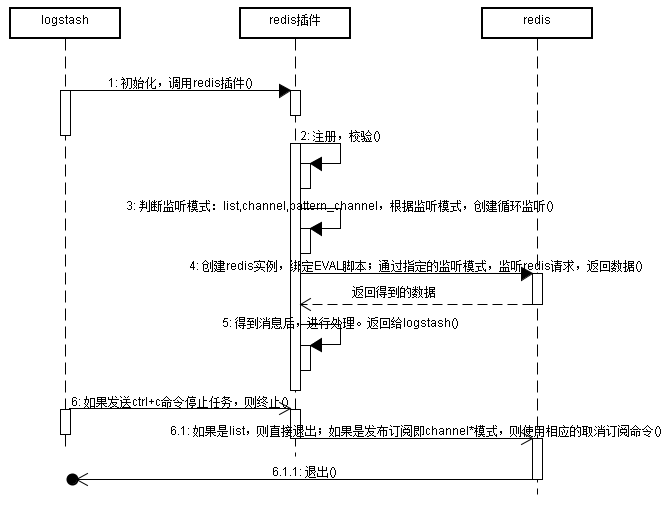
图不够专业,但是大致就如上图所示:
- logstash启动redis插件
- redis插件获取参数,进行校验工作
- 判断监听模式(list,channel,pattern_channel等),根据不同的监听模式创建监听任务
- 创建redis实例,绑定EVAL脚本;通过指定的redis模式,发送请求,监听数据
- redis返回指定内容的数(可能是列表list,也可能是某个特定的频道中的数据)
- 得到的数据,进行处理,返回给logstash
- 如果发送了停止信号,则根据不同的模式,发送不同的命令退出redis。
源码剖析
首先是程序的自定义,这里设置了redis插件需要的参数,默认值,以及校验等。
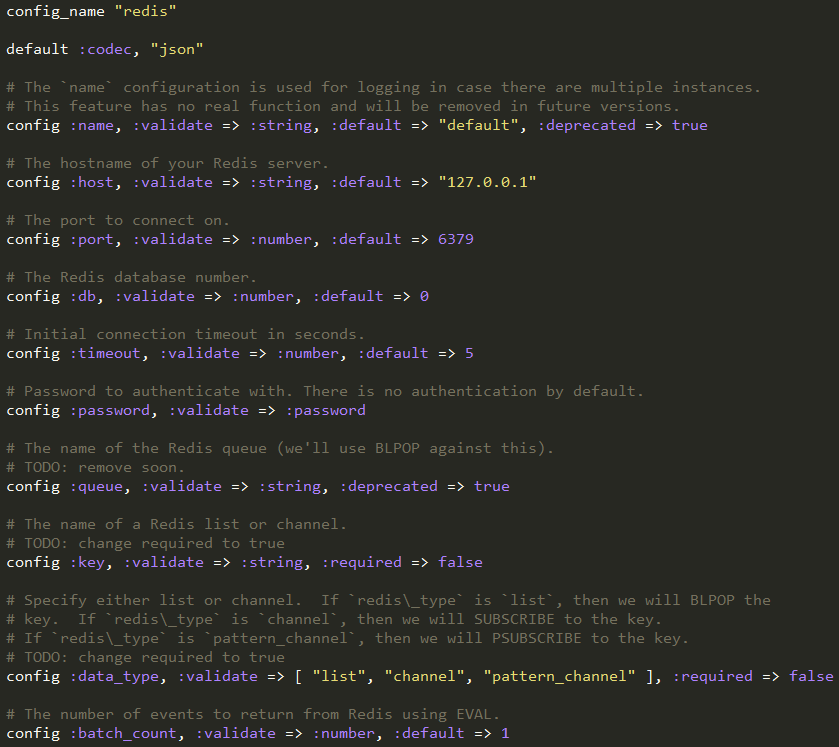
然后注册Redis实例需要的信息,比如key的名字或者url等,可以看到默认的data_type是list模式。
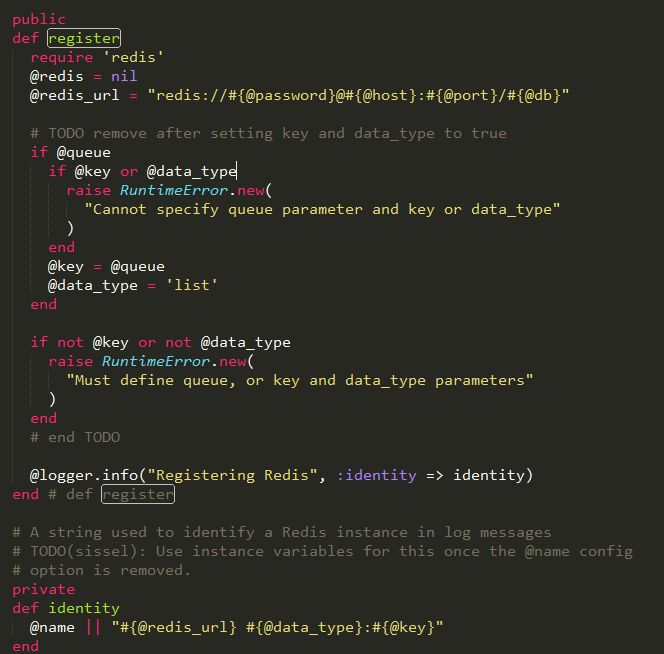
程序运行的主要入口,根据不同的data_type,传递不同的实现方法,然后调用listener_loop执行循环监听
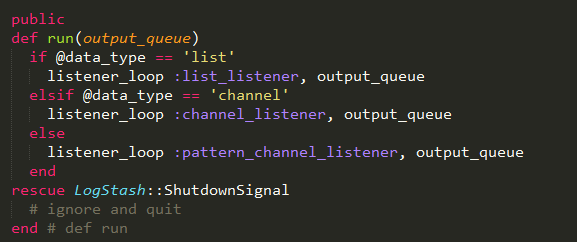
Listner_loop方法传递了两个参数,一个是监听器实现的方法,一个是处理的数据队列。循环是每秒钟执行一次,如果循环标识被设置,则退出。
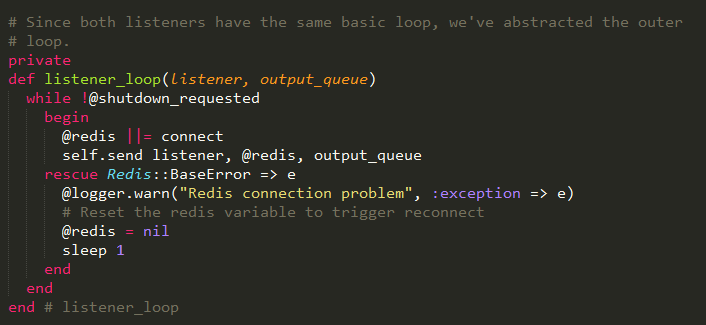
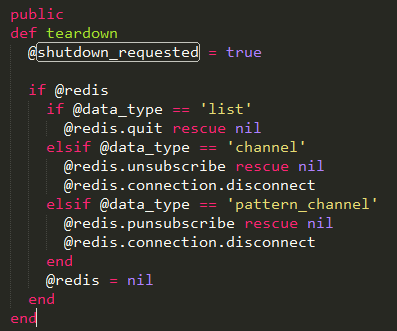
上面的循环方法可以看到,是通过一个参数shutdown_requested来判断是否继续循环。该参数通过tear_down方法设置为true,然后根据不同的模式,指定不同的退出方式。
如果是list模式,则直接退出;如果是channel模式,则发送redis的unsubsribe命令退出;如果是pattern_channel,则发送punsubscribe退出。
在循环内部,判断是否已经创建了redis实例,如果没有创建,则调用connect方法创建;否则直接执行。
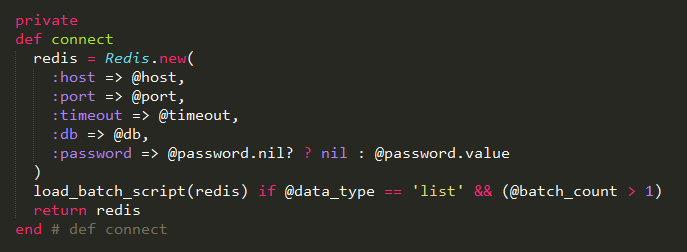
这里前一段是调用Redis的new方法,初始化一个redis实例。紧接着判断batch_count是否大于1,如果等于1,就什么也不做,然后返回redis。
如果batch_count大于1,那么就调用load_batch_script方法,加载Lua脚本,存储到redis中的lua脚本字典中,供后面使用。代码如下:
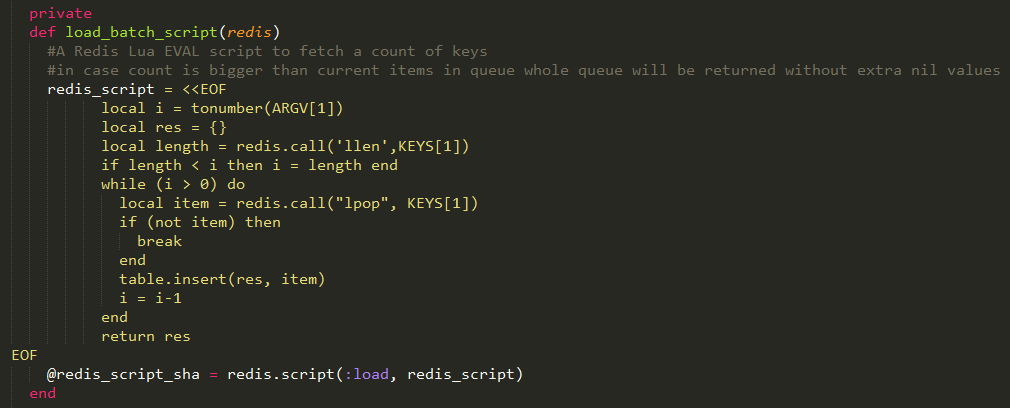
上面的代码应该是这个插件最难理解的部分了。为了弄清楚这段代码的工作,需要了解下面几个知识点:
- lua脚本基本概念
- Redis中的EVAL命令如何使用
- 理解上面脚本的工作
首先,要想运行上面的脚本,必须是Redis2.6+的版本,才支持EVAL,否则会报错!EVAL命令与js中的差不多,就是可以把某一个字符串当做命令解析,其中字符串就包括lua脚本。这样有什么好处呢?
说白了,就是能一次性进行多个操作。比如我们可以在脚本中写入一连串的操作,这些操作会以原子模式,一次性在服务器执行完,在返回回来。
Lua脚本
关于lua脚本,其实没有详细研究的必要,但是一定要知道一个local和table的概念。local是创建本地的变量,这样就不会污染redis的数据。table是lua的一种数据结构,有点类似于json,可以存储数据。
EVAL命令
另外还要知道EVAL命令的使用方法,看下面这个命令,就好理解了!
EVAL "return KEYS[1] KEYS[2] ARGV[1] ARGV[2];" 2 name:xing age:13
就会返回:
name
age
xing
13
这段代码没有经过真正的操作,但是有助于理解就好!也就是说,EVAL后面跟着一段脚本,脚本后面跟着的就是参数,可以通过KEYS和ARGV数组获得,但是下标从1开始。
再来说说EVAL命令,它的执行过程如下:
- 解析字符串脚本,根据校验和生成lua的方法
- 把校验和和函数放入一个lua_script字典里面,之后就可以通过EVALSHA命令直接使用校验和执行函数。
有了这些理论基础以后,就可以看看上面的代码都做了什么了!
首先是获取参数,这个参数赋值给i;然后创建了一个对象res;紧接着调用llen命令,获得指定list的长度;如果list的长度大于i,则什么也不做;如果小于i,那么i就等于lenth;然后执行命令lpop,取出list中的元素,一共取i次,放入res中,最后返回。
说得通俗点,就是比较一下list元素个数与设置batch_count的值。如果batch_count为5,列表list中有5条以上的数据,那么直接取5条,一次性返回;否则取length条返回。
可以看到这段脚本的作用,就是让logstash一次请求,最多获得batch_count条事件,减小了服务器处理请求的压力。
讲完这段代码,可以看看不同的工作模式的实现代码了:
首先是list的代码,其实就是执行BLPOP命令,获取数据。如果在list模式中,还会去判断batch_count的值,如果是1直接退出;如果大于1,则使用evalsha命令调用之前保存的脚本方法。
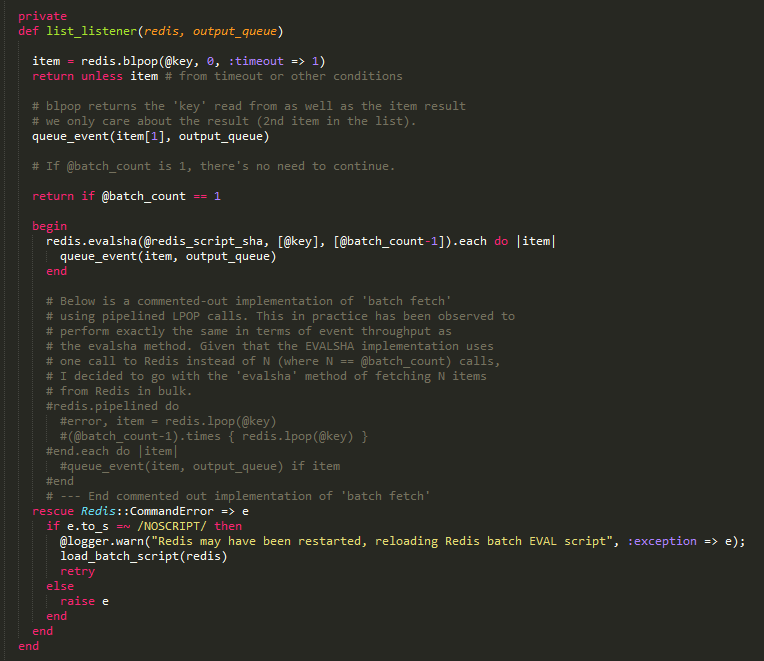
至于channel和pattern_channel,就没啥解释的了,就是分别调用subscribe和psubsribe命令而已。
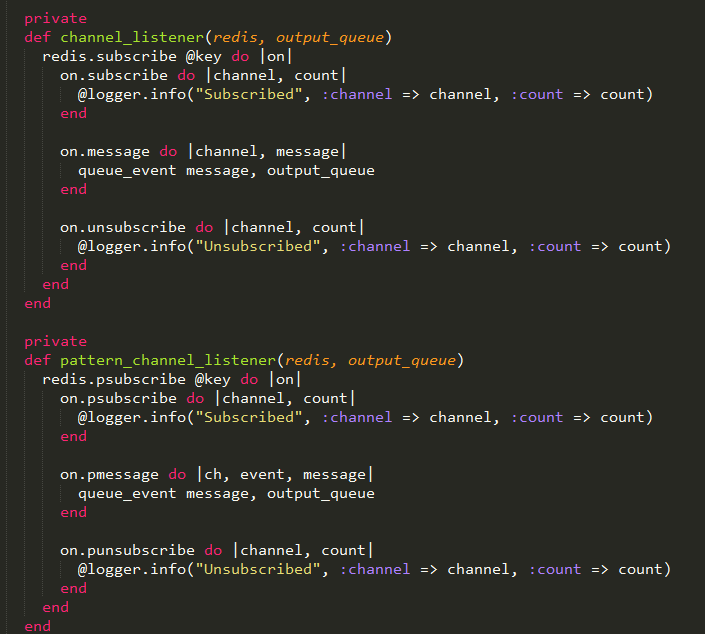
其实最难理解的,就是中间那段lua脚本~明白它的用处,redis插件也就不难理解了。
完整的代码:
# encoding: utf-8
require "logstash/inputs/base"
require "logstash/inputs/threadable"
require "logstash/namespace"
# This input will read events from a Redis instance; it supports both Redis channels and lists.
# The list command (BLPOP) used by Logstash is supported in Redis v1.3.1+, and
# the channel commands used by Logstash are found in Redis v1.3.8+.
# While you may be able to make these Redis versions work, the best performance
# and stability will be found in more recent stable versions. Versions 2.6.0+
# are recommended.
#
# For more information about Redis, see <http://redis.io/>
#
# `batch_count` note: If you use the `batch_count` setting, you *must* use a Redis version 2.6.0 or
# newer. Anything older does not support the operations used by batching.
#
class LogStash::Inputs::Redis < LogStash::Inputs::Threadable
config_name "redis"
default :codec, "json"
# The `name` configuration is used for logging in case there are multiple instances.
# This feature has no real function and will be removed in future versions.
config :name, :validate => :string, :default => "default", :deprecated => true
# The hostname of your Redis server.
config :host, :validate => :string, :default => "127.0.0.1"
# The port to connect on.
config :port, :validate => :number, :default => 6379
# The Redis database number.
config :db, :validate => :number, :default => 0
# Initial connection timeout in seconds.
config :timeout, :validate => :number, :default => 5
# Password to authenticate with. There is no authentication by default.
config :password, :validate => :password
# The name of the Redis queue (we'll use BLPOP against this).
# TODO: remove soon.
config :queue, :validate => :string, :deprecated => true
# The name of a Redis list or channel.
# TODO: change required to true
config :key, :validate => :string, :required => false
# Specify either list or channel. If `redis\_type` is `list`, then we will BLPOP the
# key. If `redis\_type` is `channel`, then we will SUBSCRIBE to the key.
# If `redis\_type` is `pattern_channel`, then we will PSUBSCRIBE to the key.
# TODO: change required to true
config :data_type, :validate => [ "list", "channel", "pattern_channel" ], :required => false
# The number of events to return from Redis using EVAL.
config :batch_count, :validate => :number, :default => 1
public
def register
require 'redis'
@redis = nil
@redis_url = "redis://#{@password}@#{@host}:#{@port}/#{@db}"
# TODO remove after setting key and data_type to true
if @queue
if @key or @data_type
raise RuntimeError.new(
"Cannot specify queue parameter and key or data_type"
)
end
@key = @queue
@data_type = 'list'
end
if not @key or not @data_type
raise RuntimeError.new(
"Must define queue, or key and data_type parameters"
)
end
# end TODO
@logger.info("Registering Redis", :identity => identity)
end # def register
# A string used to identify a Redis instance in log messages
# TODO(sissel): Use instance variables for this once the @name config
# option is removed.
private
def identity
@name || "#{@redis_url} #{@data_type}:#{@key}"
end
private
def connect
redis = Redis.new(
:host => @host,
:port => @port,
:timeout => @timeout,
:db => @db,
:password => @password.nil? ? nil : @password.value
)
load_batch_script(redis) if @data_type == 'list' && (@batch_count > 1)
return redis
end # def connect
private
def load_batch_script(redis)
#A Redis Lua EVAL script to fetch a count of keys
#in case count is bigger than current items in queue whole queue will be returned without extra nil values
redis_script = <<EOF
local i = tonumber(ARGV[1])
local res = {}
local length = redis.call('llen',KEYS[1])
if length < i then i = length end
while (i > 0) do
local item = redis.call("lpop", KEYS[1])
if (not item) then
break
end
table.insert(res, item)
i = i-1
end
return res
EOF
@redis_script_sha = redis.script(:load, redis_script)
end
private
def queue_event(msg, output_queue)
begin
@codec.decode(msg) do |event|
decorate(event)
output_queue << event
end
rescue LogStash::ShutdownSignal => e
# propagate up
raise(e)
rescue => e # parse or event creation error
@logger.error("Failed to create event", :message => msg, :exception => e, :backtrace => e.backtrace);
end
end
private
def list_listener(redis, output_queue)
item = redis.blpop(@key, 0, :timeout => 1)
return unless item # from timeout or other conditions
# blpop returns the 'key' read from as well as the item result
# we only care about the result (2nd item in the list).
queue_event(item[1], output_queue)
# If @batch_count is 1, there's no need to continue.
return if @batch_count == 1
begin
redis.evalsha(@redis_script_sha, [@key], [@batch_count-1]).each do |item|
queue_event(item, output_queue)
end
# Below is a commented-out implementation of 'batch fetch'
# using pipelined LPOP calls. This in practice has been observed to
# perform exactly the same in terms of event throughput as
# the evalsha method. Given that the EVALSHA implementation uses
# one call to Redis instead of N (where N == @batch_count) calls,
# I decided to go with the 'evalsha' method of fetching N items
# from Redis in bulk.
#redis.pipelined do
#error, item = redis.lpop(@key)
#(@batch_count-1).times { redis.lpop(@key) }
#end.each do |item|
#queue_event(item, output_queue) if item
#end
# --- End commented out implementation of 'batch fetch'
rescue Redis::CommandError => e
if e.to_s =~ /NOSCRIPT/ then
@logger.warn("Redis may have been restarted, reloading Redis batch EVAL script", :exception => e);
load_batch_script(redis)
retry
else
raise e
end
end
end
private
def channel_listener(redis, output_queue)
redis.subscribe @key do |on|
on.subscribe do |channel, count|
@logger.info("Subscribed", :channel => channel, :count => count)
end
on.message do |channel, message|
queue_event message, output_queue
end
on.unsubscribe do |channel, count|
@logger.info("Unsubscribed", :channel => channel, :count => count)
end
end
end
private
def pattern_channel_listener(redis, output_queue)
redis.psubscribe @key do |on|
on.psubscribe do |channel, count|
@logger.info("Subscribed", :channel => channel, :count => count)
end
on.pmessage do |ch, event, message|
queue_event message, output_queue
end
on.punsubscribe do |channel, count|
@logger.info("Unsubscribed", :channel => channel, :count => count)
end
end
end
# Since both listeners have the same basic loop, we've abstracted the outer
# loop.
private
def listener_loop(listener, output_queue)
while !@shutdown_requested
begin
@redis ||= connect
self.send listener, @redis, output_queue
rescue Redis::BaseError => e
@logger.warn("Redis connection problem", :exception => e)
# Reset the redis variable to trigger reconnect
@redis = nil
sleep 1
end
end
end # listener_loop
public
def run(output_queue)
if @data_type == 'list'
listener_loop :list_listener, output_queue
elsif @data_type == 'channel'
listener_loop :channel_listener, output_queue
else
listener_loop :pattern_channel_listener, output_queue
end
rescue LogStash::ShutdownSignal
# ignore and quit
end # def run
public
def teardown
@shutdown_requested = true
if @redis
if @data_type == 'list'
@redis.quit rescue nil
elsif @data_type == 'channel'
@redis.unsubscribe rescue nil
@redis.connection.disconnect
elsif @data_type == 'pattern_channel'
@redis.punsubscribe rescue nil
@redis.connection.disconnect
end
@redis = nil
end
end
end # class LogStash::Inputs::Redis
[Logstash-input-redis] 使用详解的更多相关文章
- redis配置详解
##redis配置详解 # Redis configuration file example. # # Note that in order to read the configuration fil ...
- CentOS7/RHEL7安装Redis步骤详解
CentOS7/RHEL7安装Redis步骤详解 CentOS7/RHEL7安装Redis还是头一次测试安装了,因为centos7升级之后与centos6有比较大的区别了,下面我们就一起来看看Cent ...
- Redis协议详解
smark Beetle可靠.高性能的.Net Socket Tcp通讯组件 支持flash amf3,protobuf,Silverlight,windows phone Redis协议详解 由于前 ...
- Redis学习——详解Redis配置文件(三)
一.Redis脚本简介 在我们介绍Redis的配置文件之前,我们先来说一下Redis安装完成后生成的几个可执行文件: redis-server .redis-cli .redis-benchmark ...
- Redis:默认配置文件redis.conf详解
转: Redis:默认配置文件redis.conf详解 # Redis配置文件样例 # Note on units: when memory size is needed, it is possibl ...
- Python操作redis学习系列之(集合)set,redis set详解 (六)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import redis r = redis.Redis(host=") 1. Sadd 命令将一个或多个成员元素加入到集合中,已经存在于集合 ...
- Redis配置文件redis.conf详解
一.Redis配置文件redis.conf详解 # Note on units: when memory size is needed, it is possible to specifiy # it ...
- [转]使用python来操作redis用法详解
转自:使用python来操作redis用法详解 class CommRedisBase(): def __init__(self): REDIS_CONF = {} connection_pool = ...
- linux离线部署redis及redis.conf详解
一.离线部署redis 由于博主部署的虚拟机没有网络也没有gcc编译器,所以就寻找具备gcc编译器的编译环境把redis编译安装好,Copy Redis安装目录文件夹到目标虚拟机的目录下.copy时r ...
- 5种Redis数据结构详解
本文主要和大家分享 5种Redis数据结构详解,希望文中的案例和代码,能帮助到大家. 转载链接:https://www.php.cn/php-weizijiaocheng-388126.html 2. ...
随机推荐
- 七牛php sdk 生成上传凭证时出现 undefined function Qiniu_SetKeys()
将qiniu/http.php文件改名即可,原因是xampp等集成环境会安装pear存在了http.php
- 灰色预测原理及JAVA实现
最近在做项目时,用户不想使用平均值来判断当前数据状态,想用其他的方式来分析数据的变化状态,在查找了一些资料后,想使用灰色预测来进行数据的预测.下面的内容是从网上综合下来的,java代码也做了一点改动, ...
- Replication的犄角旮旯(一)--变更订阅端表名的应用场景
<Replication的犄角旮旯>系列导读 Replication的犄角旮旯(一)--变更订阅端表名的应用场景 Replication的犄角旮旯(二)--寻找订阅端丢失的记录 Repli ...
- App开发如何利用Fidder,在api接口还没有实现的情况下模拟数据,继续开发
相信app开发很多时候,都是等后台出接口,拿到数据调试错误.殊不知,我们完全可以不用等,只要有约定好的接口定义文档,借助工具就能做到,自己模拟数据返回~ 下面主要是在项目组开发过程中,使用F ...
- 为自己搭建一个鹊桥 -- Native Page与Web View之间的JSBridge实现方式
说起JSBridge,大家最熟悉的应该就是微信的WeixinJSBridge,通过它各个公众页面可以调用后台方法和微信进行交互,为用户提供相关功能.我们就来说说UWP下怎么样实现我们自己的JSBrid ...
- Ng Http Request/response格式转换
angular作为Single Page Application推荐的交互方式当然是基于json的ajax调用.但今天要说的是当你不幸工作在一个遗留或者不可控制的服务上,而这服务是基于非json提交方 ...
- [ACM_模拟] POJ1068 Parencodings (两种括号编码转化 规律 模拟)
Description Let S = s1 s2...s2n be a well-formed string of parentheses. S can be encoded in two diff ...
- 【译】用jQuery 处理XML--写在前面的话
用jQuery 处理XML--写在前面的话 用jQuery 处理XML-- DOM(文本对象模型)简介 用jQuery 处理XML--浏览器中的XML与JavaScript 用jQuery 处理XML ...
- 翻译-DevOps究竟是什么?
原文地址:http://www.drdobbs.com/architecture-and-design/what-exactly-is-devops/240009147 作者:Neil Garnich ...
- 在github上写个人简历——先弄个主页
起因 不知道园友们在使用智联招聘等网站填写简历的时候对要求输入的内容有没有一种无力感,不吐槽了反正就一句话,按照它提供的格式我没法儿写简历,而且面试的时候总会被问道有没有自己作品,哥们儿天天上班,下班 ...
