Render OpenCascade Geometry Surfaces in OpenSceneGraph
在OpenSceneGraph中绘制OpenCascade的曲面
Render OpenCascade Geometry Surfaces in OpenSceneGraph
摘要Abstract:本文对OpenCascade中的几何曲面数据进行简要说明,并结合OpenSceneGraph将这些曲面显示。
关键字Key Words:OpenCascade、OpenSceneGraph、Geometry Surface、NURBS
一、引言 Introduction
《BRep Format Description White Paper》中对OpenCascade的几何数据结构进行了详细说明。BRep文件中用到的曲面总共有11种:
1.Plane 平面;
2.Cylinder 圆柱面;
3.Cone 圆锥面;
4.Sphere 球面;
5.Torus 圆环面;
6.Linear Extrusion 线性拉伸面;
7.Revolution Surface 旋转曲面;
8.Bezier Surface 贝塞尔面;
9.B-Spline Surface B样条曲面;
10.Rectangle Trim Surface 矩形裁剪曲面;
11.Offset Surface 偏移曲面;
曲面的几何数据类都有一个共同的基类Geom_Surface,类图如下所示:
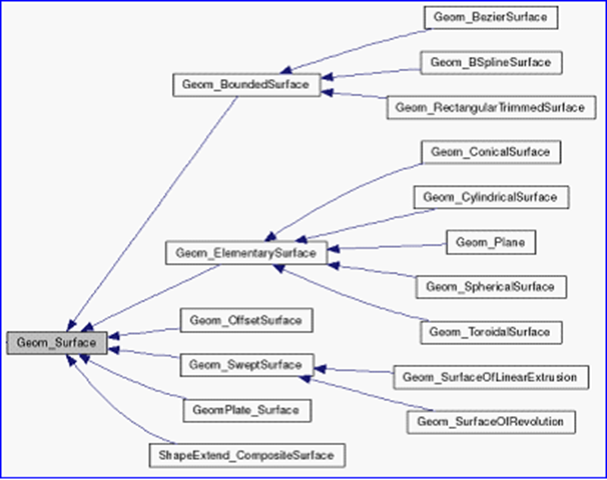
Figure 1.1 Geometry Surface class diagram
抽象基类Geom_Surface有几个纯虚函数Bounds()、Value()等,可用来计算曲面上的点。类图如下所示:
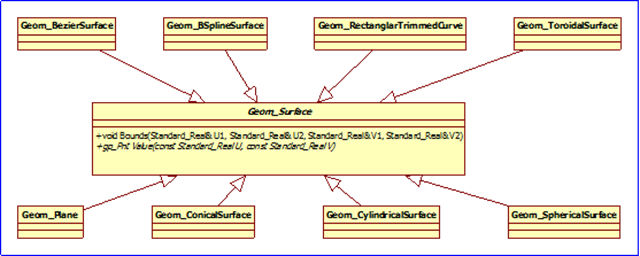
Figure 1.2 Geom_Surface class diagram
与另一几何内核sgCore中的几何的概念一致,几何(geometry)是用参数方程对曲线曲面精确表示的。
每种曲面都对纯虚函数进行实现,使计算曲面上点的方式统一。
曲线C(u)是单参数的矢值函数,它是由直线段到三维欧几里得空间的映射。曲面是关于两个参数u和v的矢值函数,它表示由uv平面上的二维区域R到三维欧几里得空间的映射。把曲面表示成双参数的形式为:
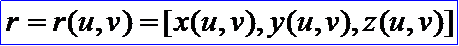
它的参数方程为:
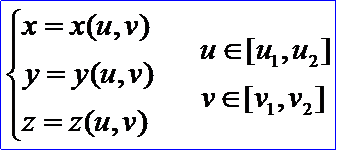
u,v参数形成了一个参数平面,参数的变化区间在参数平面上构成一个矩形区域。正常情况下,参数域内的点(u,v)与曲面上的点r(u,v)是一一对应的映射关系。
给定一个具体的曲面方程,称之为给定了一个曲面的参数化。它既决定了所表示的曲面的形状,也决定了该曲面上的点与其参数域内的点的一种对应关系。同样地,曲面的参数化不是唯一的。
曲面双参数u,v的变化范围往往取为单位正方形,即u∈[0,1],v∈[0,1]。这样讨论曲面方程时,即简单、方便,又不失一般性。
二、程序示例 Code Example
使用函数Value(u, v)根据参数计算出曲面上的点,将点分u,v方向连成线,可以绘制出曲面的线框模型。程序如下所示:
/*
* Copyright (c) 2013 eryar All Rights Reserved.
*
* File : Main.cpp
* Author : eryar@163.com
* Date : 2013-08-11 10:36
* Version : V1.0
*
* Description : Draw OpenCascade Geometry Surfaces in OpenSceneGraph.
*
*/ // OpenSceneGraph
#include <osgDB/ReadFile>
#include <osgViewer/Viewer>
#include <osgGA/StateSetManipulator>
#include <osgViewer/ViewerEventHandlers> #pragma comment(lib, "osgd.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "osgDBd.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "osgGAd.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "osgViewerd.lib") // OpenCascade
#define WNT
#include <TColgp_Array2OfPnt.hxx>
#include <TColStd_HArray1OfInteger.hxx>
#include <TColGeom_Array2OfBezierSurface.hxx>
#include <GeomConvert_CompBezierSurfacesToBSplineSurface.hxx> #include <Geom_Surface.hxx>
#include <Geom_BezierSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_BSplineSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_ConicalSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_CylindricalSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_Plane.hxx>
#include <Geom_ToroidalSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_SphericalSurface.hxx> #pragma comment(lib, "TKernel.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKMath.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKG3d.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKGeomBase.lib") // Approximation Delta.
const double APPROXIMATION_DELTA = 0.1; /**
* @breif Build geometry surface.
*/
osg::Node* buildSurface(const Geom_Surface& surface)
{
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Geode> geode = new osg::Geode(); gp_Pnt point;
Standard_Real uFirst = 0.0;
Standard_Real vFirst = 0.0;
Standard_Real uLast = 0.0;
Standard_Real vLast = 0.0; surface.Bounds(uFirst, uLast, vFirst, vLast); Precision::IsNegativeInfinite(uFirst) ? uFirst = -1.0 : uFirst;
Precision::IsInfinite(uLast) ? uLast = 1.0 : uLast; Precision::IsNegativeInfinite(vFirst) ? vFirst = -1.0 : vFirst;
Precision::IsInfinite(vLast) ? vLast = 1.0 : vLast; // Approximation in v direction.
for (Standard_Real u = uFirst; u <= uLast; u += APPROXIMATION_DELTA)
{
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Geometry> linesGeom = new osg::Geometry();
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec3Array> pointsVec = new osg::Vec3Array(); for (Standard_Real v = vFirst; v <= vLast; v += APPROXIMATION_DELTA)
{
point = surface.Value(u, v); pointsVec->push_back(osg::Vec3(point.X(), point.Y(), point.Z()));
} // Set the colors.
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec4Array> colors = new osg::Vec4Array;
colors->push_back(osg::Vec4(1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f));
linesGeom->setColorArray(colors.get());
linesGeom->setColorBinding(osg::Geometry::BIND_OVERALL); // Set the normal in the same way of color.
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec3Array> normals = new osg::Vec3Array;
normals->push_back(osg::Vec3(0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f));
linesGeom->setNormalArray(normals.get());
linesGeom->setNormalBinding(osg::Geometry::BIND_OVERALL); // Set vertex array.
linesGeom->setVertexArray(pointsVec);
linesGeom->addPrimitiveSet(new osg::DrawArrays(osg::PrimitiveSet::LINE_STRIP, , pointsVec->size())); geode->addDrawable(linesGeom.get());
} // Approximation in u direction.
for (Standard_Real v = vFirst; v <= vLast; v += APPROXIMATION_DELTA)
{
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Geometry> linesGeom = new osg::Geometry();
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec3Array> pointsVec = new osg::Vec3Array(); for (Standard_Real u = vFirst; u <= uLast; u += APPROXIMATION_DELTA)
{
point = surface.Value(u, v); pointsVec->push_back(osg::Vec3(point.X(), point.Y(), point.Z()));
} // Set the colors.
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec4Array> colors = new osg::Vec4Array;
colors->push_back(osg::Vec4(1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f));
linesGeom->setColorArray(colors.get());
linesGeom->setColorBinding(osg::Geometry::BIND_OVERALL); // Set the normal in the same way of color.
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec3Array> normals = new osg::Vec3Array;
normals->push_back(osg::Vec3(0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f));
linesGeom->setNormalArray(normals.get());
linesGeom->setNormalBinding(osg::Geometry::BIND_OVERALL); // Set vertex array.
linesGeom->setVertexArray(pointsVec);
linesGeom->addPrimitiveSet(new osg::DrawArrays(osg::PrimitiveSet::LINE_STRIP, , pointsVec->size())); geode->addDrawable(linesGeom.get());
} return geode.release();
} /**
* @breif Test geometry surfaces of OpenCascade.
*/
osg::Node* buildScene(void)
{
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Group> root = new osg::Group(); // Test Plane.
Geom_Plane plane(gp::XOY());
root->addChild(buildSurface(plane)); // Test Bezier Surface and B-Spline Surface.
TColgp_Array2OfPnt array1(,,,);
TColgp_Array2OfPnt array2(,,,);
TColgp_Array2OfPnt array3(,,,);
TColgp_Array2OfPnt array4(,,,); array1.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array1.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array1.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array1.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array1.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array1.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array1.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array1.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array1.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,)); array2.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array2.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array2.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array2.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array2.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array2.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array2.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array2.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array2.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,)); array3.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array3.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array3.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array3.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array3.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array3.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array3.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array3.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array3.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,)); array4.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array4.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array4.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array4.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array4.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array4.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array4.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array4.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,));
array4.SetValue(,,gp_Pnt(,,)); Geom_BezierSurface BZ1(array1);
Geom_BezierSurface BZ2(array2);
Geom_BezierSurface BZ3(array3);
Geom_BezierSurface BZ4(array4);
root->addChild(buildSurface(BZ1));
root->addChild(buildSurface(BZ2));
root->addChild(buildSurface(BZ3));
root->addChild(buildSurface(BZ4)); Handle_Geom_BezierSurface BS1 = new Geom_BezierSurface(array1);
Handle_Geom_BezierSurface BS2 = new Geom_BezierSurface(array2);
Handle_Geom_BezierSurface BS3 = new Geom_BezierSurface(array3);
Handle_Geom_BezierSurface BS4 = new Geom_BezierSurface(array4);
TColGeom_Array2OfBezierSurface bezierarray(,,,);
bezierarray.SetValue(,,BS1);
bezierarray.SetValue(,,BS2);
bezierarray.SetValue(,,BS3);
bezierarray.SetValue(,,BS4); GeomConvert_CompBezierSurfacesToBSplineSurface BB (bezierarray); if (BB.IsDone())
{
Geom_BSplineSurface BSPLSURF(
BB.Poles()->Array2(),
BB.UKnots()->Array1(),
BB.VKnots()->Array1(),
BB.UMultiplicities()->Array1(),
BB.VMultiplicities()->Array1(),
BB.UDegree(),
BB.VDegree() ); BSPLSURF.Translate(gp_Vec(,,)); root->addChild(buildSurface(BSPLSURF));
} // Test Spherical Surface.
Geom_SphericalSurface sphericalSurface(gp::XOY(), 1.0);
sphericalSurface.Translate(gp_Vec(2.5, 0.0, 0.0));
root->addChild(buildSurface(sphericalSurface)); // Test Conical Surface.
Geom_ConicalSurface conicalSurface(gp::XOY(), M_PI/, 1.0);
conicalSurface.Translate(gp_Vec(5.0, 0.0, 0.0));
root->addChild(buildSurface(conicalSurface)); // Test Cylindrical Surface.
Geom_CylindricalSurface cylindricalSurface(gp::XOY(), 1.0);
cylindricalSurface.Translate(gp_Vec(8.0, 0.0, 0.0));
root->addChild(buildSurface(cylindricalSurface)); // Test Toroidal Surface.
Geom_ToroidalSurface toroidalSurface(gp::XOY(), 1.0, 0.2);
toroidalSurface.Translate(gp_Vec(11.0, 0.0, 0.0));
root->addChild(buildSurface(toroidalSurface)); return root.release();
} int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
osgViewer::Viewer myViewer; myViewer.setSceneData(buildScene()); myViewer.addEventHandler(new osgGA::StateSetManipulator(myViewer.getCamera()->getOrCreateStateSet()));
myViewer.addEventHandler(new osgViewer::StatsHandler);
myViewer.addEventHandler(new osgViewer::WindowSizeHandler); return myViewer.run();
}
程序效果如下图所示:
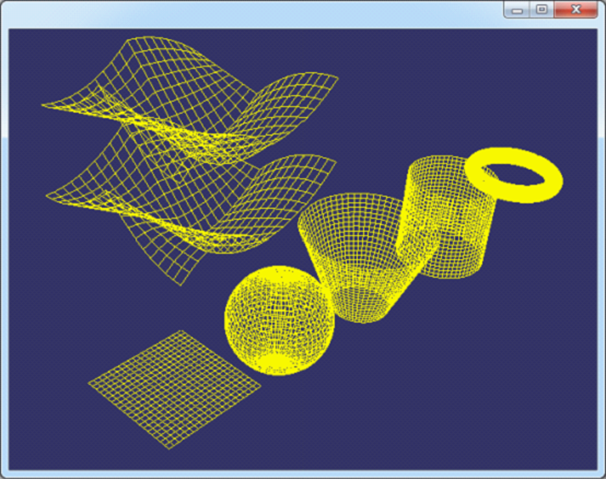
Figure 2.1 OpenCascade Geometry Surfaces in OpenSceneGraph
三、结论 Conclusion
根据OpenCascade中的几何曲面的函数Value(u, v)可以计算出曲面上的点。分u方向和v方向分别绘制曲面上的点,并将之连接成线,即可以表示出曲面的线框模型。因为这样的模型没有面的信息,所以不能有光照效果、材质效果等。要有光照、材质的信息,必须将曲面进行三角剖分。相关的剖分算法有Delaunay三角剖分等。
PDF Version: Draw OpenCascade Geometry Surfaces in OpenSceneGraph
Render OpenCascade Geometry Surfaces in OpenSceneGraph的更多相关文章
- Render OpenCascade Geometry Curves in OpenSceneGraph
在OpenSceneGraph中绘制OpenCascade的曲线 Render OpenCascade Geometry Curves in OpenSceneGraph eryar@163.com ...
- OpenCascade Shape Representation in OpenSceneGraph
OpenCascade Shape Representation in OpenSceneGraph eryar@163.com 摘要Abstract:本文通过程序实例,将OpenCascade中的拓 ...
- Opencascade、OpenGL和OpenSceneGraph的区别与联系
OpenGL只是三维显示 Openscenegraph基于场景图的概念,它提供一个在OpenGL之上的面向对象的框架,从而能把开发者从实现和优化底层图形的调用中解脱出来 Opencascade更适合算 ...
- OpenCASCADE Linear Extrusion Surface
OpenCASCADE Linear Extrusion Surface eryar@163.com Abstract. OpenCASCADE linear extrusion surface is ...
- Polynomial Library in OpenCascade
Polynomial Library in OpenCascade eryar@163.com 摘要Abstract:分析幂基曲线即多项式曲线在OpenCascade中的计算方法,以及利用OpenSc ...
- Representation Data in OpenCascade BRep
Representation Data in OpenCascade BRep eryar@163.com 摘要Abstract:现在的显示器大多数是光栅显示器,即可以看做一个像素的矩阵.在光栅显示器 ...
- Open Cascade 转化为OpenSceneGraph中的Mesh
#include <osgDB/ReadFile> #include <osgViewer/Viewer> #include <osgGA/StateSetManipul ...
- OpenCASCADE Data Exchange - 3D PDF
OpenCASCADE Data Exchange - 3D PDF eryar@163.com Abstract. Today most 3D engineering model data are ...
- Visualize Surface by Delaunay Triangulator
Visualize Surface by Delaunay Triangulator eryar@163.com Abstract. Delaunay Triangulation is the cor ...
随机推荐
- Android Activity生命周期
从android api文档摘抄出来的activity生命周期图如下: Activity有如下四种状态 a.活动状态 activity处于屏幕前台,获取到了焦点可以和用户进行交互,同一时刻只有一个a ...
- 《Linux内核分析》之第四章读书笔记
4.1多任务 多任务操作系统:同时并发地交互执行多个进程的操作系统 多任务操作系统会使多个进程处于堵塞或者睡眠状态.这些任务尽管位于内存,但是并不处于可运行状态.这些进程利用内核堵塞自己,直到某一事件 ...
- 第47讲:Scala多重界定代码实战及其在Spark中的应用源码解析
今天学习了scala的多重界定 T >: A <: B 表示T同时有下界和下界,下界为A,上界为B,A为B的子类型.下界必须写在前面,上界必须写在后面,位置不能颠倒. T<:A wi ...
- 查询Oracle锁表和解决方法
Oracle数据库操作中,我们有时会用到锁表查询以及解锁和kill进程等操作,那么这些操作是怎么实现的呢?本文我们主要就介绍一下这部分内容.(1)锁表查询的代码有以下的形式:select count( ...
- spring简介
在SSH框假中spring充当了管理容器的角色.我们都知道Hibernate用来做持久层,因为它将JDBC做了一个良好的封装,程序员在与数据库进行交互时可以不用书写大量的SQL语句.Struts是用来 ...
- 使用Axure来仿真Vogue网站
用户体验包括三部分:用户研究.视觉设计和交互设计.按顺序进行,在用户研究和视觉设计之后,开始交互设计,Axure是最好的交互设计的软件. Vogue是著名的奢侈品品牌,网站设计“高大上”,用Axure ...
- Ubuntu16.04使用阿里云镜像安装Mongodb
一.概述 近日要在新的Ubuntu16.04系统上安装MongoDB,某度结果后直接从Mongo官网直接获得3.2版本的下载链接,结果在下载时发觉速度慢的可怜.迫于无奈,只能找国内的镜像下载.切换国内 ...
- (转)Unity AssetBundle爬坑手记
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/ybgame/p/3973177.html 这篇文章从AssetBundle的打包,使用,管理以及内存占用各个方面进行了比较全面的分析,对Asset ...
- iOS 直播类APP开发流程分解:
1 . 音视频处理的一般流程: 数据采集→数据编码→数据传输(流媒体服务器) →解码数据→播放显示1.数据采集:摄像机及拾音器收集视频及音频数据,此时得到的为原始数据涉及技术或协议:摄像机:CCD.C ...
- 003. Asp.Net Routing与MVC 之一: 请求如何到达MVC
基础知识 本文用到的基础知识:URL.HttpModule 与 HttpHandler.IIS 的请求处理过程. URL HttpModule与HttpHandler IIS7.0的请求处理过程 OK ...
