[c++] STL = Standard Template Library
序列容器
C++ Standard Library
一、特点
并没怎么用面向对象的特性。
For efficiency reasons, STL is not object-oriented:
- Makes little use of inheritance, and
- Makes no use of virtual functions
二、分类
STL是c++的精华,开始前先在此提一下。
有助于总体理解的链接:[C++ STL] 各容器简单介绍
The Standard Template Library (STL) is a part of the C++ standard library, Some others are:
分类一
- The C standard library
- Language support: <exception>, <ctime>, ...
- Strings: <string>, <cstring>, ...
- Numerics: <cmath>, <complex>, ...
- I/O: <iostream>, <fstream>, <cstdio>, ...
- Exception classes
- Smart pointers
- Classes for internationalisation support
分类二
- Containers: vector, list, stack, ...
- Algorithms: find, sort, copy, ...
- Iterators are the glue between the two!
Containers 蓝图
一、c++11新特性
四大板块

In reality, not all operations are supported in all containers,
More details: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/stl/
适配器 Adaptors
适配器?Adaptors和序列容器的关系是什么?
本质上,适配器是使一事物的行为类似于另一类事物的行为的一种机制。
容器适配器让一种已存在的容器类型采用另一种不同的抽象类型的工作方式实现。
例如,stack适配器可使任何一种顺序容器以栈的方式工作。
二、效率对比
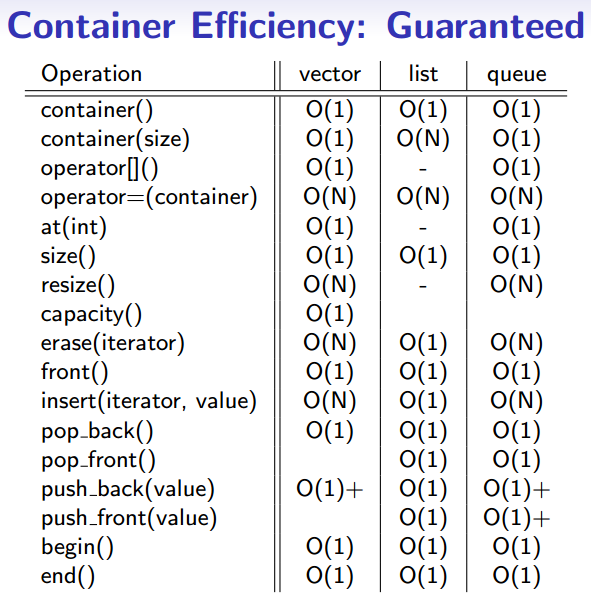
需要逐个实践下,为下一节做准备

容器解密
Vector
一、插入操作
resize()
Ref: 关于vector的resize()的理解
resize()的作用是改变vector中元素的数目。
如果n比当前的vector元素数目要小,vector的容量要缩减到resize的第一个参数大小,既n。并移除那些超出n的元素同时销毁他们。
如果n比当前vector元素数目要大,在vector的末尾扩展需要的元素数目,如果第二个参数val指定了,扩展的新元素初始化为val的副本,否则按类型默认初始化。
注意:如果n大于当前的vector的容量(是容量,并非vector的size),将会引起自动内存分配。所以现有的pointer, references, iterators将会失效。
综合操作示范
int func_vector_insert(void)
{
cout << "== vector insert() show ==" << endl; std::vector<int> myvector (,);
std::vector<int>::iterator it; it = myvector.begin();
it = myvector.insert ( it , ); //某位置插入一个数字
for (auto p = myvector.begin(); p != myvector.end(); p++)
{
std::cout << (*p) << ", ";
}
std::cout << std::endl; myvector.insert (it,,); //某位置插入若干数字 for (auto p = myvector.begin(); p != myvector.end(); p++)
{
std::cout << (*p) << ", ";
}
std::cout << std::endl; // "it" no longer valid, get a new one:
it = myvector.begin(); std::vector<int> anothervector (,);
myvector.insert (it+, anothervector.begin(), anothervector.end()); //某位置插入一段动态同类的数字 for (auto p = myvector.begin(); p != myvector.end(); p++)
{
std::cout << (*p) << ", ";
}
std::cout << std::endl; int myarray [] = { ,, };
myvector.insert (myvector.begin(), myarray, myarray+); //某位置插入一段静态同类的数字 std::cout << "myvector contains:";
for (it=myvector.begin(); it<myvector.end(); it++)
std::cout << ' ' << *it;
std::cout << '\n'; return ;
} //****************************************************************************** void func_vector(void)
{
// vector<int> vec= new vector();
vector<int> vec= {, , , , };
cout << vec.at() << endl;
cout << "size = " << vec.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity = " << vec.capacity() << endl; cout << "resize(10)\n";
vec.resize(); /* Jeff --> I don't like unsigned here. */
// for (unsigned int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++)
// {
// cout << vec.at(i) << "\n";
// } for (auto p = vec.begin(); p != vec.end(); p++)
{
// Jeff --> endl == \n + flush
cout << (*p) << ' ';
}
cout << endl; cout << "size = " << vec.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity = " << vec.capacity() << endl; cout << "vec.clear()" << endl;
vec.clear(); cout << "size = " << vec.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity = " << vec.capacity() << endl; //-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
for (int i = ; i <= ; i++)
{
vec.push_back(i);
} // Jeff --> vector<int>::iterator iter = vec.begin();
// 可使用通用的iterator方式,毕竟list不能直接l.begin()+1这么用!
cout << "erase(0-2)" << endl;
vec.erase(vec.begin(), vec.begin() + ); for (auto p = vec.begin(); p != vec.end(); p++)
{
// Jeff --> endl == \n + flush
cout << (*p) << ' ';
}
cout << endl; cout << "size = " << vec.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity = " << vec.capacity() << endl; //----------------------------------------------------------------------------- func_vector_insert(); //----------------------------------------------------------------------------- cout << "vec.front() = " << vec.front() << endl; cout << "push_back(111)" << endl;
vec.push_back(); for (auto p = vec.begin(); p != vec.end(); p++)
{
// Jeff --> endl == \n + flush
cout << (*p) << ' ';
}
cout << endl; cout << "size = " << vec.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity = " << vec.capacity() << endl;
}
常见的修改操作示范
二、二维 vector
auto类型的好处,没以及使用的“指针”在遍历。
void func_vector2(void)
{
vector<vector<int>> vector2;
vector<int> v1 = {, , , , };
vector<int> v2 = {, , , , }; vector2.push_back(v1);
vector2.push_back(v2); for (auto it_v = vector2.begin(); it_v != vector2.end(); it_v++)
{
for (auto it_sub_v = (*it_v).begin(); it_sub_v != (*it_v).end(); it_sub_v++)
{
cout << (*it_sub_v) << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
}
三、vector.at() 更安全
如果你不能确信程序是否能做到不越界,C++VECTOR提供边界检查(at函数)。
因为,提供处理越界的异常的 “机会”。
void func_catch(void)
{
vector<string> words = { "Hello", "World" };
for (unsigned int i = ; i < words.size(); ++i) {
cout << words[i] << endl;
}
try {
cout << words.at() << endl;
} catch(const std::out_of_range &e) {
cout << e.what() << endl;
}
}
四、assign()
区别在于处理类时,如果有malloc就有有不同,会涉及到引用计数的问题。详见:assign、retain和copy的区别。
assign是浅拷贝。retain的意思是保持引用,也就是说,如果想保持某个对象的引用,避免它被正统传人释放。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector> int main ()
{
// 三个列表
std::vector<int> first;
std::vector<int> second;
std::vector<int> third; first.assign (, ); // 分配 七个100
for (auto p = first.begin(); p != first.end(); p++)
{
std::cout << (*p) << std::endl;
} std::cout << "============================" << std::endl; std::vector<int>::iterator it;
it=first.begin()+;
second.assign (it, first.end()-); // first上的一段数据 (动态数组)
for (auto p = second.begin(); p != second.end(); p++)
{
std::cout << (*p) << std::endl;
} int myints[] = {, , };
third.assign (myints, myints+); // myints上的一段数据 (静态数组)
std::cout << "Size of first: " << int (first.size()) << '\n';
std::cout << "Size of second: " << int (second.size()) << '\n';
std::cout << "Size of third: " << int (third.size()) << '\n';
return ;
} void func_assign()
{
vector<int> v1(10);
// vector<float> v2 = v1;
vector<float> v2; v2.assign(v1.begin(), v1.end()); // 可能的优势:v1转化为了v2类型
}
五、copy()
读文件
copy() 作为输入的技巧,以及map的使用。
#include <string.h>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <iterator>
int test02(void)
{
using namespace std;
std::vector<string> v;
std::map<string, int> m; // (1) 定义该文件的输入流 in
std::ifstream in("words.txt");
std::copy(std::istream_iterator<string>(in), std::istream_iterator<string>(), std::back_inserter(v)); // The number of times it occurs in a file.
for (auto vi = v.begin(); vi != v.end(); ++vi)
++m[*vi]; for (auto mi = m.begin(); mi != m.end(); ++mi)
std::cout << mi->first << ": " << mi->second << std::endl; return ;
}
打印出
copy() 作为输出的技巧:拷贝到ostream。
int test03(void)
{
std::vector<int> v = {, , , , , };
std::string s("string"); std::sort(v.begin(), v.end());
std::copy(v.begin(), v.end(), std::ostream_iterator<int>(std::cout, ","));
std::cout << std::endl; std::sort(s.begin(), s.end());
std::copy(s.begin(), s.end(), std::ostream_iterator<char>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl; return ;
}
List
一、链表上的递增 advance()
在链表上的指针位移操作,弥补 ++ 功能。
void func_list(void)
{
list<int> l = {, , , , };
list<int> l2(, ); list<int>::iterator iter = l.begin();
list<int>::iterator iter2 = l.begin(); // Jeff --> 不能直接++, 就设计了这个函数
advance (iter2, );
l.erase(iter, iter2); for(auto p = l.begin(); p != l.end(); p++)
{
cout << (*p) << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Jeff --> notice: 在erase之后,iter will be a 野指针!
// l2.insert(l2.begin(), iter, iter2);
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
l2.insert(l2.begin(), l.begin(), l.end()); for(auto p = l2.begin(); p != l2.end(); p++)
{
cout << (*p) << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
二、链表上的插入 splice()
list::splice实现list拼接的功能。将源list的内容 部分或全部元素删除,拼插入到目的list。
#include <iostream>
#include <list> int main ()
{
std::list<int> mylist1, mylist2;
std::list<int>::iterator it; // set some initial values:
for (int i=; i<=; ++i)
mylist1.push_back(i); // mylist1: 1 2 3 4 for (int i=; i<=; ++i)
mylist2.push_back(i*); // mylist2: 10 20 30 it = mylist1.begin();
++it; // points to 2 --> 这里要改用 advance()
mylist1.splice (it, mylist2); // mylist1: 1 10 20 30 2 3 4
// mylist2 (empty)
// "it" still points to 2 (the 5th element)
mylist2.splice (mylist2.begin(), mylist1, it);
// mylist1: 1 10 20 30 3 4
// mylist2: 2
// "it" is now invalid.
it = mylist1.begin();
std::advance(it,); // "it" points now to 30
mylist1.splice ( mylist1.begin(), mylist1, it, mylist1.end());
// mylist1: 30 3 4 1 10 20
std::cout << "mylist1 contains:";
for (it=mylist1.begin(); it!=mylist1.end(); ++it)
std::cout << '' << *it;
std::cout << '\n'; std::cout << "mylist2 contains:";
for (it=mylist2.begin(); it!=mylist2.end(); ++it)
std::cout << '' << *it;
std::cout << '\n'; return ;
} void func_splice(void)
{
list<string> words = {"hello", "world"};
list<string> words2 = {"lovely"}; words.splice(++words.begin(), words2);
for (auto p = words.begin(); p != words.end(); p++)
{
cout << *p << endl;
}
cout << "=============================" << endl;
//-------------------------------------------------
// 单向链表
//-------------------------------------------------
forward_list<int> myfl1 = {1, 2, 3};
forward_list<int> myfl2 = {4, 5, 6}; // Jeff --> iterator's next position.
myfl1.splice_after(myfl1.begin(), myfl2); for (auto p = myfl1.begin(); p != myfl1.end(); p++)
{
cout << *p << endl;
}
}
Adaptor Class
一、必要性
在顺序容器的基础上再包装一层,形成常见的数据结构。
More details: 容器适配器
我们已有的容器(比如vector、list、deque)支持的操作很多,比如插入,删除,迭代器访问等等。而我们希望这个容器表现出来的是栈的样子:先进后出,入栈出栈等等,此时,我们没有必要重新动手写一个新的数据结构,而是把原来的容器重新封装一下,改变它的接口,就能把它当做栈使用了。
C++中定义了三种容器适配器,它们让容器提供的接口变成了我们常用的的3种数据结构:栈(先进后出), 队列(先进先出), 优先级队列。
二、实现原理
至于具体是怎么变的,我们可以先了解一个大概:
- 默认情况下,栈和队列都是基于deque实现的,
- 而优先级队列则是基于vector实现的。
当然,我们也可以指定自己的实现方式。但是由于数据结构的关系,我们也不能胡乱指定:
- 栈 的特点是后进先出,所以它关联的基本容器可以是任意一种顺序容器,因为这些容器类型结构都可以提供栈的操作有求,它们都提供了push_back、pop_back和back操作。
- 队列 的特点是先进先出,适配器要求其关联的基础容器必须提供pop_front操作,因此其不能建立在vector容器上 (内存的是固定的);
- 优先级队列,由于它要求支持 随机访问 的功能,所以可以建立在vector或者deque上,不能建立在list上。

三、操作示范
栈 Stack
一些常用的方法,例如:push, pop。
void func_stack(void)
{
std::stack<int> foo, bar;
foo.push();
foo.push();
foo.push(); bar.push ();
bar.push(); // 交换了两个container的内容
foo.swap(bar); std::cout << foo.top() << std::endl;
foo.pop();
std::cout << foo.top() << std::endl;
foo.pop(); std::cout << "size of foo: " << foo.size() << '\n';
std::cout << "size of bar: " << bar.size() << '\n';
}
队列 Queue
void func_queue(void)
{
std::queue<int> que;
for (int i = ; i <= ; i++)
{
que.push(i);
} cout << que.size() << endl; while(!que.empty())
{
// print & pop 是两码事!
cout << que.front() << ' ';
que.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
优先级队列 priority_queue
底层原理是通过 [Max/Min-heap] 来实现的。
STL中的优先队列-priorit_queue,包含在头文件”queue”中,
- 可以使用具有默认优先级的已有数据结构;
- 也可以再定义优先队列的时候传入自定义的优先级比较对象;
- 或者使用自定义对象(数据结构),但是必须重载好< 操作符。
模板申明带3个参数:priority_queue<Type, Container, Functional>,其中Type 为数据类型,Container为保存数据的容器,Functional 为元素比较方式。
Container必须是用数组实现的容器,比如vector,deque等等,但不能用 list。STL里面默认用的是vector。
#include <string.h>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <list>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <iterator> using namespace std; void func_priority_queue(void)
{
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// (1) default way
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
std::priority_queue<int> mypq;
// this uses default way to do it.
// actually the details shows as following.
//
// std::priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater_equal<int>> mypq; mypq.push(rand());
mypq.push(rand());
mypq.push(rand());
mypq.push(rand());
mypq.push(rand()); while(!mypq.empty())
{
cout << mypq.top() << endl;
mypq.pop();
} //--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// (2) custom way
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------- // custom type
typedef struct Node_t
{
int a;
int b;
} Node; // custom sequence container
Node *myNode = new Node[]; // custom compare method.
struct cmp
{
bool operator()(const Node &t1, const Node &t2)
{
return t1.b < t2.b;
}
}; // prepare data in this custom type.
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
myNode[i].a = i;
myNode[i].b = i+;
} // init the priority queue.
std::priority_queue<Node, vector<Node>, cmp> Q(myNode, myNode+); // <---- 之前使用的push添加数据,这里用了如此的初始化方式 // print the elements one by one in priority queue.
while(!Q.empty())
{
cout << Q.top().b << endl;
Q.pop();
}
}
四、常用操作接口
Stack
.empty() 堆栈为空则返回真
.pop() 移除栈顶元素
.push() 在栈顶增加元素
.size() 返回栈中元素数目
.top() 返回栈顶元素
Queue
.back() 返回一个引用,指向最后一个元素
.empty() 如果队列空则返回真
.front() 返回第一个元素
.pop() 删除第一个元素
.push() 在末尾加入一个元素
.size() 返回队列中元素的个数
Priority_queue
.empty() 如果优先队列为空,则返回真
.pop() 删除第一个元素
.push() 加入一个元素
.size() 返回优先队列中拥有的元素的个数
.top() 返回优先队列中有最高优先级的元素
End.
[c++] STL = Standard Template Library的更多相关文章
- C++ Standard Template Library STL(undone)
目录 . C++标准模版库(Standard Template Library STL) . C++ STL容器 . C++ STL 顺序性容器 . C++ STL 关联式容器 . C++ STL 容 ...
- C++ Standard Template Library (STL) 高级容器
更多 STL 数据结构请阅读 NOIp 数据结构专题总结(STL structure 章节) std::map Definition: template < class Key, // map: ...
- <Standard Template Library>标准模板库专项复习总结(二)
4.队列 先进先出(FIFO)表 头文件:#include<queue> 变量的定义:queue<TYPE>queueName 成员函数: bool empty() 空队列返回 ...
- <Standard Template Library>标准模板库专项复习总结(一)
看了看博客园的申请时间也一年多了...想想自己一年多以来一直处于各种划水状态,现在又要面临ACM的冲击... 还是要抓紧时间赶紧复习一下了- -毕竟校园新生赛还是有奖金的.. 1.栈 先进后出(LIF ...
- 自定义标签 与 JSTL(JSP Standard Tag Library)
1.自定义标签 [理解] [1]简介 > 在JSP2.0以后,在jsp页面中不建议使用脚本片段<% %>和JSP表达式<%= %> ...
- JSTL的全称:JSP Standard Tag Library, jsp 标准标签库
JSTL的全称:JSP Standard Tag Library, jsp 标准标签库 JSTL的作用 提供给Java web开发人员一个标准通过的标签函数库和EL来取代传统直接在页面上嵌入j ...
- JSTL(JSP Standard Tag Library ,JSP标准标签库)
JSTL标签之核心标签 JSTL(JSP Standard Tag Library ,JSP标准标签库)是一个实现 Web应用程序中常见的通用功能的定制标记库集,这些功能包括迭代和条件判断.数据管 ...
- JSTL 标准标签库 (JavaServer Pages Standard Tag library, JSTL)
JSP标准标签库(JavaServer Pages Standard Tag Library,JSTL)是一个定制标签库的集合,用来解决 像遍历Map或集合.条件测试.XML处理,甚至数据 库访问和数 ...
- php spl标准库简介(SPL是Standard PHP Library(PHP标准库)(直接看代码实例,特别方便)
php spl标准库简介(SPL是Standard PHP Library(PHP标准库)(直接看代码实例,特别方便) 一.总结 直接看代码实例,特别方便易懂 thinkphp控制器利眠宁不支持(说明 ...
随机推荐
- maven pox配置
Maven教程初级篇02:pom.xml配置初步 1. 创建项目并更改项目基本配置信息 在命令行下运行如下命令创建一个项目: 1 mvn archetype:create -DgroupId=net. ...
- String 归档
1.古罗马皇帝凯撒在打仗时曾经使用过以下方法加密军事情报:,请编写一个程序,使用上述算法加密或解密用户输入的英文字串要求设计思想.程序流程图.源代码.结果截图. 设计思想: 1)输入一个字符串str( ...
- 我的ORM之十一 -- 缓存
我的ORM索引 对某一个查询频繁重复,应该使用缓存. 缓存应该是可以配置. 配置 Web.config: <configuration> <configSections> &l ...
- 用JQ仿造礼德财富网的图片查看器
现在就职于一家P2P平台,自然也会关注同行其它网站的前端技术,今天要仿造的是礼德内页的一个图片查看器效果.不过说白了,无论人人贷也好礼德财富也好,很多地方的前端都做的不尽如人意,比如忽略细节.缺乏交互 ...
- node(redis)
给出node下redis操作的简单例子: var redis = require("redis"), client = redis.createClient(6379,'127.0 ...
- 给Java程序猿们推荐一些值得一看的好书
学习的最好途径就是看书 "学习的最好途径就是看书",这是我自己学习并且小有了一定的积累之后的第一体会.个人认为看书有两点好处: 1.能出版出来的书一定是经过反复的思考.雕琢和审核的 ...
- MySQL2:四种MySQL存储引擎
前言 数据库存储引擎是数据库底层软件组织,数据库管理系统(DBMS)使用数据引擎进行创建.查询.更新和删除数据.不同的存储引擎提供不同的存储机制.索引技巧.锁定水平等功能,使用不同的存储引擎,还可以 ...
- Alpha阶段冲刺总结
Alpha阶段冲刺阶段总结 预期计划: 本阶段的预期计划是实现打地鼠游戏的基本功能,包括:游戏功能.难度调节功能.计时功能.计数记分功能.DIY设置功能.分数记录功能. 实际进展: 在经过三周的Alp ...
- FusionCharts简单教程(六)-----如何自定义图表上的工具提示
所谓图表上的工具提示就是当鼠标放在某个特定的数据块上时所显示的提示信息.如下: 禁用显示工具提示 在默认情况下工具提示功能是显示的,但是有时候我们并不是很想需要这个功能提示功能 ...
- [php入门] 3、WAMP中的集成MySQL相关基础操作
前言:本文以小白视角了解WAMP集成开发环境中的MYSQL,涉及的面广而浅,算是导读性质. 1.启动运行熟悉WAMP中的MySQL 先有库.再有表.数据最终以记录的形式插入表中.其中对数据进行操作使用 ...
